Online Schema Upgrade in MySQL Galera Cluster using TOI Method
http://severalnines.com/blog/online-schema-upgrade-mysql-galera-cluster-using-toi-method
As a follow-up to the Webinar on Zero Downtime Schema Changes in Galera Cluster, we’ll now walk you through the detailed steps on how to update your schema. The two methods (TOI and RSU) have both their pros and cons, and given parameters like table size, indexes, key_buffer_size, disk speed, etc., it is possible to estimate the time taken for the schema to be upgraded. Also, please note that a schema change is non-transactional so it would not be possible to rollback the DDL if it fails midway. Therefore, it is always recommended to test the schema changes and ensure you have recoverable backups before performing this on your production clusters.
This post examines the way DDL changes are propagated in Galera, and outlines the steps to upgrade the schema using the TOI method with Percona’s pt-online-schema-change.
Schema Changes in MySQL
MySQL handle table altering by exporting the table data into a temporary table, changing the table structure, and then importing the data back into the table before finally rebuilding all the indexes. Thus, write blocking is the only choice to maintain data integrity. This stalls all the writes after the ALTER command has been issued, up until it completes.
Percona has built a tool to overcome this problem with its Percona Toolkit bundle called pt-online-schema-change. It allows altering of tables without locking them, and works in the following manner:
- Creates a shadow copy of target table
- Installs triggers in source table to forward updates to target table
- Copies source table data in small chunks to target table
- Renames target table to replace the source table
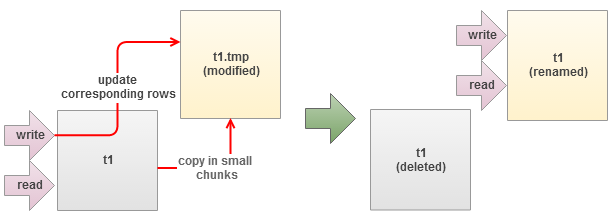
However, the tool will not work if any triggers are already defined on the table. For more detailed explanation about the tool, please refer to Percona Toolkit documentation page.
Schema Changes in Galera
DDL statements (ALTER, CREATE, RENAME, TRUNCATE, DROP) are replicated in statement level. Galera has two inbuilt methods in handling these statements:
- Total Order Isolation (TOI)
- Rolling Schema Upgrade (RSU)
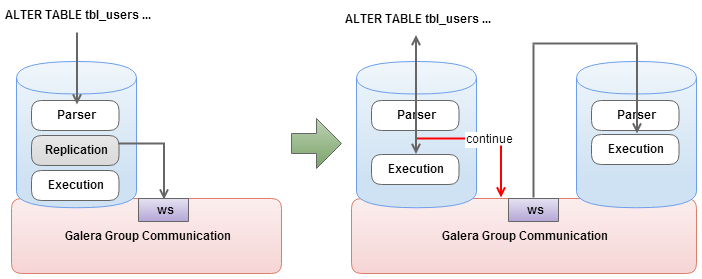
Total Order Isolation
This is the default DDL replication method. Master node (node that originates the writeset) detects DDL at parsing time and sends out a replication event for the SQL statement before even starting the DDL processing. The DDL replication happens in STATEMENT format and every node in the cluster will process the replicated DDL at the same “slot” in the cluster transaction stream (comply to Total Order).
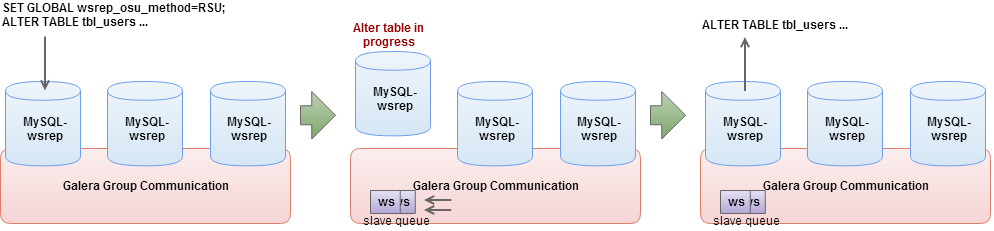
Rolling Schema Upgrade
This method will desynchronize the node from replication for the duration of corresponding DDL command. All incoming replications are buffered and nothing will be replicated out of the node. When the DDL processing is over, the node will automatically join back in cluster and catch up missed transactions from the buffer (gcache). Adjust the gcache size big enough to contain the pending writesets and to allow IST after the DDL is over. Once the node has rejoined and caught up with the rest of the cluster, repeat the process on the next node in the cluster.
Comparison
| Total Order Isolation (TOI) | Rolling Schema Upgrade (RSU) | |
| Advantages |
|
|
| Disadvantages |
|
|
| Use Cases |
|
|
Performing Schema Upgrade
With respect to how Galera handles DDL statements, we have two categories of methods:
Instant method:
- TOI only – Perform schema upgrade to all nodes in the cluster. This method will lock the table similar to how default schema changes happened in MySQL.
- TOI with pt-online-schema-changes – Perform schema upgrade to all nodes in the cluster without locking up the table.
Rolling method:
- RSU with wsrep_desync and wsrep_on – Perform schema upgrade on the local node and keep receiving replication events but not sending out replication events. This method is good for non-conflicting operations and it will not slow down the cluster. Even though the upgraded node replicates writesets, in case of conflicts, note that the writeset will be aborted.
- RSU with node dropping – Perform schema upgrade on the local node in isolation mode where the designated node is taken out of the cluster. The node will not receiving/sending any replication events. When DDL is over, the node will automatically join the cluster and catch up on missed transactions from the buffer (gcache) . Joining the node back must only happen through IST.
Performing an online upgrade requires backward schema compatibility, whereby your application should be able to use both old and new schema. MySQL guarantees ROW replication event compatibility with some limitations:
- Source and target can have different number of columns
- Columns must be in the same order
- New columns in the end, and must have default values
- Some data type conversions are also supported
Newer MySQL versions tolerate more variation between source and target tables as described in details at MySQL Documentation page.
Step-by-step – Performing Online Schema Upgrade in Galera using TOI and pt-online-schema-change
Assume we have a table called tbl_points with 1.2 million of rows. We will add one column called remarks in the end using TOI method with pt-online-schema-changes. Here’s our table definition:
CREATE TABLE `tbl_points` (
`id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT,
`name` varchar(45) NOT NULL,
`point` int(11) NOT NULL,
`user_id` int(11) NOT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`id`),
KEY `fk_users_points_idx` (`user_id`),
CONSTRAINT `fk_users_points` FOREIGN KEY (`user_id`) REFERENCES `tbl_users` (`id`) ON DELETE CASCADE ON UPDATE NO ACTION
) ENGINE=InnoDB AUTO_INCREMENT=3610262 DEFAULT CHARSET=latin1
1. Download and install Percona Toolkit on one of the DB node in primary component:
$ wget percona.com/get/percona-toolkit.rpm
$ rpm -Uhv percona-toolkit-2.2.5-2.noarch.rpm
2. Make sure wsrep_OSU_method value is TOI:
mysql> SHOW VARIABLES LIKE '%wsrep_osu%';
+------------------+-------+
| Variable_name | Value |
+------------------+-------+
| wsrep_OSU_method | TOI |
+------------------+-------+
3. Start the schema upgrade using pt-online-schema-change:
$ pt-online-schema-change -uroot -pMyR00tPassword --alter=”ADD COLUMN remarks VARCHAR(255)” D=mydb,T=tbl_points --execute
Operation, tries, wait:
copy_rows, 10, 0.25
create_triggers, 10, 1
drop_triggers, 10, 1
swap_tables, 10, 1
update_foreign_keys, 10, 1
Altering `mydb`.`tbl_points`...
Creating new table...
Created new table mydb._tbl_points_new OK.
Altering new table...
Altered `mydb`.`_tbl_points_new` OK.
2013-12-10T10:09:44 Creating triggers...
2013-12-10T10:09:44 Created triggers OK.
2013-12-10T10:09:44 Copying approximately 1203656 rows...
...
Copying `mydb`.`tbl_points`: 97% 01:43 remain
Copying `mydb`.`tbl_points`: 98% 01:14 remain
Copying `mydb`.`tbl_points`: 98% 00:49 remain
Copying `mydb`.`tbl_points`: 99% 00:24 remain
2013-12-10T11:15:00 Copied rows OK.
2013-12-10T11:15:00 Swapping tables...
2013-12-10T11:15:01 Swapped original and new tables OK.
2013-12-10T11:15:01 Dropping old table...
2013-12-10T11:15:01 Dropped old table `mydb`.`_tbl_points_old` OK.
2013-12-10T11:15:01 Dropping triggers...
2013-12-10T11:15:01 Dropped triggers OK.
Successfully altered `mydb`.`tbl_points`.
The copy process is performed in small chunks of data, which are varied to attempt to make them execute in a specific amount of time. The tool also reports the remaining time for copying, which is especially helpful when estimating the operation time. At the same time, applications can still read/write to the old table while triggers transparently update the corresponding rows into the new table.
When the tool has finished copying data into the new table, it will rename the original and the new tables before finally dropping the original table. Take note that foreign key object name for this table has been changed slightly to avoid object name collisions in MySQL and InnoDB (fk_users_points → _fk_users_points).
In a next post, we will cover the steps on how to do schema changes using the RSU method.
References
- Webinar Replay & Slides: Galera Cluster Best Practices - Zero Downtime Schema Changes – http://www.severalnines.com/blog/webinar-replay-slides-galera-cluster-best-practices-zero-downtime-schema-changes
- Percona Toolkit Documentation page – http://www.percona.com/doc/percona-toolkit/2.2/
Online Schema Upgrade in MySQL Galera Cluster using TOI Method的更多相关文章
- 关于Oracle的rac集群和mysql Galera Cluster的想法
到了新公司,公司用的是rac,我比较熟悉mysql第三方的集群方案Galera Cluster这类多主集群, 下面是我参考了他人对rac的介绍,然后和mysql方案进行的臆测级别的分析对比. rac和 ...
- mysql galera cluster 集群的分裂与仲裁机制
集群的分裂 当集群由于网络原因分裂为几个单独的组时(一组可能是单节点,也可能是几个互联的节点),数据出现不一致,此时可能产生脑裂及数据不一致.这种情况 下,只有一组节点能够继续提供服务,这组节点的状态 ...
- Ubuntu16.04环境下搭建基于三台主机的mysql galera cluster集群(实测有效)
(注意: (1)文中红色字体部分不一定需要操作 (2)由于word文档编辑的原因,实际操作时部分命令需要手动输入!!直接复制粘贴会提示错误!! ) 一 搭建环境: 1 Ubuntu16.04版本(系 ...
- Ubuntu 下 Galera cluster for MySQL 集群安装
mysql galera cluster官网:http://galeracluster.com/documentation-webpages/ 相关安装教程:(不一定管用) http://blog.c ...
- Percona XtraDB Cluster vs Galera Cluster vs MySQL Group Replication
Percona XtraDB Cluster vs Galera Cluster vs MySQL Group Replication Overview Galera Cluster 由 Coders ...
- 从 MySQL+MMM 到 MariaDB+Galera Cluster : 一个高可用性系统改造
很少有事情比推出高可用性(HA)系统之后便经常看到的系统崩溃更糟糕.对于我们这个Rails运行机的团队来说,这个失效的HA系统是MySQL多主复制管理器(MMM). 我们已经找寻MMM的替代品有一段时 ...
- 【原】基于 HAproxy 1.6.3 Keeplived 在 Centos 7 中实现mysql mariadb galera cluster 集群分发读写 —— 上篇
前言 有一段时间没有写blogs,乘着周末开始整理下haproxy + keeplived 实现 mysql mariadb galera cluster 集群访问环境的搭建工作. 本文集中讲hapr ...
- Galera Cluster——一种新型的高一致性MySQL集群架构
原文链接:https://www.sohu.com/a/147032902_505779,最近被分配定位mysql的问题,学习下. 1. 何谓Galera Cluster 何谓Galera Clust ...
- Galera Cluster mysql+keepalived集群部署
1.卸载mysql 查找本机安装的mysqlrpm -qa | grep -i mysql --nodeps --force rpm -ev MySQL-server-5.6.15-1.el6.x86 ...
随机推荐
- 【管理工具】Git的安装与使用
公司与公司合并,需要学习一下git的使用.从网上找了一篇资料,完全满足需求,先赞一个. http://www.cnblogs.com/Bonker/p/3441781.html 下面记录一下自己的安装 ...
- 翻译【ElasticSearch Server】第一章:开始使用ElasticSearch集群(7)
检索文档(Retrieving documents) 我们已经有文档存储在我们的实例.现在,让我们尝试检索它们: curl -XGET http://localhost:9200/blog/artic ...
- 【windows核心编程】一个API拦截的例子
API拦截 修改PE文件导入段中的导入函数地址 为 新的函数地址 这涉及PE文件格式中的导入表和IAT,PE文件中每个隐式链接的DLL对应一个IMAGE_IMPORT_DESCRIPTOR描述符结构, ...
- c++ Map使用
引入头文件: #include <map>1.初始化map<int, int> a, b;map<sting, int> a, b;2.添加数据 map<in ...
- 关于OpenCV做图像处理内存释放的一些问题
转载:http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_67a7426a0101czyr.html 工程运行,发现内存持续增长,到一定的时候就发生了内存泄漏. 内存泄露的定义 内存泄露是说 ...
- HDU-4751 Divide Groups 染色问题
题目链接:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=4751 题意:有n个人,每个人都认识一些人,要求把他们分成两个集合,使得两个集合中的人都相符两两认识. ...
- Gym 100507C Zhenya moves from parents (线段树)
Zhenya moves from parents 题目链接: http://acm.hust.edu.cn/vjudge/contest/126546#problem/C Description Z ...
- MySQL Update语句用法
用一个表的某列值更新另外一个表的某列值的sql语句: update tableA a innner join tableB b on a.column_1 = b.column_1 set a.col ...
- 命令行刷机教程( 以Linux系统为例 )
//第一步adb device // 如果不能cd AndroidSDK/platform-toolsadb kill-server adb start-server //第二步adb reboot ...
- cloudstack4.2+xenserver6.0.2 详细配置攻略
搭建一台安装了XenServer的服务器 搭建一台安装了CloudStack的服务器用以管理云平台 可以使用CloudStack云平台进行虚拟机管理 使用远程桌面访问windows虚拟机 由于最近实验 ...

