Optimal binary search trees
问题
该问题的实际应用
Suppose that we are designing a program to translate text from English to French. For each occurrence of each English word in the text, we need to look up its French equivalent. We could perform these lookup operations by building a binary search tree with n English words as keys and their French equivalents as satellite data.
Because we will search the tree for each individual word in the text, we want the total time spent searching to be as low as possible. We could ensure an O(lg n) search time per occurrence by using a red-black tree or any other balanced binary search tree.
Words appear with different frequencies, however, and a frequently used word such as the may appear far from the root while a rarely used word such as machicolation appears near the root. Such an organization would slow down the translation, since the number of nodes visited when searching for a key in a binary search tree equals one plus the depth of the node containing the key. We want words that occur frequently in the text to be placed nearer the root.
Moreover, some words in the text might have no French translation, and such words would not appear in the binary search tree at all. How do we organize a binary search tree so as to minimize the number of nodes visited in all searches, given that we know how often each word occurs?(被给定时间相同)
该问题涉及的概念以及特点
an optimal binary search tree,其概念如下:
we are given a sequence K = { k1, k2, ... , kn } of n distinct keys in sorted order (so that k1< k2< ... < kn), and we wish to build a binary search tree from these keys. For each key ki , we have a probability pi that a search will be for ki.
Some searches may be for values not in K, and so we also have n + 1 “dummy keys” d0, d1, ... , dn representing values not in K. For each dummy key di , we have a probability qi that a search will correspond to di .
In particular, d0 represents all values less than k1, dn represents all values greater than kn,and for i = 1, 2, ... , n-1, the dummy key di represents all values between ki and ki+1.
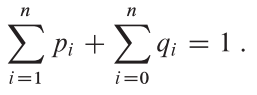
Each key ki is an internal node, and each dummy key di is a leaf.
the expected cost of a search in an binary search tree T is:

问题形式化定义
Input:
{ k1, k2, ... , kn } && { p1, p2, ... , pn }
{ d0, d1, ... , dn } && { q0, q1, ... , qn }
Output
- an optimal binary search tree
暴力算法或其他可行算法分析

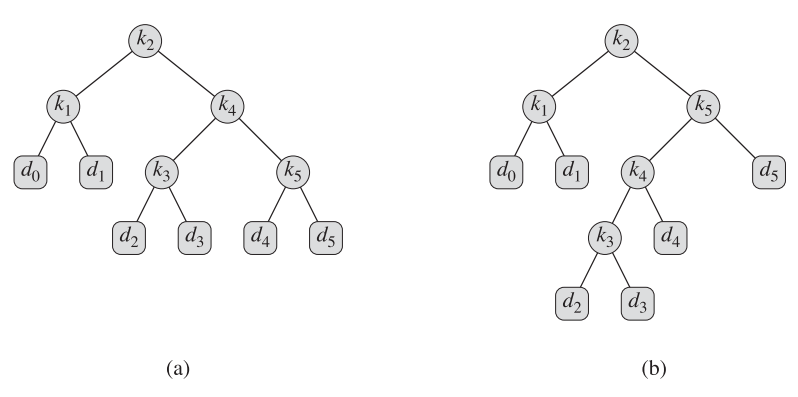
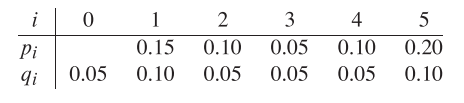
Figure 15.9(b) shows an optimal binary search tree for the probabilities given in the figure caption; its expected cost is 2.75. Figure 15.9(b)'s cost is 2.80
This example shows that an optimal binary search tree is not necessarily a tree whose overall height is smallest. Nor can we necessarily construct an optimal binary search tree by always putting the key with the greatest probability at the root.
We can label the nodes of any n-node binary tree with the keys k1;k2; :::; kn to construct a binary search tree, and then add in the dummy keys as leaves. In Problem 12-4, we saw that the number of binary trees with n nodes is Ω(4n/n3/2), and so we would have to examine an exponential number of binary search trees in an exhaustive search. Not surprisingly, we shall solve this problem with dynamic programming.
动态规划解法
优化子结构
Theorem (Optimal substructure of Optimal binary search trees)
if an optimal binary search tree T has a subtree T' containing keys ki ... kj , then this subtree T' must be optimal as well for the subproblem with keys ki ... kj and dummy keys di-1 ... dj.
Proof
If there were a subtree T00 whose expected cost is lower than that of T0, then we could cut T0 out of T and paste in T00, resulting in a binary search tree of lower expected cost than T, thus contradicting the optimality of T.
DETAIL
There is one detail worth noting about “empty” subtrees. Suppose that in a subtree with keys ki ... kj , we select ki as the root. By the above argument, ki ’s left subtree contains the keys ki ... ki-1. We interpret this sequence as containing no keys. Bear in mind, however, that subtrees also contain dummy keys. We adopt the convention that a subtree containing keys ki ... ki-1 has no actual keys but does contain the single dummy key di-1. Symmetrically, if we select kj as the root, then kj ’s right subtree contains the keys kj-1 ,..., kj ; this right subtree contains no actual keys, but it does contain the dummy key dj .
子问题重叠性
We need to use the optimal substructure to show that we can construct an optimal solution to the problem from optimal solutions to subproblems. Given keys ki ... kj , one of these keys, say kr (i <= r <= j ), is the root of an optimal subtree containing these keys. The left subtree of the root kr contains the keys ki ,..., kr-1 (and dummy keys di-1 ,..., dr-1), and the right subtree contains the keys kr+1 ,..., kj (and dummy keys dr ,.., dj ). As long as we examine all candidate roots kr,where i <= r <= j , and we determine all optimal binary search trees containing ki ,..., kr-1 and those containing kr+1 ,.., kj , we are guaranteed that we will find an optimal binary search tree.
以上文字说明了此问题的最优解构建其实与矩阵链乘问题的最优解的构建基本类似。那么自然可以论证其子问题优化解的存在。
递归的定义优化解的代价
Let us define e[i, j] as the expected cost of searching an optimal binary search tree containing the keys ki ... kj .
基准情况十分简单:
- The easy case occurs when j = i - 1. Then we have just the dummy key di-1. The expected search cost is e[i, i - 1] = qi-1.
其他情况的论述:
When j >= i , we need to select a root kr from among ki ... kj and then make an optimal binary search tree with keys ki ,..., kr-1 as its left subtree and an optimal binary search tree with keys kr+1 ,..., kj as its right subtree.
What happens to the expected search cost of a subtree when it becomes a subtree of a node? The depth of each node in the subtree increases by 1. So:

最后的递归解的表示:
计算优化解的代价算法

we store the e[i, j] values in a table e[1...n+1 , 0...n]. The first index needs to run to n-1 rather than n because in order to have a subtree containing only the dummy key dn, we need to compute and store e[n + 1, n]. The second index needs to start from 0 because in order to have a subtree containing only the dummy key d0, we need to compute and store e[1, 0].
这里对于矩阵边界的理解,十分精辟,建议结合图示进行观看,可以帮助理解。
下面将说明 w[i, j]的构建以及递归方程。
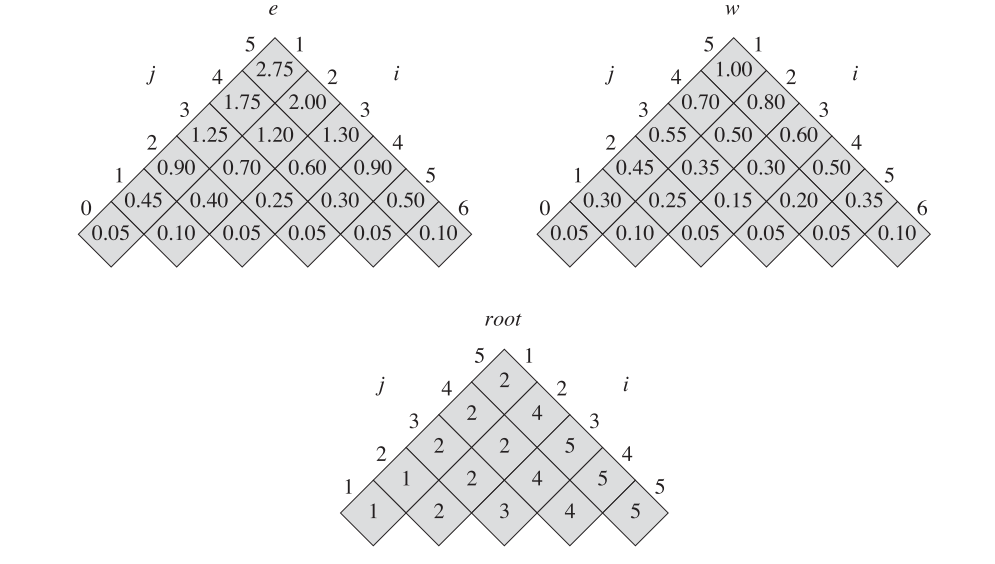
We will need one other table for efficiency. Rather than compute the value of w[i, j] from scratch every time we are computing e[i, j] —which would take Θ(j - i) additions—we store these values in a table w[1 .. n + 1, 0 ... n].

- For the base case, we compute w[i, i - 1] = qi-1 for 1 <= i <= n + 1.
- For j >= i,we compute : w[i, j] = w[i, j - 1] + pj + qj.
空间结构:
M[1:n+1; 0:n]: 存储优化解搜索代价
W[1: n+1; 0:n]: 存储代价增量Wm(i, j)
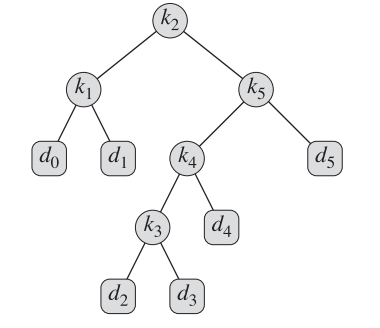
Root[1:n; 1:n]: root(i, j)记录子问题{ki, …, kj}优化解的根
Optimal-BST(p, q, n)
For i=1 To n+1 Do
E(i, i-1) = qi-1;
W(i, i-1) = qi-1;
For l=1 To n Do
For i=1 To n-l+1 Do
j=i+l-1;
E(i, j)=正无穷;
W(i, j)=W(i, j-1)+pj+qj;
For r=i To j Do
t=E(i, r-1)+E(r+1, j)+W(i, j);
If t<E(i, j)
Then E(i, j)=t;
Root(i, j)=r;
Return E and Root
Eg:
构造最优解的算法
最终的最优解将采用如下形式进行输出,其形式对应于上面所给例子。

伪代码为:
CONSTRUCT-OPTIMAL-BST(root)
n = root[0].length
print K {root[1,n]} is the root
Print-BST(root,1,n)
Print-BST(root,i,j)
if (i <= root[i,j]-1)
print k {root[i,root[i,j]-1]} is the left child of k {root[i,j]}
print-BST(root,i,root[i,j]-1)
else
print d {root[i,j]-1} is the left child of k {root[i,j]}
if (j >= root[i,j]+1)
print K {root[root[i,j]+1,j]} is the right child of K {root[i,j]}
print-BST(root,root[i,j]+1,j)
else
print d {j} is the right child of k {root[i,j]}
算法复杂度说明
时间复杂度:
- 计算代价的时间:O(n3).
The OPTIMAL-BST procedure takes O(n3) time, just like MATRIX-CHAINORDER. We can easily see that its running time is O(n3), since its for loops are nested three deep and each loop index takes on at most n values.
The loop indices in OPTIMAL-BST do not have exactly the same bounds as those in MATRIX-CHAINORDER, but they are within at most 1 in all directions. Thus, like MATRIX-CHAINORDER, the OPTIMAL-BST procedure takes Ω(n3) time.
算法代码
#include<stdio.h>
#include<string.h>
#define N 5
#define MAX_FLOAT 10.0
void OPTIMAL_BEST(float* p, float* q, int n);
void CONSTRUCT_OPTIMAL_BST(int root[N + 1][N + 1]);
void Print_BST(int root[N + 1][N + 1], int i, int j);
void main() {
float p[N + 1] = { 0.0,0.15,0.10,0.05,0.10,0.20 };
float q[N + 1] = { 0.05,0.10,0.05,0.05,0.05,0.10 };
OPTIMAL_BEST(p, q, N);
}
void OPTIMAL_BEST(float* p, float* q, int n) {
float e[N + 2][N + 1];
float w[N + 2][N + 1];
int root[N + 1][N + 1];
memset(e, 0.0, sizeof(float) * (N + 2) * (N + 1));
memset(w, 0.0, sizeof(float) * (N + 2) * (N + 1));
memset(root, 0, sizeof(int) * (N + 1) * (N + 1));
for (int i = 1; i <= n + 1; i++) {
e[i][i - 1] = q[i - 1];
w[i][i - 1] = q[i - 1];
}
for (int l = 1; l <= n; l++) {
for (int i = 1; i <= n - l + 1; i++) {
int j = i + l - 1;
e[i][j] = MAX_FLOAT;
w[i][j] = w[i][j - 1] + p[j] + q[j];
for (int r = i; r <= j; r++) {
float t = e[i][r - 1] + e[r + 1][j] + w[i][j];
if (t < e[i][j]){
e[i][j] = t;
root[i][j] = r;
}
}
}
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n + 1; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j <= n; j++) {
printf("%.2f ", e[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
printf("\n");
printf("\n");
printf("\n");
for (int i = 1; i <= n + 1; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j <= n; j++) {
printf("%.2f ", w[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
printf("\n");
printf("\n");
printf("\n");
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
printf("%d ", root[i][j]);
}
printf("\n");
}
printf("\n");
printf("\n");
printf("\n");
CONSTRUCT_OPTIMAL_BST(root);
}
void CONSTRUCT_OPTIMAL_BST(int root[N + 1][N + 1]) {
printf("K %d is the root\n", root[1][N]);
Print_BST(root, 1, N);
}
void Print_BST(int root[N + 1][N + 1], int i, int j) {
if (i <= (root[i][j] - 1)) {
printf("k %d is the left child of k %d\n", root[i][root[i][j] - 1], root[i][j]);
Print_BST(root, i, root[i][j] - 1);
}
else {
printf("d %d is the left child of k %d\n", root[i][j] - 1, root[i][j]);
}
if (j >= root[i][j] + 1) {
printf("k %d is the rightchild of k %d\n", root[root[i][j] + 1][j], root[i][j]);
Print_BST(root, root[i][j] + 1, j);
}
else {
printf("d %d is the right child of k %d\n", j, root[i][j]);
}
}
Optimal binary search trees的更多相关文章
- ITA 15.5 Optimal binary search trees
p400 页最后一段 When j >= i , we need to select a root kr from among ki ... kj and then make an optima ...
- [LeetCode] Unique Binary Search Trees 独一无二的二叉搜索树
Given n, how many structurally unique BST's (binary search trees) that store values 1...n? For examp ...
- [LeetCode] Unique Binary Search Trees II 独一无二的二叉搜索树之二
Given n, generate all structurally unique BST's (binary search trees) that store values 1...n. For e ...
- 2 Unique Binary Search Trees II_Leetcode
Given n, generate all structurally unique BST's (binary search trees) that store values 1...n. For e ...
- 【leetcode】Unique Binary Search Trees (#96)
Given n, how many structurally unique BST's (binary search trees) that store values 1...n? For examp ...
- LEETCODE —— Unique Binary Search Trees [动态规划]
Given n, how many structurally unique BST's (binary search trees) that store values 1...n? For examp ...
- 【LeetCode】95. Unique Binary Search Trees II
Unique Binary Search Trees II Given n, generate all structurally unique BST's (binary search trees) ...
- Leetcode 86. Unique Binary Search Trees
本题利用BST的特性来用DP求解.由于BST的性质,所以root左子树的node全部<root.而右子树的node全部>root. 左子树 = [1, j-1], root = j, 右子 ...
- Print Common Nodes in Two Binary Search Trees
Given two Binary Search Trees, find common nodes in them. In other words, find intersection of two B ...
随机推荐
- spring:bean的生命周期
1.spring中bean的生命周期 (1)概念 在spring框架中,所有的bean对象都有生命周期,就是指bean的创建.初始化.服务.销毁的一个过程. (2)bean的生命周期 bean的定义 ...
- c#数据处理总结(分组、交并差与递归)
前言:最近项目比较忙,完全没有时间写下总结笔记,今天抽出时间来写下笔记,供写后台的你来做数据处理后台代码编写的参考. 一.分组 var GroupForList = numberList.GroupB ...
- Linux常用命令代码大全
arch 显示机器的处理器架构(1) uname -m 显示机器的处理器架构(2) uname -r 显示正在使用的内核版本 dmidecode -q 显示硬件系统部件 – (SMBIOS / DMI ...
- 078 01 Android 零基础入门 02 Java面向对象 01 Java面向对象基础 01 初识面向对象 03 创建类
078 01 Android 零基础入门 02 Java面向对象 01 Java面向对象基础 01 初识面向对象 03 创建类 本文知识点:创建类 说明:因为时间紧张,本人写博客过程中只是对知识点的关 ...
- 022 01 Android 零基础入门 01 Java基础语法 03 Java运算符 02 算术运算符
022 01 Android 零基础入门 01 Java基础语法 03 Java运算符 02 算术运算符 本文知识点:Java中的算术运算符 算术运算符介绍 算术运算符代码示例 注意字符串连接问题和整 ...
- Matlab中image、imagesc和imshow函数用法解析
来源:https://blog.csdn.net/zhuiyuanzhongjia/article/details/79621813 1.显示RGB图像 相同点:这三个函数都是把m*n*3的矩阵中的数 ...
- 使用SignalR和XSLT进行实时注释
下载source code - 10.1 MB Introduction 众所周知,web请求(HTTP请求)是根据请求/响应机制工作的.通过这种方式,作为客户机的浏览器使用GET或POST向服务器 ...
- NOIP提高组2016 D1T2 【天天爱跑步】
码了一个下午加一个晚上吧...... 题目描述: 小c同学认为跑步非常有趣,于是决定制作一款叫做<天天爱跑步>的游戏.<天天爱跑步>是一个养成类游戏,需要玩家每天按时上线,完成 ...
- (OK) Android内核(4.9)集成最新版MPTCP---成功
Android内核(4.9)集成最新版MPTCP---成功
- python进程开启的两种方式
一.进程 1.1.方式一 from multiprocessing import Process import time #方式一 def task(name): print(f"my na ...