二叉排序树的理解和实现(Java)
二叉排序树的定义和性质
二叉排序树又称二叉排序树。它或者是一个空树,或者是一个具有下列性质的二叉树:
- 若它的左子树不空,则左子树上所有节点的值均小于它的根结构的值
- 若它的右子树不空,则右子树上所有结点的值均大于它的根节点的值
- 它的左、右子树也分别是二叉排序树
如下图是一个二叉排序树:
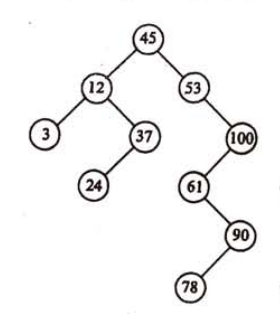
下面的代码(Java实现)基本全部基于递归实现(非递归操作复杂且效率高),简单的实现了BST的这些操作:初始二叉排序树、查找、插入、删除任意结点、遍历二叉树(中序)。
对于二叉排序树的结点定义
public class BinaryTreeNode {
public int data; //数据域
public BinaryTreeNode left, right; //指向左右子节点的指针
public BinaryTreeNode(int data, BinaryTreeNode left, BinaryTreeNode right) {
this.data = data;
this.left = left;
this.right = right;
}
}
同时,在二叉查找树实现类中定义二叉查找树的根节点:
public BinaryTreeNode root;
初始化二叉查找树
public void insertBinaryTree(int[] datas) {
if(datas.length < 1) {
System.out.println("the datas Array length small zero!");
return;
}
this.root = new BinaryTreeNode(datas[0], null, null);
for (int i = 1; i < datas.length; i++) {
this.insert(this.root, datas[i]);
}
}
private void insert(BinaryTreeNode root, int data) {
if(data > root.data) {
if(root.right == null)
root.right = new BinaryTreeNode(data, null, null);
else
this.insert(root.right, data);
}
else {
if(root.left == null)
root.left = new BinaryTreeNode(data, null, null);
else
this.insert(root.left, data);
}
}
通过传递给insertBinaryTree()存储二叉查找树值的数组来完成初始化。通过insert()方法递归的来完成对结点的初始化操作。
二叉排序树的遍历(中序)
public void inOrder(BinaryTreeNode root) {
if(root != null) {
this.inOrder(root.left);
System.out.print(root.data + "-");
this.inOrder(root.right);
}
}
根据二叉排序树的特性我们知道如果根节点非空,则根节点的左子树上所有结点的值均小于根节点,右子树上的所有结点值均大于根节点。同理对任意子树都满足上面。所以对于二叉排序树的遍历是对二叉排序树的由小到大的升序输出。在这里前序和后序遍历与中序逻辑相似,不做展示。
根据键值查询BST
public boolean SearchBST(BinaryTreeNode root, int key) {
if(root == null) {
return false;
}
else if(key == root.data) {
return true;
}
else if(key < root.data) {
return this.SearchBST(root.left, key);
}
else {
return this.SearchBST(root.right, key);
}
}
查询操作也基于递归,查询过程和节点结点值进行比较,若成功返回true。
二叉排序树的插入操作
public boolean InsertBST(BinaryTreeNode root, int key) {
if(!this.SearchBST(root, key)) {
this.insert(root, key);
return true;
}
else {
System.out.println("the key existence in BinaryTree");
return false;
}
}
该操作的思路是查询带插入的key是否已经在二叉排序树中,如果不在,执行insert()方法递归的将key插入到指定的位置,如果存在,返回错误信息并结束。
但是后面在想的时候发现这段代码虽然实现很简单,但是执行步骤却很复杂:在查找是否存在时就需要遍历一次完整的二叉排序树,之后在插入时同样需要遍历一次,将key插入。所以想到了一个优化就是在查找时保存key值应该插入的结点(注意,这个时候还没有插入,所以此时结点并不是真正存在的)的父结点。这样在执行插入时将插入操作的时间复杂度将为O(1).
二叉排序树的插入操作优化:
声明一个parent结点来用来缓存查找时查到的父节点
public BinaryTreeNode parent = null;
对查询方法做简单调整:
public boolean SearchBST2(BinaryTreeNode root, BinaryTreeNode parent, int key) {
if(root == null) {
this.parent = parent;
return false;
}
else if(key == root.data) {
this.parent = root;
return true;
}
else if(key < root.data) {
return this.SearchBST2(root.left, root, key);
}
else {
return this.SearchBST2(root.right, root, key);
}
}
首次操作时parent=null,之后保存当前查询root结点的父节点。
对插入方法做简单调整:
public boolean InsertBST2(BinaryTreeNode root, int key) {
if(!this.SearchBST2(root, this.parent, key)) {
BinaryTreeNode keyNode = new BinaryTreeNode(key, null, null);
if(this.parent == null) {
root = keyNode;
}
else if(key < this.parent.data) {
this.parent.left = keyNode;
}
else this.parent.left = keyNode;
return true;
}
else {
System.out.println("the key existence in BinaryTree");
return false;
}
}
这样在查询操作完成后通过简单的语句便可将key插入指定的位置,而不需要在做一次递归。
删除二叉排序树的任意结点
对于二叉排序树的删除操作并不是很容易,因为我们需要保证再删除了结点后,让这棵树依旧满足二叉排序树的特性,所以在删除时就需要考虑多种情况。一般分为三种情况进行讨论。
我们做一个约定:定义待删除的结点是结点x,其父结点是结点p,左子树结点是l,右子树结点是r,兄弟结点为b。其中NAN均为虚拟的null结点。
待删除的结点为叶子结点时
直接删除叶子结点x,并将父结点指向该节点的域置位NAN(null)。
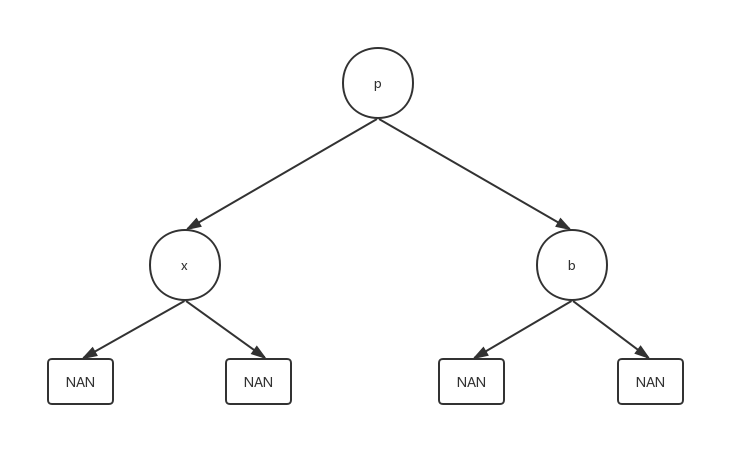
这时直接删除x结点,然后将p的左结点指向NAN结点
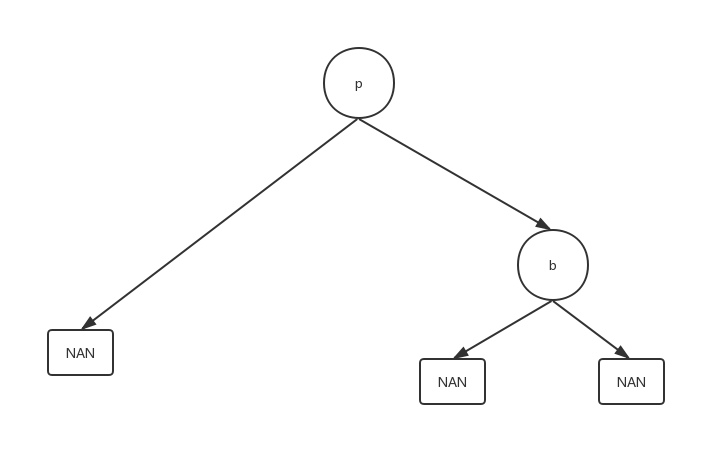
当删除的结点只有左子树或只有右子树
相对来说也好解决,那就是结点删除后,将它的左子树或右子树整个移动到删除结点的位置即可,可以理解为独子继承父业。
比如要删除结点x,直接将父结点p指向待删除的结点x的指针直接指向x结点的唯一儿子结点(l或则是r),然后删除x结点即可。
该图只演示了删除只有左子树的结点的时候,删除只有右子树的时候思路相同。
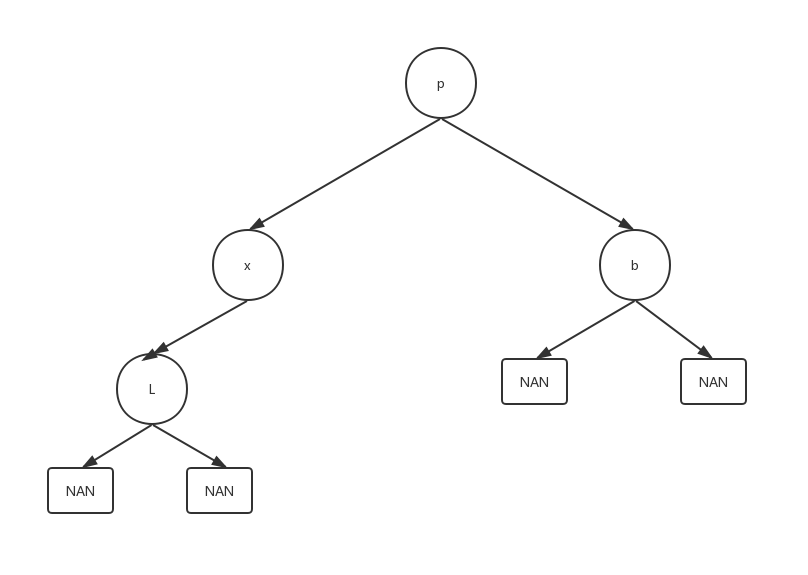
这时候将p的左子树指向x唯一的子结点L,,然后在删除x
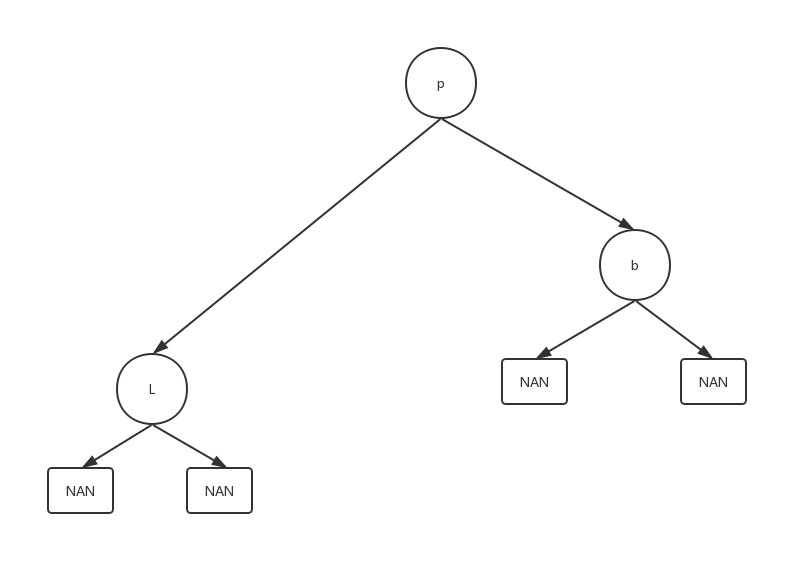
当删除的x结点存在左右结点时
这也是最麻烦的一种情况,通常的解决方式是用删除结点x的前驱(或后继)结点填补它的位置。因为x有一个左子结点,因此它的前驱结点就是左子树中的最大结点,这样替换就能保证有序性,因为x.data和它的前驱之间不存在其他的键值。
操作如下:
- 寻找到待删除的结点的前驱结点,并用s指向其前驱结点
- 找到待删除结点的前驱结点的父结点,并用q来指向前驱结点的父节点。
- 将x的前驱结点的值赋给x,完成替换操作。
- 最后修改q的指向为s的子节点,并删除s。
递归寻找待删除的结点:
public boolean DeleteBST(BinaryTreeNode root, int key) {
if(root == null) {
System.out.println("the root node is null");
return false;
}
else {
if(key == root.data) {
return this.delete(root);
}
else if(key < root.data) {
return this.DeleteBST(root.left, key);
}
else {
return this.DeleteBST(root.right, key);
}
}
}
删除指定的x结点:
public boolean delete(BinaryTreeNode root) {
BinaryTreeNode q, s;
if(root.right == null) {
root = root.left;
}
else if(root.left == null) {
root = root.right;
}
else {
q = root;
s = root.left;
while(s.right != null) {
q = s;
s = s.right;
}
root.data = s.data;
if(q != root) {
q.right = s.left;
}
else {
q.left = s.left;
}
}
return true;
}
源代码:
public class BinaryTreeBuilder {
public BinaryTreeNode root;
public BinaryTreeNode parent = null;
public void insertBinaryTree(int[] datas) {
if(datas.length < 1) {
System.out.println("the datas Array length small zero!");
return;
}
this.root = new BinaryTreeNode(datas[0], null, null);
for (int i = 1; i < datas.length; i++) {
this.insert(this.root, datas[i]);
}
}
private void insert(BinaryTreeNode root, int data) {
if(data > root.data) {
if(root.right == null)
root.right = new BinaryTreeNode(data, null, null);
else
this.insert(root.right, data);
}
else {
if(root.left == null)
root.left = new BinaryTreeNode(data, null, null);
else
this.insert(root.left, data);
}
}
public void inOrder(BinaryTreeNode root) {
if(root != null) {
this.inOrder(root.left);
System.out.print(root.data + "-");
this.inOrder(root.right);
}
}
public boolean SearchBST(BinaryTreeNode root, int key) {
if(root == null) {
return false;
}
else if(key == root.data) {
return true;
}
else if(key < root.data) {
return this.SearchBST(root.left, key);
}
else {
return this.SearchBST(root.right, key);
}
}
public boolean SearchBST2(BinaryTreeNode root, BinaryTreeNode parent, int key) {
if(root == null) {
this.parent = parent;
return false;
}
else if(key == root.data) {
this.parent = root;
return true;
}
else if(key < root.data) {
return this.SearchBST2(root.left, root, key);
}
else {
return this.SearchBST2(root.right, root, key);
}
}
public boolean InsertBST(BinaryTreeNode root, int key) {
if(!this.SearchBST(root, key)) {
this.insert(root, key);
return true;
}
else {
System.out.println("the key existence in BinaryTree");
return false;
}
}
public boolean InsertBST2(BinaryTreeNode root, int key) {
if(!this.SearchBST2(root, this.parent, key)) {
BinaryTreeNode keyNode = new BinaryTreeNode(key, null, null);
if(this.parent == null) {
root = keyNode;
}
else if(key < this.parent.data) {
this.parent.left = keyNode;
}
else this.parent.left = keyNode;
return true;
}
else {
System.out.println("the key existence in BinaryTree");
return false;
}
}
public boolean DeleteBST(BinaryTreeNode root, int key) {
if(root == null) {
System.out.println("the root node is null");
return false;
}
else {
if(key == root.data) {
return this.delete(root);
}
else if(key < root.data) {
return this.DeleteBST(root.left, key);
}
else {
return this.DeleteBST(root.right, key);
}
}
}
public boolean delete(BinaryTreeNode root) {
BinaryTreeNode q, s;
if(root.right == null) {
root = root.left;
}
else if(root.left == null) {
root = root.right;
}
else {
q = root;
s = root.left;
while(s.right != null) {
q = s;
s = s.right;
}
root.data = s.data;
if(q != root) {
q.right = s.left;
}
else {
q.left = s.left;
}
}
return true;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] datas = {62, 88, 58, 47, 35, 73, 51, 99, 37, 93};
BinaryTreeBuilder b = new BinaryTreeBuilder();
b.insertBinaryTree(datas);
b.inOrder(b.root);
b.InsertBST(b.root, 1);
System.out.println();
b.inOrder(b.root);
}
}
对于BST的总结
BST以链接方式存储,保持了链接存储结构在执行插入或删除操作时不用移动元素的优点,只要找到合适的插入和删除位置后,仅需要修改链接指针即可。插入删除的时间性能比较好。而对于BST的查找,其比较次数等于给定值的结点在二叉排序树的层数,极端情况下,最少为1次,最多不会超过树的深度。也就是说BST的查找性能取决于BST的形状。
我们希望二叉排序树是比较平衡的,其深度与完全二叉树相同,均为log2n\log_{2}nlog2n + 1,那么查找的时间复杂度也就为O(logn),近似于折半查找。这就引申出一个问题,即如何让BST平衡化。
二叉排序树的理解和实现(Java)的更多相关文章
- Atitit 深入理解命名空间namespace java c# php js
Atitit 深入理解命名空间namespace java c# php js 1.1. Namespace还是package1 1.2. import同时解决了令人头疼的include1 1.3 ...
- 理解和解决Java并发修改异常ConcurrentModificationException(转载)
原文地址:https://www.jianshu.com/p/f3f6b12330c1 理解和解决Java并发修改异常ConcurrentModificationException 不知读者在Java ...
- 深入理解和探究Java类加载机制
深入理解和探究Java类加载机制---- 1.java.lang.ClassLoader类介绍 java.lang.ClassLoader类的基本职责就是根据一个指定的类的名称,找到或者生成其对应的字 ...
- 深入理解什么是Java泛型?泛型怎么使用?【纯转】
本篇文章给大家带来的内容是介绍深入理解什么是Java泛型?泛型怎么使用?有一定的参考价值,有需要的朋友可以参考一下,希望对你们有所助. 一.什么是泛型 “泛型” 意味着编写的代码可以被不同类型的对象所 ...
- 平衡二叉树(AVL)的理解和实现(Java)
AVL的定义 平衡二叉树:是一种特殊的二叉排序树,其中每一个节点的左子树和右子树的高度差至多等于1.从平衡二叉树的名字中可以看出来,它是一种高度平衡的二叉排序树.那么什么叫做高度平衡呢?意思就是要么它 ...
- [转载] 深入理解Android之Java虚拟机Dalvik
本文转载自: http://blog.csdn.net/innost/article/details/50377905 一.背景 这个选题很大,但并不是一开始就有这么高大上的追求.最初之时,只是源于对 ...
- 如何理解和使用Java package包
Java中的一个包就是一个类库单元,包内包含有一组类,它们在单一的名称空间之下被组织在了一起.这个名称空间就是包名.可以使用import关键字来导入一个包.例如使用import java.util.* ...
- 深入理解JVM(6)——Java内存模型和线程
Java虚拟机规范中定义了Java内存模型(Java Memory Model,JMM)用来屏蔽掉各种硬件和操作系统的内存访问差异,以实现让Java程序在各种平台下都能达到一致的内存访问效果(“即Ja ...
- 理解JVM之Java内存区域
Java虚拟机运行时数据区分为以下几个部分: 方法区.虚拟机栈.本地方法栈.堆.程序计数器.如下图所示: 一.程序计数器 程序计数器可看作当前线程所执行的字节码行号指示器,字节码解释器工作时就是通过改 ...
随机推荐
- jQuery获得元素位置offset()和position()的区别
jQuery获得元素位置offset()和position()的区别 jQuery 中有两个获取元素位置的方法offset()和position(),这两个方法之间有什么异同 offset(): 获取 ...
- 2018.10.08 NOIP模拟 序列(主席树)
传送门 T2防ak题? 其实也不是很难(考试时sb了). 直接变形一下求出区间长度在[l2,r2][l2,r2][l2,r2]之间,中位数≤l1−1\le l1-1≤l1−1的区间数,和区间长度在[l ...
- 2018.10.05 NOIP模拟 上升序列(状压dp)
传送门 状压dp好题. 首先需要回忆O(nlogn)O(nlog n)O(nlogn)求lislislis的方法,我们会维护一个单调递增的ddd数组. 可以设计状态f(s1,s2)f(s1,s2)f( ...
- 2018.09.26 bzoj4326: NOIP2015 运输计划(二分+树上差分)
传送门 简单树上操作. 先转边权为点权. 显然所有的询问操作对应的路径会有一些交点,那么我们可以直接二分答案,对于所有大于二分值的询问用树上差分维护,最后dfs一遍每个点被覆盖了几次,当前情况合法当且 ...
- 2018.07.10NOIP模拟 Knapsack(单调队列优化dp)
Knapsack 题目背景 SOURCE:NOIP2016-RZZ-4 T2 题目描述 有 n 个物品,第 i 个物品的重量为 ai . 设 f(i,j,k,l,m) 为满足以下约束的物品集合数量: ...
- 改变yii2 $form最外层div样式
<?php $form = ActiveForm::begin([ 'options'=>['class' => 'form-horizontal row-border','enct ...
- spring+hibernate 整合异常 Class 'org.apache.commons.dbcp.BasicDataSource' not found
解决方法 添加 commons-dbcp.jar和commons-pool.jar包
- BaseAdapter
作者通过Java代码来实现布局,而我习惯通过.xml文件来实现,所以我对程序做了如下修改 MainActivity.java public class MainActivity extends Act ...
- modelsim仿真中遇到的问题
1.modelsim经常遇到数据位宽不相等的情况,这样往往仿真时是不会出数据的,如果用parameter定义了数据的位宽, 要注意实际的位宽数大于parameter定义参数能表示的位宽时,如: par ...
- c++中sort()及qsort()的用法总结
当并算法详解请见点我 想起来自己天天排序排序,冒泡啊,二分查找啊,结果在STL中就自带了排序函数sort,qsort,总算把自己解脱了~ 所以自己总结了一下,首先看sort函数见下表: 函数名 功能描 ...
