scikit-learn_cookbook1: 高性能机器学习-NumPy
在本章主要内容:
- NumPy基础知识
- 加载iris数据集
- 查看iris数据集
- 用pandas查看iris数据集
- 用NumPy和matplotlib绘图
- 最小机器学习配方 - SVM分类
- 介绍交叉验证
- 以上汇总
- 机器学习概述 - 分类与回归
简介
本章我们将学习如何使用scikit-learn进行预测。 机器学习强调衡量预测能力,并用scikit-learn进行准确和快速的预测。我们将检查iris数据集,该数据集由三种iris的测量结果组成:Iris Setosa,Iris Versicolor和Iris Virginica。
为了衡量预测,我们将:
- 保存一些数据以进行测试
- 仅使用训练数据构建模型
- 测量测试集的预测能力
解决问题的方法
- 类别(Classification):
- 非文本,比如Iris
- 回归
- 聚类
- 降维
技术支持 (可以加qq群:887934385)
NumPy基础
数据科学经常处理结构化的数据表。scikit-learn库需要二维NumPy数组。 在本节中,您将学习
- NumPy的shape和dimension
In [1]: import numpy as np
In [2]: np.arange(10)
Out[2]: array([0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9])
In [3]: array_1 = np.arange(10)
In [4]: array_1.shape
Out[4]: (10,)
In [5]: array_1.ndim
Out[5]: 1
In [6]: array_1.reshape((5,2))
Out[6]:
array([[0, 1],
[2, 3],
[4, 5],
[6, 7],
[8, 9]])
In [7]: array_1 = array_1.reshape((5,2))
In [8]: array_1.ndim
Out[8]: 2
- NumPy广播(broadcasting)
In [9]: array_1 + 1
Out[9]:
array([[ 1, 2],
[ 3, 4],
[ 5, 6],
[ 7, 8],
[ 9, 10]]) In [10]: array_2 = np.arange(10) In [11]: array_2 * array_2
Out[11]: array([ 0, 1, 4, 9, 16, 25, 36, 49, 64, 81]) In [12]: array_2 = array_2 ** 2 #Note that this is equivalent to array_2 * In [13]: array_2
Out[13]: array([ 0, 1, 4, 9, 16, 25, 36, 49, 64, 81]) In [14]: array_2 = array_2.reshape((5,2)) In [15]: array_2
Out[15]:
array([[ 0, 1],
[ 4, 9],
[16, 25],
[36, 49],
[64, 81]]) In [16]: array_1 = array_1 + 1 In [17]: array_1
Out[17]:
array([[ 1, 2],
[ 3, 4],
[ 5, 6],
[ 7, 8],
[ 9, 10]]) In [18]: array_1 + array_2
Out[18]:
array([[ 1, 3],
[ 7, 13],
[21, 31],
[43, 57],
[73, 91]])
- 初始化NumPy数组和dtypes
In [19]: np.zeros((5,2))
Out[19]:
array([[0., 0.],
[0., 0.],
[0., 0.],
[0., 0.],
[0., 0.]]) In [20]: np.ones((5,2), dtype = np.int)
Out[20]:
array([[1, 1],
[1, 1],
[1, 1],
[1, 1],
[1, 1]]) In [21]: np.empty((5,2), dtype = np.float)
Out[21]:
array([[0.00000000e+000, 0.00000000e+000], [6.90082649e-310, 6.90082647e-310],
[6.90072710e-310, 6.90072711e-310],
[6.90083466e-310, 0.00000000e+000],
[6.90083921e-310, 1.90979621e-310]])
- 索引
In [22]: array_1[0,0] #Finds value in first row and first column.
Out[22]: 1 In [23]: array_1[0,:] # View the first row
Out[23]: array([1, 2]) In [24]: array_1[:,0] # view the first column
Out[24]: array([1, 3, 5, 7, 9]) In [25]: array_1[2:5, :]
Out[25]:
array([[ 5, 6],
[ 7, 8],
[ 9, 10]]) In [26]: array_1
Out[26]:
array([[ 1, 2],
[ 3, 4],
[ 5, 6],
[ 7, 8],
[ 9, 10]]) In [27]: array_1[2:5,0]
Out[27]: array([5, 7, 9])
- 布尔数组
In [28]: array_1 > 5
Out[28]:
array([[False, False],
[False, False],
[False, True],
[ True, True],
[ True, True]]) In [29]: array_1[array_1 > 5]
Out[29]: array([ 6, 7, 8, 9, 10])
- 算术运算
In [30]: array_1.sum()
Out[30]: 55 In [31]: array_1.sum(axis = 1) # Find all the sums by row:
Out[31]: array([ 3, 7, 11, 15, 19]) In [32]: array_1.sum(axis = 0) # Find all the sums by column
Out[32]: array([25, 30]) In [33]: array_1.mean(axis = 0)
Out[33]: array([5., 6.])
- NaN值
# Scikit-learn不接受np.nan
In [34]: array_3 = np.array([np.nan, 0, 1, 2, np.nan]) In [35]: np.isnan(array_3)
Out[35]: array([ True, False, False, False, True]) In [36]: array_3[~np.isnan(array_3)]
Out[36]: array([0., 1., 2.]) In [37]: array_3[np.isnan(array_3)] = 0 In [38]: array_3
Out[38]: array([0., 0., 1., 2., 0.])
Scikit-learn只接受实数的二维NumPy数组,没有缺失的np.nan值。从经验来看,最好将np.nan改为某个值丢弃。 就我个人而言,我喜欢跟踪布尔模板并保持数据的形状大致相同,因为这会导致更少的编码错误和更多的编码灵活性。
加载数据
In [1]: import numpy as np In [2]: import pandas as pd In [3]: import matplotlib.pyplot as plt In [4]: from sklearn import datasets In [5]: iris = datasets.load_iris() In [6]: iris.data
Out[6]:
array([[5.1, 3.5, 1.4, 0.2],
[4.9, 3. , 1.4, 0.2],
[4.7, 3.2, 1.3, 0.2],
[4.6, 3.1, 1.5, 0.2],
[5. , 3.6, 1.4, 0.2],
[5.4, 3.9, 1.7, 0.4],
[4.6, 3.4, 1.4, 0.3],
[5. , 3.4, 1.5, 0.2],
[4.4, 2.9, 1.4, 0.2],
[4.9, 3.1, 1.5, 0.1],
[5.4, 3.7, 1.5, 0.2],
[4.8, 3.4, 1.6, 0.2],
[4.8, 3. , 1.4, 0.1],
[4.3, 3. , 1.1, 0.1],
[5.8, 4. , 1.2, 0.2],
[5.7, 4.4, 1.5, 0.4],
[5.4, 3.9, 1.3, 0.4],
[5.1, 3.5, 1.4, 0.3],
[5.7, 3.8, 1.7, 0.3],
[5.1, 3.8, 1.5, 0.3],
[5.4, 3.4, 1.7, 0.2],
[5.1, 3.7, 1.5, 0.4],
[4.6, 3.6, 1. , 0.2],
[5.1, 3.3, 1.7, 0.5],
[4.8, 3.4, 1.9, 0.2],
[5. , 3. , 1.6, 0.2],
[5. , 3.4, 1.6, 0.4],
[5.2, 3.5, 1.5, 0.2],
[5.2, 3.4, 1.4, 0.2],
[4.7, 3.2, 1.6, 0.2],
[4.8, 3.1, 1.6, 0.2],
[5.4, 3.4, 1.5, 0.4],
[5.2, 4.1, 1.5, 0.1],
[5.5, 4.2, 1.4, 0.2],
[4.9, 3.1, 1.5, 0.1],
[5. , 3.2, 1.2, 0.2],
[5.5, 3.5, 1.3, 0.2],
[4.9, 3.1, 1.5, 0.1],
[4.4, 3. , 1.3, 0.2],
[5.1, 3.4, 1.5, 0.2],
[5. , 3.5, 1.3, 0.3],
[4.5, 2.3, 1.3, 0.3],
[4.4, 3.2, 1.3, 0.2],
[5. , 3.5, 1.6, 0.6],
[5.1, 3.8, 1.9, 0.4],
[4.8, 3. , 1.4, 0.3],
[5.1, 3.8, 1.6, 0.2],
[4.6, 3.2, 1.4, 0.2],
[5.3, 3.7, 1.5, 0.2],
[5. , 3.3, 1.4, 0.2],
[7. , 3.2, 4.7, 1.4],
[6.4, 3.2, 4.5, 1.5],
[6.9, 3.1, 4.9, 1.5],
[5.5, 2.3, 4. , 1.3],
[6.5, 2.8, 4.6, 1.5],
[5.7, 2.8, 4.5, 1.3],
[6.3, 3.3, 4.7, 1.6],
[4.9, 2.4, 3.3, 1. ],
[6.6, 2.9, 4.6, 1.3],
[5.2, 2.7, 3.9, 1.4],
[5. , 2. , 3.5, 1. ],
[5.9, 3. , 4.2, 1.5],
[6. , 2.2, 4. , 1. ],
[6.1, 2.9, 4.7, 1.4],
[5.6, 2.9, 3.6, 1.3],
[6.7, 3.1, 4.4, 1.4],
[5.6, 3. , 4.5, 1.5],
[5.8, 2.7, 4.1, 1. ],
[6.2, 2.2, 4.5, 1.5],
[5.6, 2.5, 3.9, 1.1],
[5.9, 3.2, 4.8, 1.8],
[6.1, 2.8, 4. , 1.3],
[6.3, 2.5, 4.9, 1.5],
[6.1, 2.8, 4.7, 1.2],
[6.4, 2.9, 4.3, 1.3],
[6.6, 3. , 4.4, 1.4],
[6.8, 2.8, 4.8, 1.4],
[6.7, 3. , 5. , 1.7],
[6. , 2.9, 4.5, 1.5],
[5.7, 2.6, 3.5, 1. ],
[5.5, 2.4, 3.8, 1.1],
[5.5, 2.4, 3.7, 1. ],
[5.8, 2.7, 3.9, 1.2],
[6. , 2.7, 5.1, 1.6],
[5.4, 3. , 4.5, 1.5],
[6. , 3.4, 4.5, 1.6],
[6.7, 3.1, 4.7, 1.5],
[6.3, 2.3, 4.4, 1.3],
[5.6, 3. , 4.1, 1.3],
[5.5, 2.5, 4. , 1.3],
[5.5, 2.6, 4.4, 1.2],
[6.1, 3. , 4.6, 1.4],
[5.8, 2.6, 4. , 1.2],
[5. , 2.3, 3.3, 1. ],
[5.6, 2.7, 4.2, 1.3],
[5.7, 3. , 4.2, 1.2],
[5.7, 2.9, 4.2, 1.3],
[6.2, 2.9, 4.3, 1.3],
[5.1, 2.5, 3. , 1.1],
[5.7, 2.8, 4.1, 1.3],
[6.3, 3.3, 6. , 2.5],
[5.8, 2.7, 5.1, 1.9],
[7.1, 3. , 5.9, 2.1],
[6.3, 2.9, 5.6, 1.8],
[6.5, 3. , 5.8, 2.2],
[7.6, 3. , 6.6, 2.1],
[4.9, 2.5, 4.5, 1.7],
[7.3, 2.9, 6.3, 1.8],
[6.7, 2.5, 5.8, 1.8],
[7.2, 3.6, 6.1, 2.5],
[6.5, 3.2, 5.1, 2. ],
[6.4, 2.7, 5.3, 1.9],
[6.8, 3. , 5.5, 2.1],
[5.7, 2.5, 5. , 2. ],
[5.8, 2.8, 5.1, 2.4],
[6.4, 3.2, 5.3, 2.3],
[6.5, 3. , 5.5, 1.8],
[7.7, 3.8, 6.7, 2.2],
[7.7, 2.6, 6.9, 2.3],
[6. , 2.2, 5. , 1.5],
[6.9, 3.2, 5.7, 2.3],
[5.6, 2.8, 4.9, 2. ],
[7.7, 2.8, 6.7, 2. ],
[6.3, 2.7, 4.9, 1.8],
[6.7, 3.3, 5.7, 2.1],
[7.2, 3.2, 6. , 1.8],
[6.2, 2.8, 4.8, 1.8],
[6.1, 3. , 4.9, 1.8],
[6.4, 2.8, 5.6, 2.1],
[7.2, 3. , 5.8, 1.6],
[7.4, 2.8, 6.1, 1.9],
[7.9, 3.8, 6.4, 2. ],
[6.4, 2.8, 5.6, 2.2],
[6.3, 2.8, 5.1, 1.5],
[6.1, 2.6, 5.6, 1.4],
[7.7, 3. , 6.1, 2.3],
[6.3, 3.4, 5.6, 2.4],
[6.4, 3.1, 5.5, 1.8],
[6. , 3. , 4.8, 1.8],
[6.9, 3.1, 5.4, 2.1],
[6.7, 3.1, 5.6, 2.4],
[6.9, 3.1, 5.1, 2.3],
[5.8, 2.7, 5.1, 1.9],
[6.8, 3.2, 5.9, 2.3],
[6.7, 3.3, 5.7, 2.5],
[6.7, 3. , 5.2, 2.3],
[6.3, 2.5, 5. , 1.9],
[6.5, 3. , 5.2, 2. ],
[6.2, 3.4, 5.4, 2.3],
[5.9, 3. , 5.1, 1.8]]) In [7]: iris.data.shape
Out[7]: (150, 4) In [8]: iris.data[0]
Out[8]: array([5.1, 3.5, 1.4, 0.2]) In [9]: iris.feature_names
Out[9]:
['sepal length (cm)',
'sepal width (cm)',
'petal length (cm)',
'petal width (cm)'] In [10]: iris.target
Out[10]:
array([0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0,
0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1,
1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1,
1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2,
2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2,
2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2]) In [11]: iris.target.shape
Out[11]: (150,) In [12]: iris.target_names
Out[12]: array(['setosa', 'versicolor', 'virginica'], dtype='<U10')
- 用pandas查看数据
import numpy as np #Load the numpy library for fast array computations
import pandas as pd #Load the pandas data-analysis library
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt #Load the pyplot visualization library %matplotlib inline from sklearn import datasets
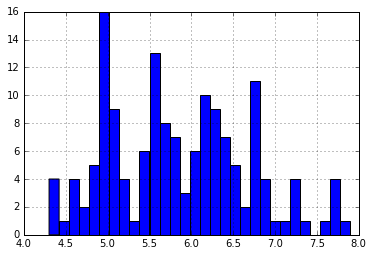
iris = datasets.load_iris() iris_df = pd.DataFrame(iris.data, columns = iris.feature_names) iris_df['sepal length (cm)'].hist(bins=30)
```
!python
for class_number in np.unique(iris.target): plt.figure(1) iris_df['sepal length (cm)'].iloc[np.where(iris.target == class_number)[0]].hist(bins=30)

```
#!python
np.where(iris.target == class_number)[0]
执行结果
array([100, 101, 102, 103, 104, 105, 106, 107, 108, 109, 110, 111, 112,
113, 114, 115, 116, 117, 118, 119, 120, 121, 122, 123, 124, 125,
126, 127, 128, 129, 130, 131, 132, 133, 134, 135, 136, 137, 138,
139, 140, 141, 142, 143, 144, 145, 146, 147, 148, 149], dtype=int64)
matplotlib和NumPy作图
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
%matplotlib inline plt.plot(np.arange(10), np.arange(10)) plt.plot(np.arange(10), np.exp(np.arange(10))) # 两张图片放在一起
plt.figure()
plt.subplot(121)
plt.plot(np.arange(10), np.exp(np.arange(10)))
plt.subplot(122)
plt.scatter(np.arange(10), np.exp(np.arange(10))) plt.figure()
plt.subplot(211)
plt.plot(np.arange(10), np.exp(np.arange(10)))
plt.subplot(212)
plt.scatter(np.arange(10), np.exp(np.arange(10))) plt.figure()
plt.subplot(221)
plt.plot(np.arange(10), np.exp(np.arange(10)))
plt.subplot(222)
plt.scatter(np.arange(10), np.exp(np.arange(10)))
plt.subplot(223)
plt.scatter(np.arange(10), np.exp(np.arange(10)))
plt.subplot(224)
plt.scatter(np.arange(10), np.exp(np.arange(10))) from sklearn.datasets import load_iris iris = load_iris()
data = iris.data
target = iris.target # Resize the figure for better viewing
plt.figure(figsize=(12,5)) # First subplot
plt.subplot(121) # Visualize the first two columns of data:
plt.scatter(data[:,0], data[:,1], c=target) # Second subplot
plt.subplot(122) # Visualize the last two columns of data:
plt.scatter(data[:,2], data[:,3], c=target)
1 |
import numpy as np |
最小机器学习快速入门 - 向量机分类
为了做出预测,我们将: * 说明要解决的问题 * 选择一个模型来解决问题 * 训练模型 * 作出预测 * 衡量模型的表现如何
scikit-learn_cookbook1: 高性能机器学习-NumPy的更多相关文章
- [机器学习]numpy broadcast shape 机制
最近在做机器学习的时候,对未知对webshell检测,发现代码提示:ValueError: operands could not be broadcast together with shapes ( ...
- 机器学习- Numpy基础 吐血整理
Numpy是专门为数据科学或者数据处理相关的需求设计的一个高效的组件.听起来是不是挺绕口的,其实简单来说就2个方面,一是Numpy是专门处理数据的,二是Numpy在处理数据方面很牛逼(肯定比Pytho ...
- 机器学习 Numpy库入门
2017-06-28 13:56:25 Numpy 提供了一个强大的N维数组对象ndarray,提供了线性代数,傅里叶变换和随机数生成等的基本功能,可以说Numpy是Scipy,Pandas等科学计算 ...
- 第四十篇 入门机器学习——Numpy.array的基本操作——向量及矩阵的运算
No.1. Numpy.array相较于Python原生List的性能优势 No.2. 将向量或矩阵中的每个元素 + 1 No.2. 将向量或矩阵中的所有元素 - 1 No.3. 将向量或矩阵中的所有 ...
- 第三十七篇 入门机器学习——Numpy基础
No.1. 查看numpy版本 No.2. 为了方便使用numpy,在导入时顺便起个别名 No.3. numpy.array的基本操作:创建.查询.修改 No.4. 用dtype查看当前元素的数据类型 ...
- 第四十三篇 入门机器学习——Numpy的基本操作——Fancy Indexing
No.1. 通过索引快速访问向量中的多个元素 No.2. 用索引对应的元素快速生成一个矩阵 No.3. 通过索引从矩阵中快速获取多个元素 No.4. 获取矩阵中感兴趣的行或感兴趣的列,重新组成矩阵 N ...
- 第四十二篇 入门机器学习——Numpy的基本操作——索引相关
No.1. 使用np.argmin和np.argmax来获取向量元素中最小值和最大值的索引 No.2. 使用np.random.shuffle将向量中的元素顺序打乱,操作后,原向量发生改变:使用np. ...
- 第四十一篇 入门机器学习——Numpy的基本操作——聚合操作
No.1. 对向量元素求和使用np.sum,也可以使用类似big_array.sum()的方式 No.2. 对向量元素求最小值使用np.min,求最大值使用np.max,也可以使用类似big_arra ...
- 第三十九篇 入门机器学习——Numpy.array的基础操作——合并与分割向量和矩阵
No.1. 初始化状态 No.2. 合并多个向量为一个向量 No.3. 合并多个矩阵为一个矩阵 No.4. 借助vstack和hstack实现矩阵与向量的快速合并.或多个矩阵快速合并 No.5. 分割 ...
随机推荐
- 有些需要禁用的PHP危险函数(disable_functions)
phpinfo() 功能描述:输出 PHP 环境信息以及相关的模块.WEB 环境等信息. 危险等级:中 passthru() 功能描述:允许执行一个外部程序并回显输出,类似于 exec(). 危险等级 ...
- 设计模式C++描述----15.策略(Strategy)模式
一. 举例说明 以前做了一个程序,程序的功能是评价几种加密算法时间,程序的使用操作不怎么变,变的是选用各种算法. 结构如下: Algorithm:抽象类,提供算法的公共接口. RSA_Algorith ...
- Python网络爬虫之cookie处理、验证码识别、代理ip、基于线程池的数据爬去
本文概要 session处理cookie proxies参数设置请求代理ip 基于线程池的数据爬取 引入 有些时候,我们在使用爬虫程序去爬取一些用户相关信息的数据(爬取张三“人人网”个人主页数据)时, ...
- Leetcode算法【34在排序数组中查找元素】
在之前ARTS打卡中,我每次都把算法.英文文档.技巧都写在一个文章里,这样对我的帮助是挺大的,但是可能给读者来说,一下子有这么多的输入,还是需要长时间的消化. 那我现在改变下方式,将每一个模块细分化, ...
- 根据多个成对的cron表达式生成的时间段,合并
场景:数据库一张表,有个startcron 和endcron 两个字段,根据表达式计算今天的所有时间段. 例:startcron :0 30 20 ? * * endcron :0 30 21 ? * ...
- [考试反思]1014csp-s模拟测试73:侵蚀
嗯...还是没有改变那个现状 依旧只是打满了暴力,虽说T2打的的确比暴力好很多,但是因为出题人没有设分所以和暴力等同. 离上面的分差还是大的很,下面还是追的很紧 而且进几场的排名也是连续下滑... 虽 ...
- [考试反思]0927csp-s模拟测试53:沦陷
很喜欢Yu-shi说过的一句话 在OI里,菜即是原罪 对啊. 都会.谁信呢? 没有分数,你说话算什么呢? 你就是菜,你就是不对,没有别的道理. 最没有用的,莫过于改题大神,这就是菜的借口. 但是其实这 ...
- Java描述设计模式(18):享元模式
本文源码:GitHub·点这里 || GitEE·点这里 一.使用场景 应用代码 public class C01_InScene { public static void main(String[] ...
- 「CF52C」Circular RMQ
更好的阅读体验 Portal Portal1: Codeforces Portal2: Luogu Description You are given circular array \(a_0, a_ ...
- java线程池的介绍与使用(Executor框架)
1. 先来看一下类构成 public interface Executor { //顶级接口Executor,定义了线程执行的方法 void execute(Runnable command); } ...
