UVa 122 Trees on the level(二叉树层序遍历)
Trees are fundamental in many branches of computer science. Current state-of-the art parallel computers such as Thinking Machines’ CM-5 are based on fat trees. Quad- and octal-trees are fundamental to many algorithms in computer graphics.
This problem involves building and traversing binary trees.
Given a sequence of binary trees, you are to write a program that prints a level-order traversal of each tree. In this problem each node of a binary tree contains a positive integer and all binary trees have have fewer than 256 nodes.
In a level-order traversal of a tree, the data in all nodes at a given level are printed in left-to-right order and all nodes at level k are printed before all nodes at level k+1.
For example, a level order traversal of the tree
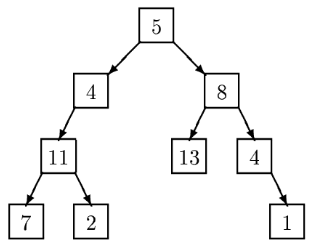
is: 5, 4, 8, 11, 13, 4, 7, 2, 1.
In this problem a binary tree is specified by a sequence of pairs (n,s) where n is the value at the node whose path from the root is given by the string s. A path is given be a sequence of L’s and R’s where L indicates a left branch and R indicates a right branch. In the tree diagrammed above, the node containing 13 is specified by (13,RL), and the node containing 2 is specified by (2,LLR). The root node is specified by (5,) where the empty string indicates the path from the root to itself. A binary tree is considered to be completely specified if every node on all root-to-node paths in the tree is given a value exactly once.
Input
The input is a sequence of binary trees specified as described above. Each tree in a sequence consists of several pairs (n,s) as described above separated by whitespace. The last entry in each tree is (). No whitespace appears between left and right parentheses.
All nodes contain a positive integer. Every tree in the input will consist of at least one node and no more than 256 nodes. Input is terminated by end-of-file.
Output
For each completely specified binary tree in the input file, the level order traversal of that tree should be printed. If a tree is not completely specified, i.e., some node in the tree is NOT given a value or a node is given a value more than once, then the string “not complete” should be printed.
Sample Input
(11,LL) (7,LLL) (8,R)
(5,) (4,L) (13,RL) (2,LLR) (1,RRR) (4,RR) ()
(3,L) (4,R) ()
Sample Output
5 4 8 11 13 4 7 2 1
not complete
题意
把给你的所有结点转成一棵树,并按层次遍历输出
题解
用链表的就不多说了,贴个数组的
代码
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int Left[],Right[],V[],failed,cnt;
vector<int> vec;
void addnode(int v,char *s)
{
int n=strlen(s);//s[0]=','后的一个字符
int u=;
for(int i=;i<n;i++)
{
if(s[i]=='L')
{
if(Left[u]==-)
{
++cnt;
Left[cnt]=Right[cnt]=V[cnt]=-;
Left[u]=cnt;
}
u=Left[u];
}
else if(s[i]=='R')
{
if(Right[u]==-)
{
++cnt;
Left[cnt]=Right[cnt]=V[cnt]=-;
Right[u]=cnt;
}
u=Right[u];
}
else break;
}
if(V[u]!=-)failed=;//节点值已经存在
V[u]=v;
}
int bfs()
{
vec.clear();
queue<int> qu;
qu.push();
while(!qu.empty())
{
int top=qu.front();qu.pop();
if(V[top]==-)return ;//节点没有赋值
vec.push_back(V[top]);
if(Left[top]!=-)qu.push(Left[top]);
if(Right[top]!=-)qu.push(Right[top]);
}
return ;
}
int read()
{
int v;
char s[];
Left[]=Right[]=V[]=-;//0为根节点
failed=;
cnt=;
for(;;)
{
if(scanf("%s",s)!=)return ;
if(!strcmp(s,"()"))break;
sscanf(&s[],"%d",&v);//从s[1]开始读一个数字
addnode(v,strchr(s,',')+);
}
return ;
}
int main()
{
while(read())
{
if(failed==||bfs()==)
printf("not complete\n");
else
for(int i=;i<vec.size();i++)
printf("%d%c",vec[i],i==vec.size()-?'\n':' ');
}
return ;
}
UVa 122 Trees on the level(二叉树层序遍历)的更多相关文章
- UVA.122 Trees on the level(二叉树 BFS)
UVA.122 Trees on the level(二叉树 BFS) 题意分析 给出节点的关系,按照层序遍历一次输出节点的值,若树不完整,则输出not complete 代码总览 #include ...
- UVa 122 Trees on the level (动态建树 && 层序遍历二叉树)
题意 :输入一棵二叉树,你的任务是按从上到下.从左到右的顺序输出各个结点的值.每个结 点都按照从根结点到它的移动序列给出(L表示左,R表示右).在输入中,每个结点的左 括号和右括号之间没有空格,相邻 ...
- UVA 122 -- Trees on the level (二叉树 BFS)
Trees on the level UVA - 122 解题思路: 首先要解决读数据问题,根据题意,当输入为“()”时,结束该组数据读入,当没有字符串时,整个输入结束.因此可以专门编写一个rea ...
- UVa 122 Trees on the level(链式二叉树的建立和层次遍历)
题目链接: https://cn.vjudge.net/problem/UVA-122 /* 问题 给出每个节点的权值和路线,输出该二叉树的层次遍历序列. 解题思路 根据输入构建链式二叉树,再用广度优 ...
- UVA - 122 Trees on the level (二叉树的层次遍历)
题意:给定结点值和从根结点到该结点的路径,若根到某个叶结点路径上有的结点输入中未给出或给出超过一次,则not complete,否则层次遍历输出所有结点. 分析:先建树,建树的过程中,沿途结点都申请了 ...
- uva 122 trees on the level——yhx
题目如下:Given a sequence of binary trees, you are to write a program that prints a level-order traversa ...
- UVa 122 Trees on the level
题目的意思: 输入很多个节点,包括路径和数值,但是不一定这些全部可以构成一棵树,问题就是判断所给的能否构成一棵树,且没有多余. 网上其他大神已经给出了题目意思:比如我一直很喜欢的小白菜又菜的博客 说一 ...
- 【LeetCode-面试算法经典-Java实现】【107-Binary Tree Level Order Traversal II(二叉树层序遍历II)】
[107-Binary Tree Level Order Traversal II(二叉树层序遍历II)] [LeetCode-面试算法经典-Java实现][全部题目文件夹索引] 原题 Given a ...
- [LeetCode] 107. Binary Tree Level Order Traversal II 二叉树层序遍历 II
Given a binary tree, return the bottom-up level order traversal of its nodes' values. (ie, from left ...
随机推荐
- TCP连接异常断开检测(转)
TCP是一种面向连接的协议,连接的建立和断开需要通过收发相应的分节来实现.某些时候,由于网络的故障或是一方主机的突然崩溃而另一方无法检测到,以致始终保持着不存在的连接.下面介绍一种方法来检测这种异常断 ...
- Zookeeper 在Linux系统的安装
注册中心Zookeeper 官方推荐使用 zookeeper 注册中心.注册中心负责服务地址的注册与查找,相当于目录服务,服务提供者和消费者只在启动时与注册中心交互,注册中心不转发请求,压力较小. Z ...
- oracle第二天笔记
多表查询 /* 多表查询: 笛卡尔积: 实际上是两张表的乘积,但是在实际开发中没有太大意义 格式: select * from 表1,表2 */ select * from emp; select * ...
- java由字符型强制转化为整型例题
此Java程序依次输出参数,参数类型为字符型,要求更改程序,使得字符型强制转化为整形,并将这些整数相加,最后输出总和. 原程序: package demo; public class CommandP ...
- 【377】only one element in a tuple
Recently I am doing the assignment of COMP9021. It is too difficult and it is about the Knight and K ...
- 处理TypeError: Converting circular structure to JSON
// Demo: Circular reference var o = {}; o.o = o; // Note: cache should not be re-used by repeated ca ...
- (转)如何禁用Windows 10系统的触摸屏
https://baijiahao.baidu.com/s?id=1593890738706748667 现在许多优质的Windows 10个人电脑都配备了触摸屏,因为触摸屏的日益普及,Windows ...
- winform下利用webBrowser执行javascript
目前很多网站为了防止恶意提交表单信息,大多都采用了加密的方式对提交信息进行处理,加密处理后通过POST提交给服务器验证,这种操作一般都是用Javascipt进行加密,若是我们想要正确提交表单到网站,就 ...
- func 的参数修饰
1.0 在声明一个 Swift的方法的时候,我们一般不去指定参数前面的修饰符,而是直接声明参数: func incrementor(variable : Int) ->Int { } 这个方法接 ...
- ubuntu14配置opencv3.4.1(转)
网站:https://blog.csdn.net/a1429331875/article/details/31539129 写此博客的目的是为了方便大家的学习,我是搞了半天,通过上网查找资料才成功的. ...
