论文解读(TAMEPT)《A Two-Stage Framework with Self-Supervised Distillation For Cross-Domain Text Classification》
论文信息
论文标题:A Two-Stage Framework with Self-Supervised Distillation For Cross-Domain Text Classification
论文作者:Yunlong Feng, Bohan Li, Libo Qin, Xiao Xu, Wanxiang Che
论文来源:2023 aRxiv
论文地址:download
论文代码:download
视屏讲解:click
1 介绍
动机:以前的工作主要集中于提取 域不变特征 或 任务不可知特征,而忽略了存在于目标域中可能对下游任务有用的域感知特征;
贡献:
- 提出一个两阶段的学习框架,使现有的分类模型能够有效地适应目标领域;
- 引入自监督蒸馏,可以帮助模型更好地从目标领域的未标记数据中捕获域感知特征;
- 在 Amazon 跨域分类基准上的实验表明,取得了 SOTA ;
2 相关
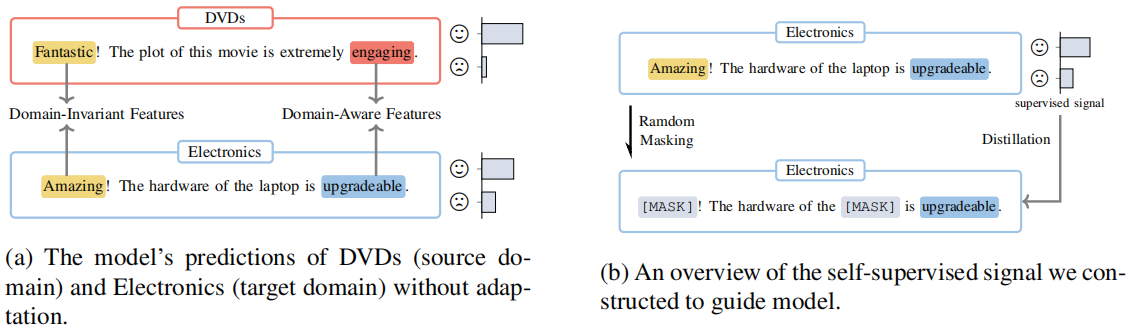
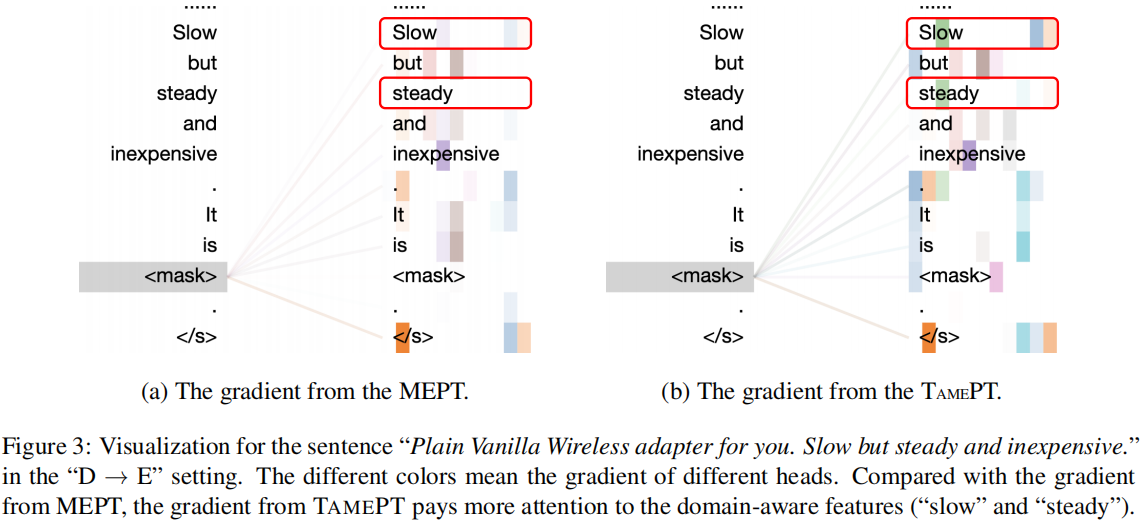
Figure 1(a):阐述域不变特征和域感知特征与任务的关系;
Figure 1(b):阐述遮蔽域不变特征和域感知特征与预测的关系:
- 通过掩盖域不变特征,模型建立预测和域感知特征的相关性;
- 通过掩盖域感知特征,模型加强了预测和域不变特征的关系;
一个文本提示组成如下:
$\boldsymbol{x}_{\mathrm{p}}=\text { "[CLS] } \boldsymbol{x} \text {. It is [MASK]. [SEP]"} \quad\quad(1)$
$\text{PLM}$ 将 $\boldsymbol{x}_{\mathrm{p}}$ 作为输入,并利用上下文信息用词汇表中的一个单词填充 $\text{[MASK]}$ 作为输出,输出单词随后被映射到一个标签 $\mathcal{Y}$。
PT 的目标:
$\mathcal{L}_{p m t}\left(\mathcal{D}^{\mathcal{T}} ; \theta_{\mathcal{M}}\right)=-\sum_{\boldsymbol{x}, y \in \mathcal{D}} y \log p_{\theta_{\mathcal{M}}}\left(\hat{y} \mid \boldsymbol{x}_{\mathrm{p}}\right)$
使用 $\text{MLM }$ 来避免快捷学习($\text{shortcut learning}$),并适应目标域分布。具体来说,构造了一个掩蔽文本提示符 $\boldsymbol{x}_{\mathrm{pm}}$:
$\boldsymbol{x}_{\mathrm{pm}}=\text { "[CLS] } \boldsymbol{x}_{\mathrm{m}} \text {. It is [MASK]. [SEP]"}$
其中,$m\left(y_{\mathrm{m}}\right)$ 和 $\operatorname{len}_{m\left(\boldsymbol{x}_{\mathrm{m}}\right)}$ 分别表示 $x_{\mathrm{m}}$ 中的掩码词和计数;
SSKD
核心:使模型能够在预测和目标域的域感知特征之间建立联系;
具体:模型迫使 $x_{\mathrm{p}}$ 的预测和 $\boldsymbol{x}_{\mathrm{pm}}$ 的未掩蔽词之间联系起来,本文在 $p_{\theta}\left(y \mid \boldsymbol{x}_{\mathrm{pm}}\right)$ 和 $p_{\theta}\left(y \mid \boldsymbol{x}_{\mathrm{p}}\right)$ 的预测之间进行 $\text{KD}$:
$\mathcal{L}_{s s d}\left(\mathcal{D} ; \theta_{\mathcal{M}}\right)=\sum_{\boldsymbol{x} \in \mathcal{D}} K L\left(p_{\theta_{\mathcal{M}}}\left(y \mid \boldsymbol{x}_{\mathrm{pm}}\right)|| p_{\theta_{\mathcal{M}}}\left(y \mid \boldsymbol{x}_{\mathrm{p}}\right)\right)$
注意:$\boldsymbol{x}_{\mathrm{pm}}$ 可能包含域不变、域感知特征,或两者都包含;
2 方法
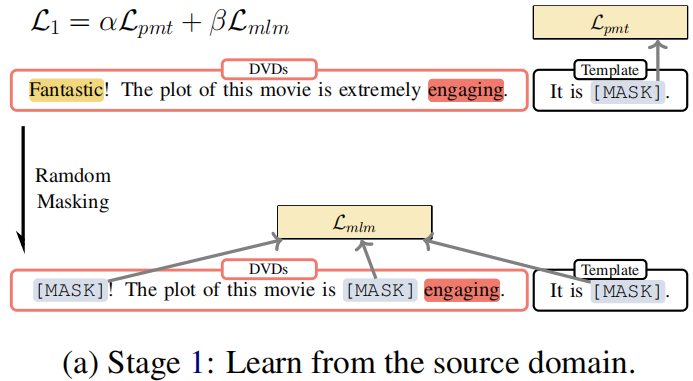
Procedure:
- Firstly, we calculate the classification loss of those sentences and update the parameters with the loss, as shown in line 5 of Algorithm 1.
- Then we mask the same sentence and calculate mask language modeling loss to update the parameters, as depicted in line 8 of Algorithm 1. The parameters of the model will be updated together by these two losses.
Objective:
$\begin{array}{l}\mathcal{L}_{1}^{\prime}\left(\mathcal{D}^{\mathcal{T}} ; \theta_{\mathcal{M}}\right)=\alpha \mathcal{L}_{p m t}\left(\mathcal{D}^{\mathcal{T}} ; \theta_{\mathcal{M}}\right) \\\mathcal{L}_{1}^{\prime \prime}\left(\mathcal{D}^{\mathcal{T}} ; \theta_{\mathcal{M}}\right)=\beta \mathcal{L}_{m l m}\left(\mathcal{D} ; \theta_{\mathcal{M}}\right)\end{array}$
Stage 2: Adapt to the target domain
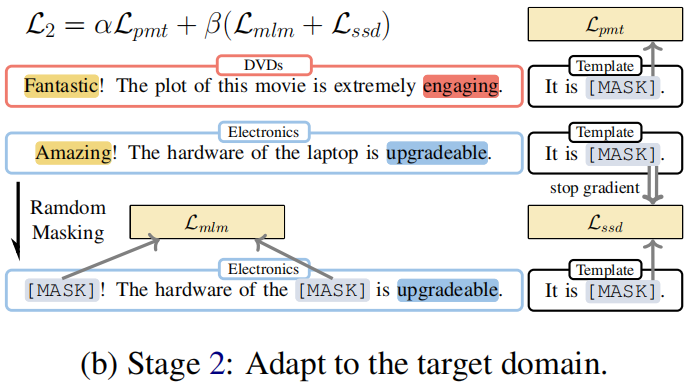
Procedure:
- Firstly, we sample labeled data from the source domain $\mathcal{D}_{S}^{\mathcal{T}} $ and calculate sentiment classification loss. The model parameters are updated using this loss in line 5 of Algorithm 2.
- Next, we sample unlabeled data from the target domain $\mathcal{D}_{T} $ and mask the unlabeled data to do a masking language model and selfsupervised distillation with the previous prediction.
Objective:
$\begin{aligned}\mathcal{L}_{2}^{\prime}\left(\mathcal{D}_{S}^{\mathcal{T}}, \mathcal{D}_{T} ; \theta_{\mathcal{M}}\right) & =\alpha \mathcal{L}_{p m t}\left(\mathcal{D}_{S}^{\mathcal{T}} ; \theta_{\mathcal{M}}\right) \\\mathcal{L}_{2}^{\prime \prime}\left(\mathcal{D}_{S}^{\mathcal{T}}, \mathcal{D}_{T} ; \theta_{\mathcal{M}}\right) & =\beta\left(\mathcal{L}_{m l m}\left(\mathcal{D}_{T} ; \theta_{\mathcal{M}}\right)\right. \left.+\mathcal{L}_{s s d}\left(\mathcal{D}_{T} ; \theta_{\mathcal{M}}\right)\right)\end{aligned}$
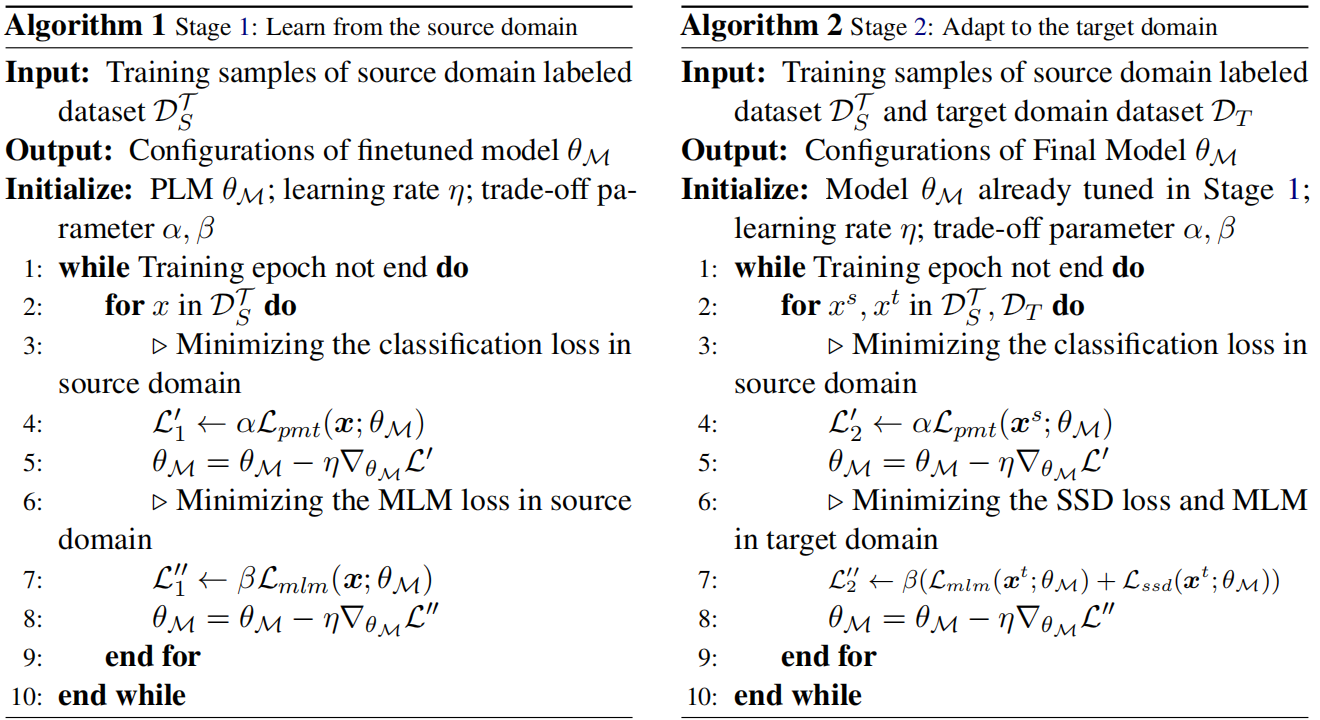
Algorithm
3 实验
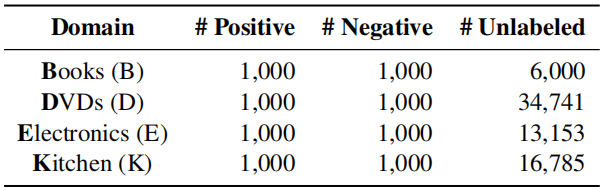
Dataset
Amazon reviews dataset
- $\text{R-PERL }$(2020): Use BERT for cross-domain text classification with pivot-based fine-tuning.
- $\text{DAAT}$ (2020): Use BERT post training for cross-domain text classification with adversarial training.
- $\text{p+CFd}$ (2020): Use XLM-R for cross-domain text classification with class-aware feature self-distillation (CFd).
- $\text{SENTIX}_{\text{Fix}}$ (2020): Pre-train a sentiment-aware language model by several pretraining tasks.
- $\text{UDALM}$ (2021): Fine-tuning with a mixed classification and MLM loss on domain-adapted PLMs.
- $\text{AdSPT}$ (2022): Soft Prompt tuning with an adversarial training object on vanilla PLMs.
- During Stage 1, we train 10 epochs with batch size 4 and early stopping (patience =3 ) on the accuracy metric. The optimizer is AdamW with learning rate 1 $\times 10^{-5}$ . And we halve the learning rate every 3 epochs. We set $\alpha=1.0$, $\beta=0.6$ for Eq.6 .
- During Stage 2, we train 10 epochs with batch size 4 and early stopping (patience =3 ) on the mixing loss of classification loss and mask language modeling loss. The optimizer is AdamW with a learning rate $1 \times 10^{-6}$ without learning rate decay. And we set $\alpha=0.5$, $\beta=0.5$ for Eq. 7 .
- In addition, for the mask language modeling objective and the self-supervised distillation objective, we randomly replace 30% of tokens to [MASK] and the maximum sequence length is set to 512 by truncation of inputs. Especially we randomly select the equal num unlabeled data from the target domain every epoch during Stage 2.
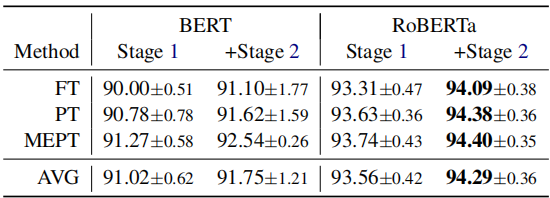
Single-source domain adaptation on Amazon reviews
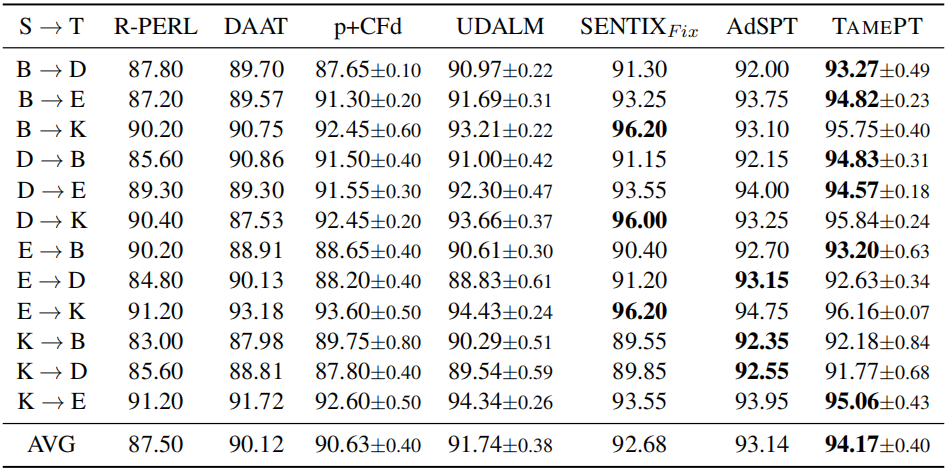
Multi-source domain adaptation on Amazon reviews
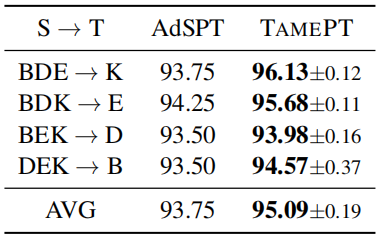
论文解读(TAMEPT)《A Two-Stage Framework with Self-Supervised Distillation For Cross-Domain Text Classification》的更多相关文章
- 论文解读(SimGRACE)《SimGRACE: A Simple Framework for Graph Contrastive Learning without Data Augmentation》
论文信息 论文标题:SimGRACE: A Simple Framework for Graph Contrastive Learning without Data Augmentation论文作者: ...
- AAAI2019 | 基于区域分解集成的目标检测 论文解读
Object Detection based on Region Decomposition and Assembly AAAI2019 | 基于区域分解集成的目标检测 论文解读 作者 | 文永亮 学 ...
- 自监督学习(Self-Supervised Learning)多篇论文解读(下)
自监督学习(Self-Supervised Learning)多篇论文解读(下) 之前的研究思路主要是设计各种各样的pretext任务,比如patch相对位置预测.旋转预测.灰度图片上色.视频帧排序等 ...
- 论文解读(SDNE)《Structural Deep Network Embedding》
论文题目:<Structural Deep Network Embedding>发表时间: KDD 2016 论文作者: Aditya Grover;Aditya Grover; Ju ...
- 论文解读(IDEC)《Improved Deep Embedded Clustering with Local Structure Preservation》
Paper Information Title:<Improved Deep Embedded Clustering with Local Structure Preservation>A ...
- 论文解读(KP-GNN)《How Powerful are K-hop Message Passing Graph Neural Networks》
论文信息 论文标题:How Powerful are K-hop Message Passing Graph Neural Networks论文作者:Jiarui Feng, Yixin Chen, ...
- 论文解读(SR-GNN)《Shift-Robust GNNs: Overcoming the Limitations of Localized Graph Training Data》
论文信息 论文标题:Shift-Robust GNNs: Overcoming the Limitations of Localized Graph Training Data论文作者:Qi Zhu, ...
- itemKNN发展史----推荐系统的三篇重要的论文解读
itemKNN发展史----推荐系统的三篇重要的论文解读 本文用到的符号标识 1.Item-based CF 基本过程: 计算相似度矩阵 Cosine相似度 皮尔逊相似系数 参数聚合进行推荐 根据用户 ...
- CVPR2019 | Mask Scoring R-CNN 论文解读
Mask Scoring R-CNN CVPR2019 | Mask Scoring R-CNN 论文解读 作者 | 文永亮 研究方向 | 目标检测.GAN 推荐理由: 本文解读的是一篇发表于CVPR ...
- Gaussian field consensus论文解读及MATLAB实现
Gaussian field consensus论文解读及MATLAB实现 作者:凯鲁嘎吉 - 博客园 http://www.cnblogs.com/kailugaji/ 一.Introduction ...
随机推荐
- 新出的Alist云盘视频助手,真的香还是假的香?
作为某云盘的重度使用者和长期受虐者,前段时间无意中看到一款新出的网盘工具,叫Alist云盘视频助手,不同于一般的网盘工具,它不是面向网盘数据下载的,它面向的是网盘视频文件隐私保护,大白话就是:加密网盘 ...
- Vulnhub Broken
Vulnhub Broken 一.操作文档 [Vulnhub - Broken-Gallery writeup (mzfr.me)](https://blog.mzfr.me/vulnhub-writ ...
- 鼠标移入select options会触发mouseleave 事件处理方案
近来遇到一项目有一侧边工具菜单,在鼠标mouseenter事件打开对应的详细操作列表,当mouseleave时进行关闭,然操作列表中有一个select , 每当鼠标移入select options 时 ...
- Python潮流周刊#3:PyPI 的安全问题
你好,我是豌豆花下猫.这里记录每周值得分享的 Python 及通用技术内容,部分为英文,已在小标题注明.(标题取自其中一则分享,不代表全部内容都是该主题,特此声明.) 文章&教程 1.掌握Py ...
- 24 式加速你的 Python
一,分析代码运行时间 第1式,测算代码运行时间 平凡方法 快捷方法(jupyter环境) 第2式,测算代码多次运行平均时间 平凡方法 快捷方法(jupyter环境) 第3式,按调用函数分析代码运行时间 ...
- C++面试八股文:C++中,设计一个类要注意哪些东西?
某日二师兄参加XXX科技公司的C++工程师开发岗位第9面: 面试官:C++中,设计一个类要注意哪些东西? 二师兄:设计一个类主要考虑以下几个方面:1.面向对象的封装.继承及多态.2.big three ...
- C#与WPF中相关字符串操作
字符串指定字符查找 例如:输入一个邮箱地址,如果正确则显示success否则显示error(正确的邮箱地址包含@,以.com结尾) //接受输入进来的字符串 string s=this.txtEmsi ...
- 使用libavcodec将mp3音频文件解码为pcm音频采样数据【[mp3float @ 0x561c1ec49940] Header missing】
一.打开和关闭输入文件和输出文件 想要解决上面提到的问题,我们需要对mp3文件的格式有个大致了解,为了方便讲解,我这里画了个示意图: ID3V2 包含了作者,作曲,专辑等信息,长度不固定,扩展了 ID ...
- 数据挖掘18大算法实现以及其他相关经典DM算法:决策分类,聚类,链接挖掘,关联挖掘,模式挖掘。图算法,搜索算法等
数据挖掘18大算法实现以及其他相关经典DM算法:决策分类,聚类,链接挖掘,关联挖掘,模式挖掘.图算法,搜索算法等 算法码源见文末 1.算法目录 18大DM算法 包名 目录名 算法名 Associati ...
- Web网页音视频通话之Webrtc相关操作(一)
目录 打开摄像头/关闭摄像头 静音/解除静音 打开视频/关闭视频 截图且下载 打开摄像头/关闭摄像头 效果图 HTML <!DOCTYPE html> <html lang=&quo ...
