SpringBoot实现限流注解
SpringBoot实现限流注解
在高并发系统中,保护系统的三种方式分别为:缓存,降级和限流。
限流的目的是通过对并发访问请求进行限速或者一个时间窗口内的的请求数量进行限速来保护系统,一旦达到限制速率则可以拒绝服务、排队或等待
1、限流类型枚举类
/**
* 限流类型
* @author ss_419
*/
public enum LimitType {
/**
* 默认的限流策略,针对某一个接口进行限流
*/
DEFAULT,
/**
* 针对某一个IP进行限流
*/
IP
}
2、自定义限流注解
/**
* @author ss_419
*/
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
public @interface RateLimiter {
/**
* 限流的 key,主要是指前缀
* @return
*/
String key() default "rate_limit:";
/**
* 在时间窗内的限流次数
* @return
*/
int count() default 100;
/**
* 限流类型
* @return
*/
LimitType limitType() default LimitType.DEFAULT;
/**
* 限流时间窗
* @return
*/
int time() default 60;
}
3、限流lua脚本
1、由于我们使用 Redis 进行限流,我们需要引入 Redis 的 maven 依赖,同时需要引入 aop 的依赖
<!-- aop依赖 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-aop</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- redis依赖 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>
2、配置redis以及lua脚本
@Configuration
public class RedisConfig {
@Bean
RedisTemplate<Object,Object> redisTemplate(RedisConnectionFactory factory) {
RedisTemplate<Object, Object> template = new RedisTemplate<>();
template.setConnectionFactory(factory);
Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer jackson2JsonRedisSerializer = new Jackson2JsonRedisSerializer(Object.class);
template.setKeySerializer(jackson2JsonRedisSerializer);
template.setValueSerializer(jackson2JsonRedisSerializer);
template.setHashKeySerializer(jackson2JsonRedisSerializer);
template.setHashValueSerializer(jackson2JsonRedisSerializer);
return template;
}
/**
* 读取lua脚本
* @return
*/
@Bean
DefaultRedisScript<Long> limitScript() {
DefaultRedisScript<Long> script = new DefaultRedisScript<>();
script.setResultType(Long.class);
script.setScriptSource(new ResourceScriptSource(new ClassPathResource("lua/limit.lua")));
return script;
}
}
通过 Lua 脚本,根据 Redis 中缓存的键值判断限流时间(也是 key 的过期时间)内,访问次数是否超出了限流次数,没超出则访问次数 +1,返回 true,超出了则返回 false。
limit.lua:
local key = KEYS[1]
local time = tonumber(ARGV[1])
local count = tonumber(ARGV[2])
local current = redis.call('get', key)
if current and tonumber(current) > count then
return tonumber(current)
end
current = redis.call('incr', key)
if tonumber(current) == 1 then
redis.call('expire', key, time)
end
return tonumber(current)
4、限流切面处理类
1、使用我们刚刚的 Lua 脚本判断是否超出了限流次数,超出了限流次数后返回一个自定义异常,然后在全局异常中去捕捉异常,返回 JSON 数据。
2、根据注解参数,判断限流类型,拼接缓存 key 值
package org.pp.ratelimiter.aspectj;
import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;
import org.aspectj.lang.reflect.MethodSignature;
import org.pp.ratelimiter.annotation.RateLimiter;
import org.pp.ratelimiter.enums.LimitType;
import org.pp.ratelimiter.exception.RateLimitException;
import org.pp.ratelimiter.utils.IpUtils;
import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.script.RedisScript;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.web.context.request.RequestContextHolder;
import org.springframework.web.context.request.ServletRequestAttributes;
import java.lang.reflect.Method;
import java.util.Collections;
@Aspect
@Component
public class RateLimiterAspect {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(RateLimiterAspect.class);
@Autowired
RedisTemplate<Object, Object> redisTemplate;
@Autowired
RedisScript<Long> redisScript;
@Before("@annotation(rateLimiter)")
public void before(JoinPoint jp, RateLimiter rateLimiter) throws RateLimitException {
int time = rateLimiter.time();
int count = rateLimiter.count();
String combineKey = getCombineKey(rateLimiter, jp);
try {
Long number = redisTemplate.execute(redisScript, Collections.singletonList(combineKey), time, count);
if (number == null || number.intValue() > count) {
//超过限流阈值
logger.info("当前接口以达到最大限流次数");
throw new RateLimitException("访问过于频繁,请稍后访问");
}
logger.info("一个时间窗内请求次数:{},当前请求次数:{},缓存的 key 为 {}", count, number, combineKey);
} catch (Exception e) {
throw e;
}
}
/**
* 这个 key 其实就是接口调用次数缓存在 redis 的 key
* rate_limit:11.11.11.11-org.javaboy.ratelimit.controller.HelloController-hello
* rate_limit:org.javaboy.ratelimit.controller.HelloController-hello
* @param rateLimiter
* @param jp
* @return
*/
private String getCombineKey(RateLimiter rateLimiter, JoinPoint jp) {
StringBuffer key = new StringBuffer(rateLimiter.key());
if (rateLimiter.limitType() == LimitType.IP) {
key.append(IpUtils.getIpAddr(((ServletRequestAttributes) RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes()).getRequest()))
.append("-");
}
MethodSignature signature = (MethodSignature) jp.getSignature();
Method method = signature.getMethod();
key.append(method.getDeclaringClass().getName())
.append("-")
.append(method.getName());
return key.toString();
}
}
5、使用与测试
@RestController
public class HelloController {
/**
* 限流 10 秒之内,这个接口可以访问3次
* @return
*/
@GetMapping("/hello")
@RateLimiter(time = 10,count = 3)
public Map<String, Object> hello() {
Map<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("status", 200);
map.put("message", "Hello RateLimiter");
return map;
}
}
十秒之内访问次数超过3次就会报异常
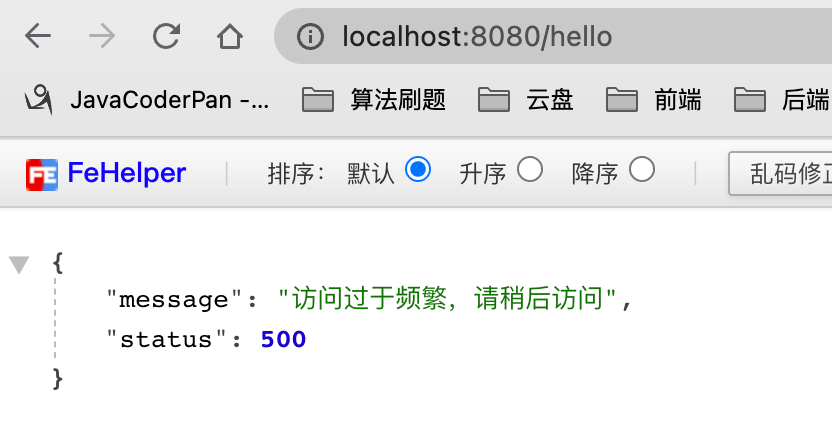
redis中的数据,每一次访问都加1
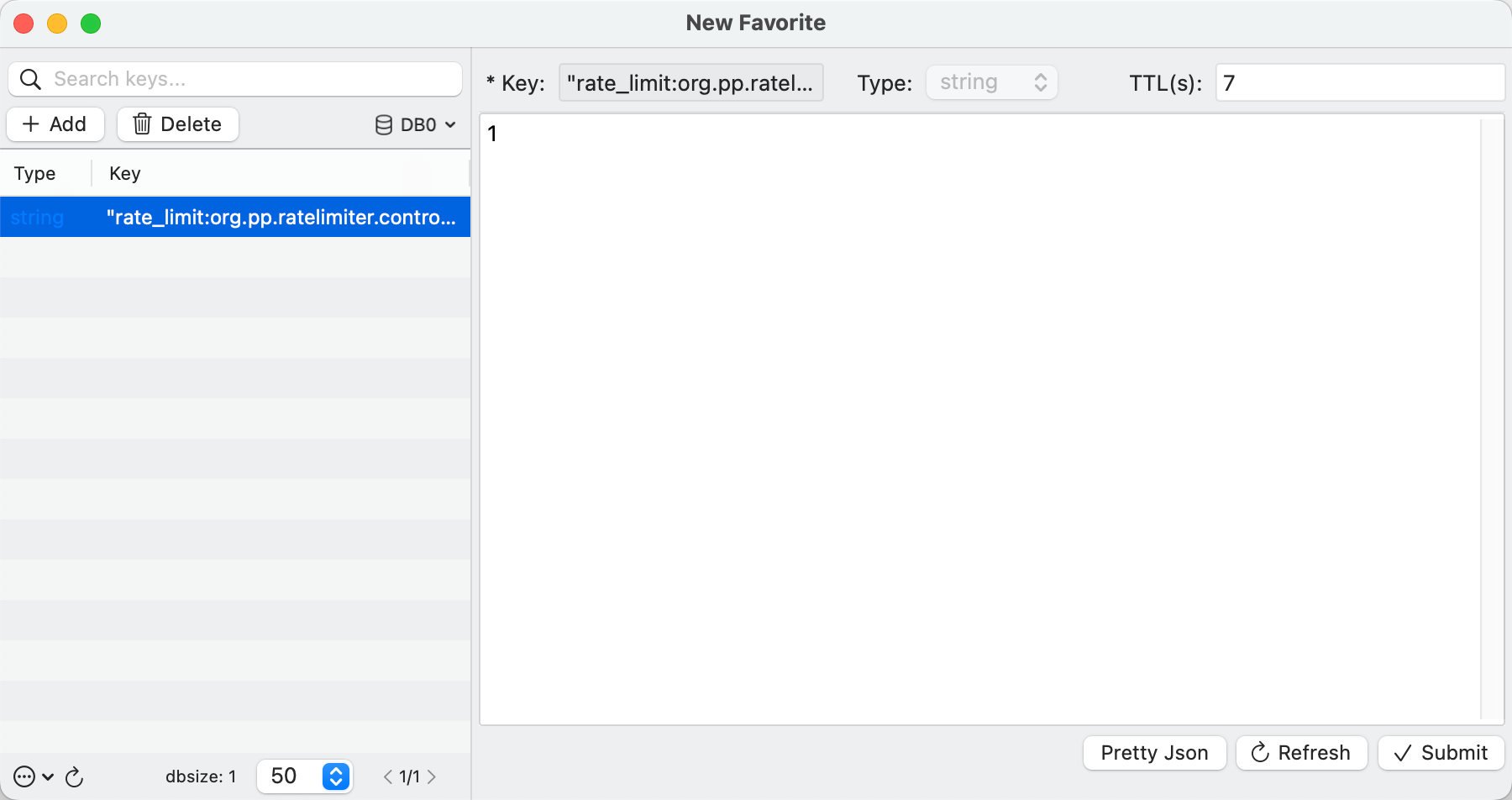
当访问次数超过3,则进行限流操作
SpringBoot实现限流注解的更多相关文章
- Springboot分布式限流实践
高并发访问时,缓存.限流.降级往往是系统的利剑,在互联网蓬勃发展的时期,经常会面临因用户暴涨导致的请求不可用的情况,甚至引发连锁反映导致整个系统崩溃.这个时候常见的解决方案之一就是限流了,当请求达到一 ...
- SpringBoot使用自定义注解+AOP+Redis实现接口限流
为什么要限流 系统在设计的时候,我们会有一个系统的预估容量,长时间超过系统能承受的TPS/QPS阈值,系统有可能会被压垮,最终导致整个服务不可用.为了避免这种情况,我们就需要对接口请求进行限流. 所以 ...
- 基于令牌桶算法实现的SpringBoot分布式无锁限流插件
本文档不会是最新的,最新的请看Github! 1.简介 基于令牌桶算法和漏桶算法实现的纳秒级分布式无锁限流插件,完美嵌入SpringBoot.SpringCloud应用,支持接口限流.方法限流.系统限 ...
- 分布式限流组件-基于Redis的注解支持的Ratelimiter
原文:https://juejin.im/entry/5bd491c85188255ac2629bef?utm_source=coffeephp.com 在分布式领域,我们难免会遇到并发量突增,对后端 ...
- springboot + aop + Lua分布式限流的最佳实践
整理了一些Java方面的架构.面试资料(微服务.集群.分布式.中间件等),有需要的小伙伴可以关注公众号[程序员内点事],无套路自行领取 一.什么是限流?为什么要限流? 不知道大家有没有做过帝都的地铁, ...
- SpringBoot 如何进行限流?老鸟们都这么玩的!
大家好,我是飘渺.SpringBoot老鸟系列的文章已经写了四篇,每篇的阅读反响都还不错,那今天继续给大家带来老鸟系列的第五篇,来聊聊在SpringBoot项目中如何对接口进行限流,有哪些常见的限流算 ...
- SpringBoot进阶教程(六十七)RateLimiter限流
在上一篇文章nginx限流配置中,我们介绍了如何使用nginx限流,这篇文章介绍另外一种限流方式---RateLimiter. v限流背景 在早期的计算机领域,限流技术(time limiting)被 ...
- Redisson多策略注解限流
限流:使用Redisson的RRateLimiter进行限流 多策略:map+函数式接口优化if判断 自定义注解 /** * aop限流注解 */ @Target({ElementType.METHO ...
- Sentinel整合Dubbo限流实战(分布式限流)
之前我们了解了 Sentinel 集成 SpringBoot实现限流,也探讨了Sentinel的限流基本原理,那么接下去我们来学习一下Sentinel整合Dubbo及 Nacos 实现动态数据源的限流 ...
- Redis实现的分布式锁和分布式限流
随着现在分布式越来越普遍,分布式锁也十分常用,我的上一篇文章解释了使用zookeeper实现分布式锁(传送门),本次咱们说一下如何用Redis实现分布式锁和分布限流. Redis有个事务锁,就是如下的 ...
随机推荐
- LLaMA大型语言模型
LLaMA (Large Language Model Meta AI)是Meta公司发布的大型语言模型系列,近日LLaMA种子文件被合并到了GitHub 上,同时一些项目维护者给予了批准,目前该项目 ...
- 关于helloworld
我们的helloworld是从一个源程序开始的,该源程序由程序员通过编译器创建并保存的文件,文件名就是hello.c.这个hello.c的源程序,实际上是有0和1组成的序列.每一个0和1都成为一位,这 ...
- windows 和 Linux 下 git status 结果不一致
解决该问题 运行一下命令即可 git config core.autocrlf true 解释 git config core.autocrlf true 这个命令是在任何支持的操作系统上都可以运行的 ...
- Programming Abstractions in C阅读笔记:p242-p245
<Programming Abstractions in C>学习第67天,p242-p245总结,总计4页. 一.技术总结 6.2小结主要讲回溯算法及递归算法在迷宫求解中应用,当然,理解 ...
- GaussDB(DWS)字符串处理函数返回错误结果集排查
摘要:在使用字符串处理函数时,有时会出现非预期结果的场景.在排除使用问题后,应该从encoding和数据本身开始排查. 本文分享自华为云社区<GaussDB(DWS)字符串处理函数返回错误结果集 ...
- 详解SQL优化必备:并行执行框架和执行计划
摘要:在关系型数据库中,优化器是数据库的核心组件之一,由于一些列因素都会影响语句的执行,优化器综合权衡各个因素,在众多的执行计划中选择认为是最佳的执行计划. 本文分享自华为云社区<华为云Gaus ...
- Axure 创建轮播图
拖一个动态面板,设置名称 双击动态面板,添加3个状态 给3个状态,分别添加3张图片 设置交互 新建交互 -> 载入时 -> 设置面板状态 双击进去,界面看得直观些 下一项.向后循环,循环间 ...
- PPT 放映电脑Office版本低怎么办
转换成全图形PPT 转成图片,无法放动画 转换成全视频 转成视频,无法控制节奏 PPT VIEWEB 本地PPT播放工具
- LSP 网络劫持(Layered Service Provider Hijacking)
LSP 简介: 分层服务提供商(Layered Service Provider,LSP)是一种可以扩展Winsock作为应用程序的 Windows 的网络套接字工具的机制.Winsock LSP 可 ...
- 【题解】Qin Shi Huang's National Road System HDU - 4081 ⭐⭐⭐⭐ 【次小生成树】
During the Warring States Period of ancient China(476 BC to 221 BC), there were seven kingdoms in Ch ...
