201771010113 李婷华 《面向对象程序设计(java)》第十五周总结
一.理论知识部分
JAR文件
Java程序的打包:程序编译完成后,程序员将.class文件压缩打包为.jar文件后,GUI界面程序就可以直接双击图标运行。
.jar文件(Java归档)既可以包含类文件,也可以包含诸如图像和声音这些其它类型的文件。
JAR文件是压缩的,它使用ZIP压缩格式。
jar命令
jar命令格式:
jar{ctxui}[vfm0Me][jar-file][manifest-file][entry-point][-Cdir]files...
Jar命令选项:
–-c创建一个新的或者空的存档文件并加入文件。
–-C暂时改变到指定的目录
–-e在清单文件中创建一个条目
–-f将JAR文件名指定为第二个命令行参数
–-i为指定的JAR文件产生索引信息
–-m将一个清单文件(manifest)添加到JAR文件中
–-M不产生所有项的清单文件(manifest)
–-t列出存档内容的列表
–-u更新已存在的JAR文件
–-v生成详细的输出结果
–-x解压存档中的命名的(或所有的〕文件
–-0只存储方式,不用ZIP压缩格式
(1)创建JAR文件
jarcfjar-fileinput-file(s)
c-wanttoCreateaJARfile.
eg:1)jarcfMenuTest.jar*.class*.gif
f-wanttheoutputtogotoafileratherthantostdout.
2)jarcvfMenuTest.jar*.class*.gif
v-Producesverboseoutputtostdout.
3)jarcvfMenuTest.jar*
*-createallcontentsincurrentdirectory.
4)jarcv0fMenuTest.jar*
0-don'twanttheJARfiletobecompressed.
(2)查看JAR文件
jartfjar-file
t-wanttoviewtheTableofcontentsoftheJARfile.
eg:1)jartvfMenuTest.jar
v-Producesverboseoutputtostdout.
(3)提取JAR文件
jarxfjar-file[archived-file(s)]
x-wanttoextractfilesfromtheJARarchive.
eg:1)jarxfMenuTest.jarcopy.gif(仅提取文件copy.gif)
2)jarxfMenuTest.jaralex/copy.gif(仅提取目录alex下的文件copy.gif)
3)jarxfMenuTest.jar(提取该JAR中的所有文件或目录)
(4)更新JAR文件
jarufjar-fileinput-file(s)
u-wanttoupdateanexistingJARfile.
eg:1)jarufMenuTest.jarcopy.gif
(5)索引JAR文件
jarijar-file
i-indexanexistingJARfile.
eg:1)jariMenuTest.jar
清单文件
每个JAR文件中包含一个用于描述归档特征的清单文件(manifest)。清单文件被命名MANIFEST.MF,它位于JAR文件的一个特殊的META-INF子目录中。
最小的符合标准的清单文件是很简单的:
Manifest-Version:1.0
复杂的清单文件包含多个条目,这些条目被分成多个节。第一节被称为主节,作用于整个JAR文件。随后的条目用来指定已命名条目的属性,可以是文件、包或者URL。
清单文件的节与节之间用空行分开,最后一行必须以换行符结束。否则,清单文件将无法被正确地读取。
创建一个包含清单的JAR文件,应该运行:
jarcfmMyArchive.jarmanifest.mfcom/*.class
–要更新一个已有JAR文件的清单,则需要将增加的部分放置到一个文本文件中,运行如下命令:
jarufmMyArchive.jarmanifest-additions.mf
运行JAR文件
用户可以通过下面的命令来启动应用程序:
java–jarMyProgram.jar
窗口操作系统,可通过双击JAR文件图标来启动应用程序。
资源
Java中,应用程序使用的类通常需要一些相关的数据文件,这些文件称为资源(Resource)。
–图像和声音文件。
–带有消息字符串和按钮标签的文本文件。
–二进制数据文件,如:描述地图布局的文件。
类加载器知道如何搜索类文件,直到在类路径、存档文件或Web服务器上找到为止。
利用资源机制对于非类文件也可以进行同样操作,具体步骤如下:
–获得资源的Class对象。
–如果资源是一个图像或声音文件,那么就需要调用getresource(filename)获得资源的URL位置,然后利用getImage或getAudioClip方法进行读取。
–如果资源是文本或二进制文件,那么就可以使用getResouceAsStream方法读取文件中的数据。
资源文件可以与类文件放在同一个目录中,也可以将资源文件放在其它子目录中。具体有以下两种方式:
–相对资源名:如data/text/about.txt
它会被解释为相对于加载这个资源的类所在的包。
–绝对资源名:如/corejava/title.txt
ResourceTest.java程序演示了资源加载的过程。
编译、创建JAR文件和执行这个程序的命令如下:
–javacResourceTest.java
–jarcvfmResourceTest.jarResourceTest.mf
*.class*.gif*.txt
–java–jarResourceTest.jar
Eclipse导出JAR文件
工程没有引用外部jar包时,直接导出。
当工程引用了其他的外部jar时,由于Eclipse不支持同时导出外部jar包的功能,导出过程比较复杂。(*)
包密封
将Java包密封(Seal)可保证不会有其它的类加入到其中。如果在代码中使用了包可见的类、方法和字段,就可能希望密封包。如果不密封,其它类就有可能放在这个包中,进而访问包可见的特性。
–例如,如果密封了com.mycompany.util包,就不能用下面的语句将密封包之外的类加入包内:
–Packagecom.mycompany.util;
要想密封一个包,需要将包中的所有类放到一个JAR文件。在默认情况下,JAR文件中的包是没有密封的。
JavaWebStart
JavaWebStart是一个用Java编写的应用程序,它是Sun公司推出的一项在Internet发布应用程序的技术;
通过JavaWebStart可以使一个应用程序很容易地通过web部署在各个平台上,包Windows,Linux,Solaris等。
JavaWebStart部署应用程序
JavaWebStart的工作过程是基于JavaNetwork LaunchProtocol(JNLP)协议的。一个后缀为JNLP的文件包含了应用程序的说明以及如何启动这个应用程序的所有信息,JavaWebStart技术部署应用程序的关键就在于JNLP文件的编写以及发布。
二.实验部分
1、实验目的与要求
(1) 掌握Java应用程序的打包操作;
(2) 了解应用程序存储配置信息的两种方法;
(3) 掌握基于JNLP协议的java Web Start应用程序的发布方法;
(5) 掌握Java GUI 编程技术。
2、实验内容和步骤
实验1: 导入第13章示例程序,测试程序并进行代码注释。
测试程序1
l 在elipse IDE中调试运行教材585页程序13-1,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
l 将所生成的JAR文件移到另外一个不同的目录中,再运行该归档文件,以便确认程序是从JAR文件中,而不是从当前目录中读取的资源。
l 掌握创建JAR文件的方法;
代码:
package resource; import java.awt.*;
import java.io.*;
import java.net.*;
import java.util.*;
import javax.swing.*; /**
* @version 1.41 2015-06-12
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class ResourceTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
EventQueue.invokeLater(() -> {
JFrame frame = new ResourceTestFrame();
frame.setTitle("ResourceTest");
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
frame.setVisible(true);
});
}
} /**
* A frame that loads image and text resources.
*/
class ResourceTestFrame extends JFrame
{
private static final int DEFAULT_WIDTH = 300;
private static final int DEFAULT_HEIGHT = 300; public ResourceTestFrame()
{
setSize(DEFAULT_WIDTH, DEFAULT_HEIGHT);
URL aboutURL = getClass().getResource("about.gif");//返回此 Object 的运行时类。查找带有给定名称的资源
Image img = new ImageIcon(aboutURL).getImage();//根据指定的 URL 创建一个 ImageIcon
setIconImage(img);//设置要作为此窗口图标显示的图像 JTextArea textArea = new JTextArea();//JTextArea 是一个显示纯文本的多行区域
InputStream stream = getClass().getResourceAsStream("about.txt");
try (Scanner in = new Scanner(stream, "UTF-8"))
{
while (in.hasNext())
textArea.append(in.nextLine() + "\n");//将给定文本追加到文档结尾
}
add(textArea);
}
}
ResourceTest
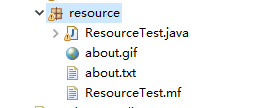
结果:
命令行方式:
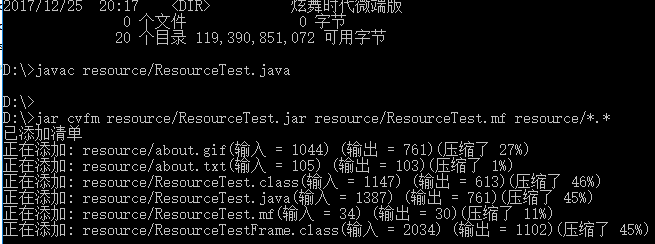
测试程序2
l 在elipse IDE中调试运行教材583页-584程序13-2,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
l 了解Properties类中常用的方法;
代码:
package properties; import java.awt.EventQueue;
import java.awt.event.*;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.Properties; import javax.swing.*; /**
* A program to test properties. The program remembers the frame position, size,
* and title.
* @version 1.01 2015-06-16
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class PropertiesTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
EventQueue.invokeLater(() -> {
PropertiesFrame frame = new PropertiesFrame();
frame.setVisible(true);
});
}
} /**
* A frame that restores position and size from a properties file and updates
* the properties upon exit.
*/
class PropertiesFrame extends JFrame
{
private static final int DEFAULT_WIDTH = 300;
private static final int DEFAULT_HEIGHT = 200; private File propertiesFile;
private Properties settings; public PropertiesFrame()
{
// get position, size, title from properties String userDir = System.getProperty("user.home");//获取指定键指示的系统属性
File propertiesDir = new File(userDir, ".corejava");
if (!propertiesDir.exists()) propertiesDir.mkdir();
propertiesFile = new File(propertiesDir, "program.properties"); Properties defaultSettings = new Properties();
defaultSettings.setProperty("left", "0");//调用 Hashtable 的方法 put。返回值是 Hashtable 调用 put 的结果。
defaultSettings.setProperty("top", "0");
defaultSettings.setProperty("width", "" + DEFAULT_WIDTH);
defaultSettings.setProperty("height", "" + DEFAULT_HEIGHT);
defaultSettings.setProperty("title", ""); settings = new Properties(defaultSettings); if (propertiesFile.exists())
try (InputStream in = new FileInputStream(propertiesFile))
{
settings.load(in);//从输入流中读取属性列表(键和元素对)
}
catch (IOException ex)
{
ex.printStackTrace();
} int left = Integer.parseInt(settings.getProperty("left"));//将字符串参数作为有符号的十进制整数进行解析
int top = Integer.parseInt(settings.getProperty("top"));
int width = Integer.parseInt(settings.getProperty("width"));
int height = Integer.parseInt(settings.getProperty("height"));
setBounds(left, top, width, height);//移动组件并调整其大小 // if no title given, ask user String title = settings.getProperty("title");
if (title.equals(""))
title = JOptionPane.showInputDialog("Please supply a frame title:");
if (title == null) title = "";
setTitle(title); addWindowListener(new WindowAdapter()//添加窗口监听器
{
public void windowClosing(WindowEvent event)
{
settings.setProperty("left", "" + getX());
settings.setProperty("top", "" + getY());
settings.setProperty("width", "" + getWidth());
settings.setProperty("height", "" + getHeight());
settings.setProperty("title", getTitle());
try (OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(propertiesFile))
{
settings.store(out, "Program Properties");
}
catch (IOException ex)
{
ex.printStackTrace();
}
System.exit(0);
}
});
}
}
PropertiesTest
结果:

测试程序3
l 在elipse IDE中调试运行教材593页-594程序13-3,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
l 了解Preferences类中常用的方法;
package preferences; import java.awt.*;
import java.io.*;
import java.util.prefs.*; import javax.swing.*;
import javax.swing.filechooser.*; /**
* A program to test preference settings. The program remembers the frame
* position, size, and title.
* @version 1.03 2015-06-12
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class PreferencesTest
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
EventQueue.invokeLater(() -> {
PreferencesFrame frame = new PreferencesFrame();
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
frame.setVisible(true);
});
}
} /**
* A frame that restores position and size from user preferences and updates the
* preferences upon exit.
*/
class PreferencesFrame extends JFrame
{
private static final int DEFAULT_WIDTH = 300;
private static final int DEFAULT_HEIGHT = 200;
private Preferences root = Preferences.userRoot();
private Preferences node = root.node("/com/horstmann/corejava"); public PreferencesFrame()
{
// get position, size, title from preferences int left = node.getInt("left", 0);//返回与此首选项节点中与指定键相关联的、由字符串表示的 int 值
int top = node.getInt("top", 0);
int width = node.getInt("width", DEFAULT_WIDTH);
int height = node.getInt("height", DEFAULT_HEIGHT);
setBounds(left, top, width, height); // if no title given, ask user String title = node.get("title", "");
if (title.equals(""))
title = JOptionPane.showInputDialog("Please supply a frame title:");
if (title == null) title = "";
setTitle(title); // set up file chooser that shows XML files final JFileChooser chooser = new JFileChooser();
chooser.setCurrentDirectory(new File("."));//设置当前目录
chooser.setFileFilter(new FileNameExtensionFilter("XML files", "xml"));//设置当前文件过滤器 // set up menus JMenuBar menuBar = new JMenuBar();
setJMenuBar(menuBar);//设置此窗体的菜单栏。
JMenu menu = new JMenu("File");
menuBar.add(menu); JMenuItem exportItem = new JMenuItem("Export preferences");
menu.add(exportItem);
exportItem
.addActionListener(event -> {
if (chooser.showSaveDialog(PreferencesFrame.this) == JFileChooser.APPROVE_OPTION)
{
try
{
savePreferences();
OutputStream out = new FileOutputStream(chooser
.getSelectedFile());
node.exportSubtree(out);
out.close();
}
catch (Exception e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}); JMenuItem importItem = new JMenuItem("Import preferences");
menu.add(importItem);
importItem
.addActionListener(event -> {
if (chooser.showOpenDialog(PreferencesFrame.this) == JFileChooser.APPROVE_OPTION)
{
try
{
InputStream in = new FileInputStream(chooser
.getSelectedFile());
Preferences.importPreferences(in);
in.close();
}
catch (Exception e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}); JMenuItem exitItem = new JMenuItem("Exit");
menu.add(exitItem);
exitItem.addActionListener(event -> {
savePreferences();
System.exit(0);
});
} public void savePreferences()
{
node.putInt("left", getX());
node.putInt("top", getY());
node.putInt("width", getWidth());
node.putInt("height", getHeight());
node.put("title", getTitle());
}
}
PreferencesTest
结果:
测试程序4
l 在elipse IDE中调试运行教材619页-622程序13-6,结合程序运行结果理解程序;
l 掌握基于JNLP协议的java Web Start应用程序的发布方法。
代码:
package webstart; import java.awt.*;
import javax.swing.*; /**
* A calculator with a calculation history that can be deployed as a Java Web Start application.
* @version 1.04 2015-06-12
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class Calculator
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
EventQueue.invokeLater(() -> {
CalculatorFrame frame = new CalculatorFrame();
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
frame.setVisible(true);
});
}
}
Calculator
package webstart; import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.ByteArrayInputStream;
import java.io.ByteArrayOutputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.io.OutputStream;
import java.io.PrintStream;
import java.net.MalformedURLException;
import java.net.URL; import javax.jnlp.BasicService;
import javax.jnlp.FileContents;
import javax.jnlp.FileOpenService;
import javax.jnlp.FileSaveService;
import javax.jnlp.PersistenceService;
import javax.jnlp.ServiceManager;
import javax.jnlp.UnavailableServiceException;
import javax.swing.JFrame;
import javax.swing.JMenu;
import javax.swing.JMenuBar;
import javax.swing.JMenuItem;
import javax.swing.JOptionPane; import com.sun.jnlp.FileSaveServiceImpl;
import com.sun.jnlp.FileSaveServiceNSBImpl; //import com.sun.jnlp.BasicServiceImpl; /**
* A frame with a calculator panel and a menu to load and save the calculator history.
*/
public class CalculatorFrame extends JFrame
{
private CalculatorPanel panel; public CalculatorFrame()
{
setTitle();
panel = new CalculatorPanel();
add(panel); JMenu fileMenu = new JMenu("File");
JMenuBar menuBar = new JMenuBar();
menuBar.add(fileMenu);
setJMenuBar(menuBar); JMenuItem openItem = fileMenu.add("Open");
openItem.addActionListener(event -> open());
JMenuItem saveItem = fileMenu.add("Save");
saveItem.addActionListener(event -> save()); pack();
} /**
* Gets the title from the persistent store or asks the user for the title if there is no prior
* entry.
*/
public void setTitle()
{
try
{
String title = null; BasicServiceImpl basic = (BasicServiceImpl) ServiceManager.lookup("javax.jnlp.BasicService");
URL codeBase = basic.getCodeBase(); PersistenceService service = (PersistenceService) ServiceManager
.lookup("javax.jnlp.PersistenceService");
URL key = new URL(codeBase, "title"); try
{
FileContents contents = service.get(key);
InputStream in = contents.getInputStream();
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(in));
title = reader.readLine();
}
catch (FileNotFoundException e)
{
title = JOptionPane.showInputDialog("Please supply a frame title:");
if (title == null) return; service.create(key, 100);
FileContents contents = service.get(key);
OutputStream out = contents.getOutputStream(true);
PrintStream printOut = new PrintStream(out);
printOut.print(title);
}
setTitle(title);
}
catch (UnavailableServiceException | IOException e)
{
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(this, e);
}
} /**
* Opens a history file and updates the display.
*/
public void open()
{
try
{
FileOpenService service = (FileOpenService) ServiceManager
.lookup("javax.jnlp.FileOpenService");
FileContents contents = service.openFileDialog(".", new String[] { "txt" }); JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(this, contents.getName());
if (contents != null)
{
InputStream in = contents.getInputStream();
BufferedReader reader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(in));
String line;
while ((line = reader.readLine()) != null)
{
panel.append(line);
panel.append("\n");
}
}
}
catch (UnavailableServiceException e)
{
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(this, e);
}
catch (IOException e)
{
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(this, e);
}
} /**
* Saves the calculator history to a file.
*/
public void save()
{
try
{
ByteArrayOutputStream out = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
PrintStream printOut = new PrintStream(out);
printOut.print(panel.getText());
InputStream data = new ByteArrayInputStream(out.toByteArray());
FileSaveServiceNSBImpl service = (FileSaveServiceImpl) ServiceManager
.lookup("javax.jnlp.FileSaveService");
service.saveFileDialog(".", new String[] { "txt" }, data, "calc.txt");
}
catch (UnavailableServiceException e)
{
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(this, e);
}
catch (IOException e)
{
JOptionPane.showMessageDialog(this, e);
}
}
}
CalculatorFrame
package webstart; import java.awt.*;
import java.awt.event.*;
import javax.swing.*;
import javax.swing.text.*; /**
A panel with calculator buttons and a result display.
*/
public class CalculatorPanel extends JPanel
{
private JTextArea display;
private JPanel panel;
private double result;
private String lastCommand;
private boolean start; /**
Lays out the panel.
*/
public CalculatorPanel()
{
setLayout(new BorderLayout()); result = 0;
lastCommand = "=";
start = true; // add the display display = new JTextArea(10, 20); add(new JScrollPane(display), BorderLayout.NORTH); ActionListener insert = new InsertAction();
ActionListener command = new CommandAction(); // add the buttons in a 4 x 4 grid panel = new JPanel();
panel.setLayout(new GridLayout(4, 4)); addButton("7", insert);
addButton("8", insert);
addButton("9", insert);
addButton("/", command); addButton("4", insert);
addButton("5", insert);
addButton("6", insert);
addButton("*", command); addButton("1", insert);
addButton("2", insert);
addButton("3", insert);
addButton("-", command); addButton("0", insert);
addButton(".", insert);
addButton("=", command);
addButton("+", command); add(panel, BorderLayout.CENTER);
} /**
Gets the history text.
@return the calculator history
*/
public String getText()
{
return display.getText();
} /**
Appends a string to the history text.
@param s the string to append
*/
public void append(String s)
{
display.append(s);
} /**
Adds a button to the center panel.
@param label the button label
@param listener the button listener
*/
private void addButton(String label, ActionListener listener)
{
JButton button = new JButton(label);
button.addActionListener(listener);
panel.add(button);
} /**
This action inserts the button action string to the
end of the display text.
*/
private class InsertAction implements ActionListener
{
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent event)
{
String input = event.getActionCommand();
start = false;
display.append(input);
}
} /**
This action executes the command that the button
action string denotes.
*/
private class CommandAction implements ActionListener
{
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent event)
{
String command = event.getActionCommand(); if (start)
{
if (command.equals("-"))
{
display.append(command);
start = false;
}
else
lastCommand = command;
}
else
{
try
{
int lines = display.getLineCount();
int lineStart = display.getLineStartOffset(lines - 1);
int lineEnd = display.getLineEndOffset(lines - 1);
String value = display.getText(lineStart, lineEnd - lineStart);
display.append(" ");
display.append(command);
calculate(Double.parseDouble(value));
if (command.equals("="))
display.append("\n" + result);
lastCommand = command;
display.append("\n");
start = true;
}
catch (BadLocationException e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
} /**
Carries out the pending calculation.
@param x the value to be accumulated with the prior result.
*/
public void calculate(double x)
{
if (lastCommand.equals("+")) result += x;
else if (lastCommand.equals("-")) result -= x;
else if (lastCommand.equals("*")) result *= x;
else if (lastCommand.equals("/")) result /= x;
else if (lastCommand.equals("=")) result = x;
}
}
CalculatorPanel
实验2:GUI综合编程练习
按实验十四分组名单,组内讨论完成以下编程任务:
练习1:采用GUI界面设计以下程序,并进行部署与发布:
编制一个程序,将身份证号.txt 中的信息读入到内存中;
按姓名字典序输出人员信息;
查询最大年龄的人员信息;
查询最小年龄人员信息;
输入你的年龄,查询身份证号.txt中年龄与你最近人的姓名、身份证号、年龄、性别和出生地;
查询人员中是否有你的同乡。
输入身份证信息,查询所提供身份证号的人员信息,要求输入一个身份证数字时,查询界面就显示满足查询条件的查询结果,且随着输入的数字的增多,查询匹配的范围逐渐缩小。
package ID;
import java.awt.*;
import javax.swing.*; public class ButtonTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
EventQueue.invokeLater(() -> {
JFrame frame = new Test();
frame.setTitle("身份证");
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
frame.setVisible(true);
});
}
}
ButtonTest
package ID;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.Scanner;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.awt.*;
import javax.swing.*;
import java.awt.event.*; public class Test extends JFrame {
private static ArrayList<Citizen> citizenlist;
private static ArrayList<Citizen> list;
private JPanel panel;
private JPanel buttonPanel;
private static final int DEFAULT_WITH = 600;
private static final int DEFAULT_HEIGHT = 300; public Test(){
citizenlist = new ArrayList<>();
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
File file = new File("E:/java/身份证号.txt");
try {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file);
BufferedReader in = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(fis));
String temp = null;
while ((temp = in.readLine()) != null) { Scanner linescanner = new Scanner(temp); linescanner.useDelimiter(" ");
String name = linescanner.next();
String id = linescanner.next();
String sex = linescanner.next();
String age = linescanner.next();
String birthplace = linescanner.nextLine();
Citizen citizen = new Citizen();
citizen.setName(name);
citizen.setId(id);
citizen.setSex(sex);
int ag = Integer.parseInt(age);
citizen.setage(ag);
citizen.setBirthplace(birthplace);
citizenlist.add(citizen); }
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
System.out.println("信息文件找不到");
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println("信息文件读取错误");
e.printStackTrace();
}
panel = new JPanel();
panel.setLayout(new BorderLayout());
JTextArea jt = new JTextArea();
panel.add(jt);
add(panel, BorderLayout.NORTH);
buttonPanel = new JPanel();
buttonPanel.setLayout(new GridLayout(1, 7));
JButton jButton = new JButton("按姓名字典序输出人员信息");
JButton jButton1 = new JButton("查询年龄最大和年龄最小的人员");
JLabel lab = new JLabel("查询是否有你的老乡");
JTextField jt1 = new JTextField();
JLabel lab1 = new JLabel("查找年龄与你相近的人:");
JTextField jt2 = new JTextField();
JLabel lab2 = new JLabel("输入你的身份证号码:");
JTextField jt3 = new JTextField();
JButton jButton2 = new JButton("退出");
jButton.setBounds(110, 90, 60, 30);
jButton1.setBounds(110, 90, 60, 30);
jt1.setBounds(110, 90, 60, 30);
jt2.setBounds(110, 90, 60, 30);
jt3.setBounds(110, 90, 60, 30);
jButton2.setBounds(110, 90, 60, 30);
jButton.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
Collections.sort(citizenlist);
jt.setText(citizenlist.toString());
}
});
jButton1.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
int max = 0, min = 100;
int j, k1 = 0, k2 = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < citizenlist.size(); i++) {
j = citizenlist.get(i).getage();
if (j > max) {
max = j;
k1 = i;
}
if (j < min) {
min = j;
k2 = i;
} }
jt.setText("年龄最大:" + citizenlist.get(k1) + "年龄最小:" + citizenlist.get(k2));
}
});
jButton2.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
dispose();
System.exit(0);
}
});
jt1.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
String find = jt1.getText();
String text="";
String place = find.substring(0, 3);
for (int i = 0; i < citizenlist.size(); i++) {
if (citizenlist.get(i).getBirthplace().substring(1, 4).equals(place)) {
text+="\n"+citizenlist.get(i);
jt.setText("老乡:" + text);
}
}
}
});
jt2.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
String yourage = jt2.getText();
int a = Integer.parseInt(yourage);
int near = agenear(a);
int value = a - citizenlist.get(near).getage();
jt.setText("年龄相近:" + citizenlist.get(near));
}
});
jt3.addActionListener(new ActionListener() {
public void actionPerformed(ActionEvent e) {
list = new ArrayList<>();
Collections.sort(citizenlist);
String key = jt3.getText();
for (int i = 1; i < citizenlist.size(); i++) {
if (citizenlist.get(i).getId().contains(key)) {
list.add(citizenlist.get(i));
jt.setText("emmm!你可能是:\n" + list);
}
}
}
});
buttonPanel.add(jButton);
buttonPanel.add(jButton1);
buttonPanel.add(lab);
buttonPanel.add(jt1);
buttonPanel.add(lab1);
buttonPanel.add(jt2);
buttonPanel.add(lab2);
buttonPanel.add(jt3);
buttonPanel.add(jButton2);
add(buttonPanel, BorderLayout.SOUTH);
setSize(DEFAULT_WITH, DEFAULT_HEIGHT);
} public static int agenear(int age) {
int min = 53, value = 0, k = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < citizenlist.size(); i++) {
value = citizenlist.get(i).getage() - age;
if (value < 0)
value = -value;
if (value < min) {
min = value;
k = i;
}
}
return k;
} }
Test
package ID;
public class Citizen implements Comparable<Citizen> { private String name;
private String id;
private String sex;
private int age;
private String birthplace;
public String getName() {
return name;
} public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
} public String getId() {
return id;
} public void setId(String id) {
this.id = id;
} public String getSex() {
return sex;
} public void setSex(String sex) {
this.sex = sex;
} public int getage() {
return age;
} public void setage(int age) {
this.age = age;
} public String getBirthplace() {
return birthplace;
} public void setBirthplace(String birthplace) {
this.birthplace = birthplace;
} public int compareTo(Citizen other) {
return this.name.compareTo(other.getName());
} public String toString() {
return name + "\t" + sex + "\t" + age + "\t" + id + "\t" + birthplace + "\n";
}
}
Citizen
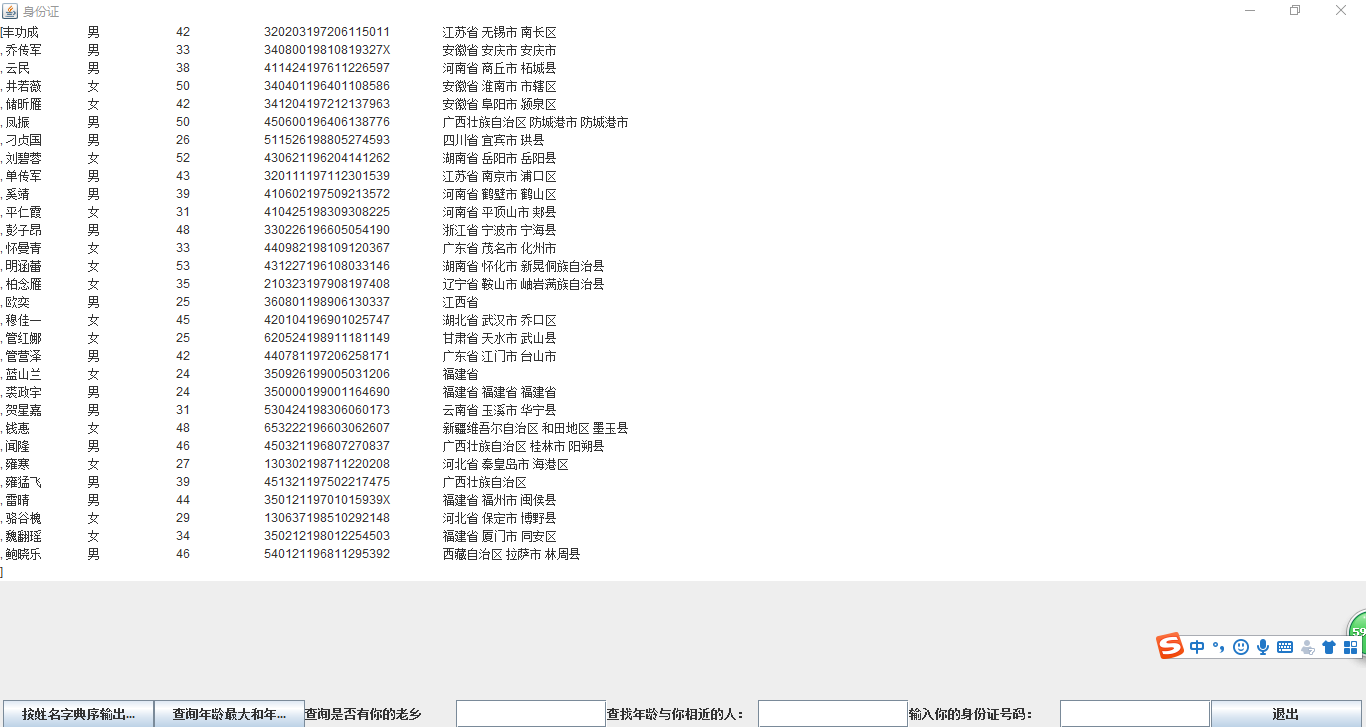

输入甘肃省:

输入28:

输入4
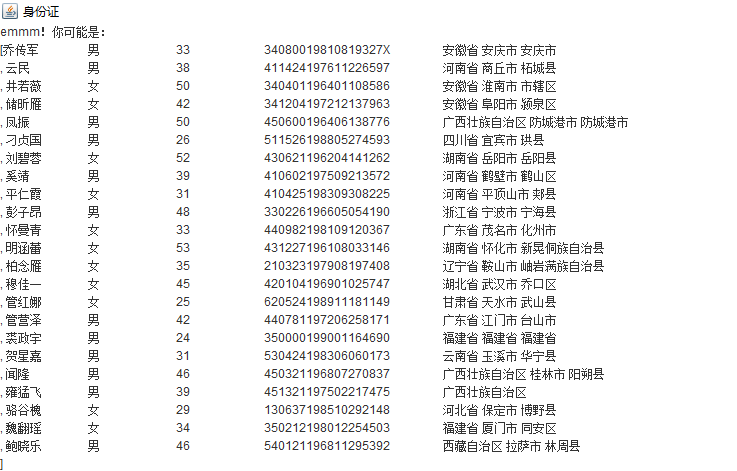
输入440
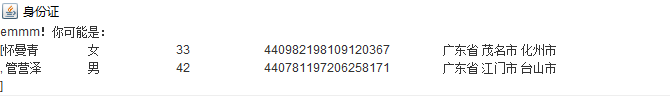
输入4409

练习2:采用GUI界面设计以下程序,并进行部署与发布
编写一个计算器类,可以完成加、减、乘、除的操作
利用计算机类,设计一个小学生100以内数的四则运算练习程序,由计算机随机产生10道加减乘除练习题,学生输入答案,由程序检查答案是否正确,每道题正确计10分,错误不计分,10道题测试结束后给出测试总分;
将程序中测试练习题及学生答题结果输出到文件,文件名为test.txt。
package counter;
import java.awt.Dimension;
import java.awt.EventQueue;
import java.awt.Toolkit;
import javax.swing.JFrame; public class Count { public static void main(String args[]) {
Toolkit t = Toolkit.getDefaultToolkit();
Dimension s = t.getScreenSize();
EventQueue.invokeLater(() -> {
JFrame frame = new Calculator();
frame.setBounds(0, 0, (int) s.getWidth() / 2, (int) s.getHeight() / 2);
frame.setTitle("计算器");
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
frame.setVisible(true);
});
} }
Count
package calculator; import java.awt.*;
import javax.swing.*; /**
* @version 1.34 2015-06-12
* @author Cay Horstmann
*/
public class Calculator
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
EventQueue.invokeLater(() -> {
CalculatorFrame frame = new CalculatorFrame();
frame.setTitle("Calculator");
frame.setDefaultCloseOperation(JFrame.EXIT_ON_CLOSE);
frame.setVisible(true);
});
}
}
Calculator

3.实验总结:
在本周的学习中,我学到了Java应用程序的打包操作,在老师还有助教学长的帮助下,学会了命令行方法。但是在后面的实验编程中,依然存在这很多的问题。
201771010113 李婷华 《面向对象程序设计(java)》第十五周总结的更多相关文章
- 20155322 2016-2017-2 《Java面向对象程序设计》第十二周课堂练习之Arrays和String单元测试
20155322 2016-2017-2 <Java面向对象程序设计>第十二周课堂练习之Arrays和String单元测试 练习目地 在IDEA中以TDD的方式对String类和Array ...
- 201571030332 扎西平措 《面向对象程序设计Java》第八周学习总结
<面向对象程序设计Java>第八周学习总结 项目 内容 这个作业属于哪个课程 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/ 这个作业的要求在哪里 https: ...
- 201771010118马昕璐《面向对象程序设计java》第八周学习总结
第一部分:理论知识学习部分 1.接口 在Java程序设计语言中,接口不是类,而是对类的一组需求描述,由常量和一组抽象方法组成.Java为了克服单继承的缺点,Java使用了接口,一个类可以实现一个或多个 ...
- 201771010134杨其菊《面向对象程序设计java》第八周学习总结
第八周学习总结 第一部分:理论知识 一.接口.lambda和内部类: Comparator与comparable接口: 1.comparable接口的方法是compareTo,只有一个参数:comp ...
- 20145209刘一阳《JAVA程序设计》第十五周补充测试
第十五周补充测试 1.实验楼Linux中可以通过(ABC)查看用户登录情况. A .who B .who am i C .who mom likes D .who are you 2.在 Linux ...
- 201771010113 李婷华 《面向java对象程序设计(Java)》第四章学习总结
一. 理论知识部分 第四章 对象与类 本章主要讲述面向对象程序设计.如何创建标准Java类库中的类对象.如何编写自己的类. 1.面向对象程序设计的几个主要概念: 抽象数据类型.类和对象.封装.类层次( ...
- 201771010134杨其菊《面向对象程序设计java》第七周学习总结
第七周学习总结 第一部分:理论知识 1.继承是面向对象程序设计(Object Oriented Programming-OOP)中软件重用的关键技术.继承机制使用已经定义的类作为基础建立新的类定义,新 ...
- 201771010123汪慧和《面向对象程序设计JAVA》第七周实验总结
一.理论部分 1.继承 如果两个类存在继承关系,则子类会自动继承父类的方法和变量,在子类中可以调用父类的方法和变量,如果想要在子类里面做一系列事情,应该放在父类无参构造器里面,在java中,只允许单继 ...
- 201871010126 王亚涛《面向对象程序设计 JAVA》 第十三周学习总结
内容 这个作业属于哪个课程 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/ 这个作业的要求在哪里 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/p/ ...
- 201777010217-金云馨《面向对象程序设计Java》第八周学习总结
项目 内容 这个作业属于哪个课程 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/ 这个作业的要求在哪里 https://www.cnblogs.com/nwnu-daizh/p ...
随机推荐
- x86汇编之栈与子程序调用
什么是栈 栈与普通数据结构所说的栈的概念是相似的,遵循后进先出原则.不同的是汇编中所说的栈是一个在内存中连续的保存数据的区域,也即是实际存在的内存区域,进栈和出栈遵循后进先出原则. 在x86架构中,栈 ...
- 阿里Canal框架数据库同步-实战教程
一.Canal简介: canal是阿里巴巴旗下的一款开源项目,纯Java开发.基于数据库增量日志解析,提供增量数据订阅&消费,目前主要支持了MySQL(也支持mariaDB). 二.背景介绍: ...
- tensorflow--filter、strides
最近还在看<TensorFlow 实战Google深度学习框架第二版>这本书,根据第六章里面对于卷基层和池化层的介绍可以发现,在执行 tf.nn.conv2d 和 tf.nn.max_po ...
- [GO] linux 下安装GO
yum install mercurial安装 mercurial包 安装git包 yum install git 安装gcc yum install gcc 然后就可以下载golang的压缩包了 对 ...
- [PHP] 生成二维码(两种方法)
方法一:(调用google二维码接口,本人测试网不好,不好用!) <?php //1.封装生成二维码图片的函数(方法) /** *利用google api生成二维码图片 * $content:二 ...
- 【考试总结】欢乐模拟赛_Day1
\(T1\) 题目描述 给出一个 \(n × n\) 的, 元素为自然数的矩阵. 这个矩阵有许许多多个子矩阵, 定义它的所有子矩阵形成的集合为 \(S\) . 对于一个矩阵 \(k\) , 定义 \( ...
- nodejs之https双向认证
说在前面 之前我们总结了https的相关知识,如果不懂可以看我另一篇文章:白话理解https 有关证书生成可以参考:自签证书生成 正题 今天使用nodejs来实现https双向认证 话不多说,直接进入 ...
- 高性能的JavaScript,这是一个高级程序员必备的技能
不知道大家有没有看过高性能JavaScript,这个书是一本好书,推荐有JavaScript的基础的同学可以看一看这本书. 下面是我根据这本书整理出来的知识: 1.将经常使用的对象成员.数组项.和域外 ...
- thinkphp5--关于多条件查询的分页处理问题
首先,我们要想搞明白,我们的分页参数起作用的原理: 正在使用的时候的语法: if(!empty($seach)){ $where['user_name|mobile'] = ['like','%'.$ ...
- 《JAVA8开发指南》使用流式操作
为什么需要流式操作 集合API是Java API中最重要的部分.基本上每一个java程序都离不开集合.尽管很重要,但是现有的集合处理在很多方面都无法满足需要. 一个原因是,许多其他的语言或者类库以声明 ...
