map的嵌套 + 例题(水果)
水果
http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1263
Problem Description
夏天来了~~好开心啊,呵呵,好多好多水果~~Joe经营着一个不大的水果店.他认为生存之道就是经营最受顾客欢迎的水果.现在他想要一份水果销售情况的明细表,这样Joe就可以很容易掌握所有水果的销售情况了.
Input
第一行正整数N(0<N<=10)表示有N组测试数据.
每组测试数据的第一行是一个整数M(0<M<=100),表示工有M次成功的交易.其后有M行数据,每行表示一次交易,由水果名称(小写字母组成,长度不超过80),水果产地(小写字母组成,长度不超过80)和交易的水果数目(正整数,不超过100)组成.
Output
对于每一组测试数据,请你输出一份排版格式正确(请分析样本输出)的水果销售情况明细表.这份明细表包括所有水果的产地,名称和销售数目的信息.水果先按产地分类,产地按字母顺序排列;同一产地的水果按照名称排序,名称按字母顺序排序.两组测试数据之间有一个空行.最后一组测试数据之后没有空行.
Sample Input
apple shandong
pineapple guangdong
sugarcane guangdong
pineapple guangdong
pineapple guangdong
Sample Output
guangdong
|----pineapple()
|----sugarcane()
shandong
|----apple()
map的嵌套
#include <stdio.h>
#include <iostream>
#include <string.h>
#include <string>
#include <algorithm>
#include <map> using namespace std; int main()
{
//freopen("sample.txt","r",stdin);
int n;
cin>>n;
for(int i=;i<n;i++)
{
if(i!=)
cout<<endl;
int m;
cin>>m;
map<string,map<string,int> > mp;
map<string,map<string,int> >::iterator it1;
map<string,int>::iterator it2;
while(m--)
{
string fruit,address;
int count;
cin>>fruit>>address>>count;
mp[address][fruit]+=count; //这一步要记住
}
for(it1=mp.begin();it1!=mp.end();it1++)
{
cout<<it1->first<<endl;
for(it2=it1->second.begin();it2!=it1->second.end();it2++)
{
cout<<" |----"<<it2->first<<"("<<it2->second<<")"<<endl;
}
}
}
return ;
}
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
#include<map>
using namespace std; struct MyStruct
{
map <string, int>MyStructma; //存放水果名以及该种水果的数量
};
int main()
{
map <string, MyStruct>ma; //地名
map <string, MyStruct>::iterator it;
map <string, int>::iterator MyStructmait;
string fruit,place;
int count;
int n,t;
cin>>t;
while(t--)
{
ma.clear();
cin>>n;
while(n--)
{
cin>>fruit>>place>>count;
ma[place].MyStructma[fruit] += count;
}
for (it = ma.begin(); it != ma.end(); it++)
{
cout<<it->first<<endl;
for (MyStructmait = it->second.MyStructma.begin(); MyStructmait != it->second.MyStructma.end(); MyStructmait++)
{ cout<<" |----"<<MyStructmait->first<<"("<<MyStructmait->second<<")"<<endl;
}
}
if(t != )cout<<endl;
}
return ;
}
也可以结构体排序,不用STL
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std; struct Node
{
char name[];
char space[];
int num;
} f[]; int cmp(Node x,Node y)
{
if(strcmp(x.space,y.space))
return strcmp(x.space,y.space)<;
return strcmp(x.name,y.name)<;
} int main()
{
int t,n,i;
scanf("%d",&t);
while(t--)
{
scanf("%d%*c",&n);
for(i = ; i<n; i++)
{
scanf("%s%s%d",f[i].name,f[i].space,&f[i].num);
}
sort(f,f+n,cmp);
char di[],min[];
int cnt = ,flag = ;
strcpy(di,f[].space);
strcpy(min,f[].name);
for(i = ; i<n; i++)
{
if(strcmp(di,f[i].space))
{
strcpy(di,f[i].space);
strcpy(min,f[i].name);
flag = ;
cnt = ;
}
if(!strcmp(di,f[i].space))
{
if(flag)
{
printf("%s\n",di);
flag = ;
}
if(!strcmp(min,f[i].name))
{
while(!strcmp(min,f[i].name) && !strcmp(di,f[i].space))//产地与水果名都必须相同
{
cnt+=f[i].num;
i++;
}
printf(" |----%s(%d)\n",min,cnt);
strcpy(min,f[i].name);
i--;
cnt = ;
}
}
}
if(t)
printf("\n");
} return ;
}
另一种解法
#include<cstdio>
#include<iostream>
#include<map>
#include<string>
using namespace std; int main(){
int n,m;
string color;
map<string,int>mp;
while(scanf("%d",&m)!=EOF && m){
while(m--){
cin>>color;
mp[color]++;
}
int max = ;
string a;
for(map<string,int>::iterator it=mp.begin();it!=mp.end();it++){
if(max<=it->second){
max = it->second;
a = it->first;
}
}
cout<<a<<endl;
mp.clear();
}
return ;
}
STL中map的嵌套使用
from:https://www.cnblogs.com/1114250779boke/archive/2012/08/07/2626477.html
对于传统的map:
#include <iostream>
#include <map> using namespace std; int main()
{
map<int, string> scores; scores.insert(make_pair(,"maxi")); scores[]="MAXI"; scores.insert(make_pair(,"xiaoyu")); scores.insert(make_pair(,"xiao")); scores[]="xiaoma"; map<int,string>::iterator pScores; for(pScores=scores.begin();pScores!=scores.end();pScores++)
{
std::cout<<pScores->first<<" "<<pScores->second<<endl;
}
return ;
}
结果输出:
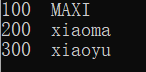
由此可以看出,scores[100]="MAXI"会直接替换掉原来100map对应的value,而如果调用scores.insert()函数,则由于本map是单映射的,300 map的value:xiao就不会替换掉原来300 map对应的value:xiaoyu
但如果我想定义嵌套的map并对它进行遍历,该如何进行呢:
#include<iostream>
#include<map> using namespace std;
int main()
{
//对于这样的map嵌套定义,有两种插入方法:
//定义一个map<int, string>变量,对其定义后在插入multiMap
map<int,map<int,string> >multiMap; map<int, string> temp; temp.insert(make_pair(,"hi")); temp.insert(pair<int,string>(,"maxi")); //pair<int,string>()和make_pair()有相同作用 multiMap.insert(make_pair(, temp)); //将临时变量插入到multiMap中
//也可以直接赋值
multiMap[][]="xiaoyu"; multiMap[][]="xiaoma"; // 以下是如何遍历本multiMap
map<int,map<int,string> >::iterator multitr;
map<int,string>::iterator intertr;
for(multitr=multiMap.begin();multitr!=multiMap.end();multitr++)
{
for(intertr= multitr ->second.begin(); intertr != multitr ->second.end(); intertr ++)
std::cout<< multitr ->first<<" "<<intertr->first<<" ("<< intertr -> second <<")"<<endl;
}
return ;
}
运行结果如下:
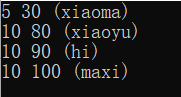
总结,map的成员加入有两种赋值方法,一种是调用map.insert()函数,这样,由于是单映射,后面加入的新的pair对如果有key值和前面一样,那么后面的pair对元素将不会被加入到map中;但如果是直接[ ]=赋值操作的话,相当于数组赋值,会直接替换掉原来具有相同key域的pair对。
map的嵌套 + 例题(水果)的更多相关文章
- 水果(map的嵌套)
夏天来了~~好开心啊,呵呵,好多好多水果~~ Joe经营着一个不大的水果店.他认为生存之道就是经营最受顾客欢迎的水果.现在他想要一份水果销售情况的明细表,这样Joe就可以很容易掌握所有水果的销售情况了 ...
- Map的嵌套 练习
Map的嵌套 练习 利用迭代和增强for循环的两种方式实现如下效果 package cn.ccc; import java.util.HashMap;import java.util.Iterat ...
- Map的嵌套,HDU(1263)
题目链接:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1263 新学的map的嵌套 #include <stdio.h> #include < ...
- 双列集合Map的嵌套遍历
双列集合Map的嵌套使用,例如HashMap中还有一个HashMap,这样的集合遍历起来稍微有点儿复杂.例如一个集合:HashMap<Integer,HashMap<String,Inte ...
- Map接口----Map中嵌套Map
package cn.good.com; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Iterator; import java.util.Map; impo ...
- Map的嵌套
package cn.lijun.demo2; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Iterator; import java.util.Set; p ...
- Map的嵌套使用
Map嵌套Map: 例: AAA: Javas班: 001 熊大 002 熊二 Hdoop班 001 小猪猪 002 小菲菲 ★使用增强for循环遍历Set数组: import java.util.H ...
- fastjson排序 Map多层嵌套转换自动排序问题终极解决方案
阅读更多 最近项目中用到了fastjson(1.2.15)需要将前端多层嵌套json转换为map,由于map的无序性,想了很多办法,最终找到使用 Map m= JSONArray.parseObjec ...
- map练习小例题
"fdgavcbsacdfs" 获取该字符串中,每一个字母出现的次数. 要求打印结果是:a(2)b(1)...; 思路: 对于结果的分析发现,字母和次数之间存在着映射关系.而且这种 ...
随机推荐
- php语言注意点
PHP大小写问题 http://www.jb51.net/article/38579.htm 推荐大家始终坚持“大小写敏感”,遵循统一的代码规范.1. 变量名区分大小写 2. 函数名.方法名.类名不区 ...
- qt 字符串 转换 hex
1. qt 中两个字符的字符串直接转换为 hex,类似于 "1A" 要转换成 16进制的 0x1A,使用 int QString::toInt(bool *ok, int base ...
- Vue v-bind
指令作用: 给元素的属性赋值 它是一个 vue 指令,用于绑定 html 属性 写法: 正常写法 <div v-bind:原属性名="变量||"常量""& ...
- 越南CTF的crypto 100
自己做CTF还是没有经验,本来以为crypto更多应该是python编程的,结果这个100的题目是Do you love Arithmetic? 打开文件来看内容是 # charset = " ...
- Zookeeper--复制模式安装
参考: https://www.cnblogs.com/lsdb/p/7297731.html https://zookeeper.apache.org/doc/r3.4.13/zookeeperSt ...
- js数组全等
js 数组全等(对象) if(this.eqOrNotEq(arr)){} eqOrNotEq(arr) { return !arr.some(function(value, index) { ret ...
- BZOJ [HAOI2006]旅行comf
题解:枚举最大边,然后对<=最大边的边做最大生成树,使最小边最大 #include<iostream> #include<cstdio> #include<cstr ...
- blueimp,预览遮罩范围控制
blueimg gallery github地址:https://github.com/blueimp/Gallery/blob/master/README.md 使用前提,引用css和js < ...
- UVA 11987 - Almost Union-Find 并查集的活用 id化查找
受教了,感谢玉斌大神的博客. 这道题最难的地方就是操作2,将一个集合中的一个点单独移到另一个集合,因为并查集的性质,如果该点本身作为root节点的话,怎么保证其他点不受影响. 玉斌大神的思路很厉害,受 ...
- 直击JDD | 共建智能新城 京东云让城市生活变得简单美好
技术快速革新,创新持续激发.在"智能+"时代,云计算.大数据.5G等新技术,已成为社会生产方式变革.创新人类生活空间的重要力量--11月19日,JDD-2019京东全球科技探索者大 ...
