Java 异常处理与输入输出
一、异常

1.1
package exception;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ArrayIndex {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] a=new int[10];
Scanner in=new Scanner(System.in);
int index=in.nextInt();
try
{
a[index]=25;
System.out.println("right");
}
catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException b)
{
System.out.println("there is a wrong");
}
in.close();
}
}

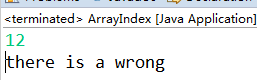
出现异常就会到catch。
1.2 调用的函数中出现异常
package exception;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ArrayIndex {
public static void f()
{
int[] a=new int[10];
a[10]=15;
System.out.println("right");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
try
{
f();
}
catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException b)
{
System.out.println("there is a wrong");
}
System.out.println("end");
}
}
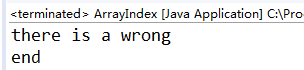
1.3
package exception;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ArrayIndex {
public static void f()
{
int[] a=new int[10];
a[10]=15;
System.out.println("hello");
}
public static void g()
{
f();
}
public static void h()
{
int i=10;
if(i<100)
g();
}
public static void k()
{
try {
h();
}
catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e)
{
System.out.println("k()");
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
try
{
k();
}
catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e)
{
System.out.println("there is a wrong");
}
System.out.println("end");
}
}

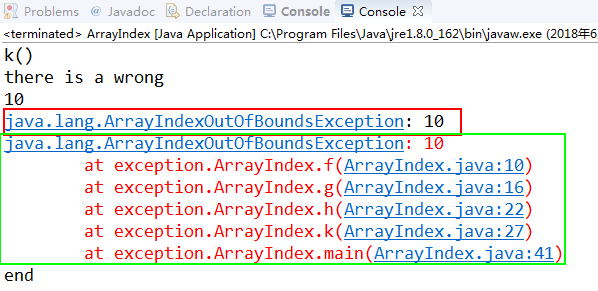
try ...catch 里出现嵌套时,只会输出里层嵌套的内容。
catch的存在就是为了处理出现的异常。
相当于在k()函数中发现了异常,并且利用catch已经将异常解决了。所以在main()中便默认k()没有了异常,所以不会输出“there is a wrong”。
1.4
package exception;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class ArrayIndex {
public static void f()
{
int[] a=new int[10];
a[10]=15;
System.out.println("hello");
}
public static void g()
{
f();
}
public static void h()
{
int i=10;
if(i<100)
g();
}
public static void k()
{
try {
h();
}
catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e)
{
System.out.println("k()");
throw e;//抛出异常
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
try
{
k();
}
catch(ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e)
{
System.out.println("there is a wrong");
System.out.println(e.getMessage());//输出e的值,10,这是指数组a[10]处赋值出现问题
System.out.println(e);
e.printStackTrace();//显示调用路径
}
System.out.println("end");
}
}
throw e:相当于将处理的异常又重新添加加进来,这样“there is a wrong ”也便会输出。
或者说对于异常catch没有处理完全。所以还需要再度输出。
1.5
二、流


2.1 二进制数据
package Hello; import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Scanner; public class test { public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Hello world");
byte[] buffer=new byte[1024];//定义了字节数组
try {
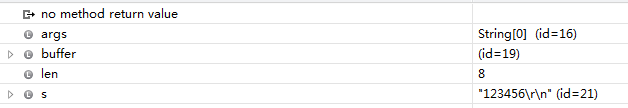
int len=System.in.read(buffer);//往buffer中写入数据,并返回长度
String s=new String(buffer, 0, len);//从buffer中0的位置开始,获取len长度的字节
System.out.println("读到了"+len+"字节");
System.out.println(s);
System.out.println("s的长度是:"+s.length());
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
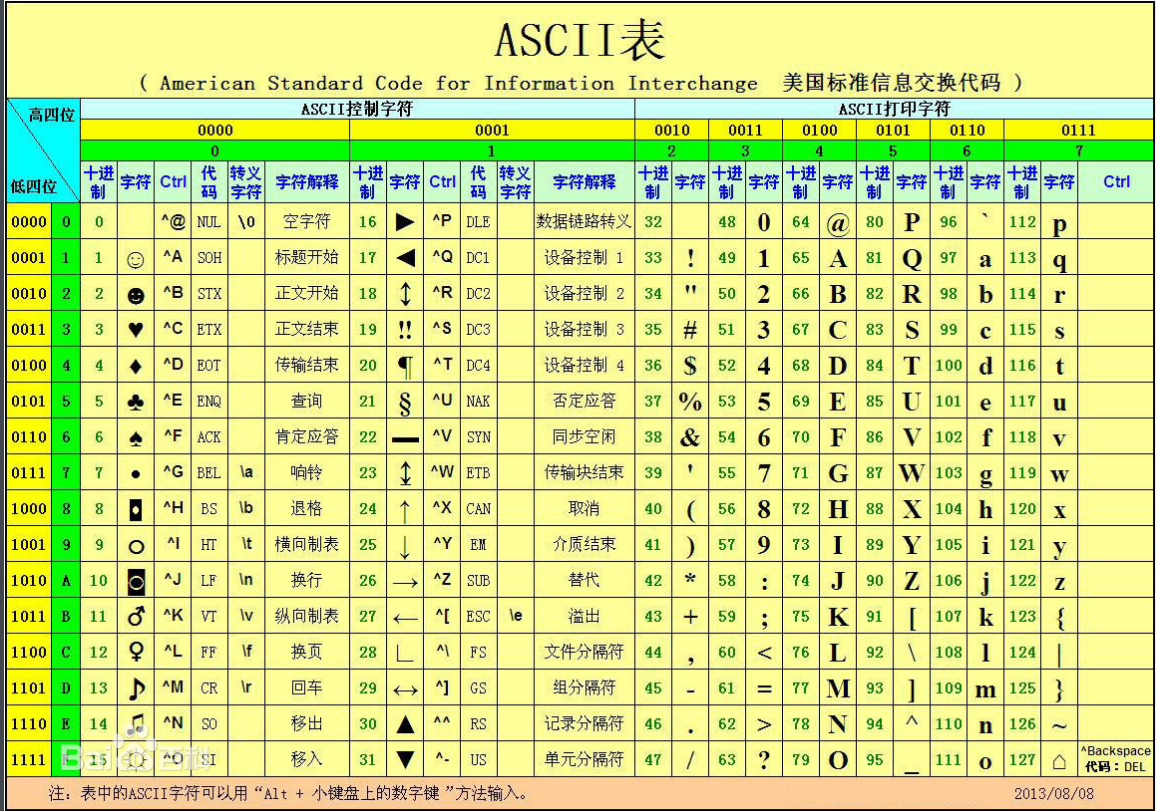
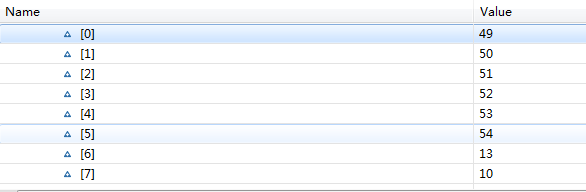

回车和换行算两个字符。

2.2
package Hello; import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Scanner; public class test { public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Hello world");
byte[] buffer=new byte[5];
for(int i=0;i<buffer.length;i++)
{
buffer[i]='a';
}
try {
FileOutputStream out=new FileOutputStream("a.txt");
out.write(buffer);
out.close();
} catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
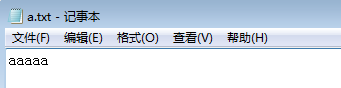

2.3 过滤器

package Hello; import java.io.BufferedInputStream;
import java.io.BufferedOutputStream;
import java.io.DataInputStream;
import java.io.DataOutputStream;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.Scanner; import javax.imageio.stream.FileImageOutputStream; public class test { public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Hello world");
byte[] buffer=new byte[10];
for(int i=0;i<buffer.length;i++)
{
buffer[i]=(byte) i;
}
try {
DataOutputStream out=new DataOutputStream(
new BufferedOutputStream(
new FileOutputStream("b.dat")));//只能处理字节
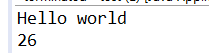
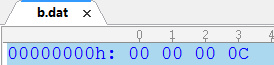
int i=123454;
out.writeInt(i);
out.close(); DataInputStream in=new DataInputStream(
new BufferedInputStream(
new FileInputStream("b.dat")));
int j=in.readInt();
System.out.println(j); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
以16进制存储。
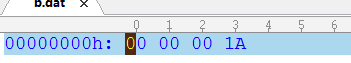

2.4 文本


package Hello; import java.io.BufferedInputStream;
import java.io.BufferedOutputStream;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.BufferedWriter;
import java.io.DataInputStream;
import java.io.DataOutputStream;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.io.OutputStreamWriter;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.util.Scanner; import javax.imageio.stream.FileImageOutputStream; public class test { public static void main(String[] args) {
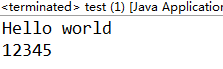
System.out.println("Hello world");
byte[] buffer=new byte[10];
for(int i=0;i<buffer.length;i++)
{
buffer[i]=(byte) i;
}
try {
PrintWriter out=new PrintWriter(
new BufferedWriter(
new OutputStreamWriter(
new FileOutputStream("c.txt"))));//
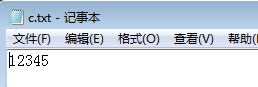
int i=12345;
out.println(i);
out.close(); BufferedReader in=new BufferedReader(
new InputStreamReader(
new FileInputStream("c.txt")));
String line;
while((line=in.readLine())!=null)
System.out.println(line); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}



2.5编码格式
package Hello; import java.io.BufferedInputStream;
import java.io.BufferedOutputStream;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.BufferedWriter;
import java.io.DataInputStream;
import java.io.DataOutputStream;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.io.OutputStreamWriter;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.util.Scanner; import javax.imageio.stream.FileImageOutputStream; public class test { public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Hello world");
byte[] buffer=new byte[10];
for(int i=0;i<buffer.length;i++)
{
buffer[i]=(byte) i;
}
try {
PrintWriter out=new PrintWriter(
new BufferedWriter(
new OutputStreamWriter(
new FileOutputStream("c.txt"))));//
int i=12345;
out.println(i);
out.close(); BufferedReader in=new BufferedReader(
new InputStreamReader(
new FileInputStream("a.txt"),"GBk"));//设置编码格式
String line;
while((line=in.readLine())!=null)
System.out.println(line); } catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
GBK编码时,正确读出

utf8时

2.6 格式化输出


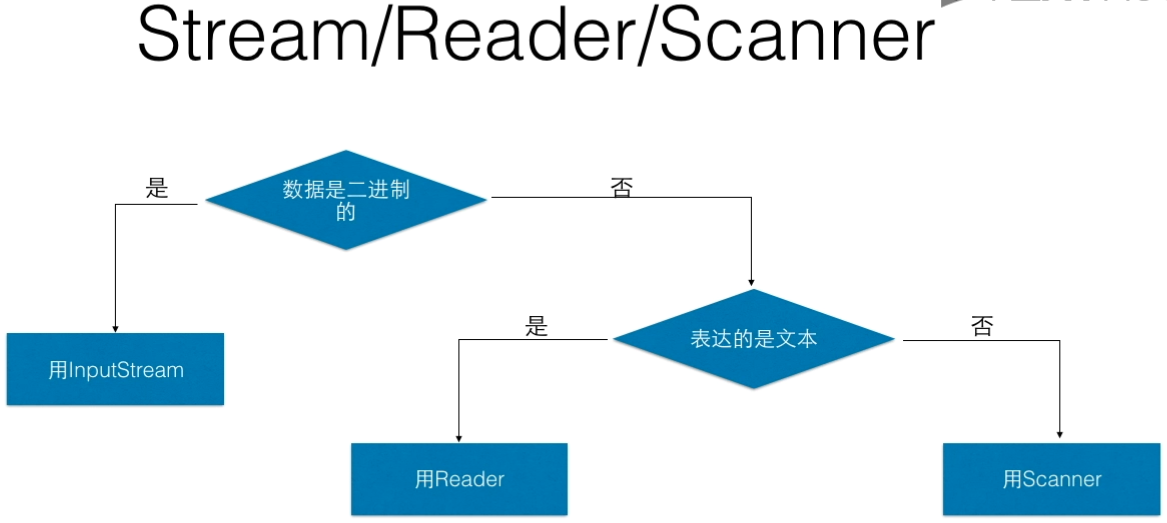
三、流应用
package Hello; import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.BufferedWriter;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.io.OutputStreamWriter;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.net.InetAddress;
import java.net.Socket; public class hello { public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
Socket socket=new Socket(InetAddress.getByName("localhost"),12345);
PrintWriter out=new PrintWriter(
new BufferedWriter(
new OutputStreamWriter(
socket.getOutputStream())));//
out.println("hello"); BufferedReader in=new BufferedReader(
new InputStreamReader(
socket.getInputStream()));//设置编码格式
String line;
line=in.readLine();
System.out.println(line);
out.close();
socket.close();
}catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
四、对象串行化
package Hello; import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.BufferedWriter;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
import java.io.ObjectOutput;
import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
import java.io.OutputStreamWriter;
import java.io.PrintWriter;
import java.io.Serializable;
import java.net.InetAddress;
import java.net.Socket; class Student implements Serializable{ //可串行化的类
private String name;
private int age;
private int grade; public Student(String name,int age,int grade)
{
this.name=name;
this.age=age;
this.grade=grade;
} public String toString()
{
return name+" "+age+" "+grade;
}
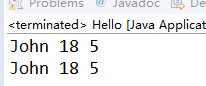
} public class hello { public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
Student s1=new Student("John",18,5);
System.out.println(s1);
ObjectOutputStream out=new ObjectOutputStream(
new FileOutputStream("obj.dat"));
out.writeObject(s1);
out.close();
ObjectInputStream in=new ObjectInputStream(
new FileInputStream("obj.dat"));
Student s2=(Student)in.readObject();
System.out.println(s2);
}catch (IOException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
保存在obj.dat中的值

Java 异常处理与输入输出的更多相关文章
- Java—异常处理总结
异常处理是程序设计中一个非常重要的方面,也是程序设计的一大难点,从C开始,你也许已经知道如何用if...else...来控制异常了,也许是自发的,然而这种控制异常痛苦,同一个异常或者错误如果多个地方出 ...
- [ Java学习基础 ] Java异常处理
一.异常概述 异常是程序中的一些错误,但并不是所有的错误都是异常,并且错误有时候是可以避免的.比如说,你的代码少了一个分号,那么运行出来结果是提示是错误 java.lang.Error:如果你用Sys ...
- 2017.4.7 java异常处理总结
目录 1.java异常处理的几种错误做法 2.异常处理示例 3.常用异常 4.异常类的继承关系 5.异常处理机制 6.Throw和Throws的区别 7.e.toString(), e.getCaus ...
- Java异常处理总结Exception\Error
Java异常处理总结Exception\Error 2012-12-28 08:17:17| 分类: JAVA | 标签:java |举报|字号 订阅 Java异常处理总结 ...
- 这几种Java异常处理方法,你会吗?
摘要:我们在软件开发的过程中,任何语言的开发过程中都离不开异常处理. 本文分享自华为云社区<Java异常处理学习总结>,作者: zekelove . 我们在软件开发的过程中,任何语言的开发 ...
- 札记:Java异常处理
异常概述 程序在运行中总会面临一些"意外"情况,良好的代码需要对它们进行预防和处理.大致来说,这些意外情况分三类: 交互输入 用户以非预期的方式使用程序,比如非法输入,不正当的操作 ...
- java异常处理(父子异常的处理)
我当初学java异常处理的时候,对于父子异常的处理,我记得几句话“子类方法只能抛出父类方法所抛出的异常或者是其子异常,子类构造器必须要抛出父类构造器的异常或者其父异常”.那个时候还不知道子类方法为什么 ...
- Java 异常处理
异常是程序中的一些错误,但并不是所有的错误都是异常,并且错误有时候是可以避免的. 比如说,你的代码少了一个分号,那么运行出来结果是提示是错误java.lang.Error:如果你用System.out ...
- 《转载》Java异常处理的10个最佳实践
本文转载自 ImportNew - 挖坑的张师傅 异常处理在编写健壮的 Java 应用中扮演着非常重要的角色.异常处理并不是功能性需求,它需要优雅地处理任何错误情况,比如资源不可用.非法的输入.nul ...
随机推荐
- 01 Taro_Mall 开源多端小程序框架设计
项目介绍 Taro_Mall是一款多端开源在线商城应用程序,后台是基于litemall基础上进行开发,前端采用Taro框架编写,现已全部完成小程序和h5移动端,后续会对APP,淘宝,头条,百度小程序进 ...
- 前端开发: webStorm手机真机调试
目录 1. 做好准备工作 2. 开始设置 3. 配置路径 4. 匹配路径设置 5. 设置完成,即可体验 文章首发微信公众号飙码人生 2018-05-21 18:21:15 1. 做好准备工作 安装we ...
- python实验一
安徽工程大学 Python程序设计实验报告 班级物流管理191 姓名彭艺 学号3190505139成绩 日期 2020年3月3日 指导老师 修宇 实验名称 ...
- Asp.Net Core 中IdentityServer4 授权中心之应用实战
一.前言 查阅了大多数相关资料,查阅到的IdentityServer4 的相关文章大多是比较简单并且多是翻译官网的文档编写的,我这里在 Asp.Net Core 中IdentityServer4 的应 ...
- Javascript中String()和new String()的区别——JS的包装对象
最近在看Symbol不能使用new操作符,然后类比到Number,String,Boolean,因为它们同属于基本类型,但是有有所差异:Number,String,Boolean是可以使用new操作符 ...
- C# 简单地使用下 音频解码器Bass.Net
在C#中有许多音频播放的方案,例如WinForm里调用系统自带MediaPlayer的COM组件和WPF的MediaPlayer(实质上还是WindowsMediaPlayer) 以及一堆API播放和 ...
- NSFileHandle的用法(用于读写文件)
利用NSFilehandle类提供的方法,允许更有效地使用文件. 一般而言,处理文件时都要经历以下三个步骤: 1.打开文件,并获取一个NSFileHandle对象,以便在后面的I/O操作中引用该文件 ...
- python初学者必看学习路线图!!!
python应该是近几年比较火的语言之一,很多人刚学python不知道该如何学习,尤其是没有编程基础想要从事程序员工作的小白,想必应该都会有此疑惑,包括我刚学python的时候也是通过从网上查找相关资 ...
- python学习的新篇章--面向对象
面向对象的学习笔记 关键要素: 类:class 用来描述具有相同的属性和方法的对象的集合,它定义了该集合中每个对象所共有的属性和方法. 数据成员: 类的不同属性数据 对象: 类的一个实例 ...
- lesson01
题目: Action3: 统计全班的成绩 班里有5名同学,现在需要你用numpy来统计下这些人在语文.英语.数学中的平均成绩.最小成绩.最大成绩.方差.标准差.然后把这些人的总成绩排序,得出名次进行 ...
