Python数据结构应用1——Stack
自学一下数据结构,学完之后刷leetcode,使用python,从stack开始
Stack建立
class Stack:
def __init__(self):
self.items = []
def is_empty(self):
return self.items == []
def push(self,item):
self.items.append(item)
def pop(self):
return self.items.pop()
def peek(self):
return self.items[-1]
def size(self):
return len(self.items)以上stack的top位置位于list的ending位置,如果要设置stack的top位置为list的beginning位置,只需要做如下改动
class Stack:
def __init__(self):
self.items = []
def is_empty(self):
return self.items == []
def push(self,item):
self.items.insert(0,item)
def pop(self):
return self.items.pop(0)
def peek(self):
return self.items[0]
def size(self):
return len(self.items)这两种方式的时间复杂度明显不同,具体可以参见下表中的list处理的时间复杂度 
pop(i)和insert(i,item)的时间复杂度为O(n),而pop()和append()的时间复杂度为O(1)
用stack在python中解决实际问题
括号对称问题
这个问题貌似是个很经典的stack问题了,判断string中的括号是否对称:
如:
()(()((()))) 为对称
(()()(()(()))) 为不对称
基本思路:
遍历string中的每个字符
- 当遇到左括号
(时,push到stack里 - 当遇到右括号
)时,pop对应的左括号( - 如果在遇到右括号
)时,此时stack为空,则该右括号)没有对应的左括号,返回False - 如果遍历完所有字符后,stack不为空,则stack里全为左括号
(,返回False
def par_checker(symbol_string):
s = Stack()
balanced = True
index =0
while index<len(symbol_string) and balanced:
symbol = symbol_string[index]
if symbol == '(':
s.push(symbol)
else:
if s.is_empty():
balanced = False
else:
s.pop()
index = index+1
if balanced and s.is_empty():
return True
else:
return Falseprint(par_checker('()((()))'))
print(par_checker('()(()'))True
False
运用以上方法,可以解决类似问题,如括号为({[的问题
将十进制数转换为二进制数
很简单,这里用的是高中的方法,除2取余,除2取余……
def divide_by_2(dec_number):
rem_stack = Stack()
while dec_number > 0:
rem = dec_number%2
rem_stack.push(rem)
dec_number = dec_number//2
# '//' 取整除,返回商整数部分
bin_string = ''
while not rem_stack.is_empty():
bin_string = bin_string + str(rem_stack.pop())
return bin_string
print(divide_by_2(42))101010
这个方法可以自然的扩展到转换为8进制(octal),16进制(hex),运用的也是同样的方法,只是在代码的开始建立一个’符号字典’。
def base_converter(dec_number, base):
digits = '0123456789ABCDEF'
rem_stack = Stack()
while dec_number>0:
rem = dec_number%base
rem_stack.push(rem)
dec_number = dec_number//base
new_string = ''
while not rem_stack.is_empty():
new_string = new_string + digits[rem_stack.pop()]
return new_string
print(base_converter(25, 8))
print(base_converter(30, 16))31
1E
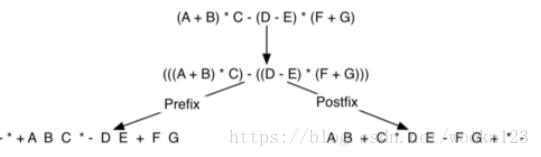
Infix, Prefix, Postfix相互转换
1、转换的作用:
Something very important has hap- pened. Where did the parentheses go? Why don’t we need them in prefix and postfix? The answer is that the operators are no longer ambiguous with respect to the operands that they work on. Only infix notation requires the additional symbols. The order of operations within prefix and postfix expressions is completely determined by the position of the operator and nothing else. In many ways, this makes infix the least desirable notation to use.
2、转换结果:
简单来说,这一切都跟运算符的先后顺序有关。乘除法的优先率要高于加减法,如果要改变这种定律,只能加括号。而perfix和postfix的表示方法给了一种用加括号的方式来改变这种运算顺序。
Prefix:将运算符置于运算数之前,如
+AB表示A+B;
+A*BC表示A+B*C;
若要表示(?+?)*?,只需写*+ABC(先执行+AB,后执行*(+AB)C)
3、转换方法(postfix):
- 创建一个stack来储存运算符,创建一个list来做输出
- 将infix表达式转换为list from string
- 从左往右遍历2中的list,假设每一遍历的元素为token:
- 如果token是运算数,直接输出
- 如果token是左括号
(,push到stack里 - 如果token是右括号
),将stack里的元素逐个pop出来并输出直到遇到对应的左括号( - 如果token是运算符,push到stack里。然而,在push之前,首先按顺序pop出stack里比该运算符优先级相同或者更高的运算符,并输出。
def infix_to_postfix(infix_expr):
# 建立一个字典用来表示运算符的优先级:其中左括号的优先级最低
prec = {}
prec["*"] =3
prec["/"] =3
prec["+"] =2
prec["-"] =2
prec["("] =1
op_stack = Stack()
postfix_list=[] # output
token_list = infix_expr.split()
for token in token_list:
# 如果token是运算数,直接输出
if token in "ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ" or token in "0123456789":
postfix_list.append(token)
# 如果token是左括号(,push到stack里
elif token == '(':
op_stack.push(token)
# 如果token是右括号),将stack里的元素逐个pop出来并输出直到遇到对应的左括号(
elif token == ')':
top_token = op_stack.pop()
while top_token != '(':
postfix_list.append(top_token)
top_token = op_stack.pop()
else:
# 如果token是运算符,push到stack里。然而,在push之前,首先按顺序pop出stack里比该运算符优先级相同或者更高的运算符,并输出。
while (not op_stack.is_empty()) and (prec[op_stack.peek()]>=prec[token]):
postfix_list.append(op_stack.pop())
op_stack.push(token)
while not op_stack.is_empty():
postfix_list.append(op_stack.pop())
# str.join() 方法用于将序列中的元素以指定的字符连接生成一个新的字符串
return ' '.join(postfix_list)
print(infix_to_postfix("A * B + C * D"))
print(infix_to_postfix("( A + B ) * C - ( D - E ) * ( F + G )"))A B * C D * +
A B + C * D E - F G + * -
Postfix使用
当转换成postfix格式后,使用确实是一个问题,但下图已经很好的诠释了这一过程。 
- 创建一个stack用来储存运算数
- 将string转换成list
- 从左往右遍历上述list,for evevy token in list:
- 如果token是一个运算数,将其转换为interger并push到stack中
- 如果token是一个运算符,它需要两个运算数来进行计算。pop两次,第一次pop的数在左,第二次pop的数在右,并用该运算符进行计算,将计算后的值push到stack里
- 当list中的值处理完毕,最后的结果在stack中
def postfix_eval(postfix_expr):
operand_stack = Stack()
token_list = postfix_expr.split()
for token in token_list:
if token in "0123456789":
operand_stack.push(int(token))
else:
operand2 = operand_stack.pop()
operand1 = operand_stack.pop()
result = do_math(token, operand1, operand2)
operand_stack.push(result)
return operand_stack.pop()
def do_math(op, op1, op2):
if op == "*":
return op1 * op2
elif op == "/":
return op1 / op2
elif op == "+":
return op1 + op2
else:
return op1 - op2
print(postfix_eval('7 8 + 3 2 + /'))Python数据结构应用1——Stack的更多相关文章
- [Python数据结构] 使用List实现Stack
[Python数据结构] 使用List实现Stack 1. Stack 堆栈(Stack)又称为栈或堆叠,是计算机科学中一种特殊的串列形式的抽象数据类型(ADT),其特殊之处在于只能允许在阵列的一端进 ...
- python数据结构之栈与队列
python数据结构之栈与队列 用list实现堆栈stack 堆栈:后进先出 如何进?用append 如何出?用pop() >>> >>> stack = [3, ...
- Python - 数据结构 - 第十五天
Python 数据结构 本章节我们主要结合前面所学的知识点来介绍Python数据结构. 列表 Python中列表是可变的,这是它区别于字符串和元组的最重要的特点,一句话概括即:列表可以修改,而字符串和 ...
- Python数据结构汇总
Python数据结构汇总 作者:尹正杰 版权声明:原创作品,谢绝转载!否则将追究法律责任. 一.线性数据结构 1>.列表(List) 在内存空间中是连续地址,查询速度快,修改也快,但不利于频繁新 ...
- python数据结构之二叉树的统计与转换实例
python数据结构之二叉树的统计与转换实例 这篇文章主要介绍了python数据结构之二叉树的统计与转换实例,例如统计二叉树的叶子.分支节点,以及二叉树的左右两树互换等,需要的朋友可以参考下 一.获取 ...
- Python数据结构与算法之图的广度优先与深度优先搜索算法示例
本文实例讲述了Python数据结构与算法之图的广度优先与深度优先搜索算法.分享给大家供大家参考,具体如下: 根据维基百科的伪代码实现: 广度优先BFS: 使用队列,集合 标记初始结点已被发现,放入队列 ...
- python数据结构与算法
最近忙着准备各种笔试的东西,主要看什么数据结构啊,算法啦,balahbalah啊,以前一直就没看过这些,就挑了本简单的<啊哈算法>入门,不过里面的数据结构和算法都是用C语言写的,而自己对p ...
- python数据结构与算法——链表
具体的数据结构可以参考下面的这两篇博客: python 数据结构之单链表的实现: http://www.cnblogs.com/yupeng/p/3413763.html python 数据结构之双向 ...
- python数据结构之图的实现
python数据结构之图的实现,官方有一篇文章介绍,http://www.python.org/doc/essays/graphs.html 下面简要的介绍下: 比如有这么一张图: A -> B ...
随机推荐
- JavaScript脚本放在哪里用户体验好
javascript代码写在<head>里面: 由于这时候网页主体(body)还未加载,所以这里适合放一些不是立即执行的自定义函数,立即执行的语句则很可能会出错(视浏览器而定) javas ...
- 修改flume源码,使其HTTPSource具备访问路径功能
目前有一个需求,就是Flume可以作为一个类似于tomcat的服务器,可以通过post请求进行访问,并且路径需要:ip:port/contextPath格式. 经过一些资料获悉,httpSource只 ...
- Day 网络协议介绍 简单通信的实现
比如说实现两个手机之间的通信,需要做的几部: 服务端: 1,买手机 2,插卡 3,开机 4,等电话链接 5,基于建立的链接,收发协议 6,挂电话 7,关机 import socket #买手机 pho ...
- IOS Swift语言开发 tableView的重用以及自cell的自适应高度
http://www.aichengxu.com/iOS/11143168.htm 一.准备数据 (这是一个元组,第一个元素为英雄的名字;第二个元素为英雄头像图片的名字,格式为.PNG,如果为其他的格 ...
- [ SSH框架 ] Struts2框架学习之一
一.Struts2框架的概述 Struts2是一种基于MVC模式的轻量级Web框架,它自问世以来,就受到了广大Web开发者的关注,并广泛应用于各种企业系统的开发中.目前掌握 Struts2框架几乎成为 ...
- YOLO_Online 将深度学习最火的目标检测做成在线服务实战经验分享
YOLO_Online 将深度学习最火的目标检测做成在线服务 第一次接触 YOLO 这个目标检测项目的时候,我就在想,怎么样能够封装一下让普通人也能够体验深度学习最火的目标检测项目,不需要关注技术细节 ...
- python笔记:#008#变量的命名
变量的命名 目标 标识符和关键字 变量的命名规则 0.1 标识符和关键字 1.1 标识符 标示符就是程序员定义的 变量名.函数名 名字 需要有 见名知义 的效果,见下图: 标示符可以由 字母.下划线 ...
- docker学习笔记(一)—— ubuntu16.04下安装docker
docker学习笔记(一)—— ubuntu16.04下安装docker 原创 2018年03月01日 14:53:00 标签: docker / ubuntu 1682 本文开发环境为Ubuntu ...
- Django+xadmin打造在线教育平台(五)
目录 在线教育平台(一) 在线教育平台(二) 在线教育平台(三) 在线教育平台(四) 在线教育平台(五) 在线教育平台(六) 在线教育平台(七) 在线教育平台( ...
- 利用css实现hover动态效果
.font em:hover { font-size: 2em } .font strong:hover { font-weight: normal } .font span:hover { colo ...

