Analysis of Variance ANOVA versus T test 方差分析和T检验
Levels are different groupings within the same independent variable(factor).
Eg. if the independent variable is “eggs” the levels might be Non-Organic, Organic, and Free Range Organic.
Analysis of Variance ANOVA 方差分析
Goal
whether there is a significant difference between/among the levels of the independent variables.
Assumptions
- Independence of observations
- Normality the distributions of the residuals are normal
- Equality (or "homogeneity") of variances —the variance of data in groups should be the same.
Levels are different groupings within the same independent variable(factor).
Eg. if the independent variable is “eggs” the levels might be Non-Organic, Organic, and Free Range Organic.
Eg.
You recruit 9 anxious individuals and randomly assign them to receive CBT, EMDR, M, 3 kinds of treatment for 5 weeks
Treatment is a between-groups factor with 3 levels. It’s called a between-groups factor because patients are assigned to one and only one group.
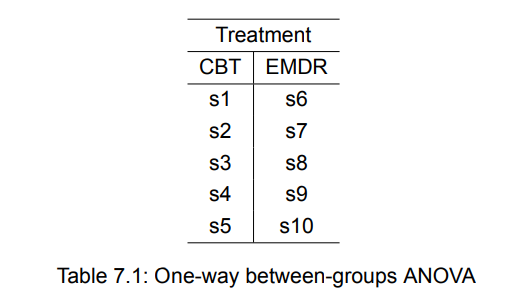
Because there are an equal number of observations in each treatment condition, you have a balanced design. When the sample sizes are unequal across the cells of a design, you have an unbalanced design.
If you are interested in the effect of CBT on anxiety over time, you could place 9 patients in the CBT group and assess them at the end of therapy and again 6 months later.
Time is a within-groups factor with two levels. It’s called a within-groups factor because each patient is measured under both levels.
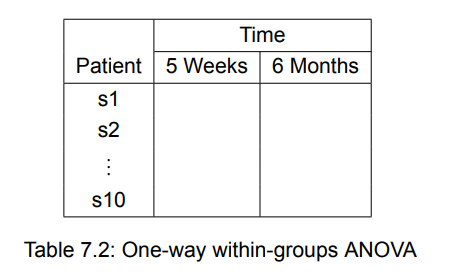
within-groups ANOVA is also called repeated measures ANOVA.
Hypothesis
\(H_0\) : \(\mu_1 = \mu_2\)
One-way ANOVA
\]
\(Y_{ij}\) is the -th observation in the -th out of \(\) groups and \(\) is the overall sample size, \(n_i\) is the sample size of each group
d.f.1= K - 1
d.f.2 = N - K
The F statistic will be large if the between-group variability is large relative to the within-group variability, which means the mean value of each group is not the same.
F large, reject \(H_0\)
Two-way ANOVA
![[Pasted image 20221128143527.png]]
Therapy (averaged across time), Time (averaged across therapy type) are called the main effects, and the interaction of Therapy and Time called interaction effect.
When you cross two or more factors, as you’ve done here, you have a factorial ANOVA design. Crossing two factors produces a two-way ANOVA, crossing three factors produces a three-way ANOVA, and so forth. When a factorial design includes both between-groups and within-groups factors, it’s also called a mixed-model ANOVA. The current design is a two-way mixed-model factorial ANOVA.
In this case you’ll have three F tests: one for Therapy, one for Time, and one for the Therapy_Time interaction.
The above focus on axiety, however, depression and anxiety often co-occur. Because depression could also explain the group differences on the dependent variable, it’s a confounding factor and its value is a covariate. And if you’re not interested in depression, it’s called a nuisance variable. If you are, then the design would be called an analysis of covariance (ANCOVA)
Finally, you’ve recorded a single dependent variable in this study (the STAI ). You could increase the validity of this study by including additional measures of anxiety (such as family ratings, therapist ratings, and a measure assessing the impact of anxiety on their daily functioning). When there’s more than one dependent variable, the design is called a multivariate analysis of variance (MANOVA). If there are covariates present, it’s called a multivariate analysis of covariance (MANCOVA).
Implementation with R
aov()
- usage:
aov(formula, data = dataframe) - symbols-used-for-ANOVA-in-R-formulas
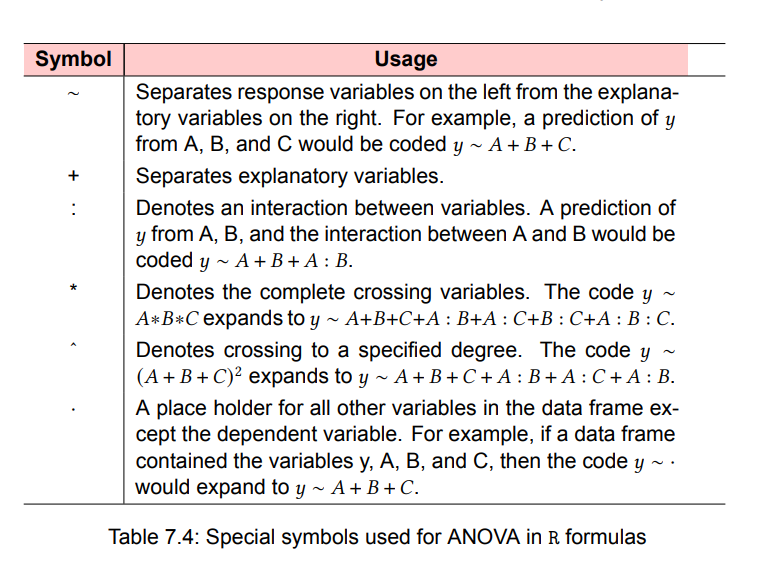
Below are formulas for several common research designs. In this table, lowercase letters are quantitative variables, uppercase letters are grouping factors, and Subject is a unique identifier variable for subjects.

Type I (sequential) Effects are adjusted for those that appear earlier in the formula. is unadjusted. B is adjusted for the . The : interaction is adjusted for and .
Type II (hierarchical) Effects are adjusted for other effects at the same or lower level. is adjusted for . is adjusted for . The : interaction is adjusted for both and .
Type III (marginal) Each effect is adjusted for every other effect in the model. is adjusted for and : . is adjusted for and : . The : interaction is adjusted for and .
R employs the Type I approach by default. Other programs such as SAS and SPSS employ the Type III approach by default.The first model can be written out as ∼ + + : . The resulting R ANOVA table will assess
• The impact of on
• The impact of on , controlling for
• The interaction of and , controlling for the and main effects.
The greater the imbalance in sample sizes, the greater the impact that the order of the terms will have on the results. In general, more fundamental effects should be listed earlier in the formula. In particular, covariates should be listed first, followed by main effects, followed by two-way interactions, followed by three-way interactions, and so on.
Note that the Anova() function in the car package provides the option of using the Type II or Type III approach, rather than the Type I approach used by the aov() function. You may want to use the Anova() function if you’re concerned about matching your results to those provided by other packages such as SAS and SPSS .
T test
Assumptions
- Independence of observations
- Normality:the distributions of the residuals are normal
- Equality (or "homogeneity") of variances —the variance of data in groups should be the same.
Analysis of Variance ANOVA 方差分析 vs T test
formulas
ANOVA: $$F = \frac{MST}{MSE} = \frac{\text{Mean sum of squares due to treatment}}{\text{Mean sum of squares due to error}}$$
t-test: 2groups (通常是两种疗法把样本分成两类)
ANOVA: 2 or more groups (one factor 2/3/4...levels (groups) / many factors)
when 2 group, n < 50 t-test; otherwise ANOVA
Analysis of Variance ANOVA versus T test 方差分析和T检验的更多相关文章
- 方差分析、T检验、卡方分析如何区分?
差异研究的目的在于比较两组数据或多组数据之间的差异,通常包括以下几类分析方法,分别是方差分析.T检验和卡方检验. 三个方法的区别 其实核心的区别在于:数据类型不一样.如果是定类和定类,此时应该使用卡方 ...
- Analysis of variance(ANOVA)
方差分析,也称为"变异数分析",用于两个及两个以上样本均值(group means)差别的显著性检验.在 ANOVA 的环境下,一个观测得到的方差视为是由不同方差的源组合而成.
- Hotelling T2检验和多元方差分析
1.1 Hotelling T2检验 Hotelling T2检验是一种常用多变量检验方法,是单变量检验的自然推广,常用于两组均向量的比较. 设两个含量分析为n,m的样本来自具有公共协方差阵的q维正态 ...
- 使用spss做方差分析
还记得上学那会老师专门敲了黑板,强调方差分析很重要..单因素方差分析(Analysis of Variance, ANOVA),如果变量多,就是多因素方差分析,还需要考虑到多重共线性, 也就是线性代数 ...
- 单因素方差分析(One Way ANOVA)
Analysis of variance (ANOVA) is a collection of statistical models and their associated estimation p ...
- SAS学习笔记26 方差分析
对于多于两组(k>2)样本均数的比较,t检验不再适用,方差分析(analysis of variance, ANOVA)则是解决上述问题的重要分析方法.方差分析由R.A.Fisher(1923) ...
- 方差分析(python代码实现)
python机器学习-乳腺癌细胞挖掘(欢迎关注博主主页,学习python视频资源,还有大量免费python经典文章) https://study.163.com/course/introduction ...
- ANOVA (paper from the onlinestat)
Introduction Author(s) David M. Lane Prerequisites Variance, Significance Testing,All Pairwise Compa ...
- [Reship]如何回复审稿人意见
================================= This article came from here:http://blog.renren.com/GetEntry.do?id= ...
- Multiple Regression
Multiple Regression What is multiple regression? Multiple regression is regression analysis with mor ...
随机推荐
- 07.异常、多线程、Lambda 表达式
一.异常 指的是程序在执行过程中,出现的非正常的情况,最终会导致JVM的非正常停止. 异常体系 根类 java.lang.Throwable 两个直接子类 java.lang.Error 严重错误Er ...
- Spring整合Redis学习笔记
1 Spring-Data-Redis 1.1 Spring-Data-Redis简介 Spring-Data-Redis(简称SDR)对Redis的Key-Value数据存储操作提供了更高层次的 ...
- JavaScript 包装类
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title> ...
- k8s中label和selector的基本概念以及使用方法
概述 在k8s中有一个非常核心的概念,就是label(标签),以及对label的使用,label selector label(标签) 定义: 标签这个概念和现实生活中的标签其实没有什么区别,如, ...
- MYSQL DUAL(伪表)
#DUAL是一个伪表,不存在的表. SELECT 8*9 FROM DUAL #输出72
- js延迟加载、js异步加载
1.js延迟加载 (1)js延迟加载是js性能优化的一种方式 (2)作用:为了提高网页的加载速度 (3)原理:等网页加载完成之后再加载js文件 ··需要优化的原因:HTML元素是按照其在页面中出现的次 ...
- vue element表格合计问题
vue element计算表格合计问题 问题:当表格的el-table-column标签下的属性prop属性值为'对象.属性'时,将不能自动合计.例如: <el-table border v-l ...
- java并发编程实践-线程安全性
线程是CPU资源调度的基本单位,如果一个程序中只有一个线程,则最多只能在一个处理器上运行,如果电脑/服务器是双处理器系统,则单线程的程序只能使用一半的CPU资源,所以,多线程是提高处理器资源利用率的重 ...
- ElementPlus 表单 resetFields 无效问题解决方法
最近在写一个项目,一个表单递交或者使用resetFields关闭后,再打开,原来的值还存在,后查了一下网上的方法,确定是el-form-item,必须要加prop,其值要与model相同,此问题得到完 ...
- Python练习-3.12
1.给文章中的手机号打上马赛克 也就是在文章中发现手机号之后,用*或者#等这一类无法将手机号直接识别出来的符号代替 # 文章中手机号的马赛克形式化 import re content="白日 ...
