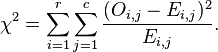spark(1.1) mllib 源码分析(一)-卡方检验
原创文章,转载请注明: 转载自http://www.cnblogs.com/tovin/p/4019131.html
在spark mllib 1.1版本中增加stat包,里面包含了一些统计相关的函数,本文主要分析其中的卡方检验的原理与实现:
一、基本原理
在stat包中实现了皮尔逊卡方检验,它主要包含以下两类
(1)适配度检验(Goodness of Fit test):验证一组观察值的次数分配是否异于理论上的分配。
(2)独立性检验(independence test) :验证从两个变量抽出的配对观察值组是否互相独立(例如:每次都从A国和B国各抽一个人,看他们的反应是否与国籍无关)
计算公式:
其中O表示观测值,E表示期望值
详细原理可以参考:http://zh.wikipedia.org/wiki/%E7%9A%AE%E7%88%BE%E6%A3%AE%E5%8D%A1%E6%96%B9%E6%AA%A2%E5%AE%9A
二、java api调用example
三、源码分析
1、外部api
通过Statistics类提供了4个外部接口
// Goodness of Fit test
def chiSqTest(observed: Vector, expected: Vector): ChiSqTestResult = {
ChiSqTest.chiSquared(observed, expected)
}
//Goodness of Fit test
def chiSqTest(observed: Vector): ChiSqTestResult = ChiSqTest.chiSquared(observed) //independence test
def chiSqTest(observed: Matrix): ChiSqTestResult = ChiSqTest.chiSquaredMatrix(observed)
//independence test
def chiSqTest(data: RDD[LabeledPoint]): Array[ChiSqTestResult] = {
ChiSqTest.chiSquaredFeatures(data)
}
2、Goodness of Fit test实现
这个比较简单,关键是根据(observed-expected)2/expected计算卡方值
/*
* Pearon's goodness of fit test on the input observed and expected counts/relative frequencies.
* Uniform distribution is assumed when `expected` is not passed in.
*/
def chiSquared(observed: Vector,
expected: Vector = Vectors.dense(Array[Double]()),
methodName: String = PEARSON.name): ChiSqTestResult = { // Validate input arguments
val method = methodFromString(methodName)
if (expected.size != 0 && observed.size != expected.size) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("observed and expected must be of the same size.")
}
val size = observed.size
if (size > 1000) {
logWarning("Chi-squared approximation may not be accurate due to low expected frequencies "
+ s" as a result of a large number of categories: $size.")
}
val obsArr = observed.toArray
// 如果expected值没有设置,默认取1.0 / size
val expArr = if (expected.size == 0) Array.tabulate(size)(_ => 1.0 / size) else expected.toArray / 如果expected、observed值都必须要大于1
if (!obsArr.forall(_ >= 0.0)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Negative entries disallowed in the observed vector.")
}
if (expected.size != 0 && ! expArr.forall(_ >= 0.0)) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Negative entries disallowed in the expected vector.")
} // Determine the scaling factor for expected
val obsSum = obsArr.sum
val expSum = if (expected.size == 0.0) 1.0 else expArr.sum
val scale = if (math.abs(obsSum - expSum) < 1e-7) 1.0 else obsSum / expSum // compute chi-squared statistic
val statistic = obsArr.zip(expArr).foldLeft(0.0) { case (stat, (obs, exp)) =>
if (exp == 0.0) {
if (obs == 0.0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Chi-squared statistic undefined for input vectors due"
+ " to 0.0 values in both observed and expected.")
} else {
return new ChiSqTestResult(0.0, size - 1, Double.PositiveInfinity, PEARSON.name,
NullHypothesis.goodnessOfFit.toString)
}
}
// 计算(observed-expected)2/expected
if (scale == 1.0) {
stat + method.chiSqFunc(obs, exp)
} else {
stat + method.chiSqFunc(obs, exp * scale)
}
}
val df = size - 1
val pValue = chiSquareComplemented(df, statistic)
new ChiSqTestResult(pValue, df, statistic, PEARSON.name, NullHypothesis.goodnessOfFit.toString)
}
3、independence test实现
先通过下面的公式计算expected值,矩阵共有 r 行 c 列
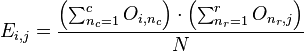
然后根据(observed-expected)2/expected计算卡方值
/*
* Pearon's independence test on the input contingency matrix.
* TODO: optimize for SparseMatrix when it becomes supported.
*/
def chiSquaredMatrix(counts: Matrix, methodName:String = PEARSON.name): ChiSqTestResult = {
val method = methodFromString(methodName)
val numRows = counts.numRows
val numCols = counts.numCols // get row and column sums
val colSums = new Array[Double](numCols)
val rowSums = new Array[Double](numRows)
val colMajorArr = counts.toArray
var i = 0
while (i < colMajorArr.size) {
val elem = colMajorArr(i)
if (elem < 0.0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Contingency table cannot contain negative entries.")
}
colSums(i / numRows) += elem
rowSums(i % numRows) += elem
i += 1
}
val total = colSums.sum // second pass to collect statistic
var statistic = 0.0
var j = 0
while (j < colMajorArr.size) {
val col = j / numRows
val colSum = colSums(col)
if (colSum == 0.0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Chi-squared statistic undefined for input matrix due to"
+ s"0 sum in column [$col].")
}
val row = j % numRows
val rowSum = rowSums(row)
if (rowSum == 0.0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Chi-squared statistic undefined for input matrix due to"
+ s"0 sum in row [$row].")
}
val expected = colSum * rowSum / total
statistic += method.chiSqFunc(colMajorArr(j), expected)
j += 1
}
val df = (numCols - 1) * (numRows - 1)
val pValue = chiSquareComplemented(df, statistic)
new ChiSqTestResult(pValue, df, statistic, methodName, NullHypothesis.independence.toString)
}
原创文章,转载请注明: 转载自http://www.cnblogs.com/tovin/p/4019131.html
spark(1.1) mllib 源码分析(一)-卡方检验的更多相关文章
- spark(1.1) mllib 源码分析(二)-相关系数
原创文章,转载请注明: 转载自http://www.cnblogs.com/tovin/p/4024733.html 在spark mllib 1.1版本中增加stat包,里面包含了一些统计相关的函数 ...
- spark(1.1) mllib 源码分析(三)-朴素贝叶斯
原创文章,转载请注明: 转载自http://www.cnblogs.com/tovin/p/4042467.html 本文主要以mllib 1.1版本为基础,分析朴素贝叶斯的基本原理与源码 一.基本原 ...
- spark(1.1) mllib 源码分析(三)-决策树
本文主要以mllib 1.1版本为基础,分析决策树的基本原理与源码 一.基本原理 二.源码分析 1.决策树构造 指定决策树训练数据集与策略(Strategy)通过train函数就能得到决策树模型Dec ...
- spark的存储系统--BlockManager源码分析
spark的存储系统--BlockManager源码分析 根据之前的一系列分析,我们对spark作业从创建到调度分发,到执行,最后结果回传driver的过程有了一个大概的了解.但是在分析源码的过程中也 ...
- 【Spark篇】---Spark中资源和任务调度源码分析与资源配置参数应用
一.前述 Spark中资源调度是一个非常核心的模块,尤其对于我们提交参数来说,需要具体到某些配置,所以提交配置的参数于源码一一对应,掌握此节对于Spark在任务执行过程中的资源分配会更上一层楼.由于源 ...
- Spark 1.6.1 源码分析
由于gitbook网速不好,所以复制自https://zx150842.gitbooks.io/spark-1-6-1-source-code/content/,非原创,纯属搬运工,若作者要求,可删除 ...
- Spark Mllib源码分析
1. Param Spark ML使用一个自定义的Map(ParmaMap类型),其实该类内部使用了mutable.Map容器来存储数据. 如下所示其定义: Class ParamMap privat ...
- 《深入理解Spark-核心思想与源码分析》(一)总体规划和第一章环境准备
<深入理解Spark 核心思想与源码分析> 耿嘉安著 本书共计486页,计划每天读书20页,计划25天完成. 2018-12-20 1-20页 凡事豫则立,不豫则废:言前定,则不跲:事 ...
- Spark MLlib - Decision Tree源码分析
http://spark.apache.org/docs/latest/mllib-decision-tree.html 以决策树作为开始,因为简单,而且也比较容易用到,当前的boosting或ran ...
随机推荐
- Eclipse中,快捷键使用总结
(1)Alt+shift+L:new ReadItem().readItems(file);的返回对象是Map<String,String>用这个快捷键有两个效果示例1:输入光标停在new ...
- 【Linux】查询文件中指定字符串的记录
语法 cat 文件 |grep 查询字符串 例如现在有文件file.dat,文件中内容如下: zhangsan Lisi wangwu123 wangwu890 zhangsan28290 现在想从文 ...
- 登录首页时报错:java.lang.IllegalArgumentException (不合法的参数异常)
处理一个老项目,DOWN下项目并配好之后,启动没问题,但是登陆之后首页显示如下: 控制台报错如下: 严重: Servlet.service() for servlet jsp threw except ...
- Python-深入理解元类(metaclass)
1.使用 type 动态创建类(type 是一个类, 用来创建类对象的元类, 所以也可以继承) type("Person", (), {"name": &quo ...
- 匿名类型 使用泛型T linq返回dynamic类型的匿名实体 如何把匿名类型.GetType()返回的对象传进泛型里面 EF实体查询出的数据List<T>转DataTable出现【DataSet 不支持 System.Nullable<>】的问题
[100分]紧急求助:LinQ下使用IQueryable<T>如何将返回类型<T>使用匿名类型 问题描述如下:我有一个方法如下:public IQueryable Dissen ...
- php5 升级 php7 版本遇到的问题处理方法总结
为了能够更好的提升系统的安全性,把原来的进销存系统源码升级,遇到了一些问题在这儿总结一下: 1.mysql引擎在php7中不在支持会导致以下错误 Uncaught Error: Call to a m ...
- Spring技术内幕:Spring AOP的实现原理(三)
生成SingleTon代理对象在getSingleTonInstance方法中完毕,这种方法时ProxyFactoryBean生成AopProxy对象的入口.代理对象会封装对target目标对象的调用 ...
- Spring jar 下载地址
Spring jar 下载地址 http://repo.springsource.org/libs-release-local/org/springframework/spring/
- app store上传图片显示错误:未能创建 屏幕快照
在iTunes Connect中加入一个app后.加入屏幕快照时,依照要求的尺寸上传照片成功,可是在保存的时候提示"未能创建Screenshots for 4-inch iPhone5 an ...
- 点滴积累【C#】---C#实现上传照片到物理路径,并且将地址保存到数据库,
效果: 思路: 首先,获取图片物理地址,然后进行判断将图片保存到文件夹下,再将图片的信息保存到数据库. 数据库: create table image1 ( ID ,) primary key, Im ...