C. Queen Codeforces Round #549 (Div. 2) dfs
1 second
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
You are given a rooted tree with vertices numerated from 11 to nn. A tree is a connected graph without cycles. A rooted tree has a special vertex named root.
Ancestors of the vertex ii are all vertices on the path from the root to the vertex ii, except the vertex ii itself. The parent of the vertex ii is the nearest to the vertex ii ancestor of ii. Each vertex is a child of its parent. In the given tree the parent of the vertex ii is the vertex pipi. For the root, the value pipi is −1−1.
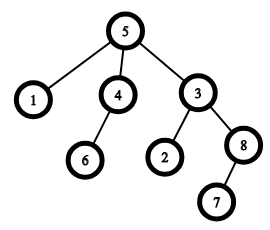 An example of a tree with n=8n=8, the root is vertex 55. The parent of the vertex 22 is vertex 33, the parent of the vertex 11 is vertex 55. The ancestors of the vertex 66 are vertices 44 and 55, the ancestors of the vertex 77 are vertices 88, 33 and 55
An example of a tree with n=8n=8, the root is vertex 55. The parent of the vertex 22 is vertex 33, the parent of the vertex 11 is vertex 55. The ancestors of the vertex 66 are vertices 44 and 55, the ancestors of the vertex 77 are vertices 88, 33 and 55
You noticed that some vertices do not respect others. In particular, if ci=1ci=1, then the vertex ii does not respect any of its ancestors, and if ci=0ci=0, it respects all of them.
You decided to delete vertices from the tree one by one. On each step you select such a non-root vertex that it does not respect its parent and none of its children respects it. If there are several such vertices, you select the one with the smallest number. When you delete this vertex vv, all children of vv become connected with the parent of vv.
 An example of deletion of the vertex 77.
An example of deletion of the vertex 77.
Once there are no vertices matching the criteria for deletion, you stop the process. Print the order in which you will delete the vertices. Note that this order is unique.
The first line contains a single integer nn (1≤n≤1051≤n≤105) — the number of vertices in the tree.
The next nn lines describe the tree: the ii-th line contains two integers pipi and cici (1≤pi≤n1≤pi≤n, 0≤ci≤10≤ci≤1), where pipi is the parent of the vertex ii, and ci=0ci=0, if the vertex ii respects its parents, and ci=1ci=1, if the vertex ii does not respect any of its parents. The root of the tree has −1−1 instead of the parent index, also, ci=0ci=0 for the root. It is guaranteed that the values pipi define a rooted tree with nn vertices.
In case there is at least one vertex to delete, print the only line containing the indices of the vertices you will delete in the order you delete them. Otherwise print a single integer −1−1.
5
3 1
1 1
-1 0
2 1
3 0
1 2 4
5
-1 0
1 1
1 1
2 0
3 0
-1
8
2 1
-1 0
1 0
1 1
1 1
4 0
5 1
7 0
5
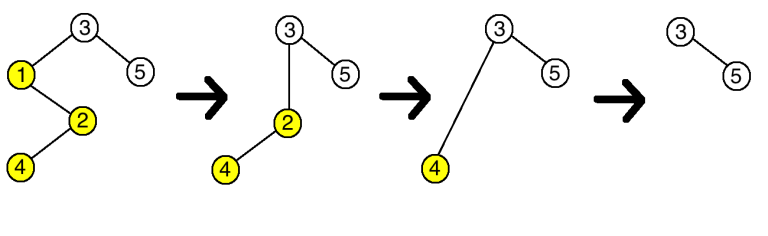
The deletion process in the first example is as follows (see the picture below, the vertices with ci=1ci=1 are in yellow):
- first you will delete the vertex 11, because it does not respect ancestors and all its children (the vertex 22) do not respect it, and 11 is the smallest index among such vertices;
- the vertex 22 will be connected with the vertex 33 after deletion;
- then you will delete the vertex 22, because it does not respect ancestors and all its children (the only vertex 44) do not respect it;
- the vertex 44 will be connected with the vertex 33;
- then you will delete the vertex 44, because it does not respect ancestors and all its children (there are none) do not respect it (vacuous truth);
- you will just delete the vertex 44;
- there are no more vertices to delete.
In the second example you don't need to delete any vertex:
- vertices 22 and 33 have children that respect them;
- vertices 44 and 55 respect ancestors.

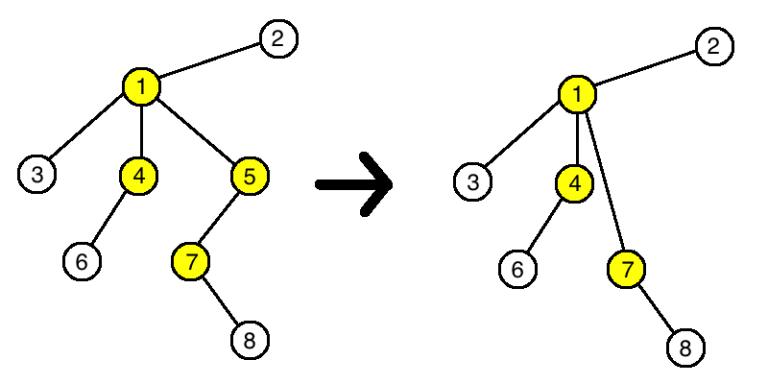
In the third example the tree will change this way:
 这个题目也比较简单,就是一个dfs,我发现一般的图都可以用dfs解决,这个题目看起来还比较可怕,实际很简单啦。看代码吧。
这个题目也比较简单,就是一个dfs,我发现一般的图都可以用dfs解决,这个题目看起来还比较可怕,实际很简单啦。看代码吧。
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#define inf 0x3f3f3f3f
using namespace std;
typedef long long ll;
const int maxn = 1e5 + 100;
struct node
{
int to, dist;
node(int to=0,int dist=0):to(to),dist(dist){}
};
vector<node>vec[maxn];
int cnt=0,a[maxn]; int dfs(int s,int d)
{
int flag = 1;
int len = vec[s].size();
// if (len == 0 && d) return 1;
// if (len == 0 && !d) return 0;
for(int i=0;i<len;i++)
{
if (dfs(vec[s][i].to, vec[s][i].dist) == 0) flag = 0;
}
if (d)
{
//printf("%d %d %d\n",cnt, s, d);
if(flag) a[cnt++] = s;
return 1;
}
return 0;
} int main()
{
int n;
cin >> n;
int root = 0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
int b, x;
cin >> b >> x;
if (b == -1) root = i;
else
{
vec[b].push_back(node(i, x));
}
}
cnt = 0;
int ans=dfs(root,0);
// printf("cnt=%d\n", cnt);
sort(a, a+cnt);
if(cnt==0)
{
printf("-1\n");
return 0;
}
for(int i=0;i<cnt-1;i++)
{
printf("%d ", a[i]);
}
printf("%d\n", a[cnt - 1]);
return 0;
}
C. Queen Codeforces Round #549 (Div. 2) dfs的更多相关文章
- C. Queen Codeforces Round #549 (Div. 2) (搜索)
---恢复内容开始--- You are given a rooted tree with vertices numerated from 11 to nn . A tree is a connect ...
- [题解] Codeforces Round #549 (Div. 2) B. Nirvana
Codeforces Round #549 (Div. 2) B. Nirvana [题目描述] B. Nirvana time limit per test1 second memory limit ...
- Codeforces Round #549 (Div. 1)
今天试图用typora写题解 真开心 参考 你会发现有很多都是参考的..zblzbl Codeforces Round #549 (Div. 1) 最近脑子不行啦 需要cf来缓解一下 A. The B ...
- Codeforces Round #549 (Div. 2)C. Queen
C. Queen time limit per test 1 second memory limit per test 256 megabytes input standard input outpu ...
- B. Nirvana Codeforces Round #549 (Div. 2) (递归dfs)
---恢复内容开始--- Kurt reaches nirvana when he finds the product of all the digits of some positive integ ...
- Codeforces Round #549 (Div. 2) 训练实录 (5/6)
The Doors +0 找出输入的01数列里,0或者1先出完的的下标. Nirvana +3 输入n,求1到n的数字,哪个数逐位相乘的积最大,输出最大积. 思路是按位比较,从低到高,依次把小位换成全 ...
- Codeforces Round #549 (Div. 2) Solution
传送门 A.The Doors 看懂题目就会写的题 给一个 $01$ 序列,找到最早的位置使得 $0$ 或 $1$ 已经全部出现 #include<iostream> #include&l ...
- CodeForces Round #549 Div.2
A. The Doors 代码: #include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; ; int N; , One = ; int a[maxn], ...
- [ Codeforces Round #549 (Div. 2)][D. The Beatles][exgcd]
https://codeforces.com/contest/1143/problem/D D. The Beatles time limit per test 1 second memory lim ...
随机推荐
- MyBatis学习笔记(二) Executor
一.概述 当我们打开一个SqlSession的时候,我们就完成了操作数据库的第一步,那MyBatis是如何执行Sql的呢?其实MyBatis的增删改查都是通过Executor执行的,Executor和 ...
- Laravel篇二之本地版本库关联github
以往的工作中都是使用svn作为版本控制,对git分布式的有些陌生,本篇主要记录的本地存储myWeb-laravel的git版本库与github建立关联. 1.首先进入本地myWeb-laravel,执 ...
- Elasticsearch alias别名管理小结
Elasticsearch alias别名管理小结 By:授客 QQ:1033553122 建创测试数据 1 创建别名 2 移除别名 3 创建测试数据 4 批量操作 5 例1. 5 例2. 把多个索引 ...
- Python 对服务器返回数据编码进行判断之chardet
对服务器返回数据编码进行判断之chardet by:授客 QQ:1033553122 测试环境 Win764Bit chardet-2.3.0 下载地址1:https://pypi.pytho ...
- Android为TV端助力 布局、绘制、内存泄露、响应速度、listview和bitmap、线程优化以及一些优化的建议!
1.布局优化 首先删除布局中无用的控件和层级,其次有选择地使用性能较低的viewgroup,比如布局中既可以使用RelativeLayout和LinearLayout,那我们就采用LinearLayo ...
- mongodb数据分组按字符串split
db.getCollection('users').aggregate([ {$match:{ZWBH:11}}, {$unwind:'$UUID'}, {$project : { PM : { $s ...
- 算法:输入一个链表,输出该链表中倒数第k个结点。
算法:输入一个链表,输出该链表中倒数第k个结点.<剑指offer> 思路加到注释里面了: 1:两个if判断是否返回值为空,首个为空,没有第k个值: 2:for循环找到倒数第k个值,返回为a ...
- 章节四、1-if条件语句
package introduction5; public class ConditionalStatement { public static void main(String[] args) { ...
- 记CSS格式化上下文
fomatting context 引言 主要讲解的是BFC上下文 本文是查看 史上最全面.最透彻的BFC原理剖析 的笔记 所以不会详解BFC, 只是记录学习心得, 以及重要规则避免原文失效 简介 F ...
- webpack项目轻松混用css module
前言 本文讲述css-loader开启css模块功能之后,如何与引用的npm包中样式文件不产生冲突. 比如antd-mobilenpm包的引入.在不做特殊处理的前提下,样式文件将会被转译成css mo ...
