Solution -「POI 2013」LAB-Maze
\(\mathscr{Description}\)
Link.
构造一个边平行与坐标轴, 顶点是整点, 相邻边互相垂直, 且逆时针遍历顶点时转向 (向左或向右) 符合给定字符串的不自交多边形.
顶点数 \(n\le10^5\).
\(\mathscr{Solution}\)
设 \(L\) 为左转数, \(R\) 为右转数, 显然, 有解的必要条件是 \(L-R=4\), 不然不可能逆时针转回起点.
接下来, 注意到相邻的一对 LR 或者 RL 一定体现为一个 "Z" 字形, 并不影响边的走向. 因此, 可以尝试通过不断去除这样的字符对来递归构造多边形.
研究递归的过程. 递归尽头一定是 LLLL, 此时我们新建一个矩形. 在回溯过程中, 我们要做的工作就是在一条直线中插入一个 "Z", 并合理调整坐标关系. 如图:
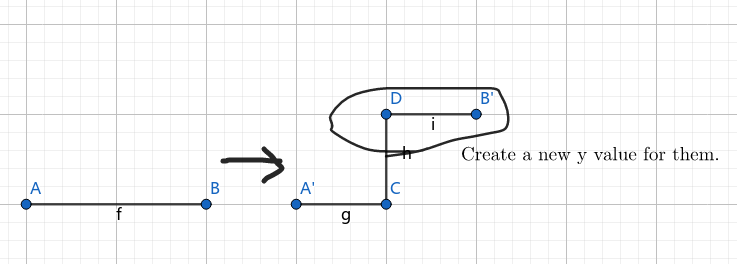
说着很简单, 怎么实现呢?
对于 LR 对的寻找, 可以用双向连边维护字符串上剩余字符的相邻关系, 然后把所有可能的 LR 和 RL 丢到队列里. 删掉 LR 之后再顺便检查一下新挨在一起的字符是否是 LR 或 RL.
对于 "合理调整坐标关系", 最好的安排方式自然是把 "Z" 的一竖变得 "很短很短", 短到不可能碰到任何其他边. 当然, 因为坐标需要是整数, 这不太可能. 不过, 我们在构造过程中并不关心一个点的具体坐标, 因而, 可以用两个双向链表维护 \(x\) 轴和 \(y\) 轴, 每个点的坐标仅仅用指向链表中元素的两个指针描述. 插入坐标通过链表插入 \(\mathcal O(1)\) 实现, 由于共用一个坐标的点一定只有两个, 所以也很容易将一个坐标 "分裂" 成两个相近坐标.
当然, 如果真的要写链表, 就需要精细地去记录当前直线的走向, 否则难以通过迭代器的关系判断左右上下. 一个懒人方法是用 Splay 维护坐标轴, 原理一样, 不过就可以直接用 rank 来描述两个坐标的相对关系啦. 取决于实现方式, 复杂度为 \(\mathcal O(n)\) 或者 \(\mathcal O(n\log n)\).
\(\mathscr{Code}\)
/*+Rainybunny+*/
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define rep(i, l, r) for (int i = l, rep##i = r; i <= rep##i; ++i)
#define per(i, r, l) for (int i = r, per##i = l; i >= per##i; --i)
const int MAXN = 1e5;
int n, pre[MAXN + 5], suf[MAXN + 5], xid[MAXN + 5], yid[MAXN + 5];
char tur[MAXN + 5];
bool vis[MAXN + 5];
std::queue<int> gap;
struct Splay {
static const int MAXND = 3e5;
int node, root, ch[MAXND][2], siz[MAXND], fa[MAXND], lab[MAXND];
Splay() {
newnd(), newnd(), root = fa[ch[1][1] = 2] = 1, siz[1] = 2;
}
inline int newnd() {
return siz[++node] = 1, node;
}
inline void pushup(const int u) {
siz[u] = siz[ch[u][0]] + siz[ch[u][1]] + 1;
}
inline void rotate(const int u) {
int v = fa[u], w = fa[v], k = ch[v][1] == u;
if ((fa[u] = w)) ch[w][ch[w][1] == v] = u;
if ((ch[v][k] = ch[u][!k])) fa[ch[v][k]] = v;
pushup(ch[fa[v] = u][!k] = v), pushup(u);
}
inline void splay(const int u, const int tar) {
for (int v, w; (v = fa[u]) != tar; rotate(u)) {
if ((w = fa[v]) != tar) {
rotate((v == ch[w][0]) == (u == ch[v][0]) ? v : u);
}
}
if (!tar) root = u;
}
inline int rank(const int u) {
splay(u, 0);
return siz[ch[u][0]] + 1;
}
inline int kth(int k) {
int u = root;
while (true) {
if (k <= siz[ch[u][0]]) u = ch[u][0];
else if (!(k -= siz[ch[u][0]] + 1)) return u;
else u = ch[u][1];
}
}
/** insert a node s.t. the rank of it is @p rk */
inline int insertAs(const int rk) {
assert(1 < rk && rk <= siz[root]);
int u = kth(rk - 1), v = kth(rk);
splay(u, 0), splay(v, u), assert(!ch[v][0]);
fa[ch[v][0] = newnd()] = v, pushup(v), pushup(u);
return ch[v][0];
}
inline void relable(const int u) {
if (!u) return ;
relable(ch[u][0]), lab[u] = ++lab[0], relable(ch[u][1]);
}
} X, Y;
inline void solve() {
if (gap.empty()) {
std::vector<int> rest;
rep (i, 0, n - 1) if (!vis[i]) rest.push_back(i);
assert(rest.size() == 4); // As a rectangle.
X.insertAs(2), X.insertAs(3);
Y.insertAs(2), Y.insertAs(3);
rep (i, 0, 3) {
xid[rest[i]] = !i || i == 3 ? 3 : 4;
yid[rest[i]] = i < 2 ? 3 : 4;
}
// printf("%d %d %d %d\n", rest[0], rest[1], rest[2], rest[3]);
return ;
}
int p = gap.front(), q = suf[p], s = pre[p], t = suf[q];
gap.pop();
if (vis[p] || vis[q] || tur[p] == tur[q]) return solve();
vis[p] = vis[q] = true, suf[s] = suf[q], pre[t] = pre[p];
assert(!vis[s] && !vis[t]);
if (tur[s] != tur[t]) gap.push(s);
solve();
// printf("%d --> %d - %d <-- %d\n", s, p, q, t);
if (yid[s] == yid[t]) {
int sxr = X.rank(xid[s]), txr = X.rank(xid[t]);
xid[p] = xid[q] = X.insertAs(std::min(sxr, txr) + 1);
yid[p] = yid[s];
if ((tur[p] == 'L') == (sxr < txr)) {
yid[q] = yid[t] = Y.insertAs(Y.rank(yid[p]) + 1);
} else {
yid[q] = yid[t] = Y.insertAs(Y.rank(yid[p]));
}
} else {
int syr = Y.rank(yid[s]), tyr = Y.rank(yid[t]);
yid[p] = yid[q] = Y.insertAs(std::min(syr, tyr) + 1);
xid[p] = xid[s];
if ((tur[p] == 'R') == (syr < tyr)) {
xid[q] = xid[t] = X.insertAs(X.rank(xid[p]) + 1);
} else {
xid[q] = xid[t] = X.insertAs(X.rank(xid[p]));
}
}
}
int main() {
// freopen("test.in", "r", stdin);
// freopen("test.out", "w", stdout);
scanf("%s", tur), n = strlen(tur);
std::replace(tur, tur + n, 'P', 'R'); // No Polish :(
int dlt = 0;
rep (i, 0, n - 1) dlt += tur[i] == 'L' ? 1 : -1;
if (dlt != 4) return puts("NIE"), 0;
rep (i, 0, n - 1) {
pre[i] = (i + n - 1) % n, suf[i] = (i + 1) % n;
if (tur[i] != tur[(i + 1) % n]) gap.push(i);
}
solve();
X.relable(X.root), Y.relable(Y.root);
rep (i, 0, n - 1) printf("%d %d\n", X.lab[xid[i]], Y.lab[yid[i]]);
return 0;
}
顺便, 给出自己码的一个 SPJ.
/*+Rainybunny+*/
#include "testlib.h"
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define MSG_OK \
"Congratulations~"
#define MSG_SOLUTION_EXISTS \
"You don't find a solution, but jury does."
#define MSG_NOT_PARALLEL \
"An edge isn't parallel to x-axis or y-axis (%d-th edge, 0-indexed)."
#define MSG_POINT_COINCIDE \
"Two nodes coincide in your solution."
#define MSG_NOT_VERTICAL \
"Two neighboring edges aren't vertical in your solution (%d-th edge and " \
"%d-th edges, 0-indexed)."
#define MSG_OUTSIDE_WALK \
"You're walking outside of your polygon."
#define MSG_WRONG_TURNING \
"A turning direction doesn't meet the requirement."
#define MSG_SELF_INTER \
"The polygon is self-intersecting in your solution."
#define rep(i, l, r) for (int i = l, rep##i = r; i <= rep##i; ++i)
#define per(i, r, l) for (int i = r, per##i = l; i >= per##i; --i)
typedef long long LL;
typedef std::pair<int, int> PII;
#define fi first
#define se second
const int MAXN = 1e5;
int n;
std::string tur;
struct Point {
int x, y;
inline Point operator - (const Point& u) const {
return { x - u.x, y - u.y };
}
inline LL operator * (const Point& u) const {
return 1ll * x * u.x + 1ll * y * u.y;
}
inline LL operator ^ (const Point& u) const {
return 1ll * x * u.y - 1ll * y * u.x;
}
inline bool operator < (const Point& u) const {
return x == u.x ? y < u.y : x < u.x;
}
};
Point pnt[MAXN + 5];
inline void initCheck() {
tur = inf.readToken(), n = int(tur.size());
std::rotate(tur.begin(), tur.end() - 1, tur.end());
std::string your = ouf.readToken(), jury = ans.readToken();
if (your == "NIE" && jury != "NIE") quitf(_wa, MSG_SOLUTION_EXISTS);
else if (your == "NIE") quitf(_ok, MSG_OK);
std::reverse(your.begin(), your.end());
for (char c: your) ouf.unreadChar(c);
rep (i, 0, n - 1) {
pnt[i].x = ouf.readInt(-1e9, 1e9);
pnt[i].y = ouf.readInt(-1e9, 1e9);
// fprintf(stderr, "? %d %d\n", pnt[i].x, pnt[i].y);
}
}
int fail[MAXN + 5];
std::string act;
std::set<Point> apr;
inline void turningCheck() {
rep (i, 0, n - 1) {
if ((pnt[i].x != pnt[(i + 1) % n].x)
&& (pnt[i].y != pnt[(i + 1) % n].y)) quitf(_wa, MSG_NOT_PARALLEL, i);
if (apr.count(pnt[i])) quitf(_wa, MSG_POINT_COINCIDE);
apr.insert(pnt[i]);
Point p(pnt[i] - pnt[(i + n - 1) % n]), q(pnt[(i + 1) % n] - pnt[i]);
// fprintf(stderr, "(%d,%d) -> (%d,%d)\n", p.x, p.y, q.x, q.y);
if (p * q) quitf(_wa, MSG_NOT_VERTICAL, (i + n - 1) % n, i);
act += (p ^ q) > 0 ? 'L' : 'P';
}
int dlt = 0;
for (int c: act) dlt += c == 'L' ? 1 : -1;
if (dlt == -4) {
// In this case, the answer should be "NIE", but the checker won't
// refuse to check your answer, knowing you must be wrong before.
quitf(_wa, MSG_OUTSIDE_WALK);
}
// std::cerr << "Your turning token: " << act << '\n';
fail[0] = -1;
for (int i = 1, j = -1; i < n; ++i) {
while (~j && tur[j + 1] != tur[i]) j = fail[j];
fail[i] = j += tur[j + 1] == tur[i];
}
for (int i = 0, j = -1; i < 2 * n; ++i) {
while (~j && tur[j + 1] != act[i % n]) j = fail[j];
if ((j += tur[j + 1] == act[i % n]) == n - 1) return ;
}
quitf(_wa, MSG_WRONG_TURNING);
}
int mx, dc[MAXN + 5];
std::vector<PII> evt[MAXN + 5], req[MAXN + 5];
std::set<int> cut;
inline void selfInterCheck() {
rep (i, 0, n - 1) dc[++mx] = pnt[i].x;
std::sort(dc + 1, dc + mx + 1);
mx = std::unique(dc + 1, dc + mx + 1) - dc - 1;
rep (i, 0, n - 1) {
pnt[i].x = std::lower_bound(dc + 1, dc + mx + 1, pnt[i].x) - dc;
}
rep (i, 0, n - 1) {
if (pnt[i].x == pnt[(i + 1) % n].x) {
int ya = pnt[i].y, yb = pnt[(i + 1) % n].y;
if (ya > yb) std::swap(ya, yb);
req[pnt[i].x].emplace_back(ya, yb);
} else {
int xa = pnt[i].x, xb = pnt[(i + 1) % n].x;
if (xa > xb) std::swap(xa, xb);
evt[xa].emplace_back(pnt[i].y, 1);
evt[xb].emplace_back(pnt[i].y, 0);
}
}
rep (i, 1, mx) {
for (const PII& p: evt[i]) if (!p.se) cut.erase(p.fi);
for (const PII& p: req[i]) {
auto&& it = cut.upper_bound(p.se);
if (it != cut.begin() && *--it >= p.fi) quitf(_wa, MSG_SELF_INTER);
}
for (const PII& p: evt[i]) if (p.se) {
if (cut.count(p.fi)) quitf(_wa, MSG_SELF_INTER);
cut.insert(p.fi);
}
for (const PII& p: evt[i]) if (!p.se) cut.insert(p.fi);
for (const PII& p: req[i]) if (p.fi + 2 <= p.se) {
auto&& it = cut.upper_bound(p.se - 1);
if (it != cut.begin() && *--it > p.fi) quitf(_wa, MSG_SELF_INTER);
}
for (const PII& p: evt[i]) if (!p.se) cut.erase(p.fi);
}
}
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
registerTestlibCmd(argc, argv);
initCheck();
turningCheck();
selfInterCheck();
quitf(_ok, MSG_OK);
return 0;
}
Solution -「POI 2013」LAB-Maze的更多相关文章
- Solution -「ZJOI 2013」「洛谷 P3337」防守战线
\(\mathcal{Description}\) Link. 有 \(n\) 个位置,从左至右编号 \(1\sim n\).在第 \(i\) 个位置放一座塔的代价为 \(c_i\),一个位置 ...
- Solution -「POI 2014」「洛谷 P5904」HOT-Hotels 加强版
\(\mathcal{Description}\) Link. 给定一棵 \(n\) 个点的树,求无序三元组 \((u,v,w)\) 的个数,满足其中任意两点树上距离相等. \(n\le1 ...
- Solution -「POI 2010」「洛谷 P3511」MOS-Bridges
\(\mathcal{Description}\) Link.(洛谷上这翻译真的一言难尽呐. 给定一个 \(n\) 个点 \(m\) 条边的无向图,一条边 \((u,v,a,b)\) 表示从 ...
- Solution -「POI 2011」「洛谷 P3527」MET-Meteors
\(\mathcal{Description}\) Link. 给定一个大小为 \(n\) 的环,每个结点有一个所属国家.\(k\) 次事件,每次对 \([l,r]\) 区间上的每个点点权加上 ...
- Solution -「ARC 104E」Random LIS
\(\mathcal{Description}\) Link. 给定整数序列 \(\{a_n\}\),对于整数序列 \(\{b_n\}\),\(b_i\) 在 \([1,a_i]\) 中等概率 ...
- Solution -「CTS 2019」「洛谷 P5404」氪金手游
\(\mathcal{Description}\) Link. 有 \(n\) 张卡牌,第 \(i\) 张的权值 \(w_i\in\{1,2,3\}\),且取值为 \(k\) 的概率正比于 \ ...
- Solution -「BZOJ 3812」主旋律
\(\mathcal{Description}\) Link. 给定含 \(n\) 个点 \(m\) 条边的简单有向图 \(G=(V,E)\),求 \(H=(V,E'\subseteq E)\ ...
- Solution -「CF 1342E」Placing Rooks
\(\mathcal{Description}\) Link. 在一个 \(n\times n\) 的国际象棋棋盘上摆 \(n\) 个车,求满足: 所有格子都可以被攻击到. 恰好存在 \(k\ ...
- Solution -「简单 DP」zxy 讲课记实
魔法题位面级乱杀. 「JOISC 2020 Day4」治疗计划 因为是不太聪明的 Joker,我就从头开始理思路了.中途也会说一些和 DP 算法本身有关的杂谈,给自己的冗长题解找借口. 首先,治疗方案 ...
- Solution -「基环树」做题记录
写的大多只是思路,比较简单的细节和证明过程就不放了,有需者自取. 基环树简介 简单说一说基环树吧.由名字扩展可得这是一类以环为基础的树(当然显然它不是树. 通常的表现形式是一棵树再加一条非树边,把图画 ...
随机推荐
- Jmeter并发线程场景下共享变量错乱问题解决
问题复现 问题描述 使用IF控制器获取前一个请求的后置脚本中设置的全局变量->并发线程下通过vars.get获取变量时,第一个线程和第二个线程获取的变量值一样->导致不同基础数据的请求入参 ...
- 开源 - Ideal库 -获取特殊时间扩展方法(四)
书接上回,我们继续来分享一些关于特殊时间获取的常用扩展方法. 01.获取当前日期所在月的第一个指定星期几 该方法和前面介绍的获取当前日期所在周的第一天(周一)核心思想是一样的,只是把求周一改成求周几而 ...
- isPCBroswer:检测是否为PC端浏览器模式
function isPCBroswer() { let e = navigator.userAgent.toLowerCase() , t = "ipad" == e.match ...
- Go中数组和切片
数组和切片 [1].数组 1.什么是数组 一组数 数组需要是相同类型的数据的集合 数组是需要定义大小的 数组一旦定义了大小是不可以改变的. package main import "fmt& ...
- 爱科微AIC8800D80P Wi-Fi6模块驱动移植
1. 简介 开发环境Ubuntu20.04 目标平台:瑞芯微RK356X 目标平台内核版本:4.19.234 wifi模块型号:AIC8800D80P Wi-Fi6/BT5.0 2. 硬件 wifi模 ...
- 抓包工具之Charles(windows)
激活码: https://www.zzzmode.com/mytools/charles/ 官方地址:https://www.charlesproxy.com/ PC端如何配置才能抓取到https请 ...
- TOML 1.0格式语法
github: https://github.com/BurntSushi/toml TOML 旨在成为一个语义显著而易于阅读的最低限度的配置文件格式.TOML 被设计地能够无歧义地转化为哈希表.TO ...
- Django之常见问题
总结Django在使用过程中遇到的一些问题 1.在使用model进行数据查询的时候出现错误: django matching query does not exist. 是使用get函数引起的错误.使 ...
- uView的DatetimePicker组件在confirm回调中取不到v-model的最新值
前情 uni-app是我比较喜欢的跨平台框架,它能开发小程序/H5/APP(安卓/iOS),重要的是对前端开发友好,自带的IDE让开发体验非常棒,公司项目就是主推uni-app,在uniapp生态中u ...
- ArkTs布局入门01——线性布局(Row/Column)
1.概述 布局指用特定的组件或者属性来管理用户页面所放置UI组件的大小和位置.组件按照布局的要求依次排列,构成应用的页面. 在声明式UI中,所有的页面都是由自定义组件构成,开发者可以根据自己的需求,选 ...
