Behavior Trees for Path Planning (Autonomous Driving)
Behavior Trees for Path Planning (Autonomous Driving)
2019-11-13 08:16:52
Path planning in self-driving cars
Path planning and decision making for autonomous vehicles in urban environments enable self-driving cars to find the safest, most convenient, and most economically beneficial routes from point A to point B. Finding routes is complicated by all of the static and maneuverable obstacles that a vehicle must identify and bypass. Today, the major path planning approaches include the predictive control model, feasible model, and behavior-based model. Let’s first get familiar with some terms to understand how these approaches work.
- A path is a continuous sequence of configurations beginning and ending with boundary configurations. These configurations are also referred to as initial and terminating.
- Path planning involves finding a geometric path from an initial configuration to a given configuration so that each configuration and state on the path is feasible (if time is taken into account).
- A maneuver is a high-level characteristic of a vehicle’s motion, encompassing the position and speed of the vehicle on the road. Examples of maneuvers include going straight, changing lanes, turning, and overtaking.
- Maneuver planning aims at taking the best high-level decision for a vehicle while taking into account the path specified by path planning mechanisms.
- A trajectory is a sequence of states visited by the vehicle, parameterized by time and, most probably, velocity.
- Trajectory planning or trajectory generation is the real-time planning of a vehicle’s move from one feasible state to the next, satisfying the car’s kinematic limits based on its dynamics and as constrained by the navigation mode.
This is the general view of self-driving autonomous system integration :


The blocks inside the container are the parts of the path planning procedure;

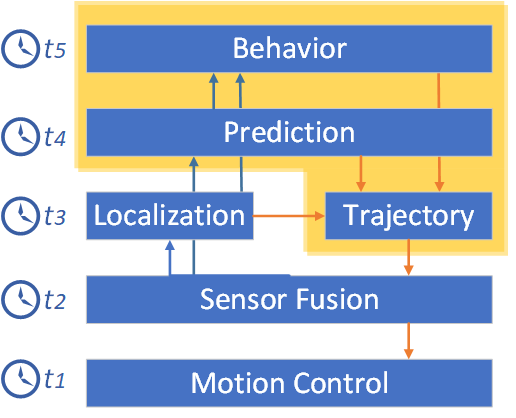
Trajectory generation :
For each efficient target, we compute the corresponding trajectory. We send commands to the controller as a set of waypoints, i.e., discrete points (supposedly closed to one another) spread across the trajectory, often at a fixed interval equal to the controller’s sampling time.


For my project, the trajectory is generated using cubic spline with four points : (Note: This explanation is in Frenet coordinates, we use the variables s and d to describe a vehicle’s position on the road. The s coordinate represents distance along the road (also known as longitudinal displacement) and the d coordinate represents a side-to-side position on the road (also known as lateral displacement). And r is the width of the road (in meters)
- Current position (s, d)
- Desired lane (s+30, r*lane+(r/2))
- Desired lane (s+60, r*lane+(r/2))
- Desired lane (s+90, r*lane+(r/2))
The controller then has to regenerate trajectory segments between two consecutive waypoints, such that manipulator reaches the next waypoint within the fixed time interval while staying within joint limits, velocity limits, and acceleration limits. However, the controller does not really consider even collision avoidance or anything else
Prediction:

We predict situations in over environment in order to get you to the destination safely and efficiently. For this project I had to build collision detection, that predicts a possible collision with two cars.
Behavior:


Behavior planner takes input :
- map of the world,
- route to the destination
- prediction about what static and dynamic obstacles are likely to do
Output: Suggested maneuver for the vehicle which the trajectory planner is responsible for reaching collision-free, smooth and safe behavior.
Behavior Tree
A Behavior Tree (BT) is a mathematical model of plan execution used in computer science, robotics, control systems, and video games. They describe switchings between a finite set of tasks in a modular fashion. Their strength comes from their ability to create very complex tasks composed of simple tasks, without worrying how the simple tasks are implemented. BTs present some similarities to hierarchical state machines with the key difference that the main building block of behavior is a task rather than a state. Its ease of human understanding make BTs less error-prone and very popular in the game developer community. BTs have been shown to generalize several other control architectures.
Pros of using Behavior trees
- Useful when we have so many transitions and states
- Transform hardly-visible state machine into the hierarchical system
- Encapsulate and separate conditional tasks into classes
- Easy automation tests for each task.
- Better when pass/fail of tasks is central
- Reusability
- The appearance of goal-driven behavior
- Multi-step behavior
- Fast
- Recover from errors
Cons of using Behavior trees
- Clunky for state-based behavior
- Changing behavior based on external changes
- Isn’t really thinking ahead about unique situations
- Only as good as the designer makes it (just follows the recipes)
Composite Node
A composite node is a node that can have one or more children. They will process one or more of these children in either a first to last sequence or random order depending on the particular composite node in question, and at some stage will consider their processing complete and pass either success or failure to their parent, often determined by the success or failure of the child nodes. During the time they are processing children, they will continue to return Running to the parent.
Leaf
These are the lowest level node type and are incapable of having any children.
Leaves are however the most powerful of node types, as these will be defined and implemented for your intelligent system to do the actions and behaviors specific or character specific tests or actions required to make your tree actually do useful stuff. A leaf node can be a condition or a Task(Action).
Condition
A condition can return true for success and false otherwise.
Task
The task can return true if it is completed, false, otherwise.
Sequences
The simplest composite node found within behavior trees, their name says it all. A sequence will visit each child in order, starting with the first, and when that succeeds will call the second, and so on down the list of children. If any child fails it will immediately return failure to the parent. If the last child in the sequence succeeds, then the sequence will return success to its parent.
It’s important to make clear that the node types in behavior trees have quite a wide range of applications. The most obvious use of sequences is to define a sequence of tasks that must be completed in entirety, and where the failure of one means further processing of that sequence of tasks becomes redundant.
In the example below is an example of Selector hierarchy, as a part of my behavioral tree used for the path planning project :


Execution: The main goal of this selector is to choose left child (detecting whether we have a car very close before us, and adapt the speed accordingly) or right child (drive normally)
This selector will return true if and only if all children return true according to the ordered steps of execution :
- The car is in second lane (IsCurentLane condition returns true/false)
— (If this block return false, then we stop examining the rest of the blocks in this sequence)
2. It is safe to switch lane (SafeToSwitchLane condition returns true)
— (if this block return false, then we stop examining the rest of the blocks in this sequence)
3. Successfully perform the switch task (SwitchLane task is successfully executed, returns true)
4. Goal achieved
Selector
Where a sequence is an AND, requiring all children to succeed to return success, a selector will return success if any of its children succeed and not process any further children. It will process the first child, and if it fails will process the second, and if that fails will process the third, until success is reached, at which point it will instantly return success. It will fail if all children fail. This means a selector is analogous with an OR gate, and as a conditional statement can be used to check multiple conditions to see if any one of them is true.
In the example below is an example of Sequence hierarchy, as a part of my behavioral tree used for the path planning project :


Execution: The main goal of this selector is to choose left child (detecting whether we have a car very close before us, and adapt the speed accordingly) or right child (drive normally)
This selector will return true only if one of its children returns true, execution is according to the following steps :
Left Child (Sequence): Returns true if there is car close before us and we are able to adapt our speed
- Is there a car close in front of us? (IsCarCloseBeforeUs condition passed)
— (If this block return false, then we stop examining the rest of the blocks in this sequence)
3. Approximate speed
— (If this block return false, then we stop examining the rest of the blocks in this sequence)
4. Drive
— (If Left Child return true, then we stop examining the rest of the blocks in this selector
— — — — — — — — — — -
Right Child (Task)
- Drive normally
Priority Selector
Very simple, It’s the same as a selector but this time they are ordered somehow. If the priority selector is used, child behaviors are ordered in a list and tried one after another.
For this project, I used a priority selector to select and prioritize which of the lanes we should drive/switch. Below there is a picture describing this behavior :

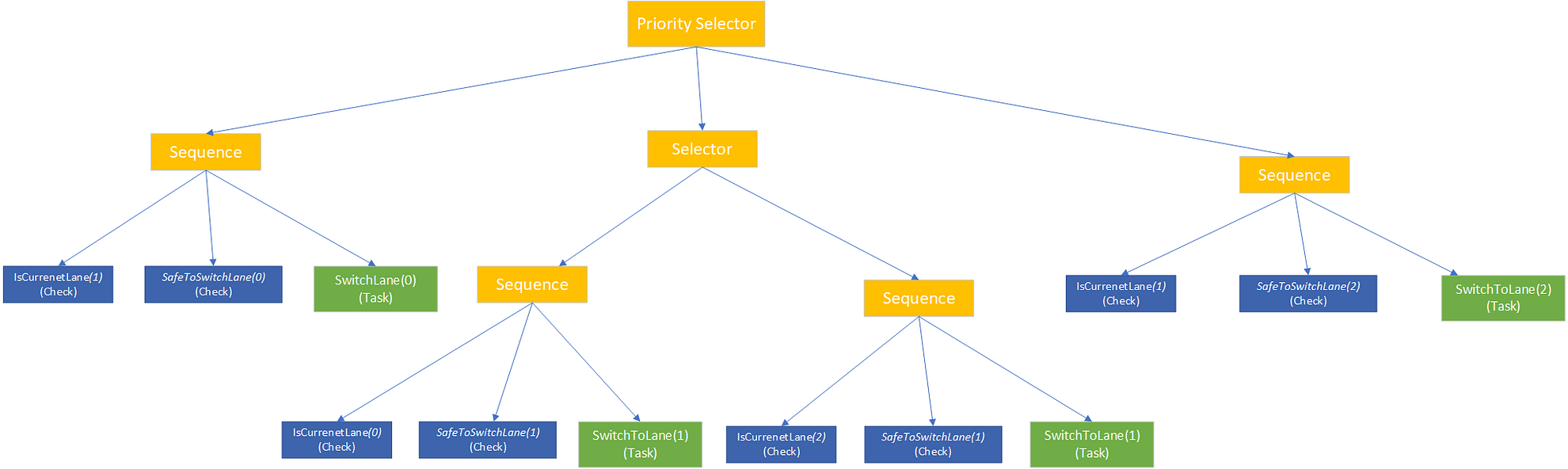
Priority Estimation
For this project I prioritize which of the lanes we should drive or switch based on the following formula :


The Bigger the reward is and smaller the penalty, priority for visiting the lane increases.
Behavior Tree Architecture for Path Planning
Bellow is the complete Path planning behavior tree architecture :


You can see the following video observing the simulation for a few minutes.
You can see my implementation on Github :
Behavior Trees for Path Planning (Autonomous Driving)的更多相关文章
- Autonomous driving - Car detection YOLO
Andrew Ng deeplearning courese-4:Convolutional Neural Network Convolutional Neural Networks: Step by ...
- Design and Implementation of Global Path Planning System for Unmanned Surface Vehicle among Multiple Task Points
Design and Implementation of Global Path Planning System for Unmanned Surface Vehicle among Multiple ...
- Behavior trees for AI: How they work
http://www.gamasutra.com/blogs/ChrisSimpson/20140717/221339/Behavior_trees_for_AI_How_they_work.php ...
- tensorfolw配置过程中遇到的一些问题及其解决过程的记录(配置SqueezeDet: Unified, Small, Low Power Fully Convolutional Neural Networks for Real-Time Object Detection for Autonomous Driving)
今天看到一篇关于检测的论文<SqueezeDet: Unified, Small, Low Power Fully Convolutional Neural Networks for Real- ...
- A*算法改进——Any-Angle Path Planning的Theta*算法与Lazy Theta*算法
本文是该篇文章的归纳http://aigamedev.com/open/tutorial/lazy-theta-star/#Nash:07 . 传统的A*算法中,寻找出来的路径只能是沿着给出的模型(比 ...
- Visual-Based Autonomous Driving Deployment from a Stochastic and Uncertainty-Aware Perspective
张宁 Visual-Based Autonomous Driving Deployment from a Stochastic and Uncertainty-Aware Perspective Le ...
- 泡泡一分钟:BLVD: Building A Large-scale 5D Semantics Benchmark for Autonomous Driving
BLVD: Building A Large-scale 5D Semantics Benchmark for Autonomous Driving BLVD:构建自主驾驶的大规模5D语义基准 Jia ...
- apollo规划控制视频-13 motion planning with autonomous driving
- Behavior Trees
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Behavior_Trees_(artificial_intelligence,_robotics_and_control) http:// ...
随机推荐
- Java 数组实例——将阿拉伯数字转换为最大写
题目:将阿拉伯数字转换为最大写,比如1234转换为壹仟贰佰叁拾肆. package my_package; public class Transform { private String[] arr1 ...
- vavr:让你像写Scala一样写Java
本文阅读时间大约7分钟. Hystrix是Netflix开源的限流.熔断降级组件,去年发现Hystrix已经不再更新了,而在github主页上将我引导到了另一个替代项目--resilience4j,这 ...
- HBase的部署与其它相关组件(Hive和Phoenix)的集成
HBase的部署与其它相关组件(Hive和Phoenix)的集成 一.HBase部署 1.1.Zookeeper正常部署 首先保证Zookeeper集群的正常部署,并启动之: /opt/module/ ...
- 《linux就该这么学》课堂笔记09 存储结构、磁盘划分
Linux一切都是文件 "/"为根目录(万物起始) **挂载后要想永久生效,需要修改开机启动项 vim /etc/fstab
- LNMP搭建后html访问正常php报404错误解决办法
环境:CentOS7.7.3.10.0-1062.el7.x86_64.nginx1.16.1 .php7.3.10 问题:nginx能解析静态文件但是不能解析php动态文件,返回404文件未发现错误 ...
- Python 去除文件中的空行
def clear_space(): with open("test","r",encoding="utf-8") as fr: for l ...
- 解决Mac OS X 系统在home文件夹下面操作不支持的方法
解决Mac OS X 系统在home文件夹下面操作不支持的方法 最近需要使用Mac OS X 系统尝试安装使用appium程序,安装过程中发现,Mac OS X 系统在home文件夹下面操作不支持 ...
- django项目中form表单和ajax的文件上传功能。
form表单文件上传 路由 # from表单上传 path('formupload/',apply.formupload,name='formupload/'), 方法 # form表单文件上传 de ...
- 摘:Selenium api学习
selenium: selenium2(WebDriver) API1.1 下载selenium2.0的包 官方download包地址:http://code.google.com/p/seleniu ...
- jmeter压测学习1-window环境准备与案例
前言 最近用jmeter做一些接口的压力测试,记录下使用过程中遇到的一些问题. 在使用window机器做并发压测的时候,发现并发数设置100的时候,会出现报错:java.net.SocketExcep ...
