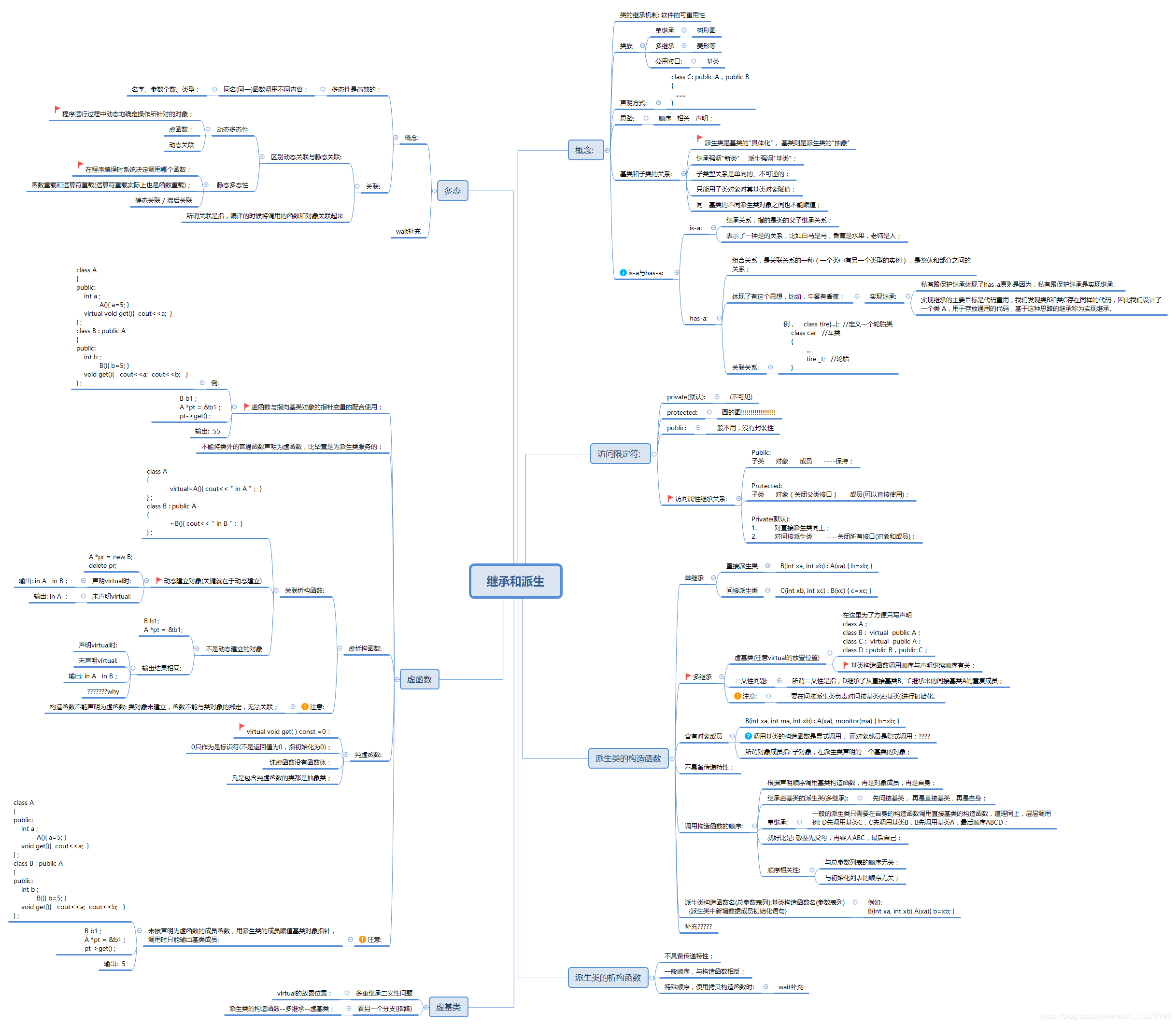
C++—多态与继承
一、基本概念
#include <iostream>
#include <time.h>
using namespace std;
class B1
{
public:
B1(int i)
{
cout<<"constructing B1 "<<i<<endl;
}
};
class B2
{
public:
B2(int j)
{
cout<<"constructing B2 "<<j<<endl;
}
};
class B3
{
public:
B3()
{
cout<<"constructing B3"<<endl;
}
};
class C: public B2, public B1, public B3
{
public:
C(int a, int b, int c, int d):B1(a), memberB2(d), memberB1(c),B2(b)
{
}
private:
B1 memberB1;
B2 memberB2;
B3 memberB3;
};
int main()
{
C obj(1,2,3,4);
return 0;
}
#include <iostream>
#include <time.h>
using namespace std;
class B1
{
public:
B1(int i)
{
cout<<"constructing B1 "<<i<<endl;
}
~B1()
{
cout<<"destructing B1"<<endl;
}
};
class B2
{
public:
B2(int j)
{
cout<<"constructing B2 "<<j<<endl;
}
~B2()
{
cout<<"destructing B2"<<endl;
}
};
class B3
{
public:
B3()
{
cout<<"constructing B3"<<endl;
}
~B3()
{
cout<<"destructing B3"<<endl;
}
};
class C: public B2, public B1, public B3
{
public:
C(int a, int b, int c, int d):B1(a), memberB2(d), memberB1(c),B2(b)
{
}
private:
B1 memberB1;
B2 memberB2;
B3 memberB3;
};
int main()
{
C obj(1,2,3,4);
return 0;
}
#include <iostream>
#include <time.h>
using namespace std;
class B1
{
public:
int nV;
void fun()
{
cout<<"member of B1 "<<nV<<endl;
}
};
class B2
{
public:
int nV;
void fun()
{
cout<<"member of B2 "<<nV<<endl;
}
};
class D1: public B1, public B2
{
public:
int nV;
void fun()
{
cout<<"member of D1 "<<nV<<endl;
}
};
int main()
{
D1 d1;
d1.nV = 1;
d1.fun();
d1.B1::nV = 2;
d1.B1::fun();
d1.B2::nV = 3;
d1.B2::fun();
return 0;
}
#include <iostream>
#include <time.h>
using namespace std;
class B0
{
public:
int nV;
void fun()
{
cout<<"member of B0 "<<nV<<endl;
}
};
class B1:public B0
{
public:
int nV1;
};
class B2:public B0
{
public:
int nV2;
};
class D1:public B1, public B2
{
public:
int nVd;
void fund()
{
cout<<"member of D1"<<endl;
}
};
int main()
{
D1 d1;
d1.B1::nV = 2;
d1.B1::fun();
d1.B2::nV = 3;
d1.B2::fun();
return 0;
}
#include <iostream>
#include <time.h>
using namespace std; class B0
{
public:
int nV;
void fun()
{
cout<<"member of B0 "<<nV<<endl;
}
}; class B1:virtual public B0
{
public:
int nV1;
}; class B2:virtual public B0
{
public:
int nV2;
}; class D1:public B1, public B2
{
public:
int nVd;
void fund()
{
cout<<"member of D1"<<endl;
}
}; int main()
{
D1 d1;
d1.nV = 2;
d1.fun(); return 0;
}
#include <iostream>
#include <time.h>
using namespace std; class B0
{
public:
B0(int n)
{
nV = n;
}
int nV;
void fun()
{
cout<<"member of B0 "<<nV<<endl;
}
}; class B1:virtual public B0
{
public:
B1(int a):B0(a)
{
}
int nV1;
}; class B2:virtual public B0
{
public:
B2(int a):B0(a)
{
}
int nV2;
}; class D1:public B1, public B2
{
public:
D1(int a):B0(a), B1(a), B2(a)
{
}
int nVd;
void fund()
{
cout<<"member of D1"<<endl;
}
}; int main()
{
D1 d1(1);
d1.nV = 2;
d1.fun(); return 0;
}
才是真正的调用了B0构造函数。
#include <iostream>
#include <time.h>
using namespace std; class B0
{
public:
void display()
{
cout<<"B0::display()"<<endl;
}
}; class B1:public B0
{
public:
void display()
{
cout<<"B1::display()"<<endl;
}
}; class B2:public B0
{
public:
void display()
{
cout<<"B2::display()"<<endl;
}
}; void fun(B0 *ptr)
{
ptr->display();
} int main()
{
B0 b0;
B1 b1;
B2 b2;
fun(&b0);
b0 = b1;
fun(&b0);
b0 = b2;
fun(&b0); return 0;
}
输出结果为:
B0::display()
B0::display()
B0::display()
通过这种赋值兼容后,每次调用的同名函数都是基类的同名函数,如果想调用派生类的,则需要使用虚函数。
五、总结
C++—多态与继承的更多相关文章
- 深入理解OOP(四): 多态和继承(抽象类)
在本文中,我们讨论OOP中的热点之一:抽象类.抽象类在各个编程语言中概念是一致的,但是C#稍微有些不一样.本文中我们会通过代码来实现抽象类,并一一进行解析. 深入理解OOP(一):多态和继承(初期绑定 ...
- 深入理解OOP(三):多态和继承(动态绑定和运行时多态)
在前面的文章中,我们介绍了编译期多态.params关键字.实例化.base关键字等.本节我们来关注另外一种多态:运行时多态, 运行时多态也叫迟绑定. 深入理解OOP(一):多态和继承(初期绑定和编译时 ...
- 深入理解OOP(二):多态和继承(继承)
本文是深入浅出OOP第二篇,主要说说继承的话题. 深入理解OOP(一):多态和继承(初期绑定和编译时多态) 深入理解OOP(二):多态和继承(继承) 深入理解OOP(三):多态和继承(动态绑定和运行时 ...
- 深入理解OOP(第一天):多态和继承(初期绑定和编译时多态)
在本系列中,我们以CodeProject上比较火的OOP系列博客为主,进行OOP深入浅出展现. 无论作为软件设计的高手.或者菜鸟,对于架构设计而言,均需要多次重构.取舍,以有利于整个软件项目的健康构建 ...
- Python入门之面向对象的多态和继承
本章内容 Python面向对象的多态和继承对比 ========================================= 在OOP程序设计中,当我们定义一个class的时候,可以从某个现有的 ...
- C++基础学习教程(七)----类编写及类的两个特性解析--->多态&继承
类引入 到眼下为止我们所写的自己定义类型都是keywordstruct,从如今起我们将採用class方式定义类,这样的方式对于学习过其它高级语言包含脚本(Such as Python)的人来说再熟悉只 ...
- .NET Core CSharp初级篇 1-6 类的多态与继承
.NET Core CSharp初级篇 1-6 本节内容为类的多态与继承 简介 终于讲到了面向对象三大特性中的两大特性--继承与多态.通过继承与多态,我们能很好的将类的拓展性发挥到了极致.在下面的内容 ...
- python极简教程07:封装、多态和继承
测试奇谭,BUG不见. 这一场主讲python的面向对象部分--封装.多态和继承. 目的:掌握Python面向对象的三个核心概念. 封装 01 什么是封装? 封装的目的是,保护隐私.通俗的讲:不想让别 ...
- 深入浅出OOP(三): 多态和继承(动态绑定/运行时多态)
在前面的文章中,我们介绍了编译期多态.params关键字.实例化.base关键字等.本节我们来关注另外一种多态:运行时多态, 运行时多态也叫迟绑定. 运行时多态或迟绑定.动态绑定 在C#语音中,运行时 ...
- 深入浅出OOP(一): 多态和继承(早期绑定/编译时多态)
在本系列中,我们以CodeProject上比较火的OOP系列博客为主,进行OOP深入浅出展现. 无论作为软件设计的高手.或者菜鸟,对于架构设计而言,均需要多次重构.取舍,以有利于整个软件项目的健康构建 ...
随机推荐
- LeetCode 787. Cheapest Flights Within K Stops
原题链接在这里:https://leetcode.com/problems/cheapest-flights-within-k-stops/ 题目: There are n cities connec ...
- 详解如何在CentOS7中使用Nginx和PHP7-FPM安装Nextcloud
转载地址:https://www.jb51.net/article/109382.htm 这篇文章主要介绍了详解如何在CentOS7中使用Nginx和PHP7-FPM安装Nextcloud,会通过 N ...
- learning scala someElements
The Scala collections library provides specialised implementations for Sets of fewer than 5 values ( ...
- java 库存管理
第一种方法: import java.util.Scanner; import java.util.Random; class kuCun { //库存管理 public static void m ...
- PostGraphile 4.4 发布,支持real time 查询
在4.4 之前,real time 是通过插件完成处理的,4.4 直接内置了,还是很方便的功能,总算 和其他类似graphql 平台看齐了,使用上还是挺方便的. 参考资料 https://www.gr ...
- SQL基础-创建新的输出字段
一.创建新的输出字段 1.建表.插数据 ### CREATE TABLE `t_stock_trans_dtl` ( `trans_id` varchar(100) NOT NULL COMMENT ...
- 2016级移动应用开发在线测试12-service
有趣有内涵的文章第一时间送达! 喝酒I创作I分享 生活中总有些东西值得分享 @醉翁猫咪 1. Service是Android系统中的四大组件之一(Acitivty.Service.ContentPr ...
- 2016android在线测试15-图像 camera2
1.ImageView类用于显示各种图像,例如:图标,图片,下面对于ImageView类加载图片方法的描述有: void setImageResource(int resld): 设置Drawanbl ...
- Symfony之入门学习
最近因业务需要,主要针对Edusoho进行二次开发.但是对于Symfony,我并不熟悉,我所了解的是,它的那套与我在Java中常用的开发模式MVC,本质上并不多大差异,就是所使用的语言不一样而已.下面 ...
- 缓存:修改Hosts不生效
修改Hosts为何不生效,是DNS缓存? - Barret李靖 - 博客园https://www.cnblogs.com/hustskyking/p/hosts-modify.html 换个未打开过的 ...
