C语言提高 (6) 第六天 文件(续) 链表的操作
1昨日回顾
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
char buf[1024] = { 0 };
int len = 0;
// !可以取代scanf
if (fgets(buf, 1024, stdin) != NULL) {
len = strlen(buf);
buf[len - 1] = '\0'; // 输入以后是qwe\n 所以最后一个\n要换成\0
}
printf("buf:%s\n", buf);
return 0;
}
刚才的读写都是字符和字符串,下面讲二进制的读写:

(ue查看二进制文件)
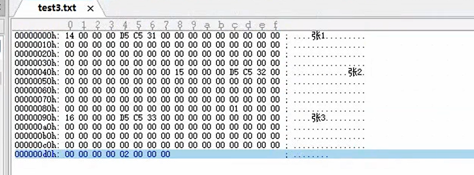
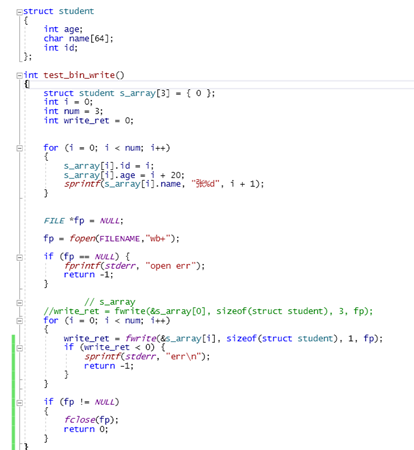
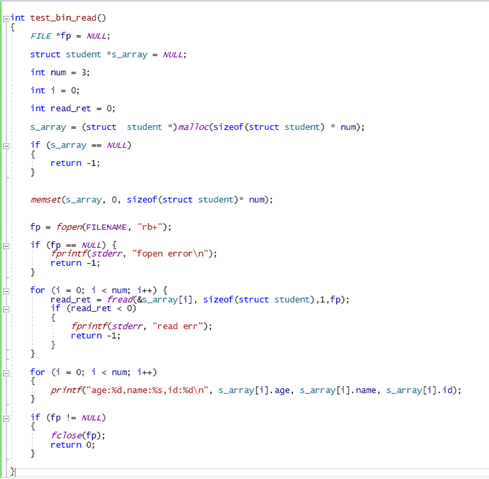
2作业题
对操作系统来说都是文件 设备文件…
是写驱动的人为我们提供了接口
3文件系统体系

问:这个能编译吗?
struct 是一种数据类型
数据类型是固定内存大小的别名

这样可以:

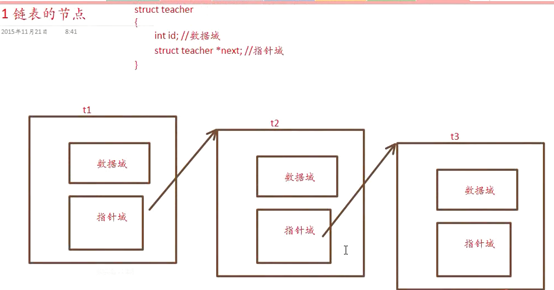
数组与链表的对比:

4文件缓冲区
再说一下fgets和fputs
fgets遇到\n结束,也就是读取一行,最后会把\n也读进去 不会读\0
fputs不会把\n put出去,fputs只是put string
5静态链表和动态链表
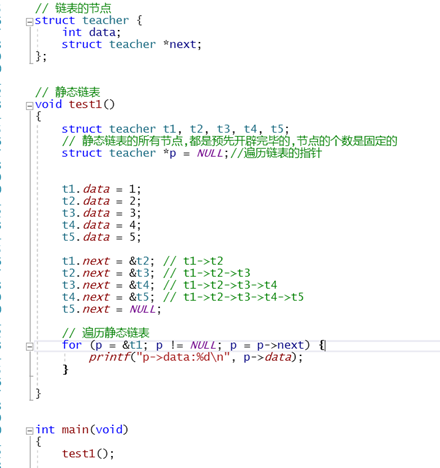
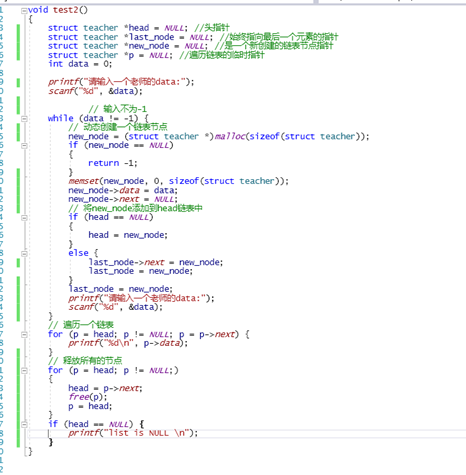
2)
带头链表和不带头链表
无头链表的插入和从头部插入,删除节点..等操作
no_head_list.h:
#ifndef _NO_HEAD_LIST_H_
#define _NO_HEAD_LIST_H_
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
// 链表的节点
struct node
{
int data; //数据域
struct node *next; //指针域
};
// 初始化链表的接口
void init_list(struct node **head_p);
// 创建一个节点的接口
struct node* make_node(int data);
// 销毁一个节点
void free_node(struct node *node);
// 将节点插入链表的接口 (插入链表的尾部
int insert_node_to_end(struct node *new_node,struct node**head_p);
// 将节点插入链表的头部
int insert_node_from_begin(struct node *new_node, struct node **head_p);
// 销毁一个链表
void destory_list(struct node **head_p);
// 遍历链表
void print_list(struct node *head);
// 删除一个节点,根据要删除节点的指针来删除
int delete_node(struct node*del_node, struct node **head_p);
// 查询一个节点
struct node * search(struct node *head, int data);
#endif
no_head_list.c:
#include "no_head_list.h"
void init_list(struct node **head_p)
{
*head_p = NULL;
}
struct node* make_node(int data)
{
struct node *new_node = NULL;
new_node = (struct node *)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
if (new_node == NULL)
{
fprintf(stderr, "make node malooc new_node error\n");
return NULL;
}
memset(new_node, 0, sizeof(struct node));
new_node->data = data;
new_node->next = NULL;
return new_node;
}
// 插入一个节点到head中
int insert_node_to_end(struct node *new_node, struct node**head_p)
{
struct node *head = NULL;
struct node* last_node = NULL;
if (new_node == NULL || head_p == NULL)
{
return 0;
}
head = *head_p;
if (head == NULL)
{
// 链表此时是空链表
head = new_node;
last_node = new_node; // 无头链表特点:需要对head是否为空 进行判断
}
else {
// 找到这个last_node
// last_node->next = new_node;
for (last_node = head; last_node->next != NULL; last_node = last_node->next);
last_node->next = new_node;
}
*head_p = head;
return 0;
}
// 遍历链表
void print_list(struct node *head)
{
struct node *p = NULL;
for (p = head; p != NULL; p = p->next) {
printf("%d\n", p->data);
}
}
int insert_node_from_begin(struct node *new_node, struct node **head_p)
{
if (new_node == NULL || head_p == NULL)
{
return -1;
}
struct node *head = *head_p;
// 插入的操作
if (head == NULL)
{
head = new_node;
}
else {
new_node->next = head;
head = new_node;
}
*head_p = head;
return 0;
}
void free_node(struct node *node)
{
if (node != NULL) {
free(node);
}
}
void destory_list(struct node **head_p)
{
struct node *head = *head_p;
struct node *p = NULL;
while (head!= NULL)
{
// 链表还有怨怒是
p = head;
head = head->next;
free(p);
}
*head_p = head;
}
int delete_node(struct node*del_node, struct node **head_p)
{
struct node *head = *head_p;
struct node *p = NULL;
if (head == del_node) {
// 如果要删除的节点就是首节点
head = head->next;
free_node(del_node);
*head_p = head;
return 0;
}
// 要删除的不是头节点
for (p = head; p != NULL; p = p->next)
{
if (p->next == del_node) {
// 找到了要删除的节点,此时p是这个要删除节点的前驱节点
p->next = p->next->next;
free_node(del_node);
break;
}
}
*head_p = head;
return 0;
}
// 查询一个节点
struct node* search(struct node*head, int data)
{
struct node *p = NULL;
for (p = head; p != NULL; p = p->next) {
if (p->data == data)
{
return p;
}
}
return NULL;
}
main.c:
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main(void)
{
struct node *head = NULL;
struct node *new_node = NULL;
int num = 10;
int i = 0;
int del_data = 0;
// 初始化头节点
init_list(&head);
// 创建一个链表节点
for (i = 0; i < num; i++) {
new_node = make_node(i + 10);
//insert_node_to_end(new_node, &head);
insert_node_from_begin(new_node,&head);
}
print_list(head);
printf("请输入要删除的节点:");
scanf("%d", &del_data);
struct node *del_node = search(head, del_data);
if (del_node != NULL)
{
delete_node(del_node, &head);
}
printf("---------\n");
print_list(head);
// 销毁一个链表
destory_list(&head);
if (head == NULL)
{
printf("head === NULL");
}
return 0;
}
带头节点链表的操作:
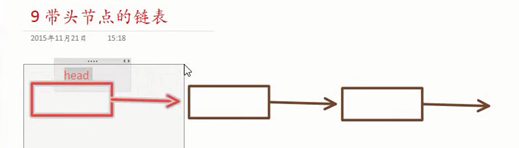
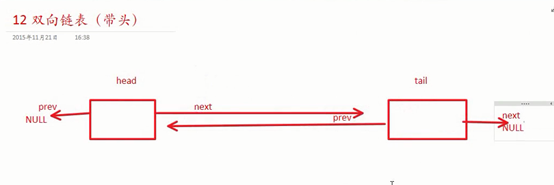
双向链表(带头):
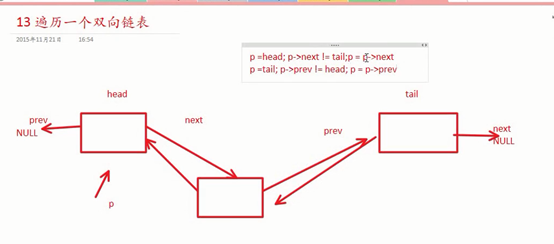
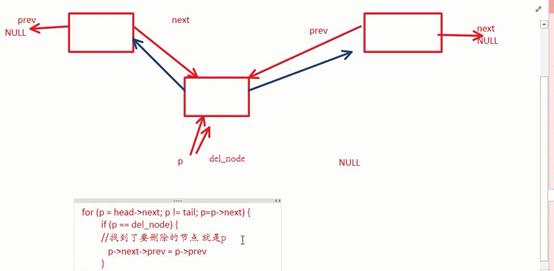
删除双向链表节点:
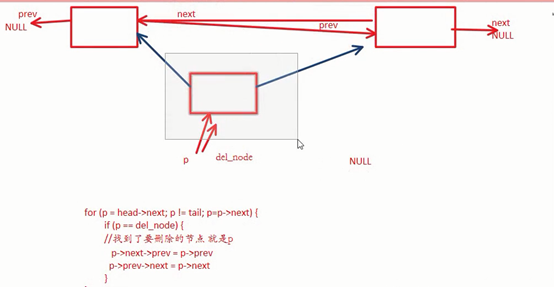
销毁一个双向链表:
dlist.h
#ifndef _D_LIST_H_
#define _D_LIST_H_
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
struct node
{
int data; //数据域
struct node *next; //下一个节点
struct node *prev; //上一个节点
};
// 初始化一个双向链表
void init_list(struct node **head_p,struct node**tail_p);
// 创建一个节点
struct node *make_node(int data);
// 销毁一个节点
void free_node(struct node *node);
// 插入一个节点
int insert_node(struct node*head, struct node*tail, struct node*new_node);
// 顺序遍历
void print_list_1(struct node *head, struct node *tail);
// 逆序遍历
void print_list_2(struct node *head, struct node *tail);
// 查找一个节点
struct node* search(struct node* head, struct node* tail, int data);
// 删除一个双向链表的节点
int delete_node(struct node* head, struct node* tail, struct node* del_node);
// 销毁一个双向链表
void destory_list(struct node* head, struct node* tail);
#endif
dlist.c:
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include "dlist.h"
// 初始化一个双向链表
void init_list(struct node **head_p, struct node**tail_p)
{
struct node *head = NULL;
struct node *tail = NULL;
if (head_p == NULL || tail_p == NULL)
{
return;
}
head = (struct node *)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
if (head == NULL)
{
return;
}
tail = (struct node*) malloc(sizeof(struct node));
if (tail == NULL) {
return;
}
head->data = tail->data = 0;
head->next = tail;
tail->prev = head;
head->prev = tail->next = NULL;
*head_p = head;
*tail_p = tail;
return;
}
// 创建一个节点
struct node *make_node(int data)
{
struct node *p = NULL;
p = (struct node*)malloc(sizeof(struct node));
if (p == NULL)
{
return NULL;
}
p->data = data;
p->next = p->prev = NULL;
return p;
}
void free_node(struct node *node) {
if (node == NULL) return;
free(node);
}
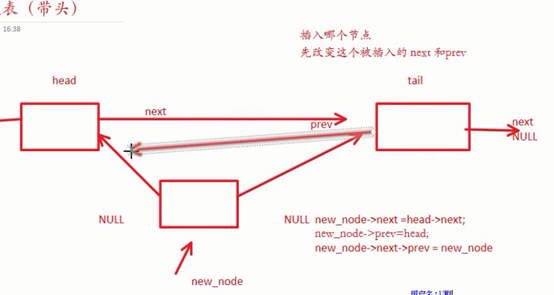
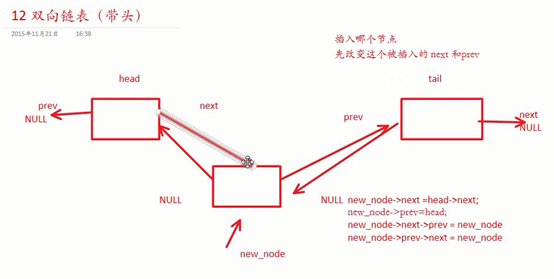
int insert_node(struct node*head, struct node*tail, struct node*new_node)
{
if (head == NULL || tail == NULL || new_node == NULL)
{
return -1;
}
//插入哪个节点就先改变哪个节点的next和prev
// 改变new_node的自身指针
new_node->next = head->next;
new_node->prev = head;
// 改变new_node两边的指针
new_node->next->prev = new_node;
new_node->prev->next = new_node;
return 0;
}
// 遍历一个链表
void print_list_1(struct node *head, struct node *tail)
{
struct node *p = NULL;
for (p = head->next; p != tail; p = p->next)
{
printf("data:%d\n", p->data);
}
}
void print_list_2(struct node *head, struct node *tail)
{
struct node *p = NULL;
for (p = tail->prev; p != head; p = p->prev)
{
printf("data:%d\n", p->data);
}
}
// 查找一个节点
struct node* search(struct node* head, struct node* tail,int data)
{
struct node* p = NULL;
for (p = head->next; p != tail; p = p->next)
{
if (p->data == data)
{
return p;
}
}
return NULL;
}
// 删除一个双向链表节点
int delete_node(struct node* head, struct node* tail, struct node* del_node)
{
struct node* p = NULL;
for (p = head->next; p != tail; p = p->next) {
//遍历链表中除了head和tail的每一个元素
if (p == del_node) {
// p是删除的节点
// 应该改变p的前驱节点和p的后继节点,p本身的两个指针不要动
p->next->prev = p->prev;
p->prev->next = p->next;
free_node(p);
break;
}
}
return 0;
}
// 销毁一个双向链表
void destory_list(struct node** head_p, struct node** tail_p)
{
if (head_p == NULL || tail_p == NULL)
{
return;
}
struct node* head = *head_p;
struct node* tail = *tail_p;
struct node* p = NULL;
for (p = head->next; p != tail;)
{
p->next->prev = p->prev;
p->prev->next = p->next;
free_node(p);
p = head->next;
}
// 以上就删除了 除了head和tail的全部元素
if (head->next = tail && tail->prev == head)
{
printf("此时链表已经空 除了head\tail \n");
free_node(head);
free_node(tail);
*head_p = NULL;
*tail_p = NULL;
}
return;
}
main.c:
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include "dlist.h"
int main(void)
{
struct node *head = NULL;//表头
struct node *tail = NULL;//表尾
struct node *new_node = NULL;
struct node* del_node = NULL;
int num = 10;
int i = 0;
int data = 0;
init_list(&head, &tail);
for (i = 0; i < num; i++)
{
new_node = make_node(i + 10);
insert_node(head, tail, new_node);
}
print_list_1(head, tail);
printf("==========\n");
print_list_2(head, tail);
printf("data:");
scanf("%d", &data);
del_node = search(head,tail,data);
if (del_node != NULL)
{
delete_node(head, tail, del_node);
}
printf("==========\n");
print_list_2(head, tail);
destory_list(&head, &tail);
if (head == NULL)
{
printf("head == NULL\n");
}
if (tail == NULL)
{
printf("tail == NULL\n");
}
return 0;
}
总结:
对于插入删除链表效率比较高
对于索引链表效率比较低,(数组可以直接偏移
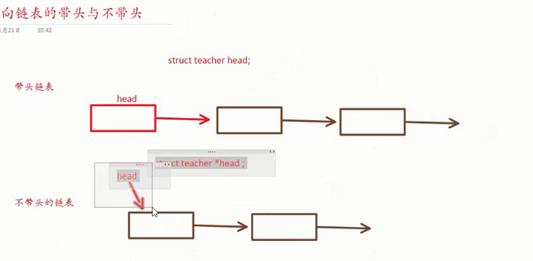
关于有头无头:
有了头结点之后,对首个结点的操作(比如删除、插入等)可以和其他节点相同,
“大家都说的差不多了,有头的好,没头的怎么找入口。”
回调函数




void(*)() 是个 返回值为 void; 参数为空 (这样些也成 void(*)(void) )的函数指针
注意 是个 函数指针
然后 把0 强制转换为 这个类型的指针
然后 取 值 *(void(*)())
这个时候 就是 取得了 一个函数指针 类型为 返回值为 void; 参数为空
然后 后面加上 括号 就是 实施这个 函数指针的调用
C语言提高 (6) 第六天 文件(续) 链表的操作的更多相关文章
- C语言之----面向对象的方法实现链表的操作
1 /* 2 * 详细运行过程: 本程序实现的是对链表的简单的操作,即链表的增 删 改 查 销毁 初始化 3 * 运用面向对象的思想,实现一个类op,op中包括了所有的链表操作方法 4 * 其他的程序 ...
- 【Go语言】集合与文件操作
本文目录 1.数据集合的主要操作 1_1.字典的声明 1_2.字典的初始化和创建 1_3.字典的访问和操作 1_4.其他类型的数据集 2.文件操作 2_1.文件操作概述os包和path包 2_2.文件 ...
- Go 语言接口及使用接口实现链表插入
@ 目录 1. 接口定义 1.1 空接口 1.2 实现单一接口 1.3 接口多方法实现 2. 多态 2.1 为不同数据类型的实体提供统一的接口 2.2 多接口的实现 3. 系统接口调用 4. 接口嵌套 ...
- Swift3.0语言教程字符串与文件的数据转换
Swift3.0语言教程字符串与文件的数据转换 Swift3.0语言教程字符串与文件的数据转换,如果想要对字符串中的字符进行永久保存,可以将字符串中的字符写入到文件中.当然,开发者也可以将写入的内容进 ...
- SQLLite 可以通过SQL语言来访问的文件型SQL数据库
Web Storage分为两类: - sessionStorage:数据保存在session 对象中(临时) - localStorage:数据保存在本地硬件设备中(永久) sessionStorag ...
- JAVA调用C语言写的SO文件
JAVA调用C语言写的SO文件 因为工作需要写一份SO文件,作为手机硬件IC读卡和APK交互的桥梁,也就是中间件,看了网上有说到JNI接口技术实现,这里转载了一个实例 // 用JNI实现 // 实例: ...
- C语言常用的库文件(头文件、函数库)
C语言常用的库文件(头文件.函数库) C系统提供了丰富的系统文件,称为库文件.C的库文件分为两类,一类是扩展名为".h"的文件,称为头文件,在前面的包含命令中我们已多次使用过.在& ...
- C语言 HTTP上传文件-利用libcurl库上传文件
原文 http://justwinit.cn/post/7626/ 通常情况下,一般很少使用C语言来直接上传文件,但是遇到使用C语言编程实现文件上传时,该怎么做呢? 借助开源的libcurl库,我们 ...
- 采用Java语言如何实现高速文件复制?
今天review代码也看到了"大神"用老方法来实现文件拷贝.今天归结一下使用Java语言怎样实现高速文件复制: 代码1--使用文件通道的方式: import java.io.Fil ...
随机推荐
- firefox历史版本下载地址
http://ftp.mozilla.org/pub/firefox/releases/
- 洛谷 P2634 BZOJ 2152 【模板】点分治(聪聪可可)
题目描述 聪聪和可可是兄弟俩,他们俩经常为了一些琐事打起来,例如家中只剩下最后一根冰棍而两人都想吃.两个人都想玩儿电脑(可是他们家只有一台电脑)……遇到这种问题,一般情况下石头剪刀布就好了,可是他们已 ...
- spring boot @Transactional事物处理
spring boot 添加事物使用 @Transactional注解 简单使用 在启动类上方添加 @EnableTransactionManagement注解 使用时直接在类或者方法上使用 @Tra ...
- [bzoj1070][SCOI2007]修车_费用流
修车 bzoj-1070 SCOI-2007 题目大意:有m个人要修n台车,每个工人修不同的车的时间不同,问将所有的车都修完,最少需要花费的时间. 注释:$2\le m\le 9$,$1\le n \ ...
- D - Mayor's posters
D - Mayor's posters POJ - 2528 思路:线段树+离散化. 离散化时注意特殊情况,如果两个数相差大于一,离散时也应该差1.比如 1 3 离散后应该为 1 2. 错因: 1.二 ...
- hdu2430 Beans 单调队列
// hdu2430 Beans 单调队列 // // 题目意思: // 求一个sum%p<=k的max(sum/p) // // 结题报告: // 技巧,先求出前缀和,并记录前i项对p取余的值 ...
- luogu1313 计算系数
题目大意:给定一个多项式(ax+by)^k,请求出多项式展开后x^n*y^m 项的系数. 将原式化为(ax+by)*(ax+by)*...①,然后将其拆解,拆解时x乘了多少次,a就乘了多少次,y,b同 ...
- nexus启动报错----->错误 1067: 进程意外终止。
1.今天启动nexus报错: 2.错误信息 错误 1067: 进程意外终止. 3.检查发现我之前把jdk升级了.然而nexus之前指定的jdk将不再生效. 4.解决办法 找到nexus安装目录 修改b ...
- mysql 从库落后主库太多优化
有时候为了避免master.info和中继日志崩溃,在容忍额外的fsync()带来的开销,推荐设置sync_master_info = 1sync_relay_log = 1sync_relay_lo ...
- [ASPX] 模版引擎XTemplate与代码生成器XCoder(源码)
模版引擎XTemplate是一个仿T4设计的引擎,功能上基本与T4一致(模版语法上完全兼容T4,模版头指令部分兼容). 自己设计模版引擎,就是为了代码生成器.网站模版.邮件模版等多种场合,也就是要能拿 ...
