6.Java Spring框架源码分析-AOP-Spring_AOP源码分析总结
- 源码分析
- 1. @EnableAspectJAutoProxy
- 2. AspectJAutoProxyRegistrar
- 3. AopConfigUtils
- 4. AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator
- 5. 流程分析
- 6. 目标方法执行
- 6.1. CglibAopProxy
- 6.2. AdvisedSupportAdvisedSupport
- 6.3. DefaultAdvisorChainFactory
- 6.4. DefaultAdvisorAdapterRegistry
- 6.5. ReflectiveMethodInvocation
- 6.6. ExposeInvocationInterceptor
- 6.7. MethodBeforeAdviceInterceptor
- 6.8. AspectJAfterAdvice
- 6.9. AfterReturningAdviceInterceptor
- 6.10. ThrowsAdviceInterceptor
源码分析
1. @EnableAspectJAutoProxy
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Import(AspectJAutoProxyRegistrar.class)//导入了AspectJAutoProxyRegistrar组件
public @interface EnableAspectJAutoProxy {
boolean proxyTargetClass() default false;
boolean exposeProxy() default false;
}
2. AspectJAutoProxyRegistrar
//实现了ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar接口,可以向ioc容器导入bean
class AspectJAutoProxyRegistrar implements ImportBeanDefinitionRegistrar {
@Override
public void registerBeanDefinitions(
AnnotationMetadata importingClassMetadata, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) {
//向容器中注册AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator bean
AopConfigUtils.registerAspectJAnnotationAutoProxyCreatorIfNecessary(registry);
AnnotationAttributes enableAspectJAutoProxy =
AnnotationConfigUtils.attributesFor(importingClassMetadata, EnableAspectJAutoProxy.class);
if (enableAspectJAutoProxy.getBoolean("proxyTargetClass")) {
AopConfigUtils.forceAutoProxyCreatorToUseClassProxying(registry);
}
if (enableAspectJAutoProxy.getBoolean("exposeProxy")) {
AopConfigUtils.forceAutoProxyCreatorToExposeProxy(registry);
}
}
}
3. AopConfigUtils
3.1. registerAspectJAnnotationAutoProxyCreatorIfNecessary
public static BeanDefinition registerAspectJAnnotationAutoProxyCreatorIfNecessary(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, Object source) {
//导入AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator
return registerOrEscalateApcAsRequired(AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator.class, registry, source);
}
3.2. registerOrEscalateApcAsRequired
private static BeanDefinition registerOrEscalateApcAsRequired(Class<?> cls, BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, Object source) {
Assert.notNull(registry, "BeanDefinitionRegistry must not be null");
//已经存在org.springframework.aop.config.internalAutoProxyCreator的bean
if (registry.containsBeanDefinition(AUTO_PROXY_CREATOR_BEAN_NAME)) {
BeanDefinition apcDefinition = registry.getBeanDefinition(AUTO_PROXY_CREATOR_BEAN_NAME);
if (!cls.getName().equals(apcDefinition.getBeanClassName())) {
int currentPriority = findPriorityForClass(apcDefinition.getBeanClassName());
int requiredPriority = findPriorityForClass(cls);
if (currentPriority < requiredPriority) {
apcDefinition.setBeanClassName(cls.getName());
}
}
return null;
}
//不存在则创建该AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator bean,放入ioc容器
RootBeanDefinition beanDefinition = new RootBeanDefinition(cls);
beanDefinition.setSource(source);
beanDefinition.getPropertyValues().add("order", Ordered.HIGHEST_PRECEDENCE);
beanDefinition.setRole(BeanDefinition.ROLE_INFRASTRUCTURE);
registry.registerBeanDefinition(AUTO_PROXY_CREATOR_BEAN_NAME, beanDefinition);
return beanDefinition;
}
4. AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator
4.1. 类体系
由下图可看出AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator主要实现了
BeanFactoryAware接口。setBeanFactory方法(为bean注入BeanFactory)
以及BeanPostProcessor接口。postProcessBeforeInitialization方法(bean初始化之前做一些事情)和postProcessAfterInitialization方法(bean初始化之后做一些事情))

5. 流程分析
5.1. 调试
为AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator类体系的关键方法加上断点,运行。
1)、传入配置类,创建ioc容器
2)、注册配置类,调用refresh()刷新容器
3)、registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);注册bean的后置处理器拦截bean的创建
1)、先获取ioc容器中的所有BeanPostProcessor
2)、给容器中加入别的BeanPostProcessor
3)、优先注册实现了PriorityOrdered接口的BeanPostProcessor
4)、然后注册实现了Ordered接口的BeanPostProcessor
5)、接着注册没实现接口的BeanPostProcessor
6)、注册BeanPostProcessor,实际上就是创建BeanPostProcessor保存在容器中
创建internalAutoProxyCreator的BeanPostProcessor[]
1)、创建Bean的实例
2)、populateBean,给bean的各种属性赋值
3)、initializeBean,初始化bean
1)、invokeAwareMethods(),处理Aware接口的方法回调
2)、applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization()
3)、invokeInitMethods(),执行自定义的初始化方法
4)、applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization()
4)、BeanPostProcessor(AnnotationAwareAspecJAutoProxyCreater)
7)、把BeanPostProcessor注册到BeanFactory中
beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor(processor)
通过以上过程就把AnnotationAwareAspecJAutoProxyCreater注册进容器中=================
5.2. AbstractAutoProxyCreator
5.2.1. postProcessBeforeInstantiation
public Object postProcessBeforeInstantiation(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) throws BeansException {
//获取缓存key
Object cacheKey = getCacheKey(beanClass, beanName);
if (beanName == null || !this.targetSourcedBeans.contains(beanName)) {
//判断是否在已经增强的bean里
if (this.advisedBeans.containsKey(cacheKey)) {
//是的话说明已经增强过,直接返回
return null;
}
//调用AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator的isInfrastructureClass方法以及shouldSkip方法
if (isInfrastructureClass(beanClass) || shouldSkip(beanClass, beanName)) {
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE);
return null;
}
}
// Create proxy here if we have a custom TargetSource.
// Suppresses unnecessary default instantiation of the target bean:
// The TargetSource will handle target instances in a custom fashion.
if (beanName != null) {
TargetSource targetSource = getCustomTargetSource(beanClass, beanName);
if (targetSource != null) {
this.targetSourcedBeans.add(beanName);
Object[] specificInterceptors = getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(beanClass, beanName, targetSource);
Object proxy = createProxy(beanClass, beanName, specificInterceptors, targetSource);
this.proxyTypes.put(cacheKey, proxy.getClass());
return proxy;
}
}
return null;
}
5.2.2. isInfrastructureClass
protected boolean isInfrastructureClass(Class<?> beanClass) {
//判断是否是Advice、Pointcut、Advisor、AopInfrastructureBean类
boolean retVal = Advice.class.isAAopInfrastructureBeanssignableFrom(beanClass) ||
Pointcut.class.isAssignableFrom(beanClass) ||
Advisor.class.isAssignableFrom(beanClass) ||
AopInfrastructureBean.class.isAssignableFrom(beanClass);
if (retVal && logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Did not attempt to auto-proxy infrastructure class [" + beanClass.getName() + "]");
}
return retVal;
}
5.2.3. postProcessAfterInitialization
//创建完Calc对象后会调用这个方法
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) throws BeansException {
if (bean != null) {
Object cacheKey = getCacheKey(bean.getClass(), beanName);
if (this.earlyProxyReferences.remove(cacheKey) != bean) {
//必要时包装Calc
return wrapIfNecessary(bean, beanName, cacheKey);
}
}
return bean;
}
5.2.4. wrapIfNecessary
protected Object wrapIfNecessary(Object bean, String beanName, Object cacheKey) {
if (beanName != null && this.targetSourcedBeans.contains(beanName)) {
return bean;
}
if (Boolean.FALSE.equals(this.advisedBeans.get(cacheKey))) {
return bean;
}
if (isInfrastructureClass(bean.getClass()) || shouldSkip(bean.getClass(), beanName)) {
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE);
return bean;
}
// Create proxy if we have advice.
//获取Calc所有的增强器
Object[] specificInterceptors = getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(bean.getClass(), beanName, null);
if (specificInterceptors != DO_NOT_PROXY) {
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.TRUE);
//创建代理类增强当前bean
Object proxy = createProxy(
bean.getClass(), beanName, specificInterceptors, new SingletonTargetSource(bean));
this.proxyTypes.put(cacheKey, proxy.getClass());
return proxy;
}
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.FALSE);
return bean;
}
5.2.5. createProxy
protected Object createProxy(
Class<?> beanClass, String beanName, Object[] specificInterceptors, TargetSource targetSource) {
if (this.beanFactory instanceof ConfigurableListableBeanFactory) {
AutoProxyUtils.exposeTargetClass((ConfigurableListableBeanFactory) this.beanFactory, beanName, beanClass);
}
ProxyFactory proxyFactory = new ProxyFactory();
proxyFactory.copyFrom(this);
if (!proxyFactory.isProxyTargetClass()) {
if (shouldProxyTargetClass(beanClass, beanName)) {
proxyFactory.setProxyTargetClass(true);
}
else {
evaluateProxyInterfaces(beanClass, proxyFactory);
}
}
Advisor[] advisors = buildAdvisors(beanName, specificInterceptors);
proxyFactory.addAdvisors(advisors);
proxyFactory.setTargetSource(targetSource);
customizeProxyFactory(proxyFactory);
proxyFactory.setFrozen(this.freezeProxy);
if (advisorsPreFiltered()) {
proxyFactory.setPreFiltered(true);
}
//用ProxyFactory代理工厂创建对象
return proxyFactory.getProxy(getProxyClassLoader());
}
5.3. AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator
5.3.1. isInfrastructureClass
protected boolean isInfrastructureClass(Class<?> beanClass) {
//AbstractAutoProxyCreator.isInfrastructureClass || AbstractAspectJAdvisorFactory.isAspect
return (super.isInfrastructureClass(beanClass) || this.aspectJAdvisorFactory.isAspect(beanClass));
}
5.3.2. isAspect
public boolean isAspect(Class<?> clazz) {
//有@Aspect注解 并且 没有以ajc$开头的属性
return (hasAspectAnnotation(clazz) && !compiledByAjc(clazz));
}
5.4. AspectJAwareAdvisorAutoProxyCreator
5.4.1. shouldSkip
protected boolean shouldSkip(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) {
// TODO: Consider optimization by caching the list of the aspect names
//找到所有增强的切面:就是LogAspect中的增强方法
List<Advisor> candidateAdvisors = findCandidateAdvisors();
for (Advisor advisor : candidateAdvisors) {
//只要有一个增强器是AspectJPointcutAdvisor类型的并且增强器修饰的bean就是beanName,那么返回true
if (advisor instanceof AspectJPointcutAdvisor) {
if (((AbstractAspectJAdvice) advisor.getAdvice()).getAspectName().equals(beanName)) {
return true;
}
}
}
return super.shouldSkip(beanClass, beanName);
}
5.5. AbstractAdvisorAutoProxyCreator
5.5.1. getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean
protected Object[] getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName, TargetSource targetSource) {
List<Advisor> advisors = findEligibleAdvisors(beanClass, beanName);
if (advisors.isEmpty()) {
return DO_NOT_PROXY;
}
return advisors.toArray();
}
5.5.2. findEligibleAdvisors
protected List<Advisor> findEligibleAdvisors(Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) {
//获取所有的增强器
List<Advisor> candidateAdvisors = findCandidateAdvisors();
//筛选出能应用到当前bean上的增强器
List<Advisor> eligibleAdvisors = findAdvisorsThatCanApply(candidateAdvisors, beanClass, beanName);
extendAdvisors(eligibleAdvisors);
if (!eligibleAdvisors.isEmpty()) {
eligibleAdvisors = sortAdvisors(eligibleAdvisors);
}
return eligibleAdvisors;
}
5.5.3. findAdvisorsThatCanApply
protected List<Advisor> findAdvisorsThatCanApply(
List<Advisor> candidateAdvisors, Class<?> beanClass, String beanName) {
ProxyCreationContext.setCurrentProxiedBeanName(beanName);
try {
//调用AopUtils获取能应用的增强器
return AopUtils.findAdvisorsThatCanApply(candidateAdvisors, beanClass);
}
finally {
ProxyCreationContext.setCurrentProxiedBeanName(null);
}
}
5.6. AopUtils
5.6.1. findAdvisorsThatCanApply
public static List<Advisor> findAdvisorsThatCanApply(List<Advisor> candidateAdvisors, Class<?> clazz) {
if (candidateAdvisors.isEmpty()) {
return candidateAdvisors;
}
List<Advisor> eligibleAdvisors = new LinkedList<Advisor>();
//遍历所有增强器,最后调用的都是getClassFilter().matches()方法判断的
for (Advisor candidate : candidateAdvisors) {
if (candidate instanceof IntroductionAdvisor && canApply(candidate, clazz)) {
eligibleAdvisors.add(candidate);
}
}
boolean hasIntroductions = !eligibleAdvisors.isEmpty();
for (Advisor candidate : candidateAdvisors) {
if (candidate instanceof IntroductionAdvisor) {
// already processed
continue;
}
if (canApply(candidate, clazz, hasIntroductions)) {
eligibleAdvisors.add(candidate);
}
}
return eligibleAdvisors;
}
5.7. ProxyFactory
5.7.1. getProxy
public Object getProxy(ClassLoader classLoader) {
//ProxyCreatorSupport的createAopProxy
return createAopProxy().getProxy(classLoader);
}
5.8. ProxyCreatorSupport
5.8.1. createAopProxy
protected final synchronized AopProxy createAopProxy() {
if (!this.active) {
activate();
}
//调用DefaultAopProxyFactory的createAopProxy方法
return getAopProxyFactory().createAopProxy(this);
}
5.9. DefaultAopProxyFactory
5.9.1. createAopProxy
public AopProxy createAopProxy(AdvisedSupport config) throws AopConfigException {
if (config.isOptimize() || config.isProxyTargetClass() || hasNoUserSuppliedProxyInterfaces(config)) {
Class<?> targetClass = config.getTargetClass();
if (targetClass == null) {
throw new AopConfigException("TargetSource cannot determine target class: " +
"Either an interface or a target is required for proxy creation.");
}
if (targetClass.isInterface() || Proxy.isProxyClass(targetClass)) {
return new JdkDynamicAopProxy(config);
}
//没有的话使用cglib继承
return new ObjenesisCglibAopProxy(config);
}
else {
//有接口的话使用jdk代理
return new JdkDynamicAopProxy(config);
}
}
6. 目标方法执行
6.1. CglibAopProxy
6.1.1. intercept
//拦截目标方法的执行
public Object intercept(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args, MethodProxy methodProxy) throws Throwable {
Object oldProxy = null;
boolean setProxyContext = false;
Class<?> targetClass = null;
Object target = null;
try {
if (this.advised.exposeProxy) {
// Make invocation available if necessary.
oldProxy = AopContext.setCurrentProxy(proxy);
setProxyContext = true;
}
// May be null. Get as late as possible to minimize the time we
// "own" the target, in case it comes from a pool...
target = getTarget();
if (target != null) {
targetClass = target.getClass();
}
//获取目标方法的拦截器链:AdvisedSupportAdvisedSupport.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice()
List<Object> chain = this.advised.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(method, targetClass);
Object retVal;
// Check whether we only have one InvokerInterceptor: that is,
// no real advice, but just reflective invocation of the target.
//没有拦截器链
if (chain.isEmpty() && Modifier.isPublic(method.getModifiers())) {
// We can skip creating a MethodInvocation: just invoke the target directly.
// Note that the final invoker must be an InvokerInterceptor, so we know
// it does nothing but a reflective operation on the target, and no hot
// swapping or fancy proxying.
//直接执行目标方法
Object[] argsToUse = AopProxyUtils.adaptArgumentsIfNecessary(method, args);
retVal = methodProxy.invoke(target, argsToUse);
}
else {
// We need to create a method invocation...
//把需要执行的目标对象,目标方法,拦截器链等信息传入创建CglibMethodInvocation
//接着执行这个对象的proceed方法
retVal = new CglibMethodInvocation(proxy, target, method, args, targetClass, chain, methodProxy).proceed();
}
retVal = processReturnType(proxy, target, method, retVal);
return retVal;
}
finally {
if (target != null) {
releaseTarget(target);
}
if (setProxyContext) {
// Restore old proxy.
AopContext.setCurrentProxy(oldProxy);
}
}
}
6.2. AdvisedSupportAdvisedSupport
6.2.1. getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice
public List<Object> getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(Method method, Class<?> targetClass) {
MethodCacheKey cacheKey = new MethodCacheKey(method);
List<Object> cached = this.methodCache.get(cacheKey);
if (cached == null) {
//#### DefaultAdvisorChainFactory##### getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice
cached = this.advisorChainFactory.getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(
this, method, targetClass);
this.methodCache.put(cacheKey, cached);
}
return cached;
}
6.3. DefaultAdvisorChainFactory
6.3.1. getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice
public List<Object> getInterceptorsAndDynamicInterceptionAdvice(
Advised config, Method method, Class<?> targetClass) {
// This is somewhat tricky... We have to process introductions first,
// but we need to preserve order in the ultimate list.
List<Object> interceptorList = new ArrayList<Object>(config.getAdvisors().length);
Class<?> actualClass = (targetClass != null ? targetClass : method.getDeclaringClass());
boolean hasIntroductions = hasMatchingIntroductions(config, actualClass);
AdvisorAdapterRegistry registry = GlobalAdvisorAdapterRegistry.getInstance();
//获取所有的增强器,封装成Interceptor
for (Advisor advisor : config.getAdvisors()) {
if (advisor instanceof PointcutAdvisor) {
// Add it conditionally.
PointcutAdvisor pointcutAdvisor = (PointcutAdvisor) advisor;
if (config.isPreFiltered() || pointcutAdvisor.getPointcut().getClassFilter().matches(actualClass)) {
MethodMatcher mm = pointcutAdvisor.getPointcut().getMethodMatcher();
if (MethodMatchers.matches(mm, method, actualClass, hasIntroductions)) {
//调用DefaultAdvisorAdapterRegistry的getInterceptors方法
MethodInterceptor[] interceptors = registry.getInterceptors(advisor);
if (mm.isRuntime()) {
// Creating a new object instance in the getInterceptors() method
// isn't a problem as we normally cache
for (MethodInterceptor interceptor : interceptors) {
interceptorList.add(new InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher(interceptor, mm));
}
}
else {
interceptorList.addAll(Arrays.asList(interceptors));
}
}
}
}
else if (advisor instanceof IntroductionAdvisor) {
IntroductionAdvisor ia = (IntroductionAdvisor) advisor;
if (config.isPreFiltered() || ia.getClassFilter().matches(actualClass)) {
Interceptor[] interceptors = registry.getInterceptors(advisor);
interceptorList.addAll(Arrays.asList(interceptors));
}
}
else {
Interceptor[] interceptors = registry.getInterceptors(advisor);
interceptorList.addAll(Arrays.asList(interceptors));
}
}
return interceptorList;
}
6.4. DefaultAdvisorAdapterRegistry
6.4.1. getInterceptors
public MethodInterceptor[] getInterceptors(Advisor advisor) throws UnknownAdviceTypeException {
List<MethodInterceptor> interceptors = new ArrayList<MethodInterceptor>(3);
Advice advice = advisor.getAdvice();
//如果是MethodInterceptor,直接加入进去
if (advice instanceof MethodInterceptor) {
interceptors.add((MethodInterceptor) advice);
}
for (AdvisorAdapter adapter : this.adapters) {
//使用适配器
if (adapter.supportsAdvice(advice)) {
interceptors.add(adapter.getInterceptor(advisor));
}
}
if (interceptors.isEmpty()) {
throw new UnknownAdviceTypeException(advisor.getAdvice());
}
return interceptors.toArray(new MethodInterceptor[interceptors.size()]);
}
6.5. ReflectiveMethodInvocation
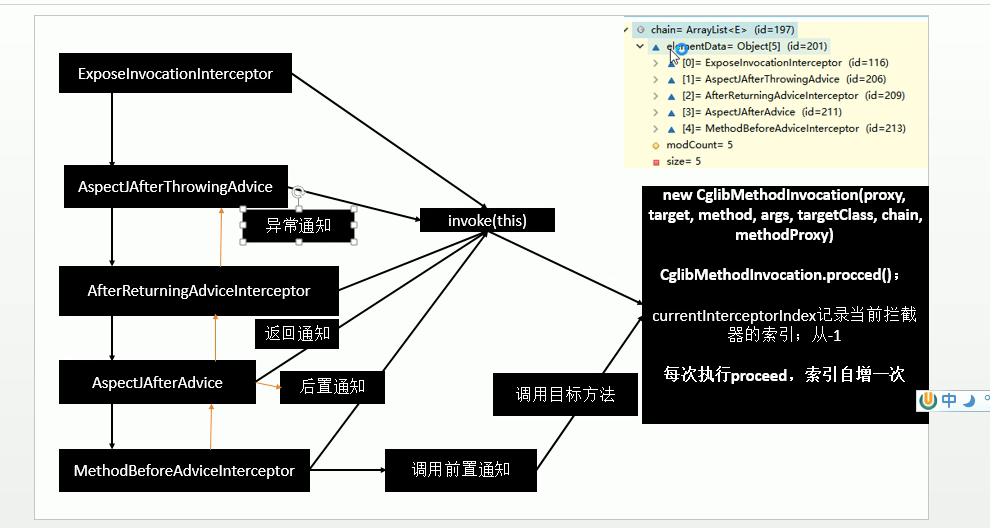
6.5.1. proceed
public Object proceed() throws Throwable {
// We start with an index of -1 and increment early.
//如果没有拦截器链或者执行到最后一个拦截器
if (this.currentInterceptorIndex == this.interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers.size() - 1) {
//通过反射执行目标方法method.invoke(target, args);
return invokeJoinpoint();
}
//获取第n个拦截器
Object interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice =
this.interceptorsAndDynamicMethodMatchers.get(++this.currentInterceptorIndex);
if (interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice instanceof InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher) {
// Evaluate dynamic method matcher here: static part will already have
// been evaluated and found to match.
InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher dm =
(InterceptorAndDynamicMethodMatcher) interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice;
if (dm.methodMatcher.matches(this.method, this.targetClass, this.arguments)) {
return dm.interceptor.invoke(this);
}
else {
// Dynamic matching failed.
// Skip this interceptor and invoke the next in the chain.
return proceed();
}
}
else {
// It's an interceptor, so we just invoke it: The pointcut will have
// been evaluated statically before this object was constructed.
//调用ExposeInvocationInterceptor的invoke方法
//最后一次会调用MethodBeforeAdviceInterceptor.invoke方法
return ((MethodInterceptor) interceptorOrInterceptionAdvice).invoke(this);
}
}
6.6. ExposeInvocationInterceptor
6.6.1. invoke
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation mi) throws Throwable {
//private static final ThreadLocal<MethodInvocation> invocation = new NamedThreadLocal<MethodInvocation>("Current AOP method invocation");
MethodInvocation oldInvocation = invocation.get();
//设置当前ThreadLocal关联的拦截器
invocation.set(mi);
try {
//继续调用ReflectiveMethodInvocation.proceed方法
return mi.proceed();
}
finally {
invocation.set(oldInvocation);
}
}
6.7. MethodBeforeAdviceInterceptor
6.7.1. invoke
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation mi) throws Throwable {
//1.执行前置通知
this.advice.before(mi.getMethod(), mi.getArguments(), mi.getThis());
//2.继续调用ReflectiveMethodInvocation.proceed方法此时执行的是目标方法
return mi.proceed();
}
6.8. AspectJAfterAdvice
6.8.1. invoke
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation mi) throws Throwable {
try {
//4.执行proceed
return mi.proceed();
}
finally {
//3.执行后置通知
invokeAdviceMethod(getJoinPointMatch(), null, null);
}
}
6.9. AfterReturningAdviceInterceptor
6.9.1. invoke
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation mi) throws Throwable {
//先执行方法
Object retVal = mi.proceed();
//没有任何问题才执行afterReturning
this.advice.afterReturning(retVal, mi.getMethod(), mi.getArguments(), mi.getThis());
return retVal;
}
6.10. ThrowsAdviceInterceptor
6.10.1. invoke
public Object invoke(MethodInvocation mi) throws Throwable {
try {
return mi.proceed();
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
Method handlerMethod = getExceptionHandler(ex);
if (handlerMethod != null) {
//执行异常处理方法
invokeHandlerMethod(mi, ex, handlerMethod);
}
throw ex;
}
}
6.Java Spring框架源码分析-AOP-Spring_AOP源码分析总结的更多相关文章
- Spring框架IOC容器和AOP解析 非常 有用
Spring框架IOC容器和AOP解析 主要分析点: 一.Spring开源框架的简介 二.Spring下IOC容器和DI(依赖注入Dependency injection) 三.Spring下面 ...
- Java开发工程师(Web方向) - 04.Spring框架 - 第3章.AOP技术
第3章--AOP技术 Spring框架 - AOP概述 笔记https://my.oschina.net/hava/blog/758873Spring框架 - AOP使用 笔记https://my.o ...
- 吴裕雄--天生自然JAVA SPRING框架开发学习笔记:Spring使用AspectJ开发AOP基于XML和基于Annotation
AspectJ 是一个基于 Java 语言的 AOP 框架,它扩展了 Java 语言.Spring 2.0 以后,新增了对 AspectJ 方式的支持,新版本的 Spring 框架,建议使用 Aspe ...
- Spring 框架基础(04):AOP切面编程概念,几种实现方式演示
本文源码:GitHub·点这里 || GitEE·点这里 一.AOP基础简介 1.切面编程简介 AOP全称:Aspect Oriented Programming,面向切面编程.通过预编译方式和运行期 ...
- Spring框架IOC容器和AOP解析
主要分析点: 一.Spring开源框架的简介 二.Spring下IOC容器和DI(依赖注入Dependency injection) 三.Spring下面向切面编程(AOP)和事务管理配置 一.S ...
- Spring框架的基本使用(AOP部分)
AOP,Aspect Oriented Programming,意为面向切面编程,是通过预编译方式和运行期间动态代理实现程序功能的统一维护的一种技术.AOP采取横向抽取机制,取代了传统纵向继承体系重复 ...
- Spring框架(6)---AspectJ实现AOP
AspectJ实现AOP 上一篇文章Spring框架(4)---AOP讲解铺垫,讲了一些基础AOP理解性的东西,那么这篇文章真正开始讲解AOP 通过AspectJ实现AOP要比普通的实现Aop要方便的 ...
- Spring框架(四)AOP面向切面编程
一.前言 在以前的项目中,很少去关注spring aop的具体实现与理论,只是简单了解了一下什么是aop具体怎么用,看到了一篇博文写得还不错,就转载来学习一下,博文地址:http://www.cnbl ...
- 深入学习Spring框架(三)- AOP面向切面
1.什么是AOP? AOP为 Aspect Oriented Programming 的缩写,即面向切面编程, 通过预编译方式和运行期动态代理实现程序功能的统一维护的一种技术..AOP是OOP的延续, ...
- Spring框架之IoC和AOP
Spring框架简介: 2003年2月,Spring框架正式成为一个开源项目,并发布于SourceForge中.致力于Java EE应用的各种解决方案,而并不是仅仅专注于某一层的方案,是企业应用开发的 ...
随机推荐
- 探秘Transformer系列之(20)--- KV Cache
探秘Transformer系列之(20)--- KV Cache 目录 探秘Transformer系列之(20)--- KV Cache 0x00 概述 0x01 自回归推理的问题 1.1 请求的生命 ...
- 流式计算(四)-Flink Stream API 篇二
个人原创文章,禁止任何形式转载,否则追究法律责任! 本文只发表在"公众号"和"博客园",其他均属复制粘贴!如果觉得排版不清晰,请查看公众号文章. 话说看图看核心 ...
- java学习-8【EnumMap】
EnumMap和EnumSet几乎是一样的,区别时EnumMap的key时Enum. public enum Types { RED,GREEN,BLACK,YELLO } @Test public ...
- ubuntu16.04安装SQLite
主流的sqlite3,占用内存小,处理时速度快,跨平台. 几乎所有版本的 Linux 操作系统都附带 SQLite.所以,只要使用下面的命令来检查您的机器上是否已经安装了 SQLite. 一.检查是否 ...
- gRPC+Proto 实现键盘记录器 —— 深度实战解析
在当今的分布式系统开发领域,RPC(Remote Procedure Call,远程过程调用) 技术犹如一颗璀璨的明星,凭借其强大的透明性和卓越的高性能,在微服务架构中占据着举足轻重的地位.本文将全方 ...
- Unity资源打包之Asset Bundle
Asset Bundle的作用: 1.AssetBundle是一个压缩包包含模型.贴图.预制体.声音.甚至整个场景,可以在游戏运行的时候被加载: 2.AssetBundle自身保存着互相的依赖关系: ...
- Rider搭建C#开发环境
1.安装DotNet-SDK 下载链接:https://dotnet.microsoft.com/download 安装完成后配置环境变量,然后在cmd窗口运行:dotnet --info命令显示当前 ...
- 机器人操作系统ROS2之简介
什么是ROS2? ROS(机器人操作系统)是用于机器人应用的开源软件开发工具包.ROS 为各行业的开发者提供了一个标准的软件平台,帮助他们从研究和原型设计一直推进到部署和生产,从驱动程序到最先进的算法 ...
- macOS终端修改DNS
以WiFi为例 networksetup -listallnetworkservices networksetup -setdnsservers Wi-Fi 8.8.8.8 networksetup ...
- 备份一个有的时候,可能需要把其它exe或者dll包含在主程序中....
1.选中附件,右键生成操作选择 嵌入的资源,例如:handle.exe 2.FileUtil 1 using System.IO; 2 using System.Reflection; 3 4 na ...
