SciTech-Mathmatics-Probability+Statistics: Assumptions, $\large P-value$, $\large overall\ F-value$ and $\large Null\ and\ Alternative\ Hypothesis$ for $\large Linear\ Regression\ Model$
Null and Alternative Hypothesis for Linear Regression
Linear regression is a technique we can use to understand the relationship between one or more predictor variables and a response variable.
To determine if there is a statistically significant relationship between a single predictor variable and the response variable, or to determine if there is a \(\large jointly\) statistically significant relationship between all predictor variables and the response variable, we need to analyze the \(\large overall\ F-value\) of the model and the corresponding \(\large P-value\).
if the \(\large P-value\) is less than .05, we can reject the \(\large NH\).
Assumptions of Linear Regression
For the results of a LR(Linear Regression) model to be valid and reliable,
we need to check that the following four assumptions are met:
- Linear relationship: There exists a linear relationship between the independent variable, x, and the dependent variable, y.
- Independence: The residuals are independent. In particular, there is no correlation between consecutive residuals in time series data.
- Homoscedasticity: The residuals have constant variance at every level of x.
- Normality: The residuals of the model are normally distributed.
If one or more of these assumptions are violated, then the results of our linear regression may be unreliable or even misleading.
Refer to this post for:
- an explanation for each assumption,
- how to determine if the assumption is met,
- what to do if the assumption is violated.
Abbreviations
- \(\large SLR\) : \(\large Simple\ Linear\ Regression\)
- \(\large MLR\) : \(\large Multiple\ Linear\ Regression\)
- \(\large NH\) : \(\large Null\ Hypotheses\)
- \(\large AH\) : \(\large Alternative\ Hypotheses\)
- \(\large NAH\) : \(\large Null\ and\ Alternative\ Hypotheses\)
SLR(Simple Linear Regression)
If we only have one predictor variable and one response variable, we can use SLR(Simple Linear Regression), which uses the following formula to estimate the relationship between the variables:
\(\large \hat{y} = \beta_0+ \beta_1 x\)
where:
- \(\large \hat{y}\) : The estimated response value.
- \(\large \beta_0\) : The average value of \(\large y\) when \(\large x\) is \(\large zero\).
- \(\large \beta_1\) : The average change in \(\large y\) associated with a one unit increase in \(\large x\).
- \(\large x\) : The value of the predictor variable.
\(\large SLR\) uses the following \(\large NAH\):
- \(\large H_0: \beta_1 = 0\)
- \(\large H_A: \beta_1 \neq 0\)
The \(\large Null\ Hypotheses\) states that the coefficient \(\large \beta_1\) is equal to zero.
In other words, there is no statistically significant relationship between the predictor variable, \(\large x\), and the response variable, \(\large y\).The \(\large Alternative\ Hypotheses\) states that the coefficient \(\large \beta_1\) is not equal to zero. In other words, there is a statistically significant relationship between the predictor variable, \(\large x\), and the response variable, \(\large y\).
MLR(Multiple Linear Regression)
If we have multiple predictor variables and one response variable, we can use MLR(Multiple Linear Regression), which uses the following formula to estimate the relationship between the variables:
\(\large \hat{y} = \beta_0+ \beta_1 x_1 + \beta_2 x_2 + \cdots + \beta_k x_k\)
where:
- \(\large \hat{y}\) : The estimated response value.
- \(\large \beta_0\) : The average value of \(\large y\) when all predictor variables are equal to \(\large zero\).
- \(\large \beta_i\) : The average change in \(\large y\) associated with a one unit increase in \(\large x_i\).
- $\large x_i $ : The value of the predictor variable $\large x_i $.
\(\large MLR\) uses the following \(\large NAH\):
- \(\large H_0: \beta_1 = \beta_2 = \cdots = \beta_k = 0\)
- \(\large H_A: \beta_1 = \beta_2 = \cdots = \beta_k \neq 0\)
The \(\large NH\) states that all coefficients in the model are equal to zero.
In other words, none of the predictor variables $\large x_i $ have a statistically significant relationship with the response variable, \(\large y\).The \(\large alternative\ hypotheses\) states that not every coefficient is \(\large simultaneously\) equal to zero.
The following examples show how to decide to reject or fail to reject the \(\large NH\) in \(\large \text{ both }SLR \text{ and }MLR\) models.
Example 1: SLR(Simple Linear Regression)
Suppose a professor would like to use the number of hours studied to predict the exam score that students will receive in his class. He collects data for 20 students and fits a simple linear regression model.
The following screenshot shows the output of the regression model:
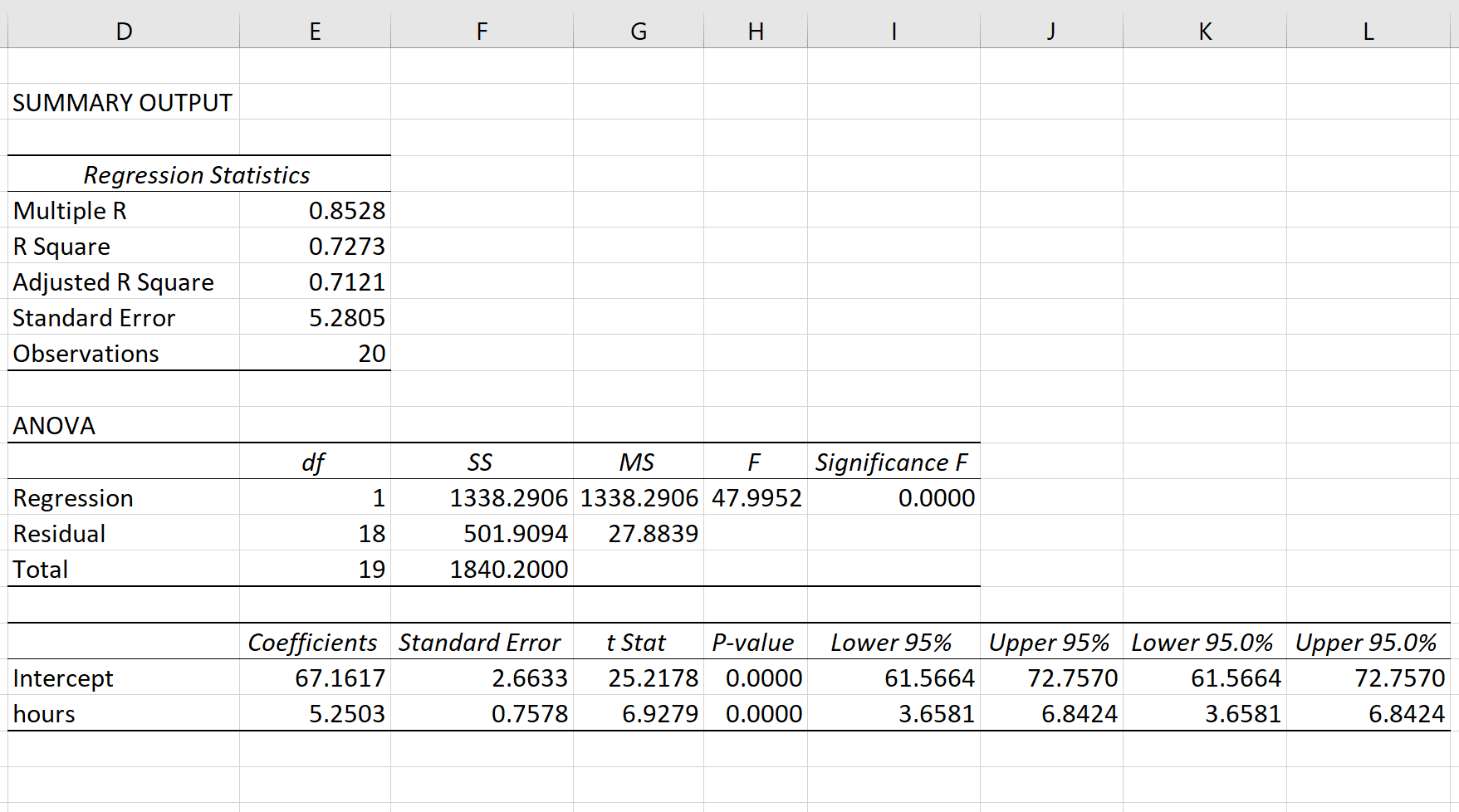
The fitted \(\large SLR\) model is:
$ Exam\ Score = 67.1617 + 5.2503*(hours\ studied)$
To determine if there is a statistically significant relationship between hours studied and exam score, we need to analyze the \(\large overall\ F-value\) of the model and the corresponding \(\large P-value\):
- \(\large Overall\ F-Value\) : 47.9952
- \(\large P-value\) : 0.000
Since this \(\large P-value\) is less than .05, we can reject the \(\large NH\).
In other words, there is a statistically significant relationship between hours studied and exam score received.
Example 2: MLR(Multiple Linear Regression)
Suppose a professor would like to use the number of hours studied and the number of prep exams taken to predict the exam score that students will receive in his class. He collects data for 20 students and fits a multiple linear regression model.
The following screenshot shows the output of the regression model(\(\large MLR\) output in Excel):
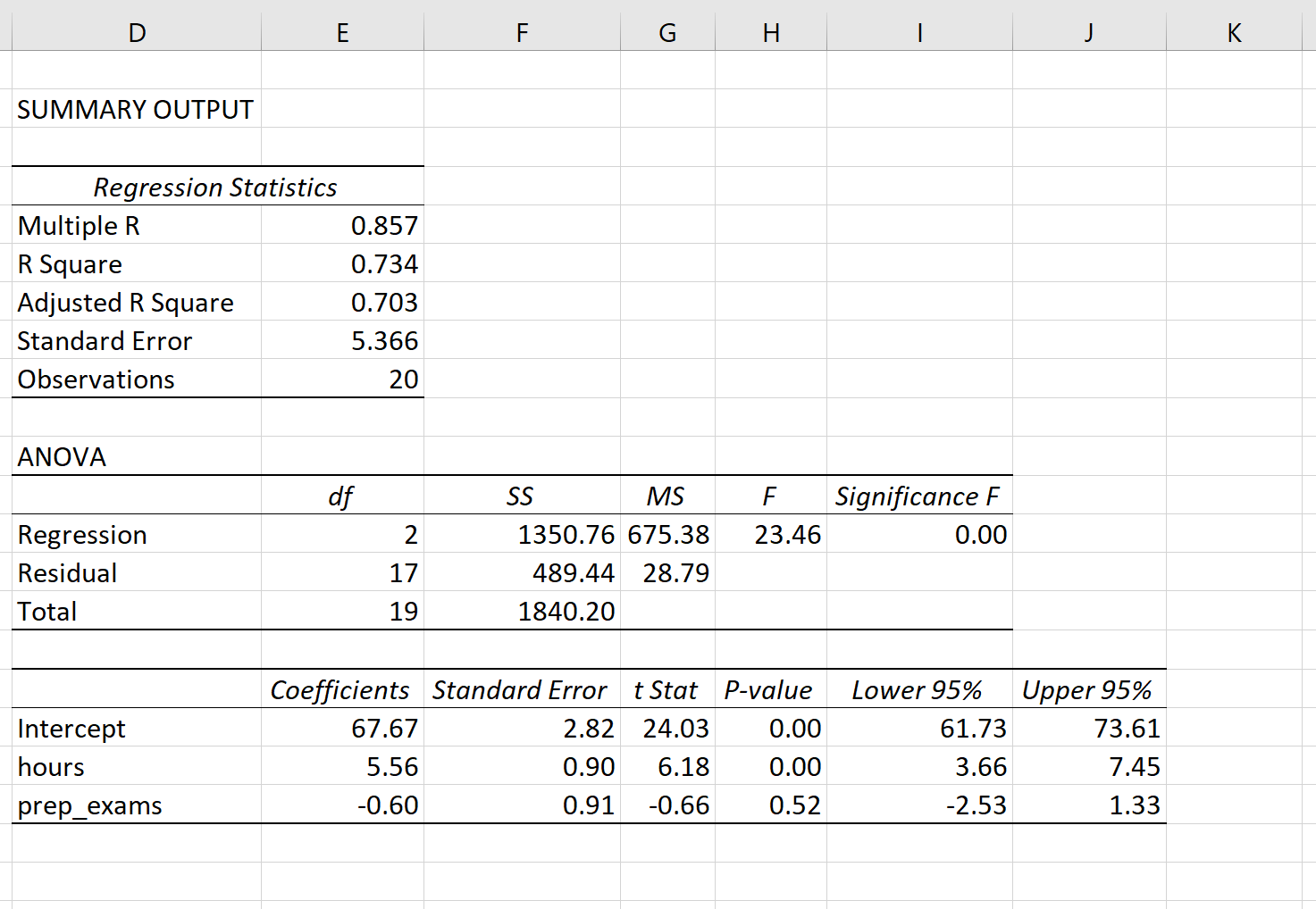
The fitted \(\large MLR\) model is:
\(Exam\ Score = 67.67 + 5.56*(hours\ studied) – 0.60*(prep\ exams\ taken)\)
To determine if there is a \(\large jointly\) statistically significant relationship between the two predictor variables and the response variable, we need to analyze the \(\large Overall\ F-Value\) of the model and the corresponding \(\large P-value\):
- \(\large Overall\ F-Value\) : 23.46
- \(\large P-value\) : 0.00
Since this \(\large P-value\) is less than .05, we can reject the \(\large NH\).
In other words, hours studied and prep exams taken have a jointly statistically significant relationship with exam score.
Note: Although the \(\large P-value\) for prep exams taken (p = 0.52) is not significant, prep exams combined with hours studied has a significant relationship with exam score.
Additional Resources
Understanding the F-Test of Overall Significance in Regression
How to Read and Interpret a Regression Table
How to Report Regression Results
How to Perform Simple Linear Regression in Excel
How to Perform Multiple Linear Regression in Excel
随机推荐
- 打造企业级AI文案助手:GPT-J+Flask全栈开发实战
一.智能文案革命的序幕:为什么需要AI文案助手? 在数字化营销时代,内容生产效率成为企业核心竞争力.据统计,营销人员平均每天需要撰写3.2篇文案,而传统人工创作存在三大痛点: 效率瓶颈:创意构思到成文 ...
- 11.7K Star!这个分布式爬虫管理平台让多语言协作如此简单!
嗨,大家好,我是小华同学,关注我们获得"最新.最全.最优质"开源项目和高效工作学习方法 分布式爬虫管理平台Crawlab,支持任何编程语言和框架的爬虫管理,提供可视化界面.任务调度 ...
- centos6分区要点
安装centos6系统时,为了以后能够扩展存储,分区时要注意几点: 1.boot引导分区要选固定分区类型存储,大小是500M 2.其余分区全部做成物理卷lvm pyshiic类型存储 3.在这个物理 ...
- layUI批量上传文件
<div class="layui-form-item"> <label class="layui-form-label febs-form-item- ...
- K8s进阶之外部访问Pod的几种方式
概述 K8s集群内部的Pod默认是不对外提供访问,只能在集群内部进行访问.这样做是为什么呢? 安全性考虑 Kubernetes设计时遵循最小权限原则,即组件仅获得完成其任务所需的最少权限.直接暴露Po ...
- 深度探索C++对象模型--读书笔记
深度探索C++对象模型 第一章:关于对象 封装之后的布局成本 C++在布局以及存取时间上主要的额外负担是由virtual引起 1.VIrtual function机制:用以支持一个有效率的" ...
- Seata源码—5.全局事务的创建与返回处理
大纲 1.Seata开启分布式事务的流程总结 2.Seata生成全局事务ID的雪花算法源码 3.生成xid以及对全局事务会话进行持久化的源码 4.全局事务会话数据持久化的实现源码 5.Seata Se ...
- PyYaml简单学习
YAML是一种轻型的配置文件的语言,远比JSON格式方便,方便人类读写,它通过缩进来表示结构,很具有Python风格. 安装:pip insall pyyaml YAML语法 文档 YAML数据流是0 ...
- 5 easybr指纹浏览器内存修改教程
目的 navigator.deviceMemory可以暴露设备的物理内存和运行状态,被用于设备唯一性识别或判断设备等级. 通过伪造这类信息,可以增强防关联.防追踪能力. easybr指纹浏览器提供演示 ...
- unbuntu离线部署K8S集群
环境准备和服务器规划部署前提已知条件: 环境准备与服务器规划总表 类别 配置项 详细信息 操作系统 版本 Ubuntu 25.04(所有节点) 容器运行时 Docker 版本 Docker 24.0. ...
