struts原理图
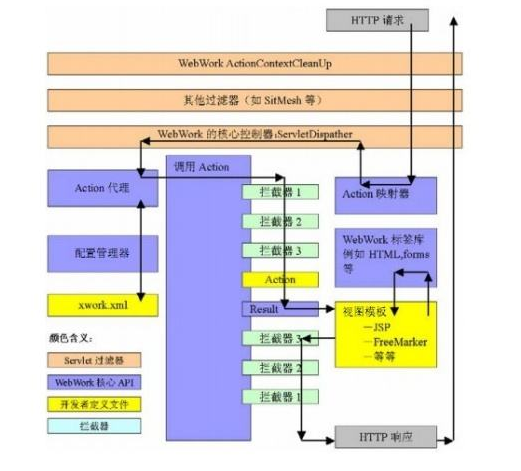

n the diagram, an initial request goes to the Servlet container (such as Jetty or Resin) which is passed through a standard filter chain. The chain includes the (optional) ActionContextCleanUp filter, which is useful when integrating technologies such as SiteMesh Plugin. Next, the required FilterDispatcher is called, which in turn consults the ActionMapper to determine if the request should invoke an action.
If the ActionMapper determines that an Action should be invoked, the FilterDispatcher delegates control to the ActionProxy. The ActionProxy consults the framework Configuration Files manager (initialized from the struts.xml file). Next, the ActionProxy creates an ActionInvocation, which is responsible for the command pattern implementation. This includes invoking any Interceptors (the before clause) in advance of invoking the Action itself.
Once the Action returns, the ActionInvocation is responsible for looking up the proper result associated with the Action result code mapped in struts.xml. The result is then executed, which often (but not always, as is the case for Action Chaining) involves a template written in JSP or FreeMarker to be rendered. While rendering, the templates can use the Struts Tags provided by the framework. Some of those components will work with the ActionMapper to render proper URLs for additional requests.
All objects in this architecture (Actions, Results, Interceptors, and so forth) are created by an ObjectFactory. This ObjectFactory is pluggable. We can provide our own ObjectFactory for any reason that requires knowing when objects in the framework are created. A popular ObjectFactory implementation uses Spring as provided by the Spring Plugin.
Interceptors are executed again (in reverse order, calling the after clause). Finally, the response returns through the filters configured in the web.xml. If the ActionContextCleanUp filter is present, the FilterDispatcher will not clean up the ThreadLocal ActionContext. If the ActionContextCleanUp filter is not present, the FilterDispatcher will cleanup all ThreadLocals.
struts原理图的更多相关文章
- 4.Struts2转向类型详解
struts2中提供了多种视图转向类型,类型由type属性指定,如: dispatcher:请求转发(默认值) redirect:重定向到页面 redirectAction:重定向到Action pl ...
- 最佳新秀SSH十六Struts2它是如何工作的内部
前面说完了Spring.Hibernate,非常自然今天轮到struts了.struts的核心原理就是通过拦截器来处理client的请求,经过拦截器一系列的处理后,再交给Action.以下先看看str ...
- 菜鸟学SSH(十六)——Struts2内部是如何工作的
前面说完了Spring.Hibernate,很自然今天轮到struts了.struts的核心原理就是通过拦截器来处理客户端的请求,经过拦截器一系列的处理后,再交给Action.下面先看看struts官 ...
- 轻量级Java EE开发框架设计系统应用架构
首先来说一下Java EE 概述 其中常说的三大框架即是:ssh Spring:功能强大的组件粘合济,能够将你的所有的java功能模块用配置文件的方式组合起来(还让你感觉不到spring的存在)成为一 ...
- Struts 2.3.24源码解析+Struts2拦截参数,处理请求,返回到前台过程详析
Struts2官网:http://struts.apache.org/ 目前最新版本:Struts 2.3.24 Struts1已经完全被淘汰了,而Struts2是借鉴了webwork的设计理念而设计 ...
- Struts 2知识回顾----拦截器(Intercept)总结
什么是Struts 2拦截器? 从软件构架上来说,拦截器是实现了面向方面编程的组件.它将影响了多个业务对象的公共行为封装到一个个可重用的模块,减少了系统的重复代码,实现功能的高度内聚,确保了业务对象的 ...
- Java Web编程的主要组件技术——Struts入门
参考书籍:<J2EE开源编程精要15讲> Struts是一个开源的Java Web框架,很好地实现了MVC设计模式.通过一个配置文件,把各个层面的应用组件联系起来,使组件在程序层面联系较少 ...
- Struts面试笔记
Struts2面试题1.struts2工作流程Struts 2框架本身大致可以分为3个部分:核心控制器FilterDispatcher.业务控制器Action和用户实现的企业业务逻辑组件. 核心控制器 ...
- struts详细解释拦截器
1.拦截器:Struts2拦截器将一个Action要么Action的方法.之前或截取后场,和Struts2拦截器是可插拔,拦截器AOP一种实现. WebWork:拦截器是动态拦截Action调用的对象 ...
随机推荐
- python——前端常用的标签
1.meat标签 meta标签的使用 meta标签共有两个属性:http-equiv和name;不同的属性又有不同的参数值,这些不同的参数值就实现了不同的网页功能. name属性 name属性主要用于 ...
- es6基础(5)--数值扩展
{ //Number.isFinite数字是有尽的 console.log(Number.isFinite(15));//true console.log(Number.isFinite(NaN)); ...
- url后面带斜杠与不带斜杠的区别
比如: https://www.baidu.com/test/ https://www.baidu.com/test 当Web服务器接收到对某个末尾不含斜杠的url请求时,例如https://www. ...
- python学习之----正则表达式
- 利用Python实现FGO自动战斗脚本,再也不用爆肝啦~
Fate/Grand Order(非的肝不过欧的)作为索尼为了拯救自己不倒闭而开发的面向月厨的骗氪养成抽卡爆肝游戏,居然没有像隔壁<阴阳师>的自动战斗系统(看看别人现在都自带脚本了).毕竟 ...
- 零基础学习python_pickle(31课)
上次我提到了对文件的读写等一系列操作,回想下,要想从文件内读取内容无论是read还是readline,读取出来的是不是都是字符串呢?那么如果想让字典.列表这些数据类型保存进文件到读取出来都是原来的类型 ...
- c#序列化Json和反序列化
1.首先确保程序集中添加了 System.Web.Extensions DLL引用 2.代码中添加命名空间:using System.Web.Script.Serialization; nam ...
- tensorflow实战系列(三)一个完整的例子
#!/usr/bin/env python2# -*- coding: utf-8 -*-"""Created on Wed Jan 18 08:42:55 2017 @ ...
- 前后台交互实现点击超链接通过指定的 url 去网络或者文件服务器下载文件
前台 VUE 界面: <el-table-column prop="attachment" align="center" label="附件详情 ...
- python中Strip()函数的用法
Python strip() 方法用于移除字符串头尾指定的字符(默认为空格或换行符)或字符序列. 注意:该方法只能删除开头或是结尾的字符,不能删除中间部分的字符. str.strip([chars]) ...
