UVALive - 4223,hdu2962(简单dijkstra)
Trucking
Time Limit: 20000/10000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 11419 Accepted Submission(s): 1101
For the given cargo truck, maximizing the height of the goods transported is equivalent to maximizing the amount of goods transported. For safety reasons, there is a certain height limit for the cargo truck which cannot be exceeded.
1 2 7 5
1 3 4 2
2 4 -1 10
2 5 2 4
3 4 10 1
4 5 8 5
1 5 10
5 6
1 2 7 5
1 3 4 2
2 4 -1 10
2 5 2 4
3 4 10 1
4 5 8 5
1 5 4
3 1
1 2 -1 100
1 3 10
0 0
maximum height = 7
length of shortest route = 20
Case 2:
maximum height = 4
length of shortest route = 8
Case 3:
cannot reach destination
题意:有c个城市,r条连接两个不同城市的道路,每条道路都有长度和限制货物的最大高度,货物的高度越高
则能运输的货物越多,所以商人老板想从城市a到城市能运输货物的高度最大可以是多少,当高度最大时,要走的路程总长最短是多少。
输入给出 c 和 r 的大小,接下来有 r 行代表着每条道路的信息,每一行给出相连的城市a,b,道路限制的最大高度(-1代表高度不受限制),道路的长度,道路是双向的。
最后一行给出出发城市,目的城市,货物能到达的初始最大高度。
思路:简单的dijkstra的运用,先用此算法求出能运输的最大高度,再以求出的最大高度为限制求出要走的最短路程。但是要注意不能同时求最大高度和最段路径,
因为当你求出一个点的最大高度和最短路程时,你不能以该点的最段路程来退出它后面点的最短路程,因为加设你当前求出的最大高度为h,最短路径为l,那么如果它连接下一个点的道路的限制小于你当前的最大高度时,你就不能保证下一个点的最短路径是最短的
看下图就知道了
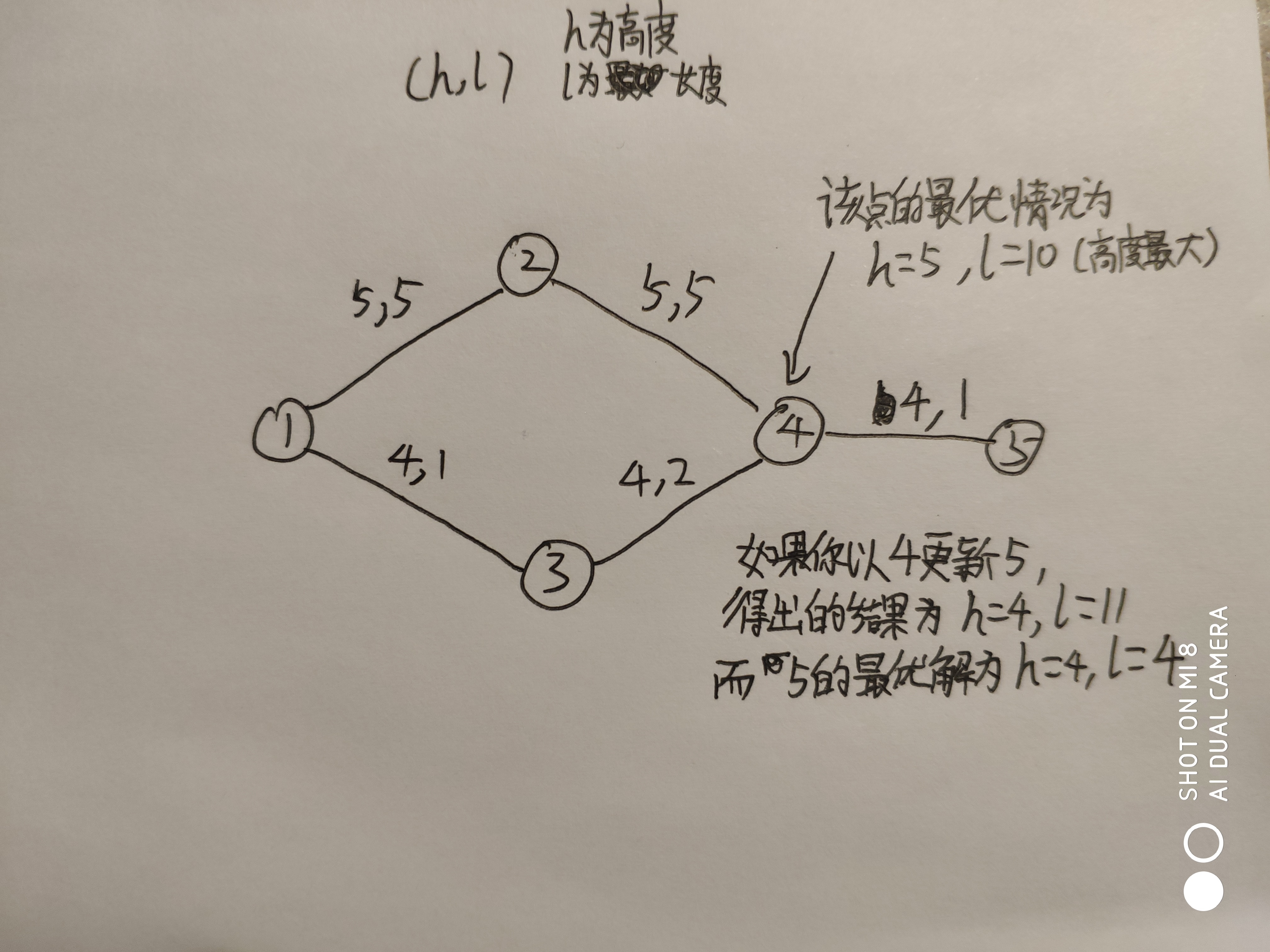
代码
#include<cstdio>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
#define INF 0x3fffffff
using namespace std;
struct st{
int h,l;
}mp[1010][1010];
st dis[1010];
int vt[1010];
int n,m,nb;
int a2,b2,h2;
int dij(){
int i,j,k;
int mx,mn;
int h;
int c,d,a1;
for(i=1;i<=n;i++){//初始化
dis[i].l=INF;
dis[i].h=-1;
}
dis[a2].l=0;//初始化开始点
dis[a2].h=h2;
k=a2;
while(k!=-1){//求高度
vt[k]=1;
mx=0;//高度
for(i=1;i<=n;i++){
if(!vt[i]&&mp[k][i].l!=-1){
if(dis[i].h<(min(mp[k][i].h,dis[k].h))){//更新每个点的最大高度
dis[i].h=min(mp[k][i].h,dis[k].h); }
}
}
k=-1;
for(i=1;i<=n;i++){
if(!vt[i]){//找出当前高度最大的点 重复操作
if(dis[i].h>mx){
mx=dis[i].h;
k=i;
}
}
} }
h=dis[b2].h;//最大高度
k=a2;
//printf("ww%d\n",h);
memset(vt,0,sizeof(vt));
while(k!=-1){//求最短路径
vt[k]=1;
mn=INF;//长度
for(i=1;i<=n;i++){
if(!vt[i]&&mp[k][i].l!=-1&&mp[k][i].h>=h){//限制条件
dis[i].l=min(dis[i].l,mp[k][i].l+dis[k].l);//更新路径长度
}
}
k=-1;
for(i=1;i<=n;i++){//找出当前路径最小的点
if(!vt[i]){
if(mn>dis[i].l){
mn=dis[i].l;
k=i;
}
}
}
} if(nb>1)
printf("\n");
printf("Case %d:\n",nb);
if(dis[b2].l==INF)//如果不能走到目的城市
printf("cannot reach destination\n");
else
printf("maximum height = %d\nlength of shortest route = %d\n",dis[b2].h,dis[b2].l);
return 0;
}
int main(){
int i,j,l;
int lg=0;
nb=0;
while(scanf("%d%d",&n,&m)&&n){
memset(mp,-1,sizeof(mp));//初始化
memset(vt,0,sizeof(vt));
for(i=0;i<m;i++){
scanf("%d%d%d%d",&a2,&b2,&h2,&l);//输入这条道路相连的两个城市,道路的限制高度,道路的长度
if(h2==-1)
h2=INF;
mp[a2][b2].h=h2;
mp[a2][b2].l=l;
mp[b2][a2]=mp[a2][b2];
}
scanf("%d%d%d",&a2,&b2,&h2);//输入出发城市,目的城市,限制的最大高度
nb++;
dij();
}
return 0;
}
A certain local trucking company would like to transport some goods on a cargo truck from one place to another. It is desirable to transport as much goods as possible each trip. Unfortunately, one cannot always use the roads in the shortest route: some roads may have obstacles (e.g. bridge overpass, tunnels) which limit heights of the goods transported. Therefore, the company would like to transport as much as possible each trip, and then choose the shortest route that can be used to transport that amount. For the given cargo truck, maximizing the height of the goods transported is equivalent to maximizing the amount of goods transported. For safety reasons, there is a certain height limit for the cargo truck which cannot be exceeded. Input The input consists of a number of cases. Each case starts with two integers, separated by a space, on a line. These two integers are the number of cities (C) and the number of roads (R). There are at most 1000 cities, numbered from 1. This is followed by R lines each containing the city numbers of the cities connected by that road, the maximum height allowed on that road, and the length of that road. The maximum height for each road is a positive integer, except that a height of ‘-1’ indicates that there is no height limit on that road. The length of each road is a positive integer at most 1000. Every road can be travelled in both directions, and there is at most one road connecting each distinct pair of cities. Finally, the last line of each case consists of the start and end city numbers, as well as the height limit (a positive integer) of the cargo truck. The input terminates when C = R = 0. Output For each case, print the case number followed by the maximum height of the cargo truck allowed and the length of the shortest route. Use the format as shown in the sample output. If it is not possible to reach the end city from the start city, print ‘cannot reach destination’ after the case number. Print a blank line between the output of the cases. Sample Input 5 6 1 2 7 5 1 3 4 2 2 4 -1 10 2 5 2 4 3 4 10 1 4 5 8 5 1 5 10 5 6 1 2 7 5 1 3 4 2 2 4 -1 10 2 5 2 4 3 4 10 1 4 5 8 5 1 5 4 3 1 1 2 -1 100 1 3 10 0 0 Sample Output Case 1: maximum height = 7 length of shortest route = 20 Case 2: maximum height = 4 length of shortest route = 8 Case 3: cannot reach destination
UVALive - 4223,hdu2962(简单dijkstra)的更多相关文章
- 二分+最短路 UVALive - 4223
题目链接:https://vjudge.net/contest/244167#problem/E 这题做了好久都还是超时,看了博客才发现可以用二分+最短路(dijkstra和spfa都可以),也可以用 ...
- UVALive 4223 Trucking 二分+spfa
Trucking 题目连接: https://icpcarchive.ecs.baylor.edu/index.php?option=com_onlinejudge&Itemid=8& ...
- UVALive - 4223(hdu 2926)
---恢复内容开始--- 题目链接:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=2962 Trucking Time Limit: 20000/10000 MS ...
- Fight Against Traffic -简单dijkstra算法使用
题目链接 http://codeforces.com/contest/954/problem/D 题目大意 n m s t 分别为点的个数, 边的个数,以及两个特殊的点 要求s与t间的距离在新增一条边 ...
- UVaLive 4256 Salesmen (简单DP)
题意:给一个无向连通图,和一个序列,修改尽量少的数,使得相邻两个数要么相等,要么相邻. 析:dp[i][j] 表示第 i 个数改成 j 时满足条件.然后就很容易了. 代码如下: #pragma com ...
- UVALive 4223 / HDU 2962 spfa + 二分
Trucking Problem Description A certain local trucking company would like to transport some goods on ...
- UVALive 6486 Skyscrapers 简单动态规划
题意: 有N个格子排成一排,在每个格子里填上1到N的数(每个只能填一次),分别代表每个格子的高度.现在给你两个数left和right,分别表示从左往右看,和从右往左看,能看到的格子数.问有多少种情况. ...
- 图论基础之Dijkstra算法的初探
图论,顾名思义就是有图有论. 图:由点"Vertex"和边"Edge "组成,且图分为有向图和无向图(本文讨论有向图),之前做毕业设计的 ...
- 一些简单二分题,简单的hash,H(i),字符串题
说在前面: 题是乱七八糟的. 几个二分的题. (但是我的做法不一定是二分,有些裸暴力. 1. Equations HDU - 1496 输入a,b,c,d问你这个方程有多少解.a*x1^2+b*x2^ ...
随机推荐
- 配置 ROS 的 apt 源
配置 ROS 的 apt 源 ROS的apt源有官方源.国内 USTC 源或新加坡源可供选择, 选择其一就可以了,建议使用国内 USTC 源或新加坡源,安装速度会快很多. 方式一:官方源 $ sudo ...
- javascript:void(0) 和 href="#"的区别
<a href="javascript:void(0);">点击 <a href="#">点击 如果使用下面一种方式,会跳到网页顶部. ...
- Linux基础命令---lpq查看打印队列
lpq lpq指令用来显示当前打印队列的状态.如果命令行中没有指定打印机或类,则将显示默认目标上排队的作业. 此命令的适用范围:RedHat.RHEL.Ubuntu.CentOS.Fedora.ope ...
- vue解决启动报错cjs loader.js Error: Cannot find module '../config'问题
vue解决启动报错cjs loader.js Error: Cannot find module '../config'问题 今天下载了一个开源项目一直运行不了,折腾了半天才找到问题所在,config ...
- es6 复制对象
var pp = {'name': '1','work': 'teacher'} var kk = [1,2] var tt = [] for(let index = 0; index<kk.l ...
- kafka消费者实时消费数据存入hdfs java scalca 代码
hadoop-client依赖很乱 调试很多次cdh版本好多jar没有 用hadoop2.7.3可以 自定义输出流的池子进行流管理 public void writeLog2HDFS(String p ...
- springmvc学习路线1-基本配置
1.第一个springmvc实例helloword 关键点拨 1.1 web.xml文件的配置 <servlet> <servlet-name>springMVC</se ...
- idea软件快速设置主题颜色
打开idea,然后在File->setting->在搜索框里面输入theme->然后点击appearance->将theme的主题设置为IntellilJ,然后就可以了,如下图 ...
- 复习-css边框和背景属性
css边框和背景属性 border:所有边框属性 border-width:四条边框的宽度 border-style:设置边框样式,主要有dotted.solid.double border-colo ...
- go 编译:交叉编译&编译执行过程
1. 交叉编译 编译Windows程序和mac程序 GOOS=windows GOARCH-amd64 go build main.go 转自:https://www.cnblogs.com/mafe ...
