chapter2 线性回归实现
1 导入包
import numpy as np
2 初始化模型参数
### 初始化模型参数
def initialize_params(dims):
w = np.zeros((dims, 1))
b = 0
return w, b
3 损失函数计算
### 包括线性回归公式、均方损失和参数偏导三部分
def linear_loss(X, y, w, b):
num_train = X.shape[0]
y_hat = np.dot(X, w) + b
# 计算预测输出与实际标签之间的均方损失
loss = np.sum((y_hat-y)**2)/num_train
# 基于均方损失对权重参数的一阶偏导数
dw = 2*np.dot(X.T, (y_hat-y)) /num_train
# 基于均方损失对偏差项的一阶偏导数
db = 2*np.sum((y_hat-y)) /num_train
return y_hat, loss, dw, db
4 定义线性回归模型训练过程
### 定义线性回归模型训练过程
def linear_train(X, y, learning_rate=0.01, epochs=10000):
loss_his = []
# 初始化模型参数
w, b = initialize_params(X.shape[1])
for i in range(1, epochs):
# 计算当前迭代的预测值、损失和梯度
y_hat, loss, dw, db = linear_loss(X, y, w, b)
# 基于梯度下降的参数更新
w += -learning_rate * dw
b += -learning_rate * db
# 记录当前迭代的损失
loss_his.append(loss)
# 每1000次迭代打印当前损失信息
if i % 10000 == 0:
print('epoch %d loss %f' % (i, loss))
params = {
'w': w,
'b': b
}
grads = {
'dw': dw,
'db': db
}
return loss_his, params, grads
5 导入数据集并划分数据集
from sklearn.datasets import load_diabetes
from sklearn.utils import shuffle
diabetes = load_diabetes()
data, target = diabetes.data, diabetes.target
X, y = shuffle(data, target, random_state=13)
# 按照8/2划分训练集和测试集
offset = int(X.shape[0] * 0.8)
X_train, y_train = X[:offset], y[:offset].reshape((-1,1))
X_test, y_test = X[offset:], y[offset:].reshape((-1,1))
# 打印训练集和测试集维度
print("X_train's shape: ", X_train.shape)
print("X_test's shape: ", X_test.shape)
print("y_train's shape: ", y_train.shape)
print("y_test's shape: ", y_test.shape)
结果:
X_train's shape: (353, 10)
X_test's shape: (89, 10)
y_train's shape: (353, 1)
y_test's shape: (89, 1)
6 线性回归模型训练
# 线性回归模型训练
loss_his, params, grads = linear_train(X_train, y_train, 0.01, 200000)
# 打印训练后得到模型参数
print(params)
结果:
epoch 10000 loss 3219.178670
epoch 20000 loss 2944.940452
epoch 30000 loss 2848.052938
epoch 40000 loss 2806.628090
epoch 50000 loss 2788.051589
epoch 60000 loss 2779.411239
epoch 70000 loss 2775.230777
epoch 80000 loss 2773.107175
epoch 90000 loss 2771.957481
epoch 100000 loss 2771.281723
epoch 110000 loss 2770.843500
epoch 120000 loss 2770.528226
epoch 130000 loss 2770.278899
epoch 140000 loss 2770.066388
epoch 150000 loss 2769.875394
epoch 160000 loss 2769.697658
epoch 170000 loss 2769.528602
epoch 180000 loss 2769.365613
epoch 190000 loss 2769.207165
{'w': array([[ 9.84972769],
[-240.38803204],
[ 491.45462983],
[ 298.20492926],
[ -87.77291402],
[ -98.36201742],
[-186.17374049],
[ 177.38726503],
[ 424.17405761],
[ 52.48952427]]), 'b': 150.8136201371859}
7 定义线性回归预测函数
### 定义线性回归预测函数
def predict(X, params):
w = params['w']
b = params['b']
y_pred = np.dot(X, w) + b
return y_pred
y_pred = predict(X_test, params)
8 定义R2系数函数
### 定义R2系数函数
def r2_score(y_test, y_pred):
# 测试标签均值
y_avg = np.mean(y_test)
# 总离差平方和
ss_tot = np.sum((y_test - y_avg)**2)
# 残差平方和
ss_res = np.sum((y_test - y_pred)**2)
# R2计算
r2 = 1 - (ss_res/ss_tot)
return r2
print(r2_score(y_test, y_pred))
结果:
0.5349331079250876
9 可视化
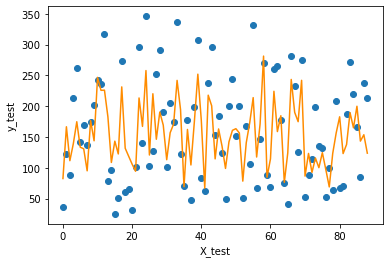
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
f = X_test.dot(params['w']) + params['b'] plt.scatter(range(X_test.shape[0]), y_test)
plt.plot(f, color = 'darkorange')
plt.xlabel('X_test')
plt.ylabel('y_test')
plt.show();
结果:
plt.plot(loss_his, color = 'blue')
plt.xlabel('epochs')
plt.ylabel('loss')
plt.show()
结果:

10 手写交叉验证
from sklearn.utils import shuffle
X, y = shuffle(data, target, random_state=13)
X = X.astype(np.float32)
data = np.concatenate((X, y.reshape((-1,1))), axis=1)
data.shape
结果:
(442, 11)
from random import shuffle
def k_fold_cross_validation(items, k, randomize=True):
if randomize:
items = list(items)
shuffle(items)
slices = [items[i::k] for i in range(k)]
for i in range(k):
validation = slices[i]
training = [item
for s in slices if s is not validation
for item in s]
training = np.array(training)
validation = np.array(validation)
yield training, validation
for training, validation in k_fold_cross_validation(data, 5):
X_train = training[:, :10]
y_train = training[:, -1].reshape((-1,1))
X_valid = validation[:, :10]
y_valid = validation[:, -1].reshape((-1,1))
loss5 = []
#print(X_train.shape, y_train.shape, X_valid.shape, y_valid.shape)
loss, params, grads = linear_train(X_train, y_train, 0.001, 100000)
loss5.append(loss)
score = np.mean(loss5)
print('five kold cross validation score is', score)
y_pred = predict(X_valid, params)
valid_score = np.sum(((y_pred-y_valid)**2))/len(X_valid)
print('valid score is', valid_score)
结果:
epoch 10000 loss 5092.953795
epoch 20000 loss 4625.210998
epoch 30000 loss 4280.106579
epoch 40000 loss 4021.857859
epoch 50000 loss 3825.526402
epoch 60000 loss 3673.689068
epoch 70000 loss 3554.135457
epoch 80000 loss 3458.274820
epoch 90000 loss 3380.033392
five kold cross validation score is 4095.209897465298
valid score is 3936.2234811935696
epoch 10000 loss 5583.270165
epoch 20000 loss 5048.748757
epoch 30000 loss 4655.620298
epoch 40000 loss 4362.817211
epoch 50000 loss 4141.575958
epoch 60000 loss 3971.714077
epoch 70000 loss 3839.037331
epoch 80000 loss 3733.533571
epoch 90000 loss 3648.114252
five kold cross validation score is 4447.019807745928
valid score is 2501.3520150018944
epoch 10000 loss 5200.950784
epoch 20000 loss 4730.397070
epoch 30000 loss 4382.133800
epoch 40000 loss 4120.944891
epoch 50000 loss 3922.113137
epoch 60000 loss 3768.255158
epoch 70000 loss 3647.113946
epoch 80000 loss 3550.018924
epoch 90000 loss 3470.811373
five kold cross validation score is 4191.91819552402
valid score is 3599.5500530218555
epoch 10000 loss 5392.825769
epoch 20000 loss 4859.145634
epoch 30000 loss 4465.914858
epoch 40000 loss 4172.706513
epoch 50000 loss 3951.112149
epoch 60000 loss 3781.128244
epoch 70000 loss 3648.633504
epoch 80000 loss 3543.627226
epoch 90000 loss 3458.998687
five kold cross validation score is 4256.231602795183
valid score is 3306.6604398106706
epoch 10000 loss 4991.290783
epoch 20000 loss 4547.454621
epoch 30000 loss 4219.702158
epoch 40000 loss 3974.018034
epoch 50000 loss 3786.721727
epoch 60000 loss 3641.292905
epoch 70000 loss 3526.175261
epoch 80000 loss 3433.256913
epoch 90000 loss 3356.818661
five kold cross validation score is 4043.189167421097
valid score is 4220.025355059865
11 导入数据集
from sklearn.datasets import load_diabetes
from sklearn.utils import shuffle
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split diabetes = load_diabetes()
data = diabetes.data
target = diabetes.target
X, y = shuffle(data, target, random_state=13)
X = X.astype(np.float32)
y = y.reshape((-1, 1))
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=42)
print(X_train.shape, y_train.shape, X_test.shape, y_test.shape)
结果:
(353, 10) (353, 1) (89, 10) (89, 1)
11 sklearn实现,并可视化
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
from sklearn import linear_model
from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error, r2_score
regr = linear_model.LinearRegression()
regr.fit(X_train, y_train)
y_pred = regr.predict(X_test)
# The coefficients
print('Coefficients: \n', regr.coef_)
# The mean squared error
print("Mean squared error: %.2f"
% mean_squared_error(y_test, y_pred))
# Explained variance score: 1 is perfect prediction
print('Variance score: %.2f' % r2_score(y_test, y_pred))
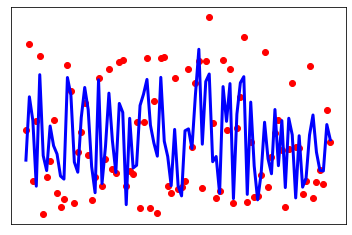
print(r2_score(y_test, y_pred)) # Plot outputs
plt.scatter(range(X_test.shape[0]), y_test, color='red')
plt.plot(range(X_test.shape[0]), y_pred, color='blue', linewidth=3)
plt.xticks(())
plt.yticks(())
plt.show();
结果:
Coefficients:
[[ -23.51037 -216.31213 472.36694 372.07175 -863.6967 583.2741
105.79268 194.76984 754.073 38.2222 ]]
Mean squared error: 3028.50
Variance score: 0.53
0.5298198993375712
12 交叉验证
from sklearn.model_selection import KFold
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
### 交叉验证
def cross_validate(model, x, y, folds=5, repeats=5):
ypred = np.zeros((len(y),repeats))
score = np.zeros(repeats)
for r in range(repeats):
i=0
print('Cross Validating - Run', str(r + 1), 'out of', str(repeats))
x,y = shuffle(x, y, random_state=r) #shuffle data before each repeat
kf = KFold(n_splits=folds,random_state=i+1000,shuffle=True) #random split, different each time
for train_ind, test_ind in kf.split(x):
print('Fold', i+1, 'out of', folds)
xtrain,ytrain = x[train_ind,:],y[train_ind]
xtest,ytest = x[test_ind,:],y[test_ind]
model.fit(xtrain, ytrain)
#print(xtrain.shape, ytrain.shape, xtest.shape, ytest.shape)
ypred[test_ind]=model.predict(xtest)
i+=1
score[r] = r2_score(ypred[:,r],y)
print('\nOverall R2:',str(score))
print('Mean:',str(np.mean(score)))
print('Deviation:',str(np.std(score)))
pass cross_validate(regr, X, y, folds=5, repeats=5)
结果:
Cross Validating - Run 1 out of 5
Fold 1 out of 5
Fold 2 out of 5
Fold 3 out of 5
Fold 4 out of 5
Fold 5 out of 5
Cross Validating - Run 2 out of 5
Fold 1 out of 5
Fold 2 out of 5
Fold 3 out of 5
Fold 4 out of 5
Fold 5 out of 5
Cross Validating - Run 3 out of 5
Fold 1 out of 5
Fold 2 out of 5
Fold 3 out of 5
Fold 4 out of 5
Fold 5 out of 5
Cross Validating - Run 4 out of 5
Fold 1 out of 5
Fold 2 out of 5
Fold 3 out of 5
Fold 4 out of 5
Fold 5 out of 5
Cross Validating - Run 5 out of 5
Fold 1 out of 5
Fold 2 out of 5
Fold 3 out of 5
Fold 4 out of 5
Fold 5 out of 5 Overall R2: [0.03209418 0.04484132 0.02542677 0.01093105 0.02690136]
Mean: 0.028038935700747846
Deviation: 0.010950454328955226
chapter2 线性回归实现的更多相关文章
- scikit-learn 线性回归算法库小结
scikit-learn对于线性回归提供了比较多的类库,这些类库都可以用来做线性回归分析,本文就对这些类库的使用做一个总结,重点讲述这些线性回归算法库的不同和各自的使用场景. 线性回归的目的是要得到输 ...
- 用scikit-learn和pandas学习线性回归
对于想深入了解线性回归的童鞋,这里给出一个完整的例子,详细学完这个例子,对用scikit-learn来运行线性回归,评估模型不会有什么问题了. 1. 获取数据,定义问题 没有数据,当然没法研究机器学习 ...
- 【scikit-learn】scikit-learn的线性回归模型
内容概要 怎样使用pandas读入数据 怎样使用seaborn进行数据的可视化 scikit-learn的线性回归模型和用法 线性回归模型的评估測度 特征选择的方法 作为有监督学习,分类问题是预 ...
- 线性回归 Linear Regression
成本函数(cost function)也叫损失函数(loss function),用来定义模型与观测值的误差.模型预测的价格与训练集数据的差异称为残差(residuals)或训练误差(test err ...
- 线性回归、梯度下降(Linear Regression、Gradient Descent)
转载请注明出自BYRans博客:http://www.cnblogs.com/BYRans/ 实例 首先举个例子,假设我们有一个二手房交易记录的数据集,已知房屋面积.卧室数量和房屋的交易价格,如下表: ...
- 回归分析法&一元线性回归操作和解释
用Excel做回归分析的详细步骤 一.什么是回归分析法 "回归分析"是解析"注目变量"和"因于变量"并明确两者关系的统计方法.此时,我们把因 ...
- R语言解读多元线性回归模型
转载:http://blog.fens.me/r-multi-linear-regression/ 前言 本文接上一篇R语言解读一元线性回归模型.在许多生活和工作的实际问题中,影响因变量的因素可能不止 ...
- R语言解读一元线性回归模型
转载自:http://blog.fens.me/r-linear-regression/ 前言 在我们的日常生活中,存在大量的具有相关性的事件,比如大气压和海拔高度,海拔越高大气压强越小:人的身高和体 ...
- deep learning 练习 多变量线性回归
多变量线性回归(Multivariate Linear Regression) 作业来自链接:http://openclassroom.stanford.edu/MainFolder/Document ...
随机推荐
- 【LeetCode】500. Keyboard Row 解题报告(Java & Python)
作者: 负雪明烛 id: fuxuemingzhu 个人博客: http://fuxuemingzhu.cn/ 目录 题目描述 题目大意 解题方法 暴力解 字典 + set 日期 题目地址:https ...
- 【LeetCode】125. Valid Palindrome 解题报告(Python & C++)
作者: 负雪明烛 id: fuxuemingzhu 个人博客: http://fuxuemingzhu.cn/ 目录 题目描述 解题方法 列表生成式 正则表达式 双指针 日期 题目地址:https:/ ...
- 【剑指Offer】二叉树中和为某一值的路径 解题报告(Python)
[剑指Offer]二叉树中和为某一值的路径 解题报告(Python) 标签(空格分隔): 剑指Offer 题目地址:https://www.nowcoder.com/ta/coding-intervi ...
- CONTRASTIVE REPRESENTATION DISTILLATION
目录 概 主要内容 超参数的选择 代码 Tian Y., Krishnan D., Isola P. CONTRASTIVE REPRESENTATION DISTILLATION. arXiv pr ...
- <学习opencv>图像、视频和数据文件
/*=========================================================================*/ // openCV中的函数 /*====== ...
- Java初学者作业——定义一个计算器类, 实现计算器类中加、 减、 乘、 除的运算方法, 每个方法能够接收2个参数。
返回本章节 返回作业目录 需求说明: 定义一个计算器类, 实现计算器类中加. 减. 乘. 除的运算方法, 每个方法能够接收2个参数. 实现思路: 定义计算器类. 定义计算器类中加.减.乘.除的方法. ...
- 编写Java程序,使用ThreadLocal类,项目中创建账户类 Account,类中包括账户名称name、 ThreadLocal 类的引用变量amount,表示存款
查看本章节 查看作业目录 需求说明: 某用户共有两张银行卡,账户名称相同,但卡号和余额不同.模拟用户使用这两张银行卡进行消费的过程,并打印出消费明细 实现思路: 项目中创建账户类 Account,类中 ...
- Storm对DRPC权限控制Version1.0.1
对Storm的DRPC进行权限控制, 并且设计相应的测试验证. 1.集群安装 请参考Storm集群安装Version1.0.1 2.使用DRPC功能 请参考Storm集群使用DRPC功能Version ...
- nginx中请求大小的限制的设置
Nginx对客户端请求缓冲区大小有个默认限制,如果超过了该值(比如在上传大文件时),会报500错误. 只需要设置三个值,就可以解决该问题: 1. client_body_buffer_size: 指定 ...
- RabbitMQ --- 直连交换机 【 有回调方法,获取消费结果 】
1.前言 上一随笔详细记录了直连交换机的方法,发送的消息是异步的,如果消息未被消费者消费,那么可以一直存在消息队列中. 那么有没有办法做一个回调,当消息被消费后,被通知消息成功被消费者消费啦? 答案是 ...
