第8章 File I/O,File类操作文件的属性
1.文件
1.1.什么是文件?
答:文件可认为是相关记录或放在一起的数据的集合
1.2.文件- -般存储在哪里?
答: 磁盘,硬盘,文件夹
1.3.JAVA程序如何访向文件属性?
JAVA API:iava.io. File类
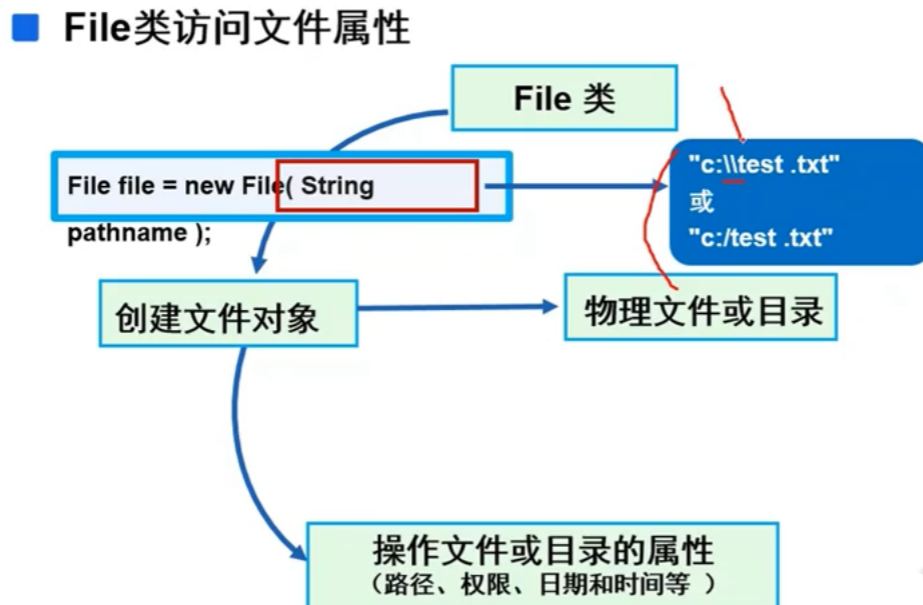
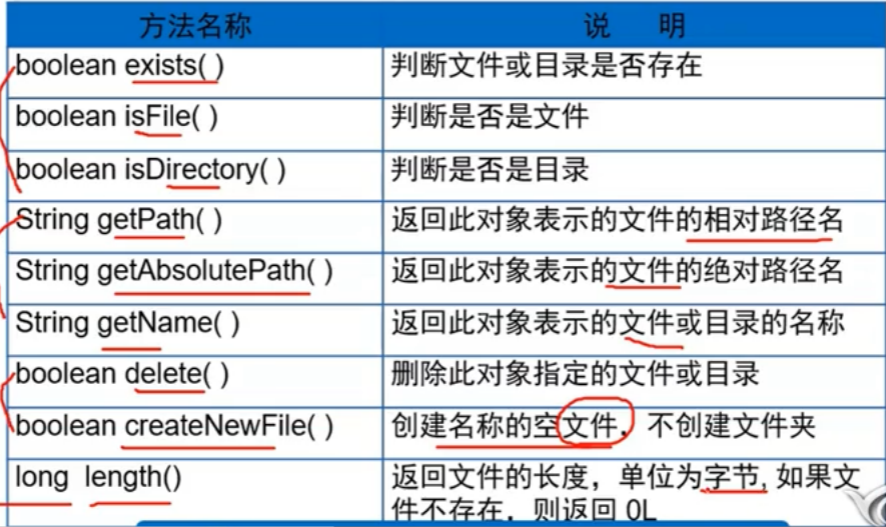
2.File类的常用方法
1 /**
2 * 案例1:使用文件操作的9大方法完成文件的判断
3 */
4 import java.io.*;//1.导入接口
5 import java.util.*;
6 public class TestFileMethods {
7 public static void main(String[] args) {
8
9 try {
10 Text();
11 } catch (IOException e) {
12 e.printStackTrace();
13 }
14 }
15 public static void Text() throws IOException {
16 Scanner input=new Scanner(System.in);
17 //2.实例化对象指定的路径
18 File file=new File("D:\\JAVA\\IDEA\\javaS2\\第8章 File类\\hello.txt");//填写路径
19 //3.判断hello.txt路径是否存在,exists()
20 if (file.exists()){
21 if (file.isDirectory()){
22 System.out.println("当前路径是文件夹");
23 }else{
24 System.out.println("当前路径是文件");
25 System.out.println("当前文件存在");
26 System.out.println("文件的相对路径,完整路径:"+file.getPath());
27 System.out.println("文件的名字为:"+file.getName());
28 System.out.println("文件的绝对路径"+file.getAbsolutePath());
29 System.out.println("文件的上一级目录"+file.getParent());
30 System.out.println("文件的长度是:"+file.length());
31 }
32 System.out.print("按1删除文件:");
33 int an=input.nextInt();
34 if (an==1){
35 //删除操作
36 boolean teue=file.delete();
37 if (teue){
38 System.out.println("删除成功");
39 }else {
40 System.out.println("删除失败");
41 }
42 }
43
44 }else {
45 System.out.println("当前文件不存在");
46 //4.创建hello文件
47 boolean bool=file.createNewFile();
48 if (bool){
49 System.out.println("hello文件创建成功");
50 }else {
51 System.out.println("hello文件创建失败");
52 }
53 }
54 }
55 }

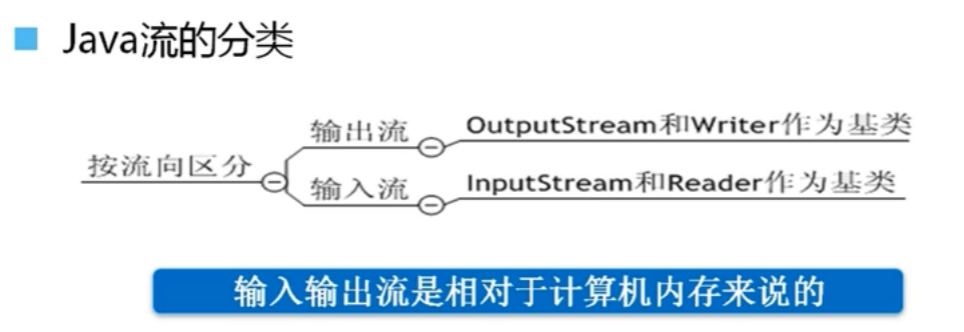
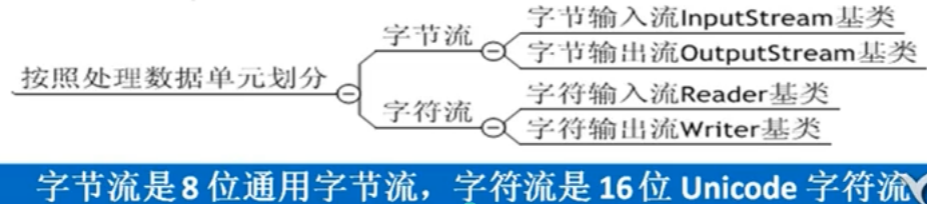
3.JAVA的流
理解Java的流和流的分类
3.1.如何读写文件?
答:通过流来读写文件,流是指一连串流动的字符是以先进先出方式发送信息的通道

字节流读写文本文件
1.文件的读写
1.1.文本文件的读写
- 用FileInputStream和FileOutputStream读写文本文件
- 用BufferedReader和BufferedWriter读写文本文件
1.2.二进制文件的读写
使用DataInputStream和DataOutputStream读写二进制文件
2.字节流
2.1.输入流
基类: InputStream
子类: FileInputStream
构造:
FileInputStream(File file)
FileInputStream (String name)
方法:
int read() 按字节读返回读到的字节
read (byte[ ] b) 读到字节数组返回读入字节数组的长度
read (byte[ ] b, int off, int len) 到字节数组返回读入字节数组的长度
1 /**
2 * 使用字节流来操作文本文件 读
3 */
4 import java.io.FileInputStream;//1.引入相关类
5 import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
6 import java.io.IOException;
7 import java.io.InputStream;
8
9 public class FileInputstreamDemo {
10 public static void main(String[] args) {
11 //创建字节输入流
12 InputStream in=null;
13 try {
14 in =new FileInputStream("D:\\hello.txt");
15 int data;//存储读到的字节
16 //实现读取操作
17 while((data=in.read())!=-1){
18 System.out.print((char) data);
19 }
20 } catch (IOException e) {
21 e.printStackTrace();
22 }
23 //关闭流
24 finally {
25 try {
26 if (in!=null){//判断文件是否为空
27 in.close();
28 }
29
30 } catch (IOException e) {
31 e.printStackTrace();
32 }
33 }
34
35 }
36 }
1 /**
2 * 使用字节流来操作文本文件
3 */
9 public class FileInputstreamDemo {
10 public static void main(String[] args) {
11 //创建字节输入流
12 InputStream in=null;
13 try {
14 in =new FileInputStream("D:\\hello.txt");
15 //使用数组的方式来读取文件,这可以识别中文字符
16 int len;//存取读入数组的长度
17 byte[]words=new byte[1024];
18 while ((len=in.read(words))!=-1){
19 System.out.println(new String(words,0,len));
20 }
21 } catch (IOException e) {
22 e.printStackTrace();
23 }
24 //关闭流
25 finally {
26 try {
27 if (in!=null){//判断文件是否为空
28 in.close();
29 }
30
31 } catch (IOException e) {
32 e.printStackTrace();
33 }
34 }
35
36 }
37 }

3.小节

4.输出流
基类: OutputStream
子类: FileOutputStream
构造:
Fil eOutputStream(File file)
Fil eOutputStream (String name)
Fi 1 eOutputStream (String name, boolean append) true
追加写.
方法:
close ()
flush() 刷新缓冲区
write (byte[] b)
write (byte门b, int off, int len) .
write(int b)
1 import java.io.File;
2 import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
3 import java.io.FileOutputStream;
4 import java.io.IOException;
5
6 /**
7 * 案例
8 * 将字符串中的信息写出到文本文件
9 */
10 public class FileOutputStreamDemo {
11 public static void main(String[] args) {
12 //1.创建字节输出流
13 FileOutputStream fos=null;
14 try {
15 fos=new FileOutputStream(new File("D:\\学好JAVA.txt"),true);//表示是否可以追加
16 //2.执行写操作
17 String str="HrlloWord学好JAVA";//要写入的字符
18 byte[] by=str.getBytes();//将字符转换为数组
19 fos.write(by,0,by.length);
20 System.out.println("文件更新成功");
21 } catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
22 e.printStackTrace();
23 }catch (IOException e){
24 e.printStackTrace();
25 }
26 finally {
27 //3.关闭流
28 if (fos!=null){
29 try {
30 fos.close();
31 } catch (IOException e) {
32 e.printStackTrace();
33 }
34 }
35 }
36
37
38 }
39 }
4.1.案例:将一个文本中的内容复制到另一个文本中
1 import java.io.FileInputStream;
2 import java.io.FileOutputStream;
3 import java.io.IOException;
4 import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
5
6 public class Texst {
7 public static void main(String[] args) {
8 FileInputStream inputStream=null;
9 FileOutputStream outputStream=null;
10
11 try {
12 inputStream=new FileInputStream("D:\\学好JAVA.txt");
13 outputStream=new FileOutputStream("D:\\hello.txt",true);
14 int num;
15 byte[]str=new byte[1024];
16 String stow;
17 while ((num=inputStream.read(str))!=-1){
18 System.out.println(stow=new String(str,0,num));
19 byte[]sum=stow.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
20 outputStream.write(sum,0, sum.length);
21 System.out.println("复制成功");
22 }
23 } catch (IOException e) {
24 e.printStackTrace();
25 }
26 }
27 }
小结

字符流和缓冲流读取文本文件
//存取读入数组的长度
------------恢复内容开始------------
1.文件
1.1.什么是文件?
答:文件可认为是相关记录或放在一起的数据的集合
1.2.文件- -般存储在哪里?
答: 磁盘,硬盘,文件夹
1.3.JAVA程序如何访向文件属性?
JAVA API:iava.io. File类

2.File类的常用方法

1 /**
2 * 案例1:使用文件操作的9大方法完成文件的判断
3 */
4 import java.io.*;//1.导入接口
5 import java.util.*;
6 public class TestFileMethods {
7 public static void main(String[] args) {
8
9 try {
10 Text();
11 } catch (IOException e) {
12 e.printStackTrace();
13 }
14 }
15 public static void Text() throws IOException {
16 Scanner input=new Scanner(System.in);
17 //2.实例化对象指定的路径
18 File file=new File("D:\\JAVA\\IDEA\\javaS2\\第8章 File类\\hello.txt");//填写路径
19 //3.判断hello.txt路径是否存在,exists()
20 if (file.exists()){
21 if (file.isDirectory()){
22 System.out.println("当前路径是文件夹");
23 }else{
24 System.out.println("当前路径是文件");
25 System.out.println("当前文件存在");
26 System.out.println("文件的相对路径,完整路径:"+file.getPath());
27 System.out.println("文件的名字为:"+file.getName());
28 System.out.println("文件的绝对路径"+file.getAbsolutePath());
29 System.out.println("文件的上一级目录"+file.getParent());
30 System.out.println("文件的长度是:"+file.length());
31 }
32 System.out.print("按1删除文件:");
33 int an=input.nextInt();
34 if (an==1){
35 //删除操作
36 boolean teue=file.delete();
37 if (teue){
38 System.out.println("删除成功");
39 }else {
40 System.out.println("删除失败");
41 }
42 }
43
44 }else {
45 System.out.println("当前文件不存在");
46 //4.创建hello文件
47 boolean bool=file.createNewFile();
48 if (bool){
49 System.out.println("hello文件创建成功");
50 }else {
51 System.out.println("hello文件创建失败");
52 }
53 }
54 }
55 }

3.JAVA的流
理解Java的流和流的分类
3.1.如何读写文件?
答:通过流来读写文件,流是指一连串流动的字符是以先进先出方式发送信息的通道



字节流读写文本文件
1.文件的读写
1.1.文本文件的读写
- 用FileInputStream和FileOutputStream读写文本文件
- 用BufferedReader和BufferedWriter读写文本文件
1.2.二进制文件的读写
使用DataInputStream和DataOutputStream读写二进制文件
2.字节流
2.1.输入流
基类: InputStream
子类: FileInputStream
构造:
FileInputStream(File file)
FileInputStream (String name)
方法:
int read() 按字节读返回读到的字节
read (byte[ ] b) 读到字节数组返回读入字节数组的长度
read (byte[ ] b, int off, int len) 到字节数组返回读入字节数组的长度
1 /**
2 * 使用字节流来操作文本文件 读
3 */
4 import java.io.FileInputStream;//1.引入相关类
5 import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
6 import java.io.IOException;
7 import java.io.InputStream;
8
9 public class FileInputstreamDemo {
10 public static void main(String[] args) {
11 //创建字节输入流
12 InputStream in=null;
13 try {
14 in =new FileInputStream("D:\\hello.txt");
15 int data;//存储读到的字节
16 //实现读取操作
17 while((data=in.read())!=-1){
18 System.out.print((char) data);
19 }
20 } catch (IOException e) {
21 e.printStackTrace();
22 }
23 //关闭流
24 finally {
25 try {
26 if (in!=null){//判断文件是否为空
27 in.close();
28 }
29
30 } catch (IOException e) {
31 e.printStackTrace();
32 }
33 }
34
35 }
36 }
1 /**
2 * 使用字节流来操作文本文件
3 */
9 public class FileInputstreamDemo {
10 public static void main(String[] args) {
11 //创建字节输入流
12 InputStream in=null;
13 try {
14 in =new FileInputStream("D:\\hello.txt");
15 //使用数组的方式来读取文件,这可以识别中文字符
16 int len;//存取读入数组的长度
17 byte[]words=new byte[1024];
18 while ((len=in.read(words))!=-1){
19 System.out.println(new String(words,0,len));
20 }
21 } catch (IOException e) {
22 e.printStackTrace();
23 }
24 //关闭流
25 finally {
26 try {
27 if (in!=null){//判断文件是否为空
28 in.close();
29 }
30
31 } catch (IOException e) {
32 e.printStackTrace();
33 }
34 }
35
36 }
37 }

3.小节

4.输出流
基类: OutputStream
子类: FileOutputStream
构造:
Fil eOutputStream(File file)
Fil eOutputStream (String name)
Fi 1 eOutputStream (String name, boolean append) true
追加写.
方法:
close ()
flush() 刷新缓冲区
write (byte[] b)
write (byte门b, int off, int len) .
write(int b)
1 import java.io.File;
2 import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
3 import java.io.FileOutputStream;
4 import java.io.IOException;
5
6 /**
7 * 案例
8 * 将字符串中的信息写出到文本文件
9 */
10 public class FileOutputStreamDemo {
11 public static void main(String[] args) {
12 //1.创建字节输出流
13 FileOutputStream fos=null;
14 try {
15 fos=new FileOutputStream(new File("D:\\学好JAVA.txt"),true);//表示是否可以追加
16 //2.执行写操作
17 String str="HrlloWord学好JAVA";//要写入的字符
18 byte[] by=str.getBytes();//将字符转换为数组
19 fos.write(by,0,by.length);
20 System.out.println("文件更新成功");
21 } catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
22 e.printStackTrace();
23 }catch (IOException e){
24 e.printStackTrace();
25 }
26 finally {
27 //3.关闭流
28 if (fos!=null){
29 try {
30 fos.close();
31 } catch (IOException e) {
32 e.printStackTrace();
33 }
34 }
35 }
36
37
38 }
39 }
4.1.案例:将一个文本中的内容复制到另一个文本中
1 import java.io.FileInputStream;
2 import java.io.FileOutputStream;
3 import java.io.IOException;
4 import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
5
6 public class Texst {
7 public static void main(String[] args) {
8 FileInputStream inputStream=null;
9 FileOutputStream outputStream=null;
10
11 try {
12 inputStream=new FileInputStream("D:\\学好JAVA.txt");
13 outputStream=new FileOutputStream("D:\\hello.txt",true);
14 int num;
15 byte[]str=new byte[1024];
16 String stow;
17 while ((num=inputStream.read(str))!=-1){
18 System.out.println(stow=new String(str,0,num));
19 byte[]sum=stow.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
20 outputStream.write(sum,0, sum.length);
21 System.out.println("复制成功");
22 }
23 } catch (IOException e) {
24 e.printStackTrace();
25 }
26 }
27 }
小结

字符流和缓冲流读取文本文件
1.字符编码:
ASCII码 0~127 8位二进制数1个字节 16位二进制数(2个字节) 010101001010 0^ 65535
Unicode编码格式
字符流
1.输入流
基类: Reader
FileReader
构造:
FileReader (File file)
FileReader (String name)
常用方法:
int read() 读取-一个字符返回字符编码
int read (char[] b)读取到一个字符数组」_
int read (char[] b, int off, int len) 读取到-一个字符数组的某一部分
2.使用FileReader读取文件的步骤
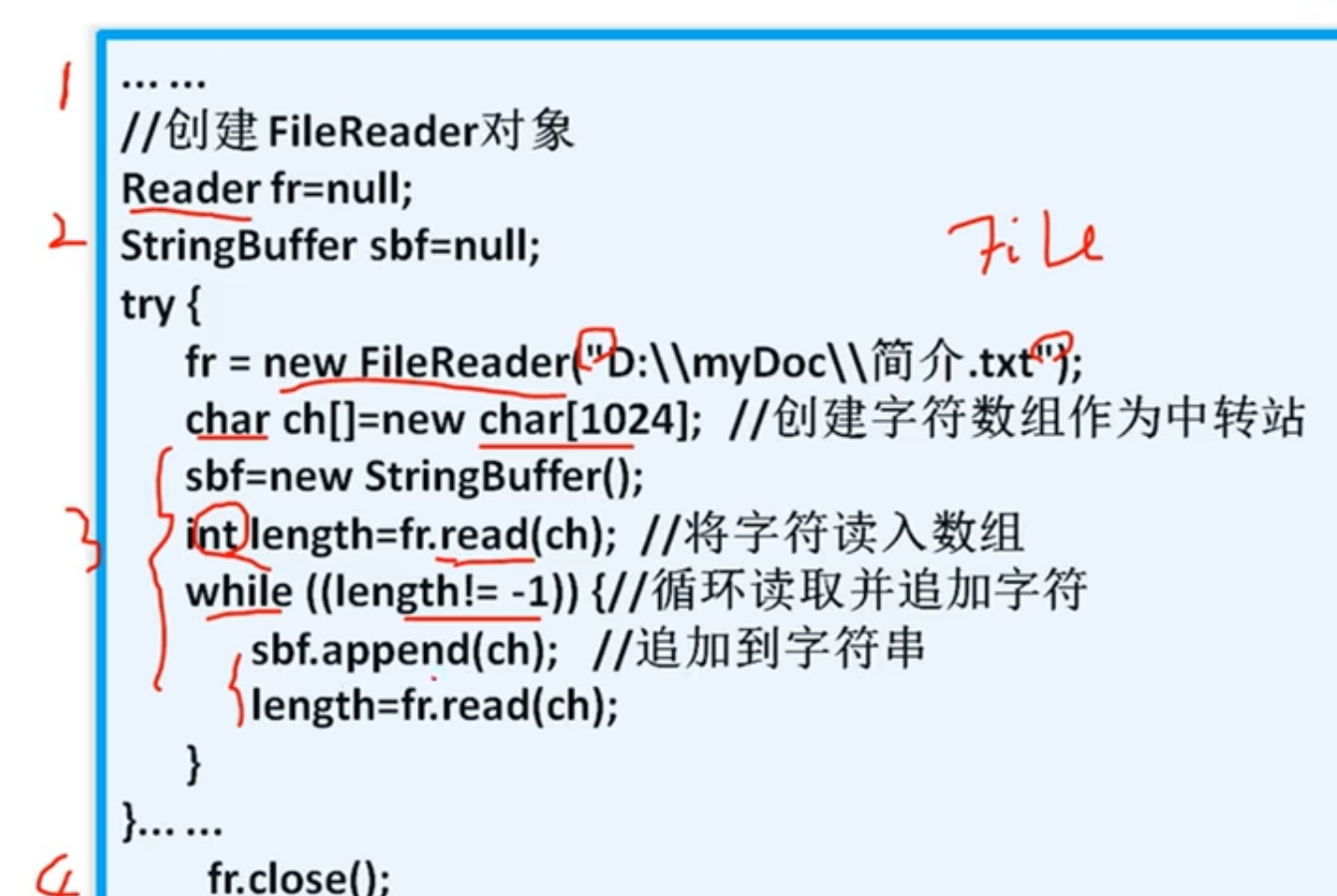
1 import java.io.FileNotFoundException;
2 import java.io.FilterReader;
3 import java.io.IOException;
4 import java.io.Reader;
5 /**
6 * 使用FileReader和StringBuffer,进行文件读取
7 */
8 public class FileReader {
9 public static void main(String[] args) {
10 Reader reader=null;
11 StringBuilder builder=null;
12 try {
13 //1.创建一个字符流对象
14 reader=new java.io.FileReader("D:\\hello.txt");
15
16 /*int num;//接受读到的字节
17 //2.读取文本文件
18 while ((num= reader.read())!=-1){
19 System.out.print((char) num);//吧读到的字节进行类型转换
20 }*/
21 char[]sum=new char[1024];//存取读到的字节
22 builder=new StringBuilder();//把字节进行重组
23 int word;//接受读到的字节
24 while ((word= reader.read(sum))!=-1){
25 builder.append(sum);
26 System.out.println(builder.toString());
27 }
28
29 } catch (IOException e) {
30 e.printStackTrace();
31 }finally {
32 //3.关闭流
33 if (reader!=null){
34 try {
35 reader.close();
36 } catch (IOException e) {
37 e.printStackTrace();
38 }
39 }
40
41 }
42
43 }
44 }
3.BufferedReader类
3.1. 问题: 如何提高字符流读取文本文件的效率?
使用FileReader类与BufferedReader类
- BufferedReader类是Reader类的子类
- BufferedReader类带有缓冲区
- 按行读取内容的readLine()方法 BufferedReader类特有的方法

■Reader类常用方法
int read()
int read(char[ ch)
read(charD c,int off,int len)
void close( )
■子 类BufferedReader常用的构造方法
BufferedReader(Reader in)
■子 类BufferedReader特有的方法
readLine() 按行读取
4.使用字符流写文本文件
4.1.输出流
基类: Writer
FileWriter
构造: FileWriter (File file)
FIleWriter(File file, boolean append) append表示是否是追加写, true 是
FileWriter (String name)
FileWriter (String name, boolean append)
方法:
close ()
flush()刷新缓冲区
write(int c)
write (char [] ch)
write(char[], int off, int len)
write (String str)
write (String str, int off, int len)
4.2.使用 FileWriter对文本进行写入的操作
1 import java.io.FileWriter;
2 import java.io.IOException;
3 import java.io.Writer;
4 /**
5 * 使用FileWriterDemo向文本文件中写信息
6 */
7 public class FileWriterDemo {
8 public static void main(String[] args) {
9 //1.创建流
10 Writer writer=null;
11 try {
12 writer=new FileWriter("D:\\我的世界.txt",true);
13 //2.写入信息
14 writer.write("你好呀,塞罗");//将字符输出到指定的流中
15 writer.flush();//刷新输出流
16 System.out.println("添加成功");
17 } catch (IOException e) {
18 e.printStackTrace();
19 }finally {
20 if (writer!=null){
21 try {
22 //3.关闭流
23 writer.close();
24 } catch (IOException e) {
25 e.printStackTrace();
26 }
27 }
28 }
29 }
30 }
4.3.使用BufferedWriter向文本文件中写信息
1 import java.io.*;
2 import java.io.FileReader;
3
4 /**
5 * 使用BufferedWriter向文本文件中写信息
6 */
7 public class BufferedWriterDemo {
8 public static void main(String[] args) {
9 Writer wr=null;
10 BufferedWriter br=null;
11 Reader re=null;
12 BufferedReader der=null;
13 try {
14 //1.创建流
15 br=new BufferedWriter(wr=new FileWriter("D:\\我是钢铁侠.txt"));
16 //2.写入信息
17 br.write("你哈钢铁侠我是你的粉丝");
18 br.newLine();//换行的意思
19 br.write("你的知识可以传给我吗");
20 br.newLine();
21 br.write("我真的很需要你的知识");
22 br.flush();//一定要记得写缓冲区
23
24 //读取文件中的信息
25 der=new BufferedReader(re=new FileReader("D:\\我是钢铁侠.txt"));
26 String str=null;//接收读取到的信息
27 while ((str=der.readLine())!=null){
28 System.out.println(str);
29 }
30 } catch (IOException e) {
31 e.printStackTrace();
32 }finally {
33 try {
34 //3.关闭流
35 wr.close();
36 } catch (IOException e) {
37 e.printStackTrace();
38 }
39 if (re!=null){
40 try {
41 re.close();
42 } catch (IOException e) {
43 e.printStackTrace();
44 }
45 }
46 }
47
48 }
49 }
 总结:
总结:
读写二-进制文件
1.DataInputStream类
■FilterInputStream的子类
■与FileInputStream类结合 使用读取二进制文件
2.DataOutputStream类
■FilterOutputStream的子 类
■与FileOutputStream类结合使用写二 进制文件
3.使用DataInputStream读二进制文件 使用DataOutputStream写=进制文件

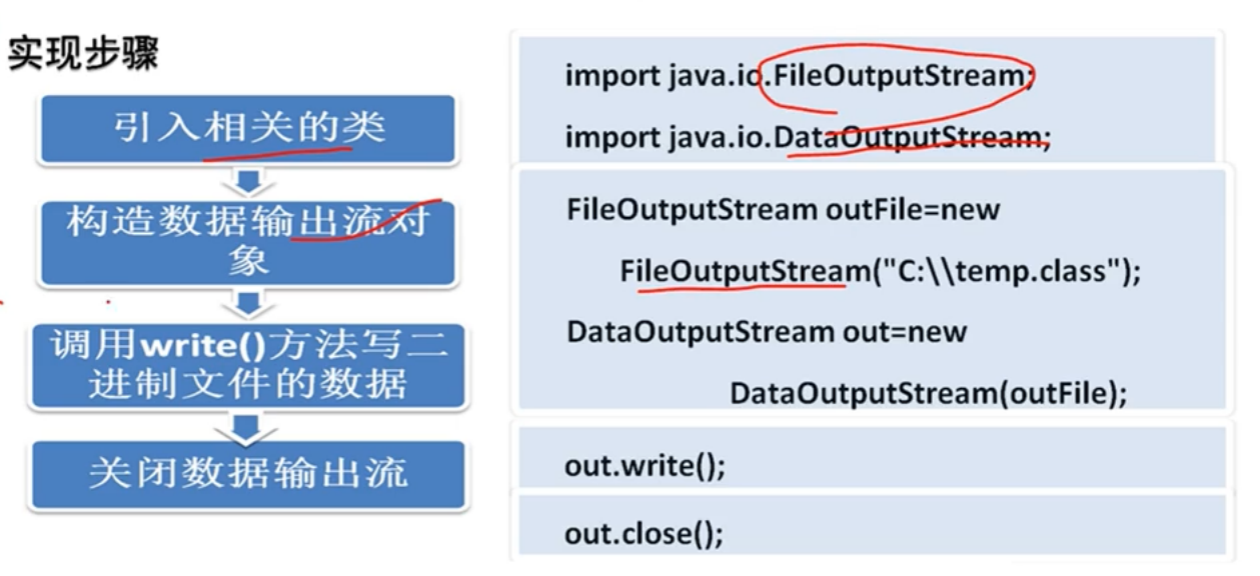
1 import java.io.*;
2
3 /**
4 * 使用DataInputStream和DataOutputStream读写文件 一般用于一些二进制文件
5 */
6 public class ReadAndWriteBinaryFile {
7 public static void main(String[] args) {
8 //1.创建流
9 DataInputStream stream=null;
10 DataOutput output=null;
11 try {
12 stream=new DataInputStream(new FileInputStream("D:\\BufferedWriterDemo.class"));//读取文件
13 output=new DataOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("D:\\FileOutputStream.class"));
14 int sum;
15 //2.实现读写操作
16 while ((sum=stream.read())!=-1){
17 output.write(sum);
18 }
19 } catch (IOException e) {
20 e.printStackTrace();
21 }finally {
22 //3.关闭流
23 if (stream!=null){
24 try {
25 stream.close();
26 } catch (IOException e) {
27 e.printStackTrace();
28 }
29 }
30 }
31 }
32 }
序列化和反序列化
1.序列化和反序列化的过程
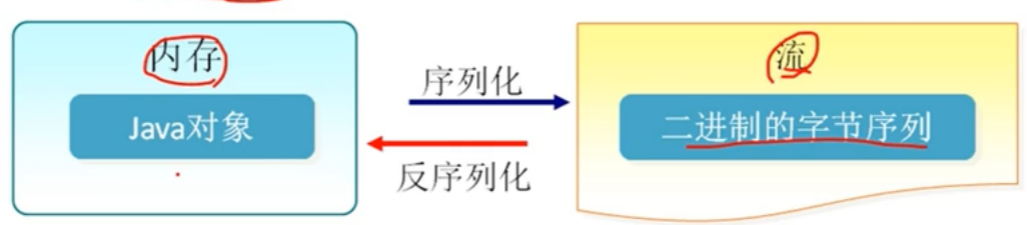
序列化是将对象的状态写入到特定的流中的过程
反序列化则是从特定的流中获取数据重新构建对象的过程
1.1.实现序列化
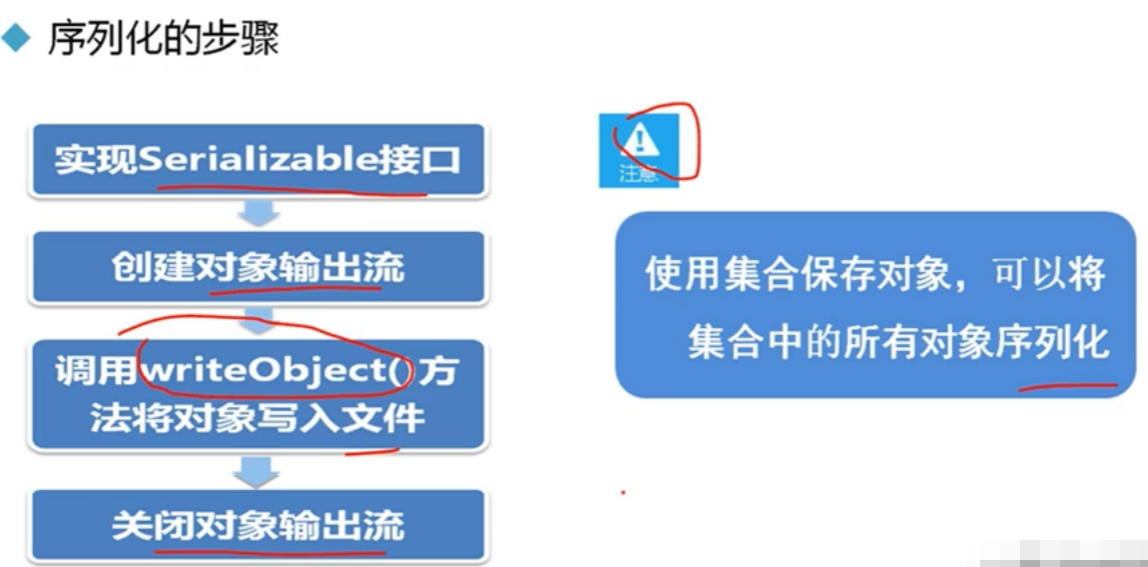
1 /**
2 * 学生类
3 */
4 public class Student implements java.io.Serializable{
5
6 private static final long serialVersionUID=1l;
7
8 private String name;//姓名
9 private int age;//年龄
10 transient private String gender;//性别
11 public Student(String name,int age,String gender){
12 this.name=name;
13 this.age= age;
14 this.gender=gender;
15 }
16 public String getName() {
17 return name;
18 }
19 public void setName(String name) {
20 this.name = name;
21 }
22 public int getAge() {
23 return age;
24 }
25 public void setAge(int age) {
26 this.age = age;
27 }
28 public String getGender() {
29 return gender;
30 }
31 public void setGender(String gender) {
32 this.gender = gender;
33 }
34 }
1 import java.io.*;
2
3 /**
4 * 序列化学生对象
5 */
6 public class Serizable0bj {
7 public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException {
8 //1.创建一个需要序列化的学生对象
9 Student dent=new Student("王饱饱",21,"男");
10 //2.创建一个对象流
11 OutputStream os=null;
12 ObjectOutputStream oos=null;
13 //3.创建一个对象输入流
14 FileInputStream is=null;
15 ObjectInputStream ois=null;
16 try {
17 os=new FileOutputStream("D:/studer.bin");
18 oos=new ObjectOutputStream(os);
19 oos.writeObject(dent);
20
21 is=new FileInputStream("D:/studer.bin");
22 ois=new ObjectInputStream(is);
23 Student stu=(Student) ois.readObject();
24 System.out.println("学生姓名:"+stu.getName()+" 年龄:"+stu.getAge()+" 性别:"+stu.getGender());
25
26 } catch (FileNotFoundException e) {
27 e.printStackTrace();
28 }catch (IOException e) {
29 e.printStackTrace();
30 }finally {
31 if (oos!=null){
32 try {
33 //.关闭
34 oos.close();
35 } catch (IOException e) {
36 e.printStackTrace();
37 }
38 }
39 if (is!=null){
40 try {
41 is.close();
42 } catch (IOException e) {
43 e.printStackTrace();
44 }
45 }
46 }
47
48 }
49 }
------------恢复内容结束------------
第8章 File I/O,File类操作文件的属性的更多相关文章
- 使用File类操作文件或目录的属性
在学I/O流之前,我先总结一下使用File类操作文件或目录的属性. package com.File; import java.io.File; import java.io.IOException; ...
- File类操作文件
简单示例: public static void main(String[] args) { // 列出系统所有的根路径 File[] listRoots = File.listRoots(); fo ...
- [19/04/04-星期四] IO技术_CommonsIO(通用IO,别人造的轮子,FileUtils类 操作文件 & IOUtilsl类 操作里边的内容 )
一.概念 JDK中提供的文件操作相关的类,但是功能都非常基础,进行复杂操作时需要做大量编程工作.实际开发中,往往需要 你自己动手编写相关的代码,尤其在遍历目录文件时,经常用到递归,非常繁琐. Apac ...
- 使用File类、StreamRead和StreamWrite读写数据、以及Path类操作文件路径和Directory
1.File类的概念: File类,是一个静态类,主要是来提供一些函数库用的.静态实用类,提供了很多静态的方法,支持对文件的基本操作,包括创建,拷贝,移动,删除和 打开一个文件. File类方法的参量 ...
- Path类 操作文件类
// Path类 IO命名空间 静态类 不能创建对象类名. string str =@"E:\C#程序设计基础入门教程\(第十一天)\122\22\nee.txt"; ////in ...
- FileStream类操作文件
private void buttonselect_Click (object sender, EventArgs e) { OpenFileDialog ofd ...
- .net学习之集合、foreach原理、Hashtable、Path类、File类、Directory类、文件流FileStream类、压缩流GZipStream、拷贝大文件、序列化和反序列化
1.集合(1)ArrayList内部存储数据的是一个object数组,创建这个类的对象的时候,这个对象里的数组的长度为0(2)调用Add方法加元素的时候,如果第一次增加元神,就会将数组的长度变为4往里 ...
- Android(java)学习笔记167:Java中操作文件的类介绍(File + IO流)
1.File类:对硬盘上的文件和目录进行操作的类. File类是文件和目录路径名抽象表现形式 构造函数: 1) File(String pathname) Creat ...
- java.io.File类操作
一.java.io.File类 String path="E:/222/aaa";//路径 String path1="aaa.txt"; File file= ...
随机推荐
- Go语言系列之依赖管理
依赖管理 为什么需要依赖管理? 最早的时候,Go所依赖的所有的第三方库都放在GOPATH这个目录下面.这就导致了同一个库只能保存一个版本的代码.如果不同的项目依赖同一个第三方的库的不同版本,应该怎么解 ...
- JSP页面中最常使用的脚本元素
注:图片如果损坏,点击文章链接:https://www.toutiao.com/i6513082449755374093/ 前面简单说了一个<JSP页面实际上就是Servlet>,接下来说 ...
- Git 基础指令
Git 基础指令 Git 基础指令 获取 Git 仓库 在已存在目录中初始化仓库 克隆现有的仓库 记录仓库与仓库的更新 仓库的记录 检查当前文件状态 三部曲 跟踪新文件 提交更新 移除文件 推送到远程 ...
- Kong 微服务网关在 Kubernetes 的实践
来源:分布式实验室译者:qianghaohao本文主要介绍将 Kong 微服务网关作为 Kubernetes (https://www.alauda.cn)集群统一入口的最佳实践,之前写过一篇文章使用 ...
- GLPK下载安装
GLPK下载安装 下载 wget http://ftp.gnu.org/gnu/glpk/glpk-4.65.tar.gz tar -zxvf glpk-4.65.tar.gz 安装 如果你有管理员权 ...
- 云计算实验二 Docker实验-docker安装
一.实验目的 1.了解Docker服务安装: 2.掌握Docker镜像操作 二.实验内容 1.Docker服务安装 查看内核版本 uname -r 安装依赖环境: yum install -y yu ...
- insert语句
7.4.插入数据insert(DML语句) 语法格式: insert into 表名(字段名1,字段名2,字段名3...) values(值1,值2,值3): 注意:字段名和值要一一对应.什么是一一对 ...
- Jquery Ajax添加header参数
在使用ajax请求接口时需要在请求头添加token来进行身份验证,方式如下: $.ajax({ type: 'GET', url: 'http://api.php', dataType: 'json' ...
- 微信小程序入门教程之二:页面样式
这个系列的上一篇教程,教大家写了一个最简单的 Hello world 微信小程序. 但是,那只是一个裸页面,并不好看.今天接着往下讲,如何为这个页面添加样式,使它看上去更美观,教大家写出实际可以使用的 ...
- 【webpack4.0】---webpack的基本使用(三)
一.webpack-dev-server 1.安装 cnpm install webpack-dev-server -D 2.作用 开启一个web服务,监听文件的变化并自动刷新网页,做到实时预 ...
