【ASP.NET Core】运行原理(2):启动WebHost
本系列将分析ASP.NET Core运行原理
- 【ASP.NET Core】运行原理[1]:创建WebHost
- 【ASP.NET Core】运行原理[2]:启动WebHost
- 【ASP.NET Core】运行原理[3]:认证
本节将分析WebHost.StartAsync();代码,确定是如何一步一步到我们注册的中间件,并介绍几种Configure的方式。
源代码参考.NET Core 2.0.0
目录
- Server.StartAsync
- Server
- IHttpApplication
- HttpContextFactory
- HttpContext
- Configure
- IApplicationBuilder
- Use
- Run
- UseMiddleware
- UseWhen
- MapWhen
- Map
Server.StartAsync
在上节我们知道WebHost.StartAsync内部是调用Server.StartAsync的。
public async Task StartAsync<TContext>(IHttpApplication<TContext> application, CancellationToken cancellationToken)
{
async Task OnBind(ListenOptions endpoint)
{
var connectionHandler = new ConnectionHandler<TContext>(endpoint, ServiceContext, application);
var transport = _transportFactory.Create(endpoint, connectionHandler);
_transports.Add(transport);
await transport.BindAsync().ConfigureAwait(false);
}
await AddressBinder.BindAsync(_serverAddresses, Options.ListenOptions, Trace, OnBind).ConfigureAwait(false);
}
参数application即为之前的new HostingApplication。在这里说下大概的流程:
KestrelServer.StartAsync -> new ConnectionHandler<TContext>().OnConnection -> new FrameConnection().StartRequestProcessing() ->
new Frame<TContext>().ProcessRequestsAsync() -> _application.CreateContext(this) && _application.ProcessRequestAsync(context)
如果你需要更细节的流程,可参考如下:
LibuvTransportFactory -> LibuvTransport.BindAsync() -> ListenerPrimary.StartAsync() ->
listener.ListenSocket.Listen(LibuvConstants.ListenBacklog, ConnectionCallback, listener) -> listener.OnConnection(stream, status) -> ConnectionCallback() ->
new LibuvConnection(this, socket).Start() -> ConnectionHandler.OnConnection() -> connection.StartRequestProcessing() ->
ProcessRequestsAsync -> CreateFrame -> await _frame.ProcessRequestsAsync()
- _application 为上面的HostingApplication;
- 每个WebHost.StartAsync 将创建唯一的一个HostingApplication实例并在每次请求时使用。
- 由Frame类调用HostingApplication的方法。
下面展示Frame以及HostingApplication:
Frame
public class Frame<TContext> : Frame
{
public override async Task ProcessRequestsAsync()
{
while (!_requestProcessingStopping)
{
Reset();
EnsureHostHeaderExists();
var messageBody = MessageBody.For(_httpVersion, FrameRequestHeaders, this);
InitializeStreams(messageBody);
var context = _application.CreateContext(this);
try
{
await _application.ProcessRequestAsync(context);
}
finally
{
_application.DisposeContext(context, _applicationException);
}
}
}
}
HostingApplication
public class HostingApplication : IHttpApplication<HostingApplication.Context>
{
private readonly RequestDelegate _application;
private readonly IHttpContextFactory _httpContextFactory;
public HostingApplication(
RequestDelegate application,
IHttpContextFactory httpContextFactory)
{
_application = application;
_httpContextFactory = httpContextFactory;
}
// Set up the request
public Context CreateContext(IFeatureCollection contextFeatures)
{
var context = new Context();
var httpContext = _httpContextFactory.Create(contextFeatures);
context.HttpContext = httpContext;
return context;
}
// Execute the request
public Task ProcessRequestAsync(Context context)
{
return _application(context.HttpContext);
}
// Clean up the request
public void DisposeContext(Context context, Exception exception)
{
var httpContext = context.HttpContext;
_httpContextFactory.Dispose(httpContext);
}
public struct Context
{
public HttpContext HttpContext { get; set; }
}
}
由此我们发现HttpContext是由HttpContextFactory创建的,其中_httpContextFactory则是上节在WebHostBuilder的BuildCommon注入的
同时在HostingApplication的ProcessRequestAsync方法中,我们看到我们的_application(Startup注册的中间件)被调用了。
IHttpContextFactory。
HttpContextFactory
public HttpContext Create(IFeatureCollection featureCollection)
{
var httpContext = new DefaultHttpContext(featureCollection);
if (_httpContextAccessor != null)
_httpContextAccessor.HttpContext = httpContext;
return httpContext;
}
而创建的HttpContext则是DefaultHttpContext类型:
public class DefaultHttpContext : HttpContext
{
public virtual void Initialize(IFeatureCollection features)
{
_features = new FeatureReferences<FeatureInterfaces>(features);
_request = InitializeHttpRequest();
_response = InitializeHttpResponse();
}
public override HttpRequest Request => _request;
public override HttpResponse Response => _response;
}
Configure
IApplicationBuilder
我们知道在Startup的Configure方法中,通过IApplicationBuilder可以注册中间件。
public interface IApplicationBuilder
{
IServiceProvider ApplicationServices { get; set; }
RequestDelegate Build();
IApplicationBuilder Use(Func<RequestDelegate, RequestDelegate> middleware);
}
默认实现类为:
public class ApplicationBuilder : IApplicationBuilder
{
private readonly IList<Func<RequestDelegate, RequestDelegate>> _components = new List<Func<RequestDelegate, RequestDelegate>>();
public IApplicationBuilder Use(Func<RequestDelegate, RequestDelegate> middleware)
{
_components.Add(middleware);
return this;
}
public RequestDelegate Build()
{
RequestDelegate app = context =>
{
context.Response.StatusCode = 404;
return Task.CompletedTask;
};
foreach (var component in _components.Reverse())
app = component(app);
return app;
}
}
其中Use方法为注册中间件。中间件的本质就是一个Func<RequestDelegate, RequestDelegate>对象。
该对象的传入参数为下一个中间件,返回对象为本中间件。
而Build方法为生成一个RequestDelegate,在HostingApplication构造函数中的参数即为该对象。
在Build方法中,我们看到最后一个中间件为404中间件。其他的中间件都是通过Use方法注册到内部维护的_components对象上。
Use
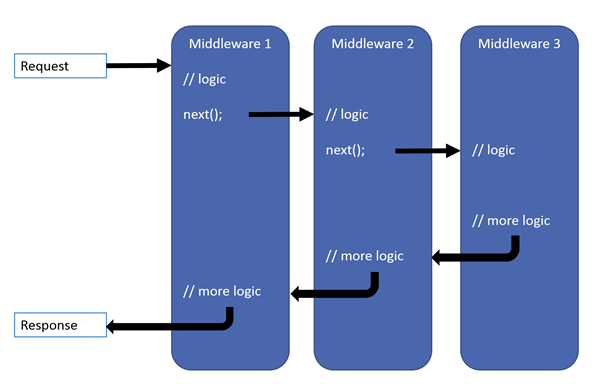
我们通过一个Use示例,来看下中间件的流程:
public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IHostingEnvironment env)
{
app.Use(next => async context =>
{
Console.WriteLine("A begin");
await next(context);
Console.WriteLine("A end");
});
app.Use(next => async context =>
{
Console.WriteLine("B begin");
await next(context);
Console.WriteLine("B end");
});
}
访问结果:
A begin
B begin
B end
A end
流程图:
Run
当我们不使用next 下一个中间件的时候,我们可以使用Run方法来实现
Run方法接受一个RequestDelegate对象,本身是IApplicationBuilder的扩展方法。
public static void Run(this IApplicationBuilder app, RequestDelegate handler);
{
app.Use(_ => handler);
}
Run示例
app.Run(context=>context.Response.WriteAsync("Run Core"));
该示例相当于:
app.Use(next => context => context.Response.WriteAsync("Run Core"));
UseMiddleware
而通常我们添加中间件的方式是通过UseMiddleware来更加方便的操作。
先看下IMiddleware:
public interface IMiddleware
{
Task InvokeAsync(HttpContext context, RequestDelegate next);
}
参数next即为下一个中间件。
有2种实现UseMiddleware的方式:
- 实现IMiddleware接口。
- 基于接口约定的方法。
IMiddleware接口
public class DemoMiddle : IMiddleware
{
public Task InvokeAsync(HttpContext context, RequestDelegate next)
{
return context.Response.WriteAsync("hello middleware");
}
}
在使用IMiddleware接口的时候,还需要注册该类到DI系统中。
约定
public class DemoMiddle
{
private RequestDelegate _next;
public DemoMiddle(RequestDelegate next)
{
_next = next;
}
public Task InvokeAsync(HttpContext context)
{
return context.Response.WriteAsync("hello middleware");
}
}
这种方式,不用再注册到DI中,如果需要对该类构造函数传入参数,直接在app.UseMiddleware<DemoMiddle>("hi1");传入参数即可。
UseWhen
app.Use(next => async context => { await context.Response.WriteAsync("Begin"); await next(context); });
app.UseWhen(context => context.Request.Path.Value == "/hello", branch => branch.Use(
next => async context => { await context.Response.WriteAsync("hello"); await next(context); }));
app.Run(context => context.Response.WriteAsync("End"));
当我们访问/hello时,结果为:BeginhelloEnd
分析源码得知在构建管道的时候,克隆一个另外的IApplicationBuilder。
public static IApplicationBuilder UseWhen(this IApplicationBuilder app, Predicate predicate, Action<IApplicationBuilder> configuration)
{
var branchBuilder = app.New();
configuration(branchBuilder);
return app.Use(main =>
{
// This is called only when the main application builder
// is built, not per request.
branchBuilder.Run(main);// 添加(调用)原来的中间件
var branch = branchBuilder.Build();
return context => predicate(context) ? branch(context): main(context);
});
}
MapWhen
app.Use(next => async context => { await context.Response.WriteAsync("Begin"); await next(context); });
app.MapWhen(context => context.Request.Path.Value == "/hello", app2 => app2.Run(context => context.Response.WriteAsync("hello")));
app.Run(context => context.Response.WriteAsync("End"));
当我们访问/hello时,结果为:Beginhello。
分析源码得知在构建管道的时候,新分支并没有再调用原来的中间件。
public static IApplicationBuilder MapWhen(this IApplicationBuilder app, Predicate predicate, Action<IApplicationBuilder> configuration)
{
var branchBuilder = app.New();
configuration(branchBuilder);
var branch = branchBuilder.Build();
return app.Use(next => context => predicate(context) ? branch(context): next(context));
}
Map
app.Map("/hello", app2 => app2.Run(context => context.Response.WriteAsync("hello")));
当我们访问/hello时,结果为:Beginhello。与MapWhen效果一样。
如果我们只是判断URLPath的话,通常我们会使用Map方法。
以上是常用的注册中间件的方式。
本文链接:http://neverc.cnblogs.com/p/8029419.html
【ASP.NET Core】运行原理(2):启动WebHost的更多相关文章
- 【ASP.NET Core】运行原理之启动WebHost
ASP.NET Core运行原理之启动WebHost 本节将分析WebHost.CreateDefaultBuilder(args).UseStartup<Startup>().Build ...
- ASP.NET Core 运行原理解剖[1]:Hosting
ASP.NET Core 是新一代的 ASP.NET,第一次出现时代号为 ASP.NET vNext,后来命名为ASP.NET 5,随着它的完善与成熟,最终命名为 ASP.NET Core,表明它不是 ...
- ASP.NET Core 运行原理解剖[2]:Hosting补充之配置介绍
在上一章中,我们介绍了 ASP.NET Core 的启动过程,主要是对 WebHost 源码的探索.而本文则是对上文的一个补充,更加偏向于实战,详细的介绍一下我们在实际开发中需要对 Hosting 做 ...
- ASP.NET Core 运行原理解剖[4]:进入HttpContext的世界
HttpContext是ASP.NET中的核心对象,每一个请求都会创建一个对应的HttpContext对象,我们的应用程序便是通过HttpContext对象来获取请求信息,最终生成响应,写回到Http ...
- ASP.NET Core 运行原理剖析1:初始化WebApp模版并运行
ASP.NET Core 运行原理剖析1:初始化WebApp模版并运行 核心框架 ASP.NET Core APP 创建与运行 总结 之前两篇文章简析.NET Core 以及与 .NET Framew ...
- ASP.NET Core 运行原理解剖[3]:Middleware-请求管道的构成
在 ASP.NET 中,我们知道,它有一个面向切面的请求管道,有19个主要的事件构成,能够让我们进行灵活的扩展.通常是在 web.config 中通过注册 HttpModule 来实现对请求管道事件监 ...
- ASP.NET Core 运行原理剖析
1. ASP.NET Core 运行原理剖析 1.1. 概述 1.2. 文件配置 1.2.1. Starup文件配置 Configure ConfigureServices 1.2.2. appset ...
- ASP.NET Core 运行原理剖析2:Startup 和 Middleware(中间件)
ASP.NET Core 运行原理剖析2:Startup 和 Middleware(中间件) Startup Class 1.Startup Constructor(构造函数) 2.Configure ...
- ASP.NET Core 运行原理解剖[5]:Authentication
在现代应用程序中,认证已不再是简单的将用户凭证保存在浏览器中,而要适应多种场景,如App,WebAPI,第三方登录等等.在 ASP.NET 4.x 时代的Windows认证和Forms认证已无法满足现 ...
随机推荐
- 铁乐学python_day05-作业
1,有如下变量(tu是个元祖),请实现要求的功能 tu = ("alex", [11, 22, {"k1": 'v1', "k2": [&q ...
- zabbix的日常监控-分布式监控(十)
参考博文:http://blog.51cto.com/jinlong/2051966 zabbix proxy 可以代替 zabbix server 检索客户端的数据,然后把数据汇报给 zabbix ...
- (1)List集合 (2)Queue集合 (3)Set集合
1.List集合(重中之重)1.1 基本概念 java.util.List接口是Collection接口的子接口,该接口中元素有先后放入次序并允许重复 该接口的主要实现类:ArrayList类.Lin ...
- python第二十五课——闭包
满足闭包的三个条件: 1).有外部函数和内部函数这样的结构 2).外部函数中定义的变量被内部函数所使用 3).内部函数对象作为返回值被外部函数返回 演示闭包的定义和使用: def outer(): a ...
- Kubernetes中的资源调度与资源管理
一.scheduling:把pod放到node上 1.最小调度单元:pod 2.1.8的版本后,最大支持5000个node 3.scheduling由两个部分组成: 3.1 Predicates:过滤 ...
- Spring Boot Mock单元测试学习总结
单元测试的方法有很多种,比如使用Postman.SoapUI等工具测试,当然,这里的测试,主要使用的是基于RESTful风格的SpringMVC的测试,我们可以测试完整的Spring MVC流程,即从 ...
- 【转】[置顶] 在Android中显示GIF动画
gif图动画在Android中还是比较常用的,比如像新浪微博中,有很多gif图片,而且展示非常好,所以我也想弄一个.经过我多方的搜索资料和整理,终于弄出来了,其实github上有很多开源的gif的展示 ...
- Day17 多线程编程
基本概念 进程:内存中正则运行的一个应用程序.一个进程包含多个线程. 线程:进程中的一个执行流程. 多线程:有两个或两个以上的并发执行流程. 线程的声明周期 说明: 1. 新建状态(New) ...
- java多线程之Callable、Future和FutureTask
Java并发编程:Callable.Future和FutureTask 在前面的文章中我们讲述了创建线程的2种方式,一种是直接继承Thread,另外一种就是实现Runnable接口. 这2种方式都有一 ...
- Linux搜索查找命令
Linux搜索查找指令 find,用于在文件树中查找文件并作相应的处理 -name:按照文件名查找文件 -perm:按照文件权限查找文件 -user:按照文件属主来查找文件 -size:按照指定的文件 ...
