第二周训练 | 搜索技术 4.3 BFS
A - Red and Black
Write a program to count the number of black tiles which he can reach by repeating the moves described above.
InputThe input consists of multiple data sets. A data set starts with a line containing two positive integers W and H; W and H are the numbers of tiles in the x- and y- directions, respectively. W and H are not more than 20.
There are H more lines in the data set, each of which includes W characters. Each character represents the color of a tile as follows.
'.' - a black tile
'#' - a red tile
'@' - a man on a black tile(appears exactly once in a data set)
OutputFor each data set, your program should output a line which contains the number of tiles he can reach from the initial tile (including itself).
Sample Input
6 9
....#.
.....#
......
......
......
......
......
#@...#
.#..#.
11 9
.#.........
.#.#######.
.#.#.....#.
.#.#.###.#.
.#.#..@#.#.
.#.#####.#.
.#.......#.
.#########.
...........
11 6
..#..#..#..
..#..#..#..
..#..#..###
..#..#..#@.
..#..#..#..
..#..#..#..
7 7
..#.#..
..#.#..
###.###
...@...
###.###
..#.#..
..#.#..
0 0
Sample Output
45
59
6
13
DFS:
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
char room[][];
int dir[][]={{-,},{,-},{,},{,}};
int Wx,Hy,num;
//Wx,Hy:长宽的边界 ,num:从初始瓷砖到能到达的瓷砖的总数
#define CHECK(x,y) (x<Wx&&x>=0&&y>=0&&y<Hy)
//检查是否越界
struct node
{
int x,y;
};
void DFS(int dx,int dy)
{
room[dx][dy]='#';
// cout<<"walk:"<<dx<<","<<dy<<endl;
num++;
for(int i=;i<;++i)
{
int newx=dx+dir[i][];
int newy=dy+dir[i][];
if(CHECK(newx,newy)&&room[newx][newy]=='.')
{
DFS(newx,newy);
// cout<<" back:"<<dx<<","<<dy<<endl;
}
}
}
int main()
{
int x,y,dx,dy;
//dx,dy: 人的站位
while(cin>>Wx>>Hy)
{
if(Wx==&&Hy==)
{
break;
}
for(y=;y<Hy;++y)
{
for(x=;x<Wx;++x)
{
cin>>room[x][y];
if(room[x][y]=='@')
{
dx=x;
dy=y;
}
}
}
for(y=;y<Hy;++y)
{
for(x=;x<Wx;++x)
{
cout<<room[x][y];
}
cout<<endl;
}
num=;
DFS(dx,dy);
cout<<num<<endl;
}
return ;
}
BFS:
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
char room[][];
int dir[][]={{-,},{,-},{,},{,}};
int Wx,Hy,num;
//Wx,Hy:长宽的边界 ,num:从初始瓷砖到能到达的瓷砖的总数
#define CHECK(x,y) (x<Wx&&x>=0&&y>=0&&y<Hy)
//检查是否越界
struct node
{
int x,y;
};
void BFS(int dx,int dy)
{
queue<node> q;
node start,next;
start.x = dx;
start.y = dy;
q.push(start);//把当前节点入队
while(!q.empty())
{
start = q.front();
q.pop();
for(int i=;i<;++i)
{
next.x=start.x+dir[i][];
next.y=start.y+dir[i][];
if(CHECK(next.x,next.y)&&room[next.x][next.y]=='.')
{
room[next.x][next.y]='#';//标记一下当前节点已经走过了
num++;//步数自增
q.push(next);//将子节点入队
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
int x,y,dx,dy;
//dx,dy: 人的站位
while(cin>>Wx>>Hy)
{
if(Wx==&&Hy==)
{
break;
}
for(y=;y<Hy;++y)
{
for(x=;x<Wx;++x)
{
cin>>room[x][y];
if(room[x][y]=='@')
{
dx=x;
dy=y;
}
}
} num=;
BFS(dx,dy);
cout<<num<<endl;
}
return ;
}
B - Catch That Cow
Farmer John has been informed of the location of a fugitive cow and wants to catch her immediately. He starts at a point N (0 ≤ N ≤ 100,000) on a number line and the cow is at a point K (0 ≤ K ≤ 100,000) on the same number line. Farmer John has two modes of transportation: walking and teleporting.
* Walking: FJ can move from any point X to the points X - 1 or X + 1 in a single minute
* Teleporting: FJ can move from any point X to the point 2 × X in a single minute.
If the cow, unaware of its pursuit, does not move at all, how long does it take for Farmer John to retrieve it?
Input
Output
Sample Input
5 17
Sample Output
4
Hint
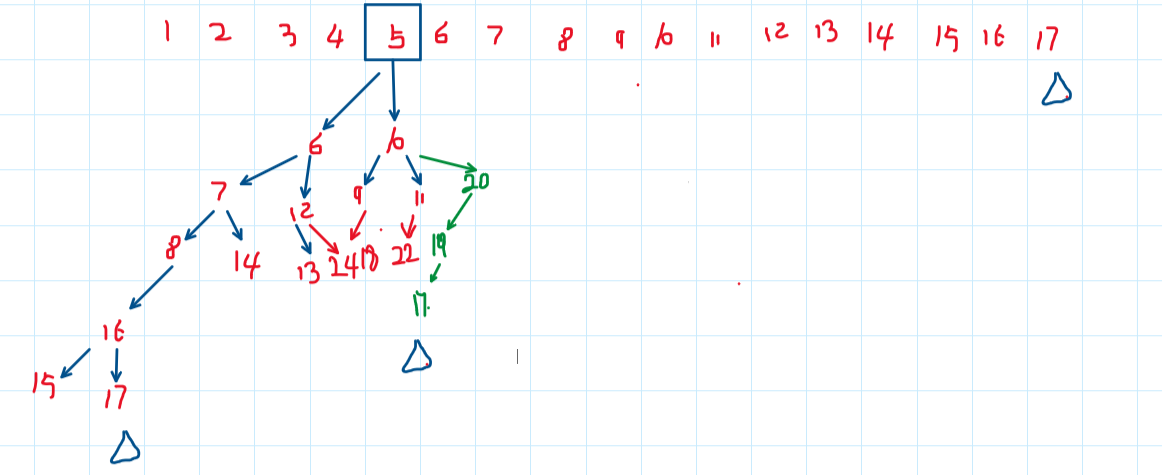
#include<iostream>
#include<string.h>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
int to[]={,-};
int a,b,sum;
int vis[];
struct place
{
int x,time;
};
int check(place k)
{
if(k.x<||k.x>||vis[k.x]==)
return ;
return ;
}
int bfs(place n)
{
place m,next;
queue<place>w;
w.push(n);
while(!w.empty())
{
m=w.front();
w.pop();
if(m.x==b)
return m.time;
for(int i=;i<;i++)
{
next.x=m.x+to[i];
next.time=m.time+;
if(next.x==b)
return next.time;
if(check(next))
{
w.push(next);
vis[next.x]=;
}
}
next.x=m.x*;
next.time=m.time+;
if(next.x==b)
return next.time;
if(check(next))
{
w.push(next);
vis[next.x]=;
}
}
return ;
}
int main()
{
int i,j,t;
place x1;
while(~scanf("%d %d",&a,&b))
{
x1.x=a;
x1.time=;
vis[x1.x]=;
sum=;
sum=bfs(x1);
printf("%d\n",sum);
}
return ;
}
第一次的awful代码:
感觉不足之处就在于我的记录步长的没有跟每一个节点一一对应,用结构体的化每一次遍历都可以得到到达当前节点的时间,这样多次累加后就可以得到通用时间,而我这里用的是num去更新result,虽然不知道哪里有问题,但是不如上面解法思路清晰,而且多次更新result容易超时,而且在操作多个数组的时候,结构体比数组更快:
在频繁操作同一个节点的情况下,用结构体更快。
用数组的那个方案是缓存不友好的,因为每次读写不同的数组都更可能无法命中缓存,从而产生额外的缓存IO操作。而用结构体的话,这个结构体整个都会被加载进缓存里(只要不是超大的结构体),程序每次读写结构体都是直接对缓存进行修改,再加上编译器的寄存器优化,这个性能就秒杀数组方案了。当然这里的“秒杀”是夸张手法,绝大多数情况下,cache missing不会产生显著的性能差异,除非真的是性能要求特别变态的场景。
作者:刘子昂
链接:https://www.zhihu.com/question/285229473/answer/442702496
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
#define LEN 1000000
int dir[]={-,,};
int Wx,Hy,num;
//检查是否访问过
int mark[LEN];
int dx,dy;
int result=LEN;
struct node
{
int number;
int steep;
};
bool flag(int x,int y)
{
if(x>y)
{
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
bool CHECK(int x)
{
if(!mark[x])
{
mark[x]=;
return true;
}
else
{
return false;
}
}
void BFS(int dx)
{
queue<int> q;
int start;
q.push(dx);//把当前人的位置入队
CHECK(dx); while(!q.empty())
{
start = q.front();
q.pop();
// cout<<"当前出队:"<<start<<endl;
// cout<<"当前的步长是:"<<num<<endl;
for(int i=;i<;++i)
{
int temp=;
if(dir[i]==)
{
temp=start*dir[i];
}
else
{
temp=start+dir[i];
} if(flag(dx,dy)&&temp>dx)
{
//当牛在人的左边时,人要往左边走
continue;
} if(!flag(dx,dy)&&temp<dx)
{
//当牛在人的右边时,人要往右边走
continue;
}
if(temp==dy)
{ if(result>num&&num!=)
result=num;
num=;
continue;
}
else if(CHECK(temp)&&temp>=&&temp<dy*)
{
//如果没有访问过就入队
q.push(temp);
}
}
num++;
}
return ;
}
int main()
{
//dx,dy: 人的站位和牛的站位
cin>>dx>>dy;
num=;
BFS(dx);
cout<<result;
return ;
}
C - Find The Multiple
Input
Output
Sample Input
2
6
19
0
Sample Output
10
100100100100100100
111111111111111111
这题只要输出的结果对就行,没有统一答案。
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int flag=1;
void dfs(long long temp,int num,int count)
{
// cout<<"temp="<<temp<<" count="<<count<<endl;
if(flag==0) return;
if(count>18) return;//long long 越界
if(temp%num==0)
{
flag=0;
cout<<temp<<endl;
return;
} dfs(temp*10,num,count+1);
dfs(temp*10+1,num,count+1);
return;
}
int main()
{
int n;
while(1){ cin>>n;
flag=1;
if(n==0) break;
dfs(1,n,0);
}
return 0;
}
D - Prime Path
— It is a matter of security to change such things every now and then, to keep the enemy in the dark.
— But look, I have chosen my number 1033 for good reasons. I am the Prime minister, you know!
— I know, so therefore your new number 8179 is also a prime. You will just have to paste four new digits over the four old ones on your office door.
— No, it’s not that simple. Suppose that I change the first digit to an 8, then the number will read 8033 which is not a prime!
— I see, being the prime minister you cannot stand having a non-prime number on your door even for a few seconds.
— Correct! So I must invent a scheme for going from 1033 to 8179 by a path of prime numbers where only one digit is changed from one prime to the next prime.
Now, the minister of finance, who had been eavesdropping, intervened.
— No unnecessary expenditure, please! I happen to know that the price of a digit is one pound.
— Hmm, in that case I need a computer program to minimize the cost. You don't know some very cheap software gurus, do you?
— In fact, I do. You see, there is this programming contest going on... Help the prime minister to find the cheapest prime path between any two given four-digit primes! The first digit must be nonzero, of course. Here is a solution in the case above.
1033
1733
3733
3739
3779
8779
8179
The cost of this solution is 6 pounds. Note that the digit 1 which got pasted over in step 2 can not be reused in the last step – a new 1 must be purchased.
Input
Output
Sample Input
3
1033 8179
1373 8017
1033 1033
Sample Output
6
7
0
#include<iostream>
#include<queue>
#include<string.h>
using namespace std;
int start,finish,prime[10001]={1,1,0},vis[10001];
struct node
{
int cur;//保存当前的素数
int step;
};
// init():生成一张素数表:不是素数标记为1,是素数标记为0
void init(){
for(int i=2;i<10001;i++)
{
if(!prime[i])
{
for(int j=2;i*j<10001;j++)
prime[i*j] = 1;
}
}
}
int BFS(){
queue<node>q;
vis[start]=1;
node m,n;
m.cur=start;
m.step=0;
q.push(m);
//将第一个素数入队 while(!q.empty())
{
int i,j;
char num[5];
m = q.front();
q.pop();
if(m.cur==finish) return m.step; for(i=0;i<4;i++)
{
sprintf(num,"%d",m.cur);//sprintf主要功能是把格式化的数据写入某个字符串中
for(j=0;j<10;j++)
{
if(j==0&&i==0) continue;//如果不是四位数就过
if (i == 0)
n.cur = j * 1000 + (num[1] - '0') * 100 + (num[2] - '0') * 10 + (num[3] - '0');//第一位数字的1-9遍历
else if (i == 1)
n.cur =(num[0] - '0') * 1000 + j * 100 + (num[2] - '0') * 10 + (num[3] - '0');//第二位数字的1-9遍历
else if (i == 2)
n.cur =(num[0] - '0') * 1000 + (num[1] - '0') * 100 + j * 10 + (num[3] - '0');//第三位数字的1-9遍历
else if (i == 3)
n.cur =(num[0] - '0') * 1000 + (num[1] - '0') * 100 + (num[2] - '0') * 10 + j ;//第四位数字的1-9遍历 if(!prime[n.cur]&&!vis[n.cur])
{
//如果是素数并且没有访问过
//当前这个数入队,并且记录到达它的步长
n.step=m.step+1;
vis[n.cur]=1;
q.push(n);
}
}
}
}
return -1;
}
int main()
{
int t,x;
cin>>t;
init();
while(t--)
{
cin>>start>>finish;
memset(vis, 0, sizeof(vis));
x=BFS();
if(x == -1) cout<<"Impossible"<<endl;
else cout<<x<<endl;
}
return 0;
}
E - Pots
这题要注意的是visited数组要开到100开外
You are given two pots, having the volume of A and B liters respectively. The following operations can be performed:
- FILL(i) fill the pot i (1 ≤ i ≤ 2) from the tap;
- DROP(i) empty the pot i to the drain;
- POUR(i,j) pour from pot i to pot j; after this operation either the pot j is full (and there may be some water left in the pot i), or the pot i is empty (and all its contents have been moved to the pot j).
Write a program to find the shortest possible sequence of these operations that will yield exactly C liters of water in one of the pots.
Input
On the first and only line are the numbers A, B, and C. These are all integers in the range from 1 to 100 and C≤max(A,B).
Output
The first line of the output must contain the length of the sequence of operations K. The following K lines must each describe one operation. If there are several sequences of minimal length, output any one of them. If the desired result can’t be achieved, the first and only line of the file must contain the word ‘impossible’.
Sample Input
3 5 4
Sample Output
6
FILL(2)
POUR(2,1)
DROP(1)
POUR(2,1)
FILL(2)
POUR(2,1)
#include<iostream>
#include<queue>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
int As,Bs,Cs;
#define LEN 109
int visited[LEN][LEN];
string mark_list[6]={"FILL(1)\n","DROP(1)\n","POUR(1,2)\n","FILL(2)\n","DROP(2)\n","POUR(2,1)\n"};
struct pots
{
int A;
int B;
int steep;
string state;
};
queue<struct pots> q;
int bfs(int A,int B)
{
pots temp,head;
head.A=A;
head.B=B;
head.steep=0;
head.state="";
visited[A][B]=1;
q.push(head); while(!q.empty())
{
head=q.front();
q.pop();
// cout<<"当前的锅(A,B+steep):"<<head.A<<" "<<","<<head.B<<"+"<<head.steep<<" state:"<<head.state<<endl;
if(head.A==Cs||head.B==Cs)
{
cout<<head.steep<<endl;
for(int i=0;i<head.state.length();++i)
{
cout<<mark_list[head.state[i]-'0'-1];
}
return 1;
}
for(int i=1;i<=6;++i)
{
temp=head;
// if(B>Bs||A>As)continue;
switch(i)
{
case 1:
temp.A=As;
break;
case 2:
temp.A=0;
break;
case 3:
if((Bs-temp.B)<=temp.A)
{
temp.A=temp.A-(Bs-temp.B);
temp.B=Bs;
}
else
{
temp.B+=temp.A;
temp.A=0;
}
break;
case 4:
temp.B=Bs;
break;
case 5:
temp.B=0;
break;
case 6:
if((As-temp.A)<=temp.B)
{
temp.B=temp.B-(As-temp.A);
temp.A=As;
}
else
{
temp.A+=temp.B;
temp.B=0;
}
break;
}
// cout<<i<<"操作后的锅(A,B+steep):"<<temp.A<<" "<<","<<temp.B<<"+"<<temp.steep<<" state:"<<temp.state<<endl;
if(visited[temp.A][temp.B]==0)
{
visited[temp.A][temp.B]=1;
temp.steep++;
temp.state+=i+'0';
q.push(temp);
}
}
};
return -1;
}
int main()
{
int A,B;
cin>>As>>Bs>>Cs;
int num=bfs(0,0);
if(num==-1)
{
cout<<"impossible"<<endl;
} return 0;
}
第二周训练 | 搜索技术 4.3 BFS的更多相关文章
- 2017-2018-2 《网络对抗技术》 20155302 第二周 Exp1 PC平台逆向破解(5)M
2017-2018-2 <网络对抗技术> 20155302 第二周 Exp1 PC平台逆向破解(5)M 1-实践目标 1.1-实践介绍 本次实践的对象是一个名为pwn1的linux可执行文 ...
- 2017-2018-2 《网络对抗技术》 20155310 第二周 Exp1 PC平台逆向破解(5)M
2017-2018-2 <网络对抗技术> 20155310 第二周 Exp1 PC平台逆向破解(5)M 一.实践目标 1.1实践介绍 本次实践的对象是一个名为pwn1的linux可执行文件 ...
- 2017-2018-2 《网络对抗技术》 20155319 第二周 Exp1 PC平台逆向破解(5)M
2017-2018-2 <网络对抗技术> 20155319 第二周 Exp1 PC平台逆向破解(5)M 一.实践目标 1.1实践介绍 本次实践的对象是一个名为pwn1的linux可执行文件 ...
- 2017-2018-2 《网络对抗技术》 20155322 第二周 Exp1 PC平台逆向破解(5)M
#2017-2018-2 <网络对抗技术> 20155322 第二周 Exp1 PC平台逆向破解(5)M [博客目录] 1-实践目标 1.1-实践介绍 1.2-实践内容 1.3-实践要求 ...
- 201521123072《Java程序》第二周总结
201521123072<Java程序>第二周总结 标签(空格分隔): Java学习 [TOC] 1,本周小结 1,字符串的使用, (字符串变量作为对象来处理),所以字符串相等就要用到eq ...
- 20175211 2018-2019-2 《Java程序设计》第二周学习总结
目录 教材学习内容总结 第二章 第三章 教材学习中的问题和解决过程 代码调试中的问题和解决过程 代码托管 上周考试错题总结 其他(感悟.思考等,可选) 学习进度条 参考资料 教材学习内容总结 第二章 ...
- 20172321 2017-2018-2 《Java程序设计》第二周学习总结
20172321 2017-2018-2 <Java程序设计>第二周学习总结 教材学习内容总结 第一章要点: 要点1 字符串:print和println用法的区别,字符串的拼接,java中 ...
- 吴恩达《深度学习》-课后测验-第五门课 序列模型(Sequence Models)-Week 2: Natural Language Processing and Word Embeddings (第二周测验:自然语言处理与词嵌入)
Week 2 Quiz: Natural Language Processing and Word Embeddings (第二周测验:自然语言处理与词嵌入) 1.Suppose you learn ...
- 吴恩达《深度学习》-第一门课 (Neural Networks and Deep Learning)-第二周:(Basics of Neural Network programming)-课程笔记
第二周:神经网络的编程基础 (Basics of Neural Network programming) 2.1.二分类(Binary Classification) 二分类问题的目标就是习得一个分类 ...
随机推荐
- delphi中如何实现文件的复制?
http://zhidao.baidu.com/link?url=nyAzCpeXAbaT8M3qqAePCF1Zr7q-oK4hpAUNIaRYpHcbmIwYsLr1TXoTt8759HtR1EB ...
- 树莓派3b折腾指南
最近入手了树梅派3b,搭建了宿舍共享的热点和NAS,搭建透明代理科学上网的计划还没实现. 先报个价,一套折腾下来花了500大洋,树梅派3加外壳200,电源加内存卡100,显示器淘宝二手150,有线键鼠 ...
- linux 截取变量字符串
STR=123456abc FINAL=`echo ${STR: -1}` 或者 FINAL=${STR: -1} 都可以让FINAL获得c这个最后一个字符 Linux 的字符串截取很有用.有八种 ...
- HDU 6538 Neko and quadrilateral(极角排序+旋转坐标系)
这道题简直太好了,对于计算几何选手需要掌握的一个方法. 首先对于求解四边形面积,我们可以将四边形按对角线划分成两个三角形,显然此时四边形的面积最大最小值就变成了求解里这个对角线最近最远的点对. 对于此 ...
- Knight Moves (双向bfs)
# 10028. 「一本通 1.4 例 3」Knight Moves [题目描述] 编写一个程序,计算一个骑士从棋盘上的一个格子到另一个格子所需的最小步数.骑士一步可以移动到的位置由下图给出. [算法 ...
- Java Collection总结
继续啊啊啊啊啊啊 7. collection基本用法 Collection: add(obj) remove(obj) size() isEmpty() contains(obj) iterator( ...
- 《死磕 Elasticsearch 方法论》:普通程序员高效精进的 10 大狠招!(完整版)
原文:<死磕 Elasticsearch 方法论>:普通程序员高效精进的 10 大狠招!(完整版) 版权声明:本文为博主原创文章,遵循CC 4.0 BY-SA版权协议,转载请附上原文出处链 ...
- win32 socket编程(二)——TCP/IP
一.大端.小端法定义 1.1小端法(Little-Endian)就是低位字节排放在内存的低地址端即该值的起始地址,高位字节排放在内存的高地址端. (主机字节顺序) 1.2 大端法(Big-Endian ...
- Sql Server 2008安装时提示重启计算机失败解决办法
在键盘上按下组合键[Win]+[R],调出运行窗口. 在窗口中输入“regedit”,点击确定,打开注册表管理界面. 在注册表左侧目录栏中找到如下位置:“HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\ ...
- C# 获取一个文件的MD5值
using System; using System.Collections.Generic; using System.IO; using System.Linq; using System.Tex ...
