HDU 1710 Binary Tree Traversals(二叉树遍历)
Description
A binary tree is a finite set of vertices that is either empty or consists of a root r and two disjoint binary trees called the left and right subtrees. There are three most important ways in which the vertices of a binary tree can be systematically traversed or ordered. They are preorder, inorder and postorder. Let T be a binary tree with root r and subtrees T1,T2.
In a preorder traversal of the vertices of T, we visit the root r followed by visiting the vertices of T1 in preorder, then the vertices of T2 in preorder.
In an inorder traversal of the vertices of T, we visit the vertices of T1 in inorder, then the root r, followed by the vertices of T2 in inorder.
In a postorder traversal of the vertices of T, we visit the vertices of T1 in postorder, then the vertices of T2 in postorder and finally we visit r.
Now you are given the preorder sequence and inorder sequence of a certain binary tree. Try to find out its postorder sequence.
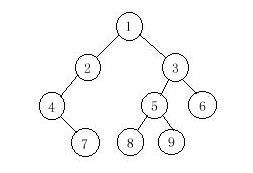
Input
The input contains several test cases. The first line of each test case contains a single integer n (1<=n<=1000), the number of vertices of the binary tree. Followed by two lines, respectively indicating the preorder sequence and inorder sequence. You can assume they are always correspond to a exclusive binary tree.
Output
For each test case print a single line specifying the corresponding postorder sequence.
Sample Input
9 1 2 4 7 3 5 8 9 6 4 7 2 1 8 5 9 3 6
Sample Output
7 4 2 8 9 5 6 3 1
思路
题意:已知前序遍历和中序遍历,求后序遍历。
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 10005;
void post(int n,int a[],int b[],int c[])
{
if (n <= 0) return;
int pos;
for (int i = 0;i < n;i++)
if (b[i] == a[0]) pos = i;
post(pos,a + 1,b,c);
post(n - pos - 1,a + pos + 1,b + pos + 1,c + pos);
c[n - 1] = a[0];
}
int main()
{
int N;
while (~scanf("%d",&N))
{
int a[maxn],b[maxn],c[maxn];
for (int i = 0;i < N;i++) scanf("%d",&a[i]);
for (int i = 0;i < N;i++) scanf("%d",&b[i]);
post(N,a,b,c);
printf("%d",c[0]);
for (int i = 1;i < N;i++) printf(" %d",c[i]);
printf("\n");
}
return 0;
}
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int maxn = 1005;
typedef struct Tree{
Tree *left,*right;
int val;
}Tree;
Tree *head;
Tree *build(int a[],int b[],int N)
{
Tree *node;
for (int i = 0;i < N;i++)
{
if (b[i] == a[0])
{
node = (Tree *)malloc(sizeof(Tree));
node->val = a[0];
node->left = build(a + 1,b,i);
node->right = build(a + i + 1,b + i + 1, N - i - 1);
return node;
}
}
return NULL;
}
void Print(Tree *p)
{
if (p == NULL) return;
Print(p->left);
Print(p->right);
if (p == head) printf("%d\n",p->val);
else printf("%d ",p->val);
free(p);
}
int main()
{
int N,a[maxn],b[maxn];
while (~scanf("%d",&N))
{
for (int i = 0;i < N;i++) scanf("%d",&a[i]);
for (int i = 0;i < N;i++) scanf("%d",&b[i]);
head = build(a,b,N);
Print(head);
}
return 0;
}
HDU 1710 Binary Tree Traversals(二叉树遍历)的更多相关文章
- hdu 1710 Binary Tree Traversals 前序遍历和中序推后序
题链;http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1710 Binary Tree Traversals Time Limit: 1000/1000 MS (J ...
- HDU 1710 Binary Tree Traversals(二叉树)
题目地址:HDU 1710 已知二叉树先序和中序求后序. #include <stdio.h> #include <string.h> int a[1001], cnt; ty ...
- HDU 1710 Binary Tree Traversals (二叉树遍历)
Binary Tree Traversals Time Limit: 1000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/O ...
- hdu1710(Binary Tree Traversals)(二叉树遍历)
Binary Tree Traversals Time Limit: 1000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/O ...
- HDU 1710 Binary Tree Traversals(树的建立,前序中序后序)
Binary Tree Traversals Time Limit: 1000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 32768/32768 K (Java/O ...
- 【二叉树】hdu 1710 Binary Tree Traversals
acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1710 [题意] 给定一棵二叉树的前序遍历和中序遍历,输出后序遍历 [思路] 根据前序遍历和中序遍历递归建树,再后续遍历输出 m ...
- HDU 1710 Binary Tree Traversals
题意:给出一颗二叉树的前序遍历和中序遍历,输出其后续遍历 首先知道中序遍历是左子树根右子树递归遍历的,所以只要找到根节点,就能够拆分出左右子树 前序遍历是按照根左子树右子树递归遍历的,那么可以找出这颗 ...
- hdu 1701 (Binary Tree Traversals)(二叉树前序中序推后序)
Binary Tree Traversals T ...
- hdu1710 Binary Tree Traversals(二叉树的遍历)
A binary tree is a finite set of vertices that is either empty or consists of a root r and two disjo ...
随机推荐
- 扩展欧几里得算法(extgcd)
相信大家对欧几里得算法,即辗转相除法不陌生吧. 代码如下: int gcd(int a, int b){ return !b ? gcd(b, a % b) : a; } 而扩展欧几里得算法,顾名思义 ...
- 开源 XFControls , 用于 Xamarin.Forms 的自定义控件集
从此以后不会在博客园上发表任何言论,观注我的同志们,洗洗睡吧. ---------------------- 博文移至: http://www.jianshu.com/p/3ed1a3f10955
- 也议 js闭包和ie内存泄露原理
可以, 但小心使用. 闭包也许是 JS 中最有用的特性了. 有一份比较好的介绍闭包原理的文档. 有一点需要牢记, 闭包保留了一个指向它封闭作用域的指针, 所以, 在给 DOM 元素附加闭包时, 很可能 ...
- 教你写一个web远程控制小工具
惯例先上图 晚上躺床上了,发现忘关电脑了,又不想起来关,来用手机控制电脑多好,百度了下,果然一大把.哈,我自己为什么不自己也实现个呢,任意的自己diy.Just do it. 如果不想看如何实现,那么 ...
- Nginx的配置文件
#user nobody; worker_processes 1; #error_log logs/error.log; #error_log logs/error.log notice; #erro ...
- 北大OJ 1001题
题目:输入一序列的正实数和幂次(正整数)对,然后打印结果(具体的比这个精细) 这道题是关于大数计算的(大数求幂),从开始建立思路,到写代码.调式到最后被AC以及最终的优化,总共用了差不多一天的时间.开 ...
- HTML5基础知识(4)--white-space属性
1.white-space 属性设置如何处理元素内的空白. 这个属性声明建立布局过程中如何处理元素中的空白符.值 pre-wrap 和 pre-line 是 CSS 2.1 中新增的. 默认值: no ...
- Android NestedScrolling与分发机制
在Android5.0之间要实现控件的嵌套滑动,都是要自己处理View事件即分发机制. 共有三个方法: dispatchTouchEvent().onInterceptTouchEvent()和 ...
- Android网络开发之实时获取最新数据
在实际开发中更多的是需要我们实时获取最新数据,比如道路流量.实时天气信息等,这时就需要通过一个线程来控制视图的更新. 示例:我们首先创建一个网页来显示系统当前的时间,然后在Android程序中每隔5秒 ...
- 【BZOJ 3879】SvT
http://www.lydsy.com/JudgeOnline/problem.php?id=3879 SvT的中文是后缀虚树? 反正本蒟蒻不懂,还是$O(nlogn)$的后缀数组和单调栈维护来做, ...
