cuda编程-矩阵乘法(2)
采用shared memory加速
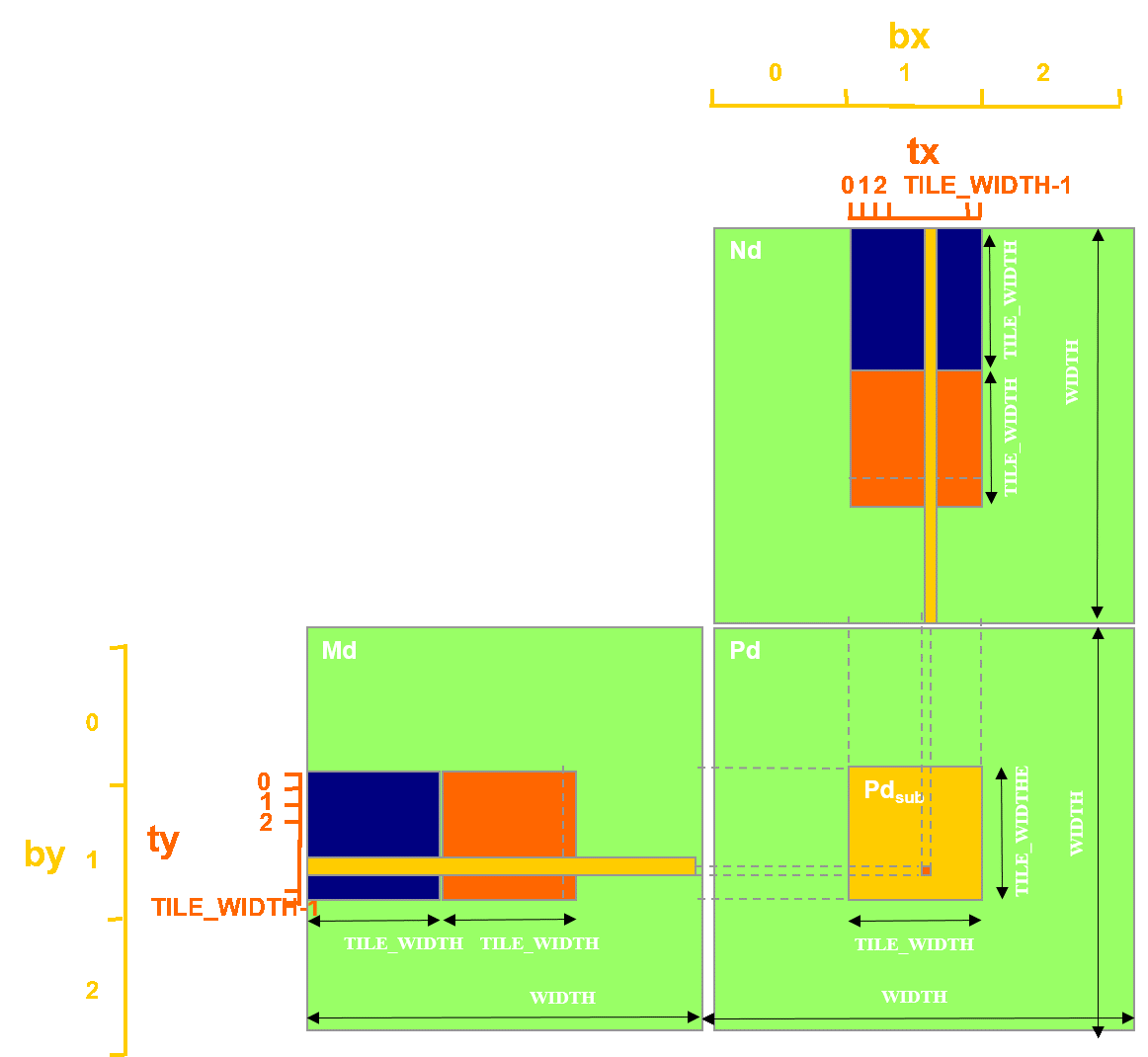
代码
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <math.h>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cuda_runtime.h>
#include <device_launch_parameters.h>
#include "functions.h" #define TILE_SIZE 16 __global__ void matrixMulKernel(float *C, float *A, float *B, int width, int height){
__shared__ float tile_A[TILE_SIZE][TILE_SIZE];
__shared__ float tile_B[TILE_SIZE][TILE_SIZE];
unsigned int tx = threadIdx.x;
unsigned int ty = threadIdx.y;
unsigned int gx = blockIdx.x * TILE_SIZE + tx;
unsigned int gy = blockIdx.y * TILE_SIZE + ty;
if (gx >= width || gy >= height)
return; // Load shared memory
int tile_num = (width + TILE_SIZE - ) / TILE_SIZE;
float sum = ;
for (int i = ; i < tile_num; ++i){
int bound = min(width, TILE_SIZE);
for (int j = tx; j < bound; j += blockDim.x){
tile_A[ty][j] = A[gy * width + i * bound + j];
}
for (int j = ty; j < bound; j += blockDim.y){
tile_B[j][tx] = B[(i * bound + j) * width + gx];
}
//Synchronize to make sure the sub-matrices are loaded before starting the computation
__syncthreads(); for (int j = ; j < bound; ++j){
sum += tile_A[ty][j] * tile_B[j][tx];
}
//Synchronize to make sure that the preceding computation is done before loading two new
//sub-matrices of M and N in the next iteration
__syncthreads();
}
C[gy*width + gx] = sum;
} void constantInit(float *data, int size, float val){
for (int i = ; i < size; ++i){
data[i] = val;
}
} void matrixMul(){
int dev_id = ;
cudaSetDevice(dev_id); // Allocate host memory for matrices A and B
int width = ;
int height = ;
unsigned int size = width * height;
unsigned int mem_size = sizeof(float)* size;
float *h_A = (float *)malloc(mem_size);
float *h_B = (float *)malloc(mem_size);
float *h_C = (float *)malloc(mem_size); // Initialize host memory
const float valB = 0.01f;
constantInit(h_A, size, 1.0f);
constantInit(h_B, size, valB); // Allocate device memory
float *d_A, *d_B, *d_C;
cudaMalloc((void **)&d_A, mem_size);
cudaMalloc((void **)&d_B, mem_size);
cudaMalloc((void **)&d_C, mem_size); // Memcpy
cudaMemcpy(d_A, h_A, mem_size, cudaMemcpyHostToDevice);
cudaMemcpy(d_B, h_B, mem_size, cudaMemcpyHostToDevice); // Config dim
dim3 block(TILE_SIZE, TILE_SIZE);
dim3 grid((width + block.x - ) / block.x, (height + block.y - ) / block.y);
matrixMulKernel <<<grid, block >>>(d_C, d_A, d_B, width, height); // Memcpy device to host
cudaMemcpy(h_C, d_C, mem_size, cudaMemcpyDeviceToHost); // Check
printf("Checking computed result for correctness: ");
bool correct = true;
// test relative error by the formula // |<x, y>_cpu - <x,y>_gpu|/<|x|, |y|> < eps
double eps = .e-;
// machine zero
for (int i = ; i < (int)(width * height); i++) {
double abs_err = fabs(h_C[i] - (width * valB));
double dot_length = width;
double abs_val = fabs(h_C[i]);
double rel_err = abs_err / abs_val / dot_length;
if (abs_err > eps) {
printf("Error! Matrix[%05d]=%.8f, ref=%.8f error term is > %E\n", i, h_C[i], (float)(width*height), eps);
correct = false;
}
}
printf("%s\n", correct ? "Result = PASS" : "Result = FAIL");
}
合并访存:tile_A按行存储,tile_B按列存储,sum=row_tile_A * row_tile_B
__global__ void matrixMulKernel(float *C, float *A, float *B, int width, int height){
__shared__ float tile_A[TILE_SIZE][TILE_SIZE];
__shared__ float tile_B[TILE_SIZE][TILE_SIZE];
unsigned int tx = threadIdx.x;
unsigned int ty = threadIdx.y;
unsigned int gx = blockIdx.x * TILE_SIZE + tx;
unsigned int gy = blockIdx.y * TILE_SIZE + ty;
if (gx >= width || gy >= height)
return;
// Load shared memory
int tile_num = (width + TILE_SIZE - ) / TILE_SIZE;
float sum = ;
for (int i = ; i < tile_num; ++i){
tile_A[tx][ty] = A[gy * width + i * TILE_SIZE + tx];
tile_B[ty][tx] = B[(i * TILE_SIZE + ty) * width + gx];
//Synchronize to make sure the sub-matrices are loaded before starting the computation
__syncthreads();
for (int j = ; j < TILE_SIZE; ++j){
sum += tile_A[j][ty] * tile_B[j][tx];
}
//Synchronize to make sure that the preceding computation is done before loading two new
//sub-matrices of M and N in the next iteration
__syncthreads();
}
C[gy*width + gx] = sum;
}
cuda编程-矩阵乘法(2)的更多相关文章
- cuda编程-矩阵乘法(1)
本方法采用简单的单线程计算每组行和列乘加运算 代码如下: #include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <iostrea ...
- cuda(2) 矩阵乘法优化过程
Created on 2013-8-5URL : http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_a502f1a30101mjch.html@author: zhxfl转载请说明出处 # ...
- CUDA编程之快速入门
CUDA(Compute Unified Device Architecture)的中文全称为计算统一设备架构.做图像视觉领域的同学多多少少都会接触到CUDA,毕竟要做性能速度优化,CUDA是个很重要 ...
- CUDA编程之快速入门【转】
https://www.cnblogs.com/skyfsm/p/9673960.html CUDA(Compute Unified Device Architecture)的中文全称为计算统一设备架 ...
- 详解CUDA编程
CUDA 是 NVIDIA 的 GPGPU 模型,它使用 C 语言为基础,可以直接以大多数人熟悉的 C 语言,写出在显示芯片上执行的程序,而不需要去学习特定的显示芯片的指令或是特殊的结构.” 编者注: ...
- CUDA 矩阵乘法终极优化指南
作者:马骏 | 旷视 MegEngine 架构师 前言 单精度矩阵乘法(SGEMM)几乎是每一位学习 CUDA 的同学绕不开的案例,这个经典的计算密集型案例可以很好地展示 GPU 编程中常用的优化技巧 ...
- OpenCL 矩阵乘法
▶ 矩阵乘法,按照书里的内容进行了几方面的优化,包括局部内存,矢量数据类型,寄存器,流水线等. ● 最直接的乘法.调用时 main.c 中使用 size_t globalSize[] = { rowA ...
- 【Cuda编程】加法归约
目录 cuda编程并行归约 AtomicAdd调用出错 gpu cpu下时间计算 加法的归约 矩阵乘法 矩阵转置 统计数目 平方和求和 分块处理 线程相邻 多block计算 cuda编程并行归约 At ...
- CUDA编程(十)使用Kahan's Summation Formula提高精度
CUDA编程(十) 使用Kahan's Summation Formula提高精度 上一次我们准备去并行一个矩阵乘法.然后我们在GPU上完毕了这个程序,当然是非常单纯的把任务分配给各个线程.也没有经过 ...
随机推荐
- 完成了Coursera的一个机器学习课程
终于完成了这个课程,从开始学习,到现在差不多过了一年的时间,中间由于一些原因耽搁了,最终还是完成了,记录一下!
- c# 利用百度图像处理【人像分割】一键抠图
百度AI开放平台-人像分割: http://ai.baidu.com/tech/body/seg 注意本文后面的话,百度这个技术效果太差劲了,国外这 https://www.remove.bg/ 个比 ...
- UVA12253 简单加密法 Simple Encryption
这题到现在还是只有我一个人过?太冷门了吧,毕竟你谷上很少有人会去做往年ACM比赛的题 题面意思很简单,每次给出\(K_1\),让你求一个\(K_2\)满足\(K_1^{K_2}\equiv K_2(\ ...
- [翻译] 初看 ASP.NET Core 3.0 即将到来的变化
[翻译] 初看 ASP.NET Core 3.0 即将到来的变化 原文: A first look at changes coming in ASP.NET Core 3.0 在我们努力完成下一个 m ...
- Python 学习 第十篇:正则表达式 - re
规则表达式(Regular Expression, RE),又称作正则表达式,通常用于检索.替换符合指定规则的文本,正则表达式定义的规则,称作模式(Pattern),即正则表达式的作用是从文本中查找到 ...
- 使用JWT来实现对API的授权访问
目录 什么是JWT JWT的结构 Header Payload Signature 解码后的JWT JWT是怎样工作的 在JAVA里使用JWT 引入依赖 JWT Service 生成JWT 解码JWT ...
- 字典 dict
# --------------------------我愿作一叶小舟,驶向远方.----------------------------------------------------------- ...
- koa入门
创建koa2工程 首先初始化项目 npm init -y 项目名称 安装koa $ npm i koa 我们创建一个目录hello-koa并作为工程目录用VS Code打开.然后,我们创建app.js ...
- Unix / Linux 线程的实质
线程与进程的比较 概述: 进程是具有一定独立功能的程序关于某个数据集合上的一次运行活动,进程是系统进行资源分配和调度的一个独立单位. 线程是进程的一个实体,是CPU调度和分派的基本单位,它是比进程更小 ...
- python中Metaclass的理解
今天在学习<python3爬虫开发实战>中看到这样一段代码3 class ProxyMetaclass(type): def __new__(cls, name, bases, attrs ...
