position 小结
position:
- static
- fixed
- relative
- absolute
- sticky
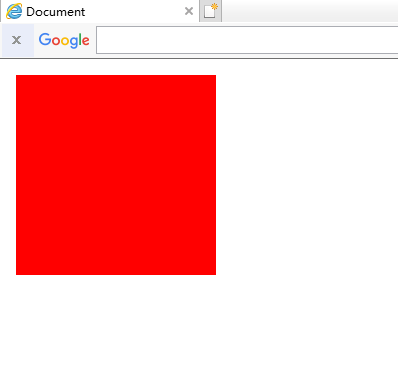
1.static
static定位是HTML元素的默认值,即没有定位,元素出现在正常的流中。因此,这种定位不会受到top,bottom,left,right的影响
正常:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Document</title>
<style type="text/css">
div{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: red;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div></div>
</body>
</html>
插入后:

<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Document</title>
<style type="text/css">
div{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: red;
/*这里*/
position: static;
top: -100px;
left: -100px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div></div>
</body>
</html>
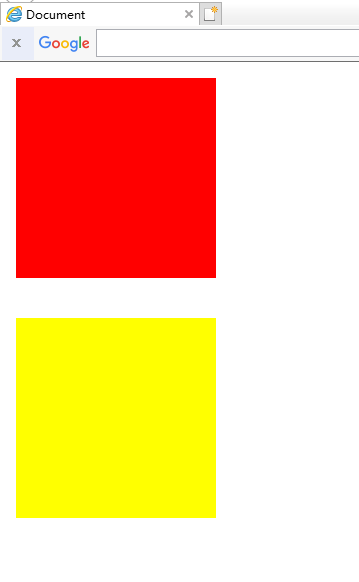
2.fixed
fixed定位是指元素的位置相对于浏览器窗口是固定的位置,即使窗口滚动它也不会滚动,且fixed定位会使元素脱离文档流,即,元素不占据空间,比如,网页经常跳出来的小广告。
正常:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Document</title>
<style type="text/css">
.top{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: red;
margin-bottom: 20px;
}
.bottom{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: yellow;
margin-bottom: 20px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="top"></div>
<div class="bottom"></div>
</body>
</html>
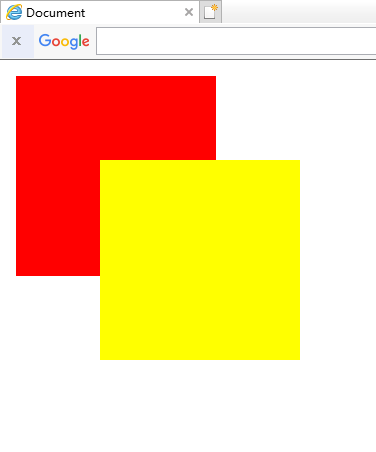
插入后:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Document</title>
<style type="text/css">
.top{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: red;
margin-bottom: 20px;
}
.bottom{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: yellow;
margin-bottom: 20px;
/*这里*/
position: fixed;
top: 50px;
left: 50px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="top"></div>
<div class="bottom"></div>
</body>
</html>
注意:fixed定位在IE7和IE8下需要描述!DOCTYPE才能支持
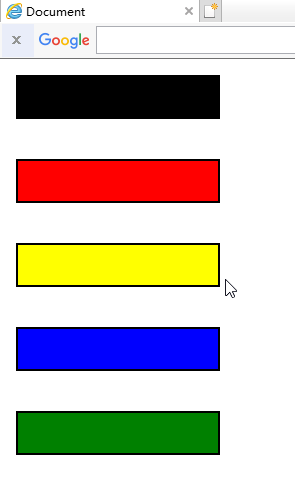
3.relative
相对定位元素的定位是相对它自己的正常位置的定位
正常:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Document</title>
<style type="text/css">
.normal{
width: 100px;
height: 20px;
background-color: black;
border: 1px solid black;
margin-bottom: 20px;
}
.top{
width: 100px;
height: 20px;
background-color: red;
border: 1px solid black;
margin-bottom: 20px;
}
.bottom{
width: 100px;
height: 20px;
background-color: yellow;
border: 1px solid black;
margin-bottom: 20px;
}
.left{
width: 100px;
height: 20px;
background-color: blue;
border: 1px solid black;
margin-bottom: 20px;
}
.right{
width: 100px;
height: 20px;
background-color: green;
border: 1px solid black;
margin-bottom: 20px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="normal"></div>
<div class="top"></div>
<div class="bottom"></div>
<div class="left"></div>
<div class="right"></div>
</body>
</html>
插入后:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Document</title>
<style type="text/css">
.normal{
width: 100px;
height: 20px;
background-color: black;
border: 1px solid black;
margin-bottom: 20px;
}
.top{
width: 100px;
height: 20px;
background-color: red;
border: 1px solid black;
margin-bottom: 20px;
/*这里*/
position: relative;
top: 10px;
left: 0px;
}
.bottom{
width: 100px;
height: 20px;
background-color: yellow;
border: 1px solid black;
margin-bottom: 20px;
/*这里*/
position: relative;
left: 0px;
bottom: 10px;
}
.left{
width: 100px;
height: 20px;
background-color: blue;
border: 1px solid black;
margin-bottom: 20px;
/*这里*/
position: relative;
left: 10px;
top: 0px;
}
.right{
width: 100px;
height: 20px;
background-color: green;
border: 1px solid black;
margin-bottom: 20px;
/*这里*/
position: relative;
right: -20px;
top: 0px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="normal"></div>
<div class="top"></div>
<div class="bottom"></div>
<div class="left"></div>
<div class="right"></div>
</body>
</html>
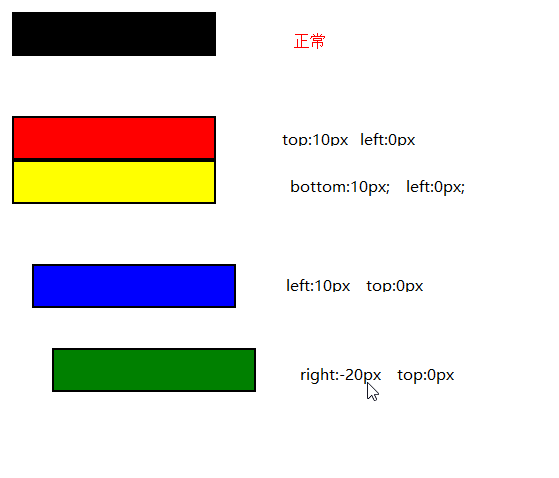
注意:这里移动后是移动前的负的位置
移动后对于移动前:如果值为负数,则直接换成正数
如果值为正数,则直接改变为相反方向
即使相对元素的内容移动了,但是预留的空间的元素,仍然保持正常流动,也就是说相对移动后不会对下面的元素造成影响


可以对比一下,蓝色的框并没有因为黄色的框移上去而跟着移上去,黄色的框仍然保持原来的占位
4.absolute
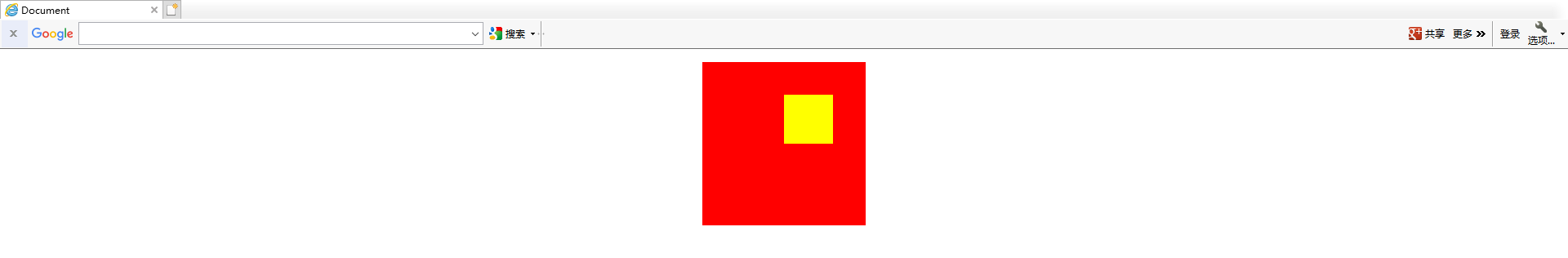
绝对定位的元素相对于最近的已经定位的父元素,如果元素没有已经定位的父元素,那么它的位置相对于<html>
正常:

<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Document</title>
<style type="text/css">
.father{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: red;
margin: 0 auto;
}
.son{
width: 30px;
height: 30px;
background-color: yellow;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="father">
<div class="son"></div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
没有已经定位的父元素:

<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Document</title>
<style type="text/css">
.father{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: red;
margin: 0 auto;
}
.son{
width: 30px;
height: 30px;
background-color: yellow;
/*这里*/
position: absolute;
top: 20px;
left: 50px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="father">
<div class="son"></div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
有已经定位的父元素:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Document</title>
<style type="text/css">
.father{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: red;
margin: 0 auto;
/*这里*/
position: relative;
}
.son{
width: 30px;
height: 30px;
background-color: yellow;
/*这里*/
position: absolute;
top: 20px;
left: 50px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="father">
<div class="son"></div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
position 小结的更多相关文章
- css position小结
relative:可使top,right,bottom,left等相对于自身位置来进行偏移:若无则这些偏移都不会起作用 absolute:寻找离自己最近position为relative或absolu ...
- 定位属性position
定位属性position小结 1.元素为fixed(固定的),则是固定定位,即使是子元素,也不参考父元素的位置,即以浏览器作为参考定位.相当于电脑屏幕的一只蚂蚁,你无论怎么滑动屏幕,还是在原来的位置. ...
- position:absolute/relative/fixed小结
1.绝对定位:position:absolute; 当一个div块的位置被定义为绝对定位absolute时,也就意味着它失去了文档流的位置,后面的文档流会紧跟着补上来接替它的位置.如果上下左右的绝对偏 ...
- position和float小结
position属性值 Position的属性值共有四个static.relative.absolute.fixed. static 所有元素在默认的情况下position属性均为static,而我们 ...
- CSS - position属性小结
Relative: 属于文档流,针对自身进行偏移: Absolute: 脱离文档流,针对最近的定位元素进行偏移,如果没有,则针对根元素,即body标签尽心偏移: Fixed: 和absolute基本一 ...
- CSS属性小结之--半透明处理
项目中经常有遇到需求半透明的情况,如图片.文字.容器.背景等等,每次都要去翻以前的项目,不甚其烦.现在一次性做个小结,方便自己查阅,也同时分享给大家: 一. 元素容器透明 .div{ opacity: ...
- 关于用display:table让元素居中的小结
我们都知道让元素垂直居中有一种简单的方法:给需要居中的元素用一个父级包起来,并给它设置样式:display:table:同时给这个父级设置好高度:再给需要居中的元素一个display:table-ce ...
- position:absolute绝对定位解读
position:absolute绝对定位解读 摘要 用四段代码解释absolute的定位问题,进而从概念的角度切实解决html布局问题. 一.背景 常常遇到这样一些问题,很容易混淆.“浏览器屏 ...
- Spring boot中使用springfox来生成Swagger Specification小结
Rest接口对应Swagger Specification路径获取办法: 根据location的值获取api json描述文件 也许有同学会问,为什么搞的这么麻烦,api json描述文件不就是h ...
随机推荐
- 【spring】使用spring过程中踩到的坑
这里简单记录一下,学习spring的时候碰过的异常: 异常:org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanDefinitionStoreException: Unexpe ...
- material palette
https://www.materialpalette.com/
- 转:vue项目如何刷新当前页面
想必大家在刨坑vue的时候也遇到过下面情形:比如在删除或者增加一条记录的时候希望当前页面可以重新刷新或者如下面这种: 如果希望点击确定的时候,Dialog 对话框关闭的时候,当前http://loca ...
- Arrays和String单元测试-20175218
Arrays和String单元测试 一.题目 在IDEA中以TDD的方式对String类和Arrays类进行学习 测试相关方法的正常,错误和边界情况 String类 charAt split Arra ...
- POJ-1860.CurrencyExchange(Spfa判断负环模版题)
本题思路:每完成一次交换之后交换余额多于原钱数则存在正环,输出YES即可. 参考代码: #include <cstdio> #include <cstring> #includ ...
- CentOS7+CDH5.14.0安装全流程记录,图文详解全程实测-5安装JDK及安装mysql数据库
1.安装JDK 可以不用卸载自带的openjdk,配好环境变量即可. 下载文件:jdk-8u151-linux-x64.tar.gz 附:JDK各版本下载地址:https://www.oracle.c ...
- php 微信自定义分享接口
<?php class JSSDK { private $appId; private $appSecret; public function __construct($appId, $appS ...
- Windows网络发现无法启动
解决方法: 运行services.msc命令,打开服务界面.分别将Function Discovery Resource Publication.SSDP Discovery.UPnP Device ...
- PIL库学习及运用
了解PIL以及安装. 个方面的功能: (1) 图像归档:对图像进行批处理.生产图像预览.图像格式转换等. (2) 图像处理:图像基本处理.像素处理.颜色处理等. 安装PIL在cmd中输入 pip in ...
- odoo 配置文件
[options] ; addons模块的查找路径 addons_path = E:\GreenOdoo8.0\source\openerp\addons ; 管理员主控密码(用于创建.还原和备份数据 ...
