hdu_1050 Moving Tables 贪心
Moving Tables
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others)
Total Submission(s): 45555 Accepted Submission(s): 14817
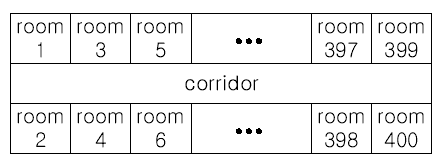
The floor has 200 rooms each on the north side and south side along the corridor. Recently the Company made a plan to reform its system. The reform includes moving a lot of tables between rooms. Because the corridor is narrow and all the tables are big, only one table can pass through the corridor. Some plan is needed to make the moving efficient. The manager figured out the following plan: Moving a table from a room to another room can be done within 10 minutes. When moving a table from room i to room j, the part of the corridor between the front of room i and the front of room j is used. So, during each 10 minutes, several moving between two rooms not sharing the same part of the corridor will be done simultaneously. To make it clear the manager illustrated the possible cases and impossible cases of simultaneous moving.

For each room, at most one table will be either moved in or moved out. Now, the manager seeks out a method to minimize the time to move all the tables. Your job is to write a program to solve the manager’s problem.
这个题真是迷了, 一开始想的就是每次能搬尽量多的桌子,这样就能最快搬完,所以按照区间的右端排的序。
Input Output
data[i].s = (data[i].s+1)/2; data[i].t = (data[i].t+1)/2;
#include <iostream>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <algorithm> using namespace std; struct dat
{
int s;
int t;
int visit;
} data[]; bool cmp(dat a, dat b)
{
return a.s<b.s; // return a.t<b.t 是错的
} int main()
{
int t, n; scanf("%d",&t);
while(t--)
{
scanf("%d",&n);
for(int i=; i<n; i++)
{
scanf("%d%d",&data[i].s, &data[i].t);
if(data[i].s>data[i].t)
{
int temp = data[i].s;
data[i].s = data[i].t;
data[i].t = temp;
}
data[i].s = (data[i].s+)/;
data[i].t = (data[i].t+)/;
data[i].visit=;
//printf("%d%d\n",data[i].s,data[i].t);
} sort(data, data+n, cmp); int ans=, j, temp; for(int i=; i<n; i++)
{
if(!data[i].visit)
{
j=i+;
temp = i;
data[i].visit=;
while(j!=n)
{
if(!data[j].visit&&data[temp].t < data[j].s)
{
data[j].visit=;
temp=j;
}
j++;
}
ans++;
}
} printf("%d\n", ans*); }
return ;
}
另一种思路就是区间覆盖,找覆盖次数最大的点的覆盖次数。
hdu_1050 Moving Tables 贪心的更多相关文章
- Moving Tables(贪心或Dp POJ1083)
Moving Tables Time Limit: 1000MS Memory Limit: 10000K Total Submissions: 28304 Accepted: 9446 De ...
- zstu.2512. Moving Tables(贪心)
Moving Tables Time Limit: 1 Sec Memory Limit: 64 MB Submit: 1182 Solved: 563 Description The famo ...
- HDU1050(Moving Tables:贪心算法)
解题思路: 这种做法是基于hdu2037的做法上考虑的,找出所有可以同时搬运的桌子,然后就很方便求出最短总时间. 还有一种更简单的做法是直接遍历一遍找出与别的重复次数最多的那片区域,重复次数*10就可 ...
- UVAlive 2326 Moving Tables(贪心 + 区间问题)
The famous ACM (Advanced Computer Maker) Company has rented a floor of a building whose shape is in ...
- --hdu 1050 Moving Tables(贪心)
题目链接:http://acm.hdu.edu.cn/showproblem.php?pid=1050 AC code: #include<stdio.h> #include<str ...
- POJ 1083 && HDU 1050 Moving Tables (贪心)
Moving Tables Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others) To ...
- hdoj 1050 Moving Tables【贪心区间覆盖】
Moving Tables Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others)Tot ...
- HDOJ 1050 Moving Tables
Moving Tables Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others)Tot ...
- Moving Tables
Moving Tables Time Limit : 2000/1000ms (Java/Other) Memory Limit : 65536/32768K (Java/Other) Total ...
随机推荐
- c语言 0与非0
------------恢复内容开始------------ 结论: 其它的编程语言中有布尔数据类型,并用百来表示逻辑真和逻辑假,C语言没有这个内置类度型,在C语言中真和假是用整型值来表示知的,0就表 ...
- vue中的$router 和 $route的区别
最近在学习vue的单页面应用开发,需要vue全家桶,其中用到了VueRouter,在路由的设置和跳转中遇到了两个对象$router 和 $route ,有些傻傻分不清,后来自己结合网上的博客和自己本地 ...
- autojs,autojs 发送http请求,autojs 解析json数据
如题,我这个就直接上代码吧 (function () { let request = http.request; // 覆盖http关键函数request,其他http返回最终会调用这个函数 http ...
- MongoDB查询mgov2的聚合方法
1.多条表数据累计相加. respCount := struct { Rebatescore int64 //变量命名必须要和查询的参数一样.}{} o := bson.M{"$match& ...
- 路由与交换,cisco路由器配置,静态路由
网络是一个大型的拓扑结构,在路由表中,最重要的是管理距离和度量值 管理距离 管理距离用来确定路由的优先级.管理距离的范围是0-255之间的整数值.值越低代表优先级越高.0代表最高优先级.并且只有直连路 ...
- 31.1 Exception 的method :getMessage()、 printStackTrace()
package day31_exception; import java.lang.Exception; /* * Throwable的常用方法: String getMessage() :原因 St ...
- 在java 中一种简单方式的声明静态Map常量的方法
我现在需要在一个类里面放一个HashMap,往里面放一些数据,每次要从数据库中取数据的时候先查找HashMap,看是否已经存在,若存在就直接提取,若不存在就从数据库中抽取数据之后再放到HashMap中 ...
- SolrCloud(solr集群+zookeeper集群)
一.集群介绍 1. 什么是SolrCloud SolrCloud(solr 云)是Solr提供的分布式搜索方案,当你需要大规模,容错,分布式索引和检索能力时使用 SolrCloud.当一个系统的索引 ...
- 新版本Xcode 6的视图调试详解
开发者会经常遇到视图或者Auto Layout约束中存在bug的情况,并且这种bug很难通过代码发现,所以开发者很有必要熟知如何进行简单高效的视图调试,而Xcode 6的发布使得视图调试变得前所未有的 ...
- AJ学IOS 之微博项目实战(7)程序启动新特性用UICollectionViewController实现
AJ分享,必须精品 一:效果 这里实现了大多数app都会有的软件新特性的功能,用的是UICollectionViewController实现的 二:思路 这里用了UICollectionViewCon ...
