Good Bye 2017
太菜了啊,一不小心就goodbye rating了
1 second
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Your friend has n cards.
You know that each card has a lowercase English letter on one side and a digit on the other.
Currently, your friend has laid out the cards on a table so only one side of each card is visible.
You would like to know if the following statement is true for cards that your friend owns: "If a card has a vowel on one side, then it has an even digit on the other side." More specifically, a vowel is one of 'a', 'e', 'i', 'o' or 'u', and even digit is one of '0', '2', '4', '6' or '8'.
For example, if a card has 'a' on one side, and '6' on the other side, then this statement is true for it. Also, the statement is true, for example, for a card with 'b' and '4', and for a card with 'b' and '3' (since the letter is not a vowel). The statement is false, for example, for card with 'e' and '5'. You are interested if the statement is true for all cards. In particular, if no card has a vowel, the statement is true.
To determine this, you can flip over some cards to reveal the other side. You would like to know what is the minimum number of cards you need to flip in the worst case in order to verify that the statement is true.
The first and only line of input will contain a string s (1 ≤ |s| ≤ 50), denoting the sides of the cards that you can see on the table currently. Each character of s is either a lowercase English letter or a digit.
Print a single integer, the minimum number of cards you must turn over to verify your claim.
ee
2
z
0
0ay1
2
In the first sample, we must turn over both cards. Note that even though both cards have the same letter, they could possibly have different numbers on the other side.
In the second sample, we don't need to turn over any cards. The statement is vacuously true, since you know your friend has no cards with a vowel on them.
In the third sample, we need to flip the second and fourth cards.
原谅我英语不好,看懂了就是统计元音和奇数个数
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
string c="aeiou13579";
int main()
{
string s;
cin>>s;
int ans=;
for(int i=;s[i];i++)
for(int j=;c[j];j++)
if(s[i]==c[j])
ans++;
cout<<ans;
return ;
}
1 second
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Bob programmed a robot to navigate through a 2d maze.
The maze has some obstacles. Empty cells are denoted by the character '.', where obstacles are denoted by '#'.
There is a single robot in the maze. It's start position is denoted with the character 'S'. This position has no obstacle in it. There is also a single exit in the maze. It's position is denoted with the character 'E'. This position has no obstacle in it.
The robot can only move up, left, right, or down.
When Bob programmed the robot, he wrote down a string of digits consisting of the digits 0 to 3, inclusive. He intended for each digit to correspond to a distinct direction, and the robot would follow the directions in order to reach the exit. Unfortunately, he forgot to actually assign the directions to digits.
The robot will choose some random mapping of digits to distinct directions. The robot will map distinct digits to distinct directions. The robot will then follow the instructions according to the given string in order and chosen mapping. If an instruction would lead the robot to go off the edge of the maze or hit an obstacle, the robot will crash and break down. If the robot reaches the exit at any point, then the robot will stop following any further instructions.
Bob is having trouble debugging his robot, so he would like to determine the number of mappings of digits to directions that would lead the robot to the exit.
The first line of input will contain two integers n and m (2 ≤ n, m ≤ 50), denoting the dimensions of the maze.
The next n lines will contain exactly m characters each, denoting the maze.
Each character of the maze will be '.', '#', 'S', or 'E'.
There will be exactly one 'S' and exactly one 'E' in the maze.
The last line will contain a single string s (1 ≤ |s| ≤ 100) — the instructions given to the robot. Each character of s is a digit from 0 to 3.
Print a single integer, the number of mappings of digits to directions that will lead the robot to the exit.
5 6
.....#
S....#
.#....
.#....
...E..
333300012
1
6 6
......
......
..SE..
......
......
......
01232123212302123021
14
5 3
...
.S.
###
.E.
...
3
0
For the first sample, the only valid mapping is 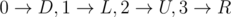 , where D is down, L is left, U is up, R is right.
, where D is down, L is left, U is up, R is right.
全排列24种情况啊,等等为毛我写的只有23种,挂了两个题果断GG(do,while都不懂的我果断GG啊,但是我感觉思路很简洁啊,就是让1 2 3 4分别去代表U D L R,然后我a[0]代表上,a[1]代表下,a[2]代表左,a[3]代表右
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
string s[];
int a[],sx,sy;
int main()
{
int n,m;
cin>>n>>m;
for(int i=;i<n;i++)
cin>>s[i];
for(int i=;i<n;i++)
for(int j=;j<m;j++)
if(s[i][j]=='S')sx=i,sy=j;
string c;
cin>>c;
for(int i=;i<;i++)
a[i]=i+;
int ans=;
do
{
int f=;
int tx=sx,ty=sy;
for(int i=;c[i];i++)
{
if(c[i]==a[])
tx-=;
else if(c[i]==a[])
tx+=;
else if(c[i]==a[])
ty-=;
else ty+=;
if(tx<||ty<||tx>=n||ty>=m)
break;
if(s[tx][ty]=='#')break;
if(s[tx][ty]=='E'){f=;break;}
}
ans+=f;
}while(next_permutation(a,a+));
cout<<ans;
return ;
}
2 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Carol is currently curling.
She has n disks each with radius r on the 2D plane.
Initially she has all these disks above the line y = 10100.
She then will slide the disks towards the line y = 0 one by one in order from 1 to n.
When she slides the i-th disk, she will place its center at the point (xi, 10100). She will then push it so the disk’s ycoordinate continuously decreases, and x coordinate stays constant. The disk stops once it touches the line y = 0or it touches any previous disk. Note that once a disk stops moving, it will not move again, even if hit by another disk.
Compute the y-coordinates of centers of all the disks after all disks have been pushed.
The first line will contain two integers n and r (1 ≤ n, r ≤ 1 000), the number of disks, and the radius of the disks, respectively.
The next line will contain n integers x1, x2, ..., xn (1 ≤ xi ≤ 1 000) — the x-coordinates of the disks.
Print a single line with n numbers. The i-th number denotes the y-coordinate of the center of the i-th disk. The output will be accepted if it has absolute or relative error at most 10 - 6.
Namely, let's assume that your answer for a particular value of a coordinate is a and the answer of the jury is b. The checker program will consider your answer correct if 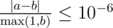 for all coordinates.
for all coordinates.
6 2
5 5 6 8 3 12
2 6.0 9.87298334621 13.3370849613 12.5187346573 13.3370849613
The final positions of the disks will look as follows:
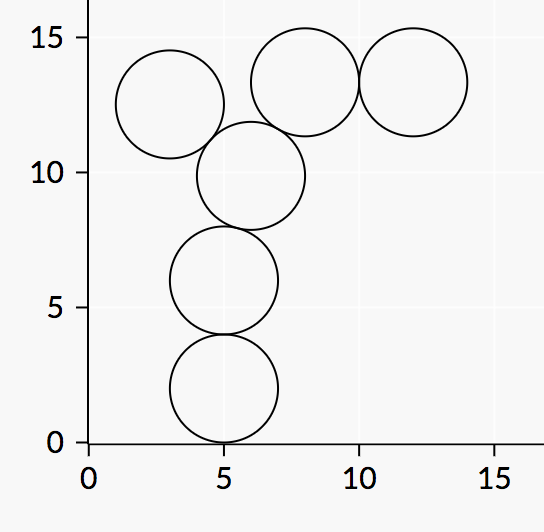
In particular, note the position of the last disk.
C我逃了开根为负的情况,但是也不会是0啊,最起码是r
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int x[];
double y[];
int main()
{
int n,r;
cin>>n>>r;
for(int i=;i<n;i++)
cin>>x[i];
for(int i=;i<n;i++)
{
y[i]=r;
for(int j=;j<i;j++)
if(fabs(x[j]-x[i])<=.*r)
y[i]=max(y[i],y[j]+sqrt(*r*r-(x[i]-x[j])*(x[i]-x[j])));
}
for(int i=;i<n;i++)
printf("%.12f ",y[i]);
return ;
}
2 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
You are given three integers k, pa and pb.
You will construct a sequence with the following algorithm: Initially, start with the empty sequence. Each second, you do the following. With probability pa / (pa + pb), add 'a' to the end of the sequence. Otherwise (with probability pb / (pa + pb)), add 'b' to the end of the sequence.
You stop once there are at least k subsequences that form 'ab'. Determine the expected number of times 'ab' is a subsequence in the resulting sequence. It can be shown that this can be represented by P / Q, where P and Q are coprime integers, and  . Print the value of
. Print the value of 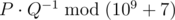 .
.
The first line will contain three integers integer k, pa, pb (1 ≤ k ≤ 1 000, 1 ≤ pa, pb ≤ 1 000 000).
Print a single integer, the answer to the problem.
1 1 1
2
3 1 4
370000006
The first sample, we will keep appending to our sequence until we get the subsequence 'ab' at least once. For instance, we get the sequence 'ab' with probability 1/4, 'bbab' with probability 1/16, and 'aab' with probability 1/8. Note, it's impossible for us to end with a sequence like 'aabab', since we would have stopped our algorithm once we had the prefix 'aab'.
The expected amount of times that 'ab' will occur across all valid sequences is 2.
For the second sample, the answer is equal to  .
.
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int MD=1e9+,N=;
int dp[N][N];
int po(int a,int x)
{
int ans=;
while(x)
{
if(x&) ans=1LL*ans*a%MD;
a=1LL*a*a%MD;
x>>=;
}
return ans;
}
int main()
{
int k,a,b,ta,tb,ans=;
scanf("%d%d%d",&k,&a,&b);
ta=1LL*a*po(a+b,MD-)%MD;
tb=MD-ta+;
dp[][]=;
for(int i=; i<=k; i++)
for(int j=; j<k-i; j++)
{
dp[i+][j]=(dp[i+][j]+1LL*dp[i][j]*ta%MD)%MD;
if(j+i+i>=k)ans=(ans+1LL*dp[i][j]*tb%MD*(j+i+i-k)%MD)%MD;
else dp[i][j+i]=(dp[i][j+i]+1LL*dp[i][j]*tb%MD)%MD;
}
ans=(ans+k+1LL*a*po(b,MD-)%MD)%MD;
printf("%d\n",ans);
}
Good Bye 2017的更多相关文章
- Good Bye 2017 A B C
Good Bye 2017 A New Year and Counting Cards 题目链接: http://codeforces.com/contest/908/problem/A 思路: 如果 ...
- Hello 2018, Bye 2017
2017年过去了,过去一年经历了太多,改变了好多好多,可以说人生进入了另一个阶段,有可能是成熟吧. 回顾2017 去年换了新工作,离开了将近工作了8年的公司,不带走一丝云彩,为其任劳任怨,最后没有任何 ...
- Good Bye 2017(送命场)
9815人数场,9500+围观神仙打架...断断续续打Codeforces也快有一年啦,第一次打Good Bye场,满怀前排膜tourist的心愿参加了这场送命场,虽然没看到tourist.不过还是得 ...
- Good Bye 2017 E. New Year and Entity Enumeration
先按照绿点进行分块 第一个绿点和最后一个绿点之后很好处理不说了 两个绿点之间的讨论: 有两种方案 1:红(蓝)点和绿点顺序连接,距离为相邻绿点距离(也就是双倍绿点距离) 2:红(蓝)点和绿点的点阵中寻 ...
- Good Bye 2017 D. New Year and Arbitrary Arrangement
看了别人的题解 首先这题是一个dp dp[i][j] i是当前有多少个a j是当前有多少个ab子序列 dp[i][j] = dp[i+1][j]*Pa + dp[i][i+j]*Pb; i,j 时加一 ...
- Good Bye 2017 G. New Year and Original Order
G. New Year and Original Order time limit per test 2 seconds memory limit per test 256 megabytes inp ...
- Good Bye 2017 C. New Year and Curling
Carol is currently curling. She has n disks each with radius r on the 2D plane. Initially she has al ...
- Good Bye 2017 部分题解
D. New Year and Arbitrary Arrangement 分析 \(dp[i][j]\) 表示已有 \(i\) 个 \(a\) 和 \(j\) 个 \(ab\) 的情况下继续构造能得 ...
- 【EOJ Monthly 2018.2 (Good bye 2017)】
23333333333333333 由于情人节要回家,所以就先只放代码了. 此题是与我胖虎过不去. [E. 出老千的 xjj] #include<cstdio> #include<c ...
随机推荐
- Python+selenium之获取请求信息
basicConfig()所捕获的log信息.不过其开启的debug模式只能捕获到客户端像服务器发送的post()请求,而无法获取服务器所返回的应答信息. from random import ran ...
- mysql-新增、更新、删除语句
1.插入数据: INSERT INTO t_book VALUES(NULL,'我爱我家',20,'张三',1); INSERT INTO t_book(id,bookName,price,autho ...
- HDU Rabbit and Grass 兔子和草 (Nim博弈)
思路:简单Nim博弈,只需要将所给的数字全部进行异或,结果为0,则先手必败.否则必胜. #include <iostream> using namespace std; int main( ...
- python基础一 day15 复习
迭代器和生成器迭代器 可迭代协议 —— 含有iter方法的都是可迭代的 迭代器协议 —— 含有next和iter的都是迭代器 特点 节省内存空间 方便逐个取值,一个迭代器只能取一次.生成器 —— 迭代 ...
- Spring boot 集成 Dubbo 快速搭建
架构: 1.ZooKeeper:服务注册中心 2.api工程:提供对外暴露的服务API 3.provider:服务提供者 4.consumer:服务消费者 示例如下: (一)新建 Maven 项目 a ...
- linux目录结构及文件管理
Linux的目录结构: / 根分区 linux文件系统的起点 /bin 普通用户的命令,普通用户能使用 /sbin 管理员使用的命令,只有管理 ...
- 10分钟搞懂toString和valueOf函数(详细版)
首先要说明的是这两种方法是toPrimitive抽象操作里会经常用到的. 默认情况下,执行这个抽象操作时会先执行valueOf方法,如果返回的不是原始值,会继续执行toString方法,如果返回的还不 ...
- [BZOJ] 1520: [POI2006]Szk-Schools
费用流解决. abs内传不了int..CE一次 #include<iostream> #include<cstring> #include<cstdio> #inc ...
- 网络流(一)——Edmonds Karp算法
首先是一些关于网络流的术语: 源点:即图的起点. 汇点:即图的终点. 容量:有向边(u,v)允许通过的最大流量. 增广路:一条合法的从源点流向汇点的路径. 网络流问题是在图上进行解决的,我们通常可以将 ...
- python入门:1-99所有数的和附带等式
#!/usr/bin/env python # -*- coding:utf-8 -*- #1-99所有数的和的等式 #start(开始,译音:思达二测)sum(合计,译音:桑木)temp(临时雇员, ...
