《Java多线程编程核心技术》读后感(一)

1、继承Thread
package First;
public class MyThread extends Thread {
public void run() {
super.run();
System.out.println("mythread");
}
}
package First;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyThread myThread = new MyThread();
myThread.start();
System.out.println("main");
}
}

在使用多线程技术时,代码的运行结果与代码执行顺序或调用顺序是无关的。
package First;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyThread myThread = new MyThread();
myThread.start();
myThread.start();
System.out.println("main");
}
}
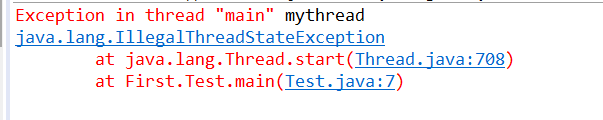
多次执行start(),会出现java.lang.IllegalThreadStateException异常
package First;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyThread myThread = new MyThread();
myThread.run();
System.out.println("main");
}
}
start()通知“”线程规划器“”此线程已经准备就绪,等待调用线程对象的run(),具有异步效果。如果直接调用run(),则是同步,从上到下顺序依次执行

执行start()顺序不代表线程启动的顺序。
2、实现runnable接口
package First;
public class MyRunnable implements Runnable {
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("运行中");
}
}
package First;
public class Run {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Runnable runnable = new MyRunnable();
Thread thread = new Thread(runnable);
thread.start();
System.out.println("运行结束");
}
}

Thread构造函数:

构造函数Thread(Runnable target)意味着不光可以传入runnable接口的对象,还可以传入Thread类的对象,这样做完全可以将一个Thread对象的run()方法交给其他线程进行调用
实例变量与线程安全
(1)不共享数据
package First;
public class MyThread extends Thread {
private int count = 5;
public MyThread(String name) {
super();
//设置线程名称
this.setName(name);
}
public void run() {
super.run();
while(count>0) {
count--;
System.out.println("由"+this.currentThread().getName()+"计算,count="+count);
}
}
}
package First;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyThread a = new MyThread("A");
MyThread b = new MyThread("B");
MyThread c = new MyThread("C");
a.start();
b.start();
c.start();
System.out.println("main");
}
}

(2)共享数据
package First;
public class MyThread extends Thread {
private int count = 5;
public void run() {
super.run();
//此实例不要用for语句,因为使用同步后其他线程就得不到运行的机会了
count--;
System.out.println("由"+this.currentThread().getName()+"计算,count="+count);
}
}
package First;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyThread myThread = new MyThread();
Thread a = new Thread(myThread,"A");
Thread b = new Thread(myThread,"B");
Thread c = new Thread(myThread,"C");
Thread d = new Thread(myThread,"D");
Thread e = new Thread(myThread,"E");
a.start();
b.start();
c.start();
d.start();
e.start();
System.out.println("main");
}
}
非线程安全问题(随机):主要是指多个线程对同一个对象中的同一个实例变量进行操作时会出现值被更改、值不同步的情况,进而影响程序的执行流程

某些JVM中,i--的操作分成三步:
1)取得原有的i值
2)计算i-1
3)对i进行赋值
在这三个步骤中,如果有多个线程同时访问,那么一定会出现非线程安全问题
package First;
public class MyThread extends Thread {
private int count = 5;
synchronized public void run() {
super.run();
count--;
System.out.println("由"+this.currentThread().getName()+"计算,count="+count);
}
}
程序改成上述,就不会出现问题了

一个非线程安全的例子:
package First;
public class LoginServlet {
private static String usernameRef;
private static String passwordRef;
public static void doPost(String username,String password) {
try {
usernameRef = username;
if(username.equals("a")) {
Thread.sleep(5000);
}
passwordRef = password;
System.out.println("username="+usernameRef+" password="+password);
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
}
}
}
package First;
public class ALogin extends Thread{
public void run() {
LoginServlet.doPost("a", "aa");
}
}
package First;
public class BLogin extends Thread{
public void run() {
LoginServlet.doPost("b", "bb");
}
}
package First;
public class Run {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ALogin a = new ALogin();
a.start();
BLogin b = new BLogin();
b.start();
}
}
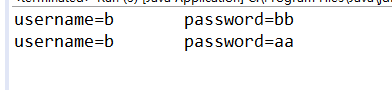
解决非线程安全问题使用synchronized
package First;
public class LoginServlet {
private static String usernameRef;
private static String passwordRef;
synchronized public static void doPost(String username,String password) {
try {
usernameRef = username;
if(username.equals("a")) {
Thread.sleep(5000);
}
passwordRef = password;
System.out.println("username="+usernameRef+" password="+password);
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
}
}
}
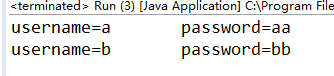
留意i--与System.out.println()
println()与i++联合使用时有可能出现另外一种异常情况
package First;
public class MyThread extends Thread {
private int i = 5;
public void run() {
//代码i--由前面项目中单独一行运行改成在当前项目中在println()方法中直接进行打印
System.out.println("i="+(i--)+" threadName="+Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
}
package First;
public class Run {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyThread run = new MyThread();
Thread t1 = new Thread(run);
Thread t2 = new Thread(run);
Thread t3 = new Thread(run);
Thread t4 = new Thread(run);
Thread t5 = new Thread(run);
t1.start();
t2.start();
t3.start();
t4.start();
t5.start();
}
}
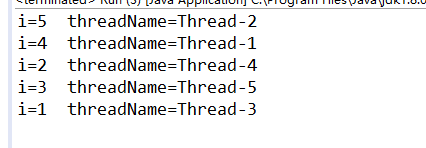

虽然println()内部是同步的,但i--的操作却是在进入println()之前发生的。所以为了防止非线程安全问题,还是应该继续使用同步方法
currentTread()方法
package First;
public class MyThread extends Thread {
public MyThread() {
System.out.println("构造方法的打印: "+Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
public void run() {
System.out.println("run方法打印:"+Thread.currentThread().getName());
}
}
package First;
public class Run {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyThread myThread = new MyThread();
myThread.start();
}
}
package First;
public class Run {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyThread myThread = new MyThread();
//myThread.start();
myThread.run();
}
}

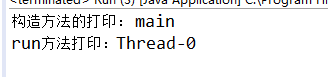
由第一个实验可以看出:Mythread的构造函数是被main函数调用的,而run()方法是被名称为Thread-0调用的
由第二个实验可以看出:直接调用run()的话,则调用者名称为main
package First;
public class CountOperate extends Thread {
public CountOperate() {
System.out.println("CountOperation---begin");
System.out.println("Thread.currentThread().getName()="+Thread.currentThread().getName());
System.out.println("this.getName()"+this.getName());
System.out.println("CountOperation---end");
}
public void run() {
System.out.println("CountOperation---begin");
System.out.println("Thread.currentThread().getName()="+Thread.currentThread().getName());
System.out.println("this.getName()"+this.getName());
System.out.println("CountOperation---end");
}
}
package First;
public class Run {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName());
CountOperate countOperate = new CountOperate();
Thread thread = new Thread(countOperate);
thread.setName("A");
thread.start();
}
}
isLive()
判断当前线程是否处于活跃状态
package First;
public class MyThread extends Thread {
public void run() {
System.out.println("run="+this.isAlive());
}
}
package First;
public class Run {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyThread myThread = new MyThread();
System.out.println("begin="+myThread.isAlive());
myThread.start();
System.out.println("end="+myThread.isAlive());
}
}

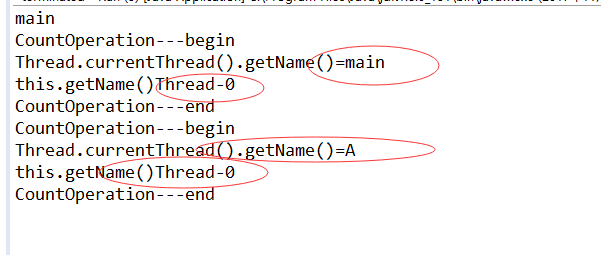
注意最后一个println()的值是不确定的
package First;
public class CountOperate extends Thread {
public CountOperate() {
System.out.println("CountOperation---begin");
System.out.println("Thread.currentThread().getName()="+Thread.currentThread().getName());
System.out.println("Thread.currentThread().isAlive()="+Thread.currentThread().isAlive());
System.out.println("this.getName()"+this.getName());
System.out.println("this.isAlive()"+this.isAlive());
System.out.println("CountOperation---end");
}
public void run() {
System.out.println("run---begin");
System.out.println("Thread.currentThread().getName()="+Thread.currentThread().getName());
System.out.println("Thread.currentThread().isAlive()="+Thread.currentThread().isAlive());
System.out.println("this.getName()"+this.getName());
System.out.println("this.isAlive()"+this.isAlive());
System.out.println("run---end");
}
}
package First;
public class Run {
public static void main(String[] args) {
CountOperate countOperate = new CountOperate();
Thread thread = new Thread(countOperate);
System.out.println("main begin t1 isAlive="+thread.isAlive());
thread.setName("A");
thread.start();
System.out.println("main end t1 isAlive="+thread.isAlive()); }
}
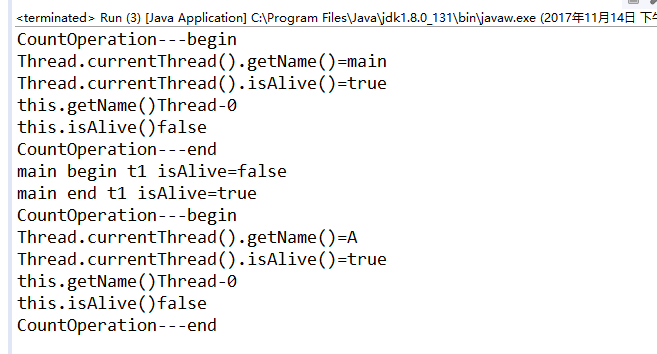
如果将线程对象以构造参数的方式传递给Thread对象进行start()启动时,运行的结果和前面实例的结果有些差异。造成这样的差异的原因还是来自于Thread.currentThread()和this之间的差异(具体解释参考:http://blog.csdn.net/yezis/article/details/57513130)
sleep()方法
是在指定的毫秒数内让当前“正在执行的线程”休眠(暂停执行)这个“正在执行的线程”是指this.currentThread()返回的线程
package First;
public class MyThread extends Thread {
public void run() {
try {
System.out.println("run threadName="+this.currentThread().getName()+" begin");
Thread.sleep(2000);
System.out.println("run threadName="+this.currentThread().getName()+" end");
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
// TODO Auto-generated catch block
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
package First;
public class Run {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyThread myThread = new MyThread();
System.out.println("begin = " +System.currentTimeMillis());
myThread.run();
//myThread.start();
System.out.println("end = " +System.currentTimeMillis()); }
}

package First;
public class Run {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyThread myThread = new MyThread();
System.out.println("begin = " +System.currentTimeMillis());
//myThread.run();
myThread.start();
System.out.println("end = " +System.currentTimeMillis()); }
}

getId()方法
作用是获取线程的唯一标识
package First;
public class Run {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread runThrad = Thread.currentThread();
System.out.println(runThrad.getId()); }
}

停止线程
Thread.stop()是不安全的,已经被弃用
大多数使用Thread.interrupt(),但这个方法不会终止一个正在运行的线程,还需要加入一个判断才可以完成线程的停止

停不了的线程
调用interrupt仅仅是在当前线程中打了一个停止的标记,并不是真的停止线程
package First;
public class MyThread extends Thread {
public void run() {
super.run();
for(int i = 0;i <50000;i++) {
System.out.println("i"+(i+1));
}
}
}
package First;
public class Run {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
Thread myThread= new MyThread();
myThread.start();
Thread.sleep(2000);
Thread.interrupted();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
System.out.println("main catch");
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}

说明调用interrupt并没有停止线程
判断线程是否是停止状态
this.interrupted();是static方法,测试当前线程是否已经中断,当前线程是指运行this.interrupted()方法的线程
package First;
public class Run {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
Thread myThread= new MyThread();
myThread.start();
Thread.sleep(2000);
Thread.interrupted();
System.out.println("是否停止1? = "+Thread.interrupted());
System.out.println("是否停止1? = "+Thread.interrupted());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
System.out.println("main catch");
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("end");
}
}

线程并未停止,这也说明了interrupted()方法的解释:测试当前线程是否已经中断。这个“当前线程”是main,它从未中断过,所以打印的是两false
package First;
public class Run {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
System.out.println("是否停止1? = " + Thread.interrupted());
System.out.println("是否停止1? = " + Thread.interrupted());
System.out.println("end");
}
}

为什么第2个布尔值是false呢?:

this.isInterrupted():方法不是static的
package First;
public class Run {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
Thread myThread= new MyThread();
myThread.start();
Thread.sleep(1000);
Thread.interrupted();
System.out.println("是否停止1? = "+myThread.isInterrupted());
System.out.println("是否停止1? = "+myThread.isInterrupted());
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
System.out.println("main catch");
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("end");
}
}
两者之间的区别:

能停止的线程-异常法(这两个实验我都没成功)
package First;
public class MyThread extends Thread {
public void run() {
super.run();
for(int i = 0;i <50000;i++) {
if(Thread.interrupted()) {
System.out.println("已经是停止的状态,退出");
break;
}
System.out.println("i"+(i+1));
}
}
}
package First;
public class Run {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
Thread myThread= new MyThread();
myThread.start();
Thread.sleep(2000);
Thread.interrupted();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
System.out.println("main catch");
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("end");
}
}

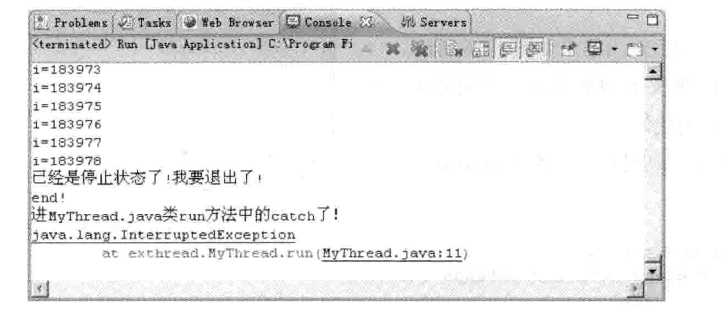
虽然停止了线程,但如果for语句下面还有语句,还是会继续执行的
package First;
public class MyThread extends Thread {
public void run() {
super.run();
try {
for(int i = 0;i <50000;i++) {
if(Thread.interrupted()) {
System.out.println("已经是停止的状态,退出");
break;
}
System.out.println("i"+(i+1));
}
System.out.println("我在for下面");
} catch (Exception e) {
System.out.println("进入MyThread.java类run方法中的catch");
}
}
}
package First;
public class Run {
public static void main(String[] args) {
try {
Thread myThread= new MyThread();
myThread.start();
Thread.sleep(2000);
Thread.interrupted();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
System.out.println("main catch");
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println("end");
}
}
《Java多线程编程核心技术》读后感(一)的更多相关文章
- Springboot揭秘-快速构建微服务体系-王福强-2016年5月第一次印刷
JavaConfig项目: spring IOC有一个非常核心的概念——Bean.由Spring容器来负责对Bean的实例化,装配和管理.XML是用来描述Bean最为流行的配置方式.Spring可以从 ...
- 《SpringBoot揭秘 快速构建微服务体系》读后感(一)
SpringIOC IOC有两种方式:一种是DI,另一种是DL,即Dependency Lookup(依赖查找).前者是当前软件实体被动接受其依赖的其他组件被IoC容器注入,而后者则是当前软件实体主动 ...
- 《SpringBoot揭秘 快速构建微服务体系》读后感(五)
应用日志和spring-boot-starter-logging 快速web应用开发与spring-boot-starter-web 1.项目结构层面的约定
- 《SpringBoot揭秘 快速构建微服务体系》读后感(三)
SpringApplication:SpringBoot程序启动的一站式解决方案 深入探索SpringApplication执行流程 因为书上的版本是1.2的,比较老,这里参考http://blog. ...
- 《SpringBoot揭秘 快速构建微服务体系》读后感(二)
最简单的springBoot应用 package com.louis.test; import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication; import o ...
- 《SpringBoot揭秘 快速构建微服务体系》读后感(四)
再谈自动配置 基于条件的自动配置 调整自动配置的顺序
- [高清] SpringBoot揭秘快速构建微服务体系
------ 郑重声明 --------- 资源来自网络,纯粹共享交流, 如果喜欢,请您务必支持正版!! --------------------------------------------- 下 ...
- SpringBoot 快速构建微服务体系 知识点总结
可以通过http://start.spring.io/构建一个SpringBoot的脚手架项目 一.微服务 1.SpringBoot是一个可使用Java构建微服务的微框架. 2.微服务就是要倡导大家尽 ...
- SpringBoot揭秘:快速构建微服务体系
chapter 2: 饮水思源:回顾与探索Spring框架本质 IoC其实有两种方式,一种是DI(dependency Injection),一种是DL(dependency Lookup 依赖查找, ...
- 通过GeneXus如何快速构建微服务架构
概览 “微服务”是一个非常广泛的话题,在过去几年里,市面上存在着各种不同的定义. 虽然对这种架构方式没有一个非常精确的定义,但仍然有一些概念具有代表性. 微服务有着许多围绕业务能力.自动化部署.终端智 ...
随机推荐
- 我的vim插件列表
一.正在使用的插件 1. NERD tree 文件浏览 2. bufexplorer buffer 浏览 3. mru.vim 最近使用的文件浏览 4. ctrlp.vim 文件模糊搜索, ...
- idea常用的快捷命令
main方法: psvm System.out.println(): sout
- 实例讲解SVN分支和合并问题(转)
本节向大家简单描述一下SVN分支和合并方面的知识,在学习SVN的过程中SVN分支和合并时经常遇到的问题,在这里和大家分享一下,希望本文对大家有用. 关于主线同SVN分支合并的概念及如何使用的误区此问题 ...
- 【git】强制覆盖本地代码
[git]强制覆盖本地代码(与git远程仓库保持一致) 2018年04月27日 23:53:57 不才b_d 阅读数:21145 版权声明:本文为博主不才b_d原创文章,未经允许不得转载. || ...
- Topcoder SRM625 题解
给出一个字符串求是palindrome和anagram的比率是多少. 知识点: 1 DBL_MAX 64位double的最长数大概是1.7E308,非常大非常大,比long long大上不知多少倍.故 ...
- poj1125--Floyd
题解: 有N个股票经济人能够互相传递消息.他们之间存在一些单向的通信路径.如今有一个消息要由某个人開始传递给其它全部人.问应该由哪一个人来传递,才干在最短时间内让全部人都接收到消息. 显然,用Floy ...
- WPF popup控件的使用
<Window x:Class="WPFPopup.RuntimePopup" xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/wi ...
- 二维码、条形码扫描——使用Google ZXing
我在项目中用到了二维码扫描的技术,用的是Google提供的ZXing开源项目,它提供二维码和条形码的扫描.扫描条形码就是直接读取条形码的内容,扫描二维码是按照自己指定的二维码格式进行编码和解码. 可以 ...
- libcurl以get方式请求服务器端文件
static size_t callbackfunction(void *ptr, size_t size, size_t nmemb, void* userdata){ FILE* strea ...
- J++ C#
J++几乎有与Java相同的编程语言和虚拟机.
