python之实现文件的读写
很早之前做自动化测试,并没有将测试数据与数据库关联,而是直接通过json、ymal、excel等文件管理的。那么怎么用python读写文件呢?
在操作文件前,都需要打开文件,打开文件用内置函数open()
open函数
用于打开文件,创建一个file对象,常用格式为:
open(file, mode, encoding)
file:文件路径(可接收相对路径或者绝对路径)
mode:文件的打开模式,可选项,当不填写时默认为r模式
encoding:可选,一般使用utf8
完整格式:
open(file, mode, buffering, encoding, errors,newline, closefd,opener)
buffering:设置缓冲,可选项
errors:报错级别,可选项
newline:区分换行符
closefd:
opener:
mode常用模式:
r: 只读模式,意味着只能读,不能其他操作(追加写入、清空等)
w: 只写模式,文件存在并有内容,则将文件内容全部清空,从0字节开始写,若文件不存在,则先创建文件后,再从0字节开始写
a: 追加模式,将光标置于内容末尾,从末尾开始写入,若文件不存在,则先创建文件后,再从末尾追加写入
b: 读写二进制文件(默认是t,表示文本),需要与上面几种模式搭配使用
实践出真知,打开个文件试试
# 传入绝对路径
f = open(file="D:\demo\htmls\html_learn_01.html")
print(f)
# 传入一个相对路径
t = open("./htmls/html_learn_01.html")
print(t)
"D:\Program Files\Python\Python37-32\python.exe" D:/demo/file_read.py
<_io.TextIOWrapper name='D:\\demo\\htmls\\html_learn_01.html' mode='r' encoding='cp936'>
<_io.TextIOWrapper name='./htmls/html_learn_01.html' mode='r' encoding='cp936'>
可以看到,open()返回了一个文件对象
文件打开了,就要对文件进行一系列操作,常用操作有:
read():读取文件内容,可以指定读取文件内容大小,也可以读取全部内容,当不传或者传入负数,则表示读取文件全部内容。
读取全部(一)
# 传入一个相对路径
t = open("./htmls/html_learn_01.html", encoding="utf-8")
# 读取全部内容
content = t.read()
print(content)
"D:\Program Files\Python\Python37-32\python.exe" D:/demo/file_read.py
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>html lean</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>我是第一个标题</h1>
<p>我的第一个段落</p>
</body>
</html> Process finished with exit code 0
读取全部(二)
# 传入一个相对路径
t = open("./htmls/html_learn_01.html", encoding="utf-8")
# 读取全部内容
content = t.read(-1)
print(content)
"D:\Program Files\Python\Python37-32\python.exe" D:/demo/file_read.py
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>html lean</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>我是第一个标题</h1>
<p>我的第一个段落</p>
</body>
</html> Process finished with exit code 0
读取部分内容
# 传入一个相对路径
t = open("./htmls/html_learn_01.html", encoding="utf-8")
# 读取部分内容
content = t.read(20)
print(content)
"D:\Program Files\Python\Python37-32\python.exe" D:/demo/file_read.py
<!DOCTYPE html>
<htm Process finished with exit code 0
readline():从文件中读取整行内容,若不传或者传入负数,则返回整行内容(包括换行符'\n'),否则返回指定字节大小内容,
读取整行内容(一)
# 传入一个相对路径
t = open("./htmls/html_learn_01.html", encoding="utf-8")
# 读取整行内容
content = t.readline()
print(content)
"D:\Program Files\Python\Python37-32\python.exe" D:/demo/file_read.py
<!DOCTYPE html> Process finished with exit code 0
读取整行内容(二)
# 传入一个相对路径
t = open("./htmls/html_learn_01.html", encoding="utf-8")
# 读取整行内容
content = t.readline(-9)
print(content)
"D:\Program Files\Python\Python37-32\python.exe" D:/demo/file_read.py
<!DOCTYPE html> Process finished with exit code 0
读取一行中部分内容
# 传入一个相对路径
t = open("./htmls/html_learn_01.html", encoding="utf-8")
# 读取一行中部分内容
content = t.readline(5)
print(content)
"D:\Program Files\Python\Python37-32\python.exe" D:/demo/file_read.py
<!DOC Process finished with exit code 0
readlines():从文件中读取文件内容,不传或者传入负数时返回所有行所组成的列表,传入时返回指定字节所在行内所组成的列表
读取全部内容(一)
# 传入一个相对路径
t = open("./htmls/html_learn_01.html", encoding="utf-8")
# 读取整个文件内容
content = t.readlines()
print(content)
"D:\Program Files\Python\Python37-32\python.exe" D:/demo/file_read.py
['<!DOCTYPE html>\n', '<html lang="en">\n', '<head>\n', ' <meta charset="UTF-8">\n', ' <title>html lean</title>\n', '</head>\n', '<body>\n', '<h1>我是第一个标题</h1>\n', '<p>我的第一个段落</p>\n', '</body>\n', '</html>'] Process finished with exit code 0
读取全部内容(二)
# 传入一个相对路径
t = open("./htmls/html_learn_01.html", encoding="utf-8")
# 读取整个文件内容
content = t.readlines(-3)
print(content)
"D:\Program Files\Python\Python37-32\python.exe" D:/demo/file_read.py
['<!DOCTYPE html>\n', '<html lang="en">\n', '<head>\n', ' <meta charset="UTF-8">\n', ' <title>html lean</title>\n', '</head>\n', '<body>\n', '<h1>我是第一个标题</h1>\n', '<p>我的第一个段落</p>\n', '</body>\n', '</html>'] Process finished with exit code 0
读取部分内容
# 传入一个相对路径
t = open("./htmls/html_learn_01.html", encoding="utf-8")
# 读取整个文件内容
content = t.readlines(19)
print(content)
"D:\Program Files\Python\Python37-32\python.exe" D:/demo/file_read.py
['<!DOCTYPE html>\n', '<html lang="en">\n'] Process finished with exit code 0
for line in file: 在读取文件时还可用迭代器获取文件内容
# 传入一个相对路径
t = open("./htmls/html_learn_01.html", encoding="utf-8")
# 逐行打印文件内容
for line in t:
print(line)
"D:\Program Files\Python\Python37-32\python.exe" D:/demo/file_read.py
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"> <title>html lean</title> </head> <body> <h1>我是第一个标题</h1> <p>我的第一个段落</p> </body> </html> Process finished with exit code 0
write():将内容写入文件并返回所写内容长度,如果要写入字符串以外的类型数据,需要进行类型转换,否则抛出TypeError: write() argument must be str, not int错误
以只写模式(w)写入已存在的文件中
# 传入一个相对路径
t = open("./htmls/html_learn_01.html", mode="w", encoding="utf-8")
tt = t.write("file test")
print(tt)
"D:\Program Files\Python\Python37-32\python.exe" D:/demo/file_read.py
9 Process finished with exit code 0
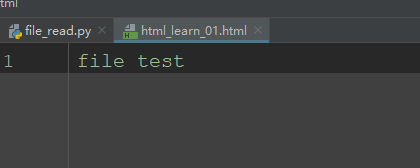
写入后文件内容:
以只写模式(w)写入不存在的文件中
# 传入一个相对路径
t = open("./htmls/create.html", mode="w", encoding="utf-8")
tt = t.write("file test")
print(tt)
"D:\Program Files\Python\Python37-32\python.exe" D:/demo/file_read.py
9 Process finished with exit code 0
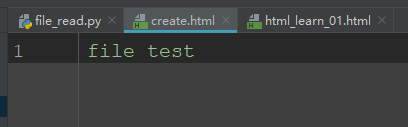
创建了一个文件并写入内容
以追加写入模式(a)写入已存在的文件中
# 传入一个相对路径
t = open("./htmls/html_learn_01.html", mode="a", encoding="utf-8")
tt = t.write("mode a")
print(tt)
"D:\Program Files\Python\Python37-32\python.exe" D:/demo/file_read.py
6 Process finished with exit code 0
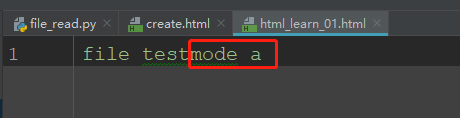
将内容追加写入到文件末尾
以追加写入模式(a)写入不存在的文件中的情况与w模式一样,此处不再举例
writelines():将内容写入文件,接收单个字符串、字符串组成的序列
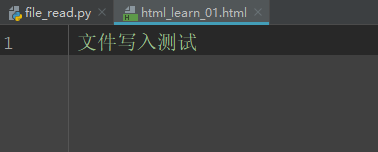
写入单个字符串
# 传入一个相对路径
t = open("./htmls/html_learn_01.html", mode="w+", encoding="utf-8")
t.writelines("文件写入测试")
写入一个字符串序列
# 传入一个相对路径
t = open("./htmls/html_learn_01.html", mode="w+", encoding="utf-8")
t.writelines(["第一行\n", "第二行\n", "第三行\n"])

写入一个由迭代对象产生的字符串序列
# 传入一个相对路径
t = open("./htmls/html_learn_01.html", mode="w+", encoding="utf-8")
t.writelines([(lambda x: str(x))(x) for x in range(5)])
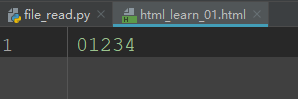
writable():判断文件是否可写,如果可写返回True,否则返回False
# 文件不可写时返回False
t = open("./htmls/html_learn_01.html", mode="r", encoding="utf-8")
result = t.writable()
print(result)
"D:\Program Files\Python\Python37-32\python.exe" D:/demo/file_read.py
False
# 文件可写时返回True
t = open("./htmls/html_learn_01.html", mode="w", encoding="utf-8")
result = t.writable()
print(result)
"D:\Program Files\Python\Python37-32\python.exe" D:/demo/file_read.py
True
close():关闭已打开的文件(使用open打开文件并操作完后不会自动关闭文件,如果不关闭文件时,进行其他类操作就会报错)
import os
# 不关闭文件时移除文件
t = open("./htmls/html_learn_01.html", mode="w", encoding="utf-8")
t.writelines(["wo\n", "wo\n"])
os.remove("./htmls/html_learn_01.html")
"D:\Program Files\Python\Python37-32\python.exe" D:/demo/file_read.py
Traceback (most recent call last):
File "D:/demo/file_read.py", line 8, in <module>
os.remove("./htmls/html_learn_01.html")
PermissionError: [WinError 32] 另一个程序正在使用此文件,进程无法访问。: './htmls/html_learn_01.html'
import os
# 关闭文件后移除文件
t = open("./htmls/html_learn_01.html", mode="w", encoding="utf-8")
t.writelines(["wo\n", "wo\n"])
t.close()
os.remove("./htmls/html_learn_01.html")
"D:\Program Files\Python\Python37-32\python.exe" D:/demo/file_read.py Process finished with exit code 0
每次打开文件后需要调用close()关闭文件也是挺麻烦的,而且若忘记关闭文件了,会造成意想不到的错误,若想避免,则可引入with
with open() as 文件打开操作完后会自动关闭文件
import os
# 使用with open() as 操作完文件后会自动关闭文件,此时调用os.remove()删除不会报异常
with open("./htmls/html_learn_011.html", mode="w", encoding="utf-8") as f:
f.writelines(["wo\n", "wo\n"])
os.remove("./htmls/html_learn_011.html")
"D:\Program Files\Python\Python37-32\python.exe" D:/demo/file_read.py Process finished with exit code 0
遍历文件后移除文件
import os
# 遍历文件内容,删除文件
with open("./htmls/html_learn_011.html", mode="r", encoding="utf-8") as f:
datas = f.readlines()
for data in datas:
print(data.strip())
os.remove("./htmls/html_learn_011.html")
"D:\Program Files\Python\Python37-32\python.exe" D:/demo/file_read.py
读
写
背 Process finished with exit code 0
文件的基础操作就这样啦,后续会继续补充,下一篇实现文件读取封装
python之实现文件的读写的更多相关文章
- 七. Python基础(7)--文件的读写
七. Python基础(7)--文件的读写 1 ● 文件读取的知识补充 f = open('file', encoding = 'utf-8') content1 = f.read() content ...
- python中 对文件的读写操作 以及如何边写入 边保存flush()
转自:https://blog.csdn.net/t8116189520/article/details/78854708 首先 python中打开文件大致常用的几类如下: 1.写入文件write # ...
- Python基础 | 数据文件的读写
目录 txt txt的读入 txt的写出 csv xls\xlsx 在线网页数据 常用的工具 爬虫的步骤 pdf pdfrw PyPDF2 提取文档信息 word文档 其他统计软件生成文件 本文总结使 ...
- python opencv3 视频文件的读写
git: https://github.com/linyi0604/Computer-Vision # coding:utf8 import cv2 """ 读取视频文件 ...
- Python中对文件的读写
读写文件前,我们先必须了解一下,在磁盘上读写文件的功能都是由操作系统提供的,现代操作系统不允许普通的程序直接操作磁盘. 读写文件就是请求操作系统打开一个文件对象(通常称为文件描述符),然后,通过操作系 ...
- python学习(11)文件的读写操作
1.读文件的7种操作模式 操作模式 具体含义 'r' 读取 (默认) 'w' 写入(会先截断之前的内容) 'x' 写入,如果文件已经存在会产生异常 'a' 追加,将内容写入到已有文件的末尾 'b' 二 ...
- python中的文件的读写
python中的 w+ 的使用方法:不能直接 write() 后,在进行读取,这样试读不到数据的,因为数据对象到达的地方为文件最后,读取是向后读的,因此,会读到空白,应该先把文件对象移到文件首位. f ...
- Python对csv文件的读写操作
python内置了csv模块,用它可以方便的操作csv文件. 1.写文件 (1)写文件的方法一 import csv # open 打开文件有多种模式,下面是常见的4种 # r:读数据,默认模式 # ...
- python pandas 中文件的读写——read_csv()读取文件
read_csv()读取文件1.python读取文件的几种方式read_csv 从文件,url,文件型对象中加载带分隔符的数据.默认分隔符为逗号read_table 从文件,url,文件型对象中加载带 ...
- python对excel文件的读写操作
import xlrd,xlwt data = xlrd.open_workbook('a.xlsx') #读 table = data.sheets()[0] data_list = [] data ...
随机推荐
- EasyExcel实现文件导出
官网:https://www.yuque.com/easyexcel/doc/easyexcel 导出 准备工作 引入依赖 <!--EasyExcel相关依赖--> <depende ...
- 关于Vue多线程的思考
在前端调用的时候,我们难免需要同一时刻向后端请求多组数据或是总是期待着是否存在一个独立的线程去处理一系列的数据.线程相应,资源的抢占这是前端较为麻烦的点.这里就来聊聊我在前端踩的坑. 首先是线程问题说 ...
- 会话跟踪技术 - Cookie 和 Session 快速上手 + 登陆注册案例
目录 1. 会话跟踪技术概述 2. Cookie 2.1 Cookie的概念和工作流程 2.2 Cookie的基本使用 2.3 Cookie的原理分析 2.4 Cookie的使用细节 2.4.1 Co ...
- 使用Pytorch进行多卡训练
当一块GPU不够用时,我们就需要使用多卡进行并行训练.其中多卡并行可分为数据并行和模型并行.具体区别如下图所示: 由于模型并行比较少用,这里只对数据并行进行记录.对于pytorch,有两种方式可以进行 ...
- TF-GNN踩坑记录(一)
引言 Batch size作为一个在训练中经常被使用的参数,在图神经网络的训练中也是必不可少,但是在TF-GNN中要求使用 merge_batch_to_components() 把batch之后的图 ...
- java连接数据库加载驱动到java项目
java连接数据库 package com.cook.zheng; import java.sql.Connection; import java.sql.DriverManager; public ...
- 鼠标悬浮上去显示小手CSS
鼠标悬浮上去显示小手CSS只需要添加一句css代码即可 cursor:pointer;
- Masked Label Prediction: Unified Message Passing Model for Semi-Supervised Classification
背景 消息传递模型(Message Passing Model)基于拉普拉斯平滑假设(领居是相似的),试图聚合图中的邻居的信息来获取足够的依据,以实现更鲁棒的半监督节点分类. 图神经网络(Graph ...
- AK/SK加密认证
AK/SK认证的实现 AK/SK概述 1.什么是AKSK ak/sk是一种身份认证方式,常用于系统间接口调用时的身份验证,其中ak为Access Key ID,sk为Secret Access Key ...
- 关于图计算&图学习的基础知识概览:前置知识点学习(Paddle Graph Learning (PGL))
关于图计算&图学习的基础知识概览:前置知识点学习(Paddle Graph Learning (PGL)) 欢迎fork本项目原始链接:关于图计算&图学习的基础知识概览:前置知识点学习 ...
