6 STL-vector
重新系统学习c++语言,并将学习过程中的知识在这里抄录、总结、沉淀。同时希望对刷到的朋友有所帮助,一起加油哦!
生命就像一朵花,要拼尽全力绽放!死磕自个儿,身心愉悦!
写在前面,本篇章主要介绍STL中常用容器vector。
1.1 vector的基本概念
vector数据结构和数组非常相似,也称为单端数组。
vector与普通数组的区别:
数组是静态空间,而vector可以自动动态扩展空间。
什么叫动态扩展?
- 并不是在原空间后继续增大新空间
- 而是找大更大的内存空间,然后将原数据拷贝到新空间,并释放原空间。
vector特点:
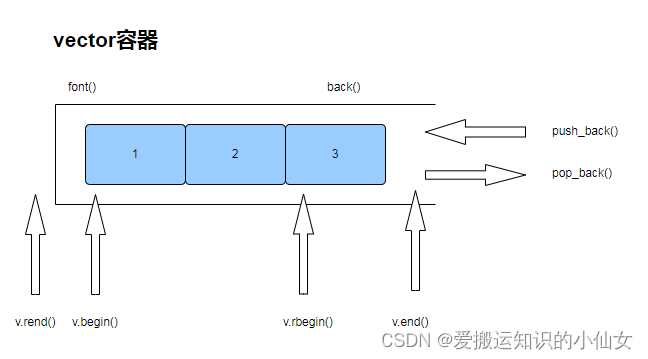
- 前端封闭,不能进行插入和删除,通常在尾部进行插入和删除。push_back()插入,pop_back()删除。
- v.begin()指向第一个元素位置,v.end()指向最后一个元素的下一个位置。
- v.rbegin()指向倒数第一个元素位置,v.rend()指向一个元素的前一个位置。
- 还提供很多其他接口,例如插入insert()、erase()删除等。
- 迭代器支持随机访问。可跳跃式访问,例如 it 指向迭代器,可以加n。
 编辑
编辑
1.2 vector构造函数
函数原型:
- vector<T> v; //采用模板实现类实现,默认构造函数
- vector(v.begin(), v.end()); //将v[begin(), end())区间中的元素拷贝给本身。
- vector(n, elem); //构造函数将n个elem拷贝给本身。
- vector(const vector& vec); //拷贝构造函数。
示例:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
//vector<T> v; //采用模板实现类实现,默认构造函数
//vector(v.begin(), v.end()); //将v[begin(), end())区间中的元素拷贝给本身。
//vector(n, elem); //构造函数将n个elem拷贝给本身。
//vector(const vector& vec); //拷贝构造函数。
void printVector(vector<int>& v) {
for (int item : v) {
cout << item << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void test() {
vector<int> v1;
for (int i = 1; i < 6; i++) {
v1.push_back(i);
}
printVector(v1);
vector<int> v2(v1.begin(), v1.end());
// 用区间的方式来构造vector,只要传入的是一个区间就可以拷贝区间内的数据到新的vector
//vector<int> v2(v1.begin(), v1.begin() + 3);
printVector(v2);
vector<int> v3(10,5);
printVector(v3);
vector<int> v4(v3);
printVector(v4);
}
int main() {
test();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
1.3 vector赋值操作
函数原型:
- vector& operator=(const vector& vec); //重载等号操作符
- assign(beg, end); //将[beg, end)区间中的数据拷贝赋值给本身。
- assign(n, elem); //将n个elem拷贝赋值给本身。
示例:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
//vector& operator=(const vector& vec); //重载等号操作符
//assign(beg, end); //将[beg, end)区间中的数据拷贝赋值给本身。
//assign(n, elem); //将n个elem拷贝赋值给本身。
void printVector(vector<int>& v) {
for (int item : v) {
cout << item << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void test() {
vector<int> v1;
for (int i = 1; i < 6; i++) {
v1.push_back(i);
}
printVector(v1);
//vector& operator=(const vector& vec); //重载等号操作符
vector<int> v2;
v2 = v1;
printVector(v2);
//assign(beg, end);//将[beg, end)区间中的数据拷贝赋值给本身。
vector<int> v3;
v3.assign(v1.begin(), v1.end());
printVector(v3);
//assign(n, elem);//将n个elem拷贝赋值给本身。
v3.assign(10, 3);
printVector(v3);
}
int main() {
test();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
1.4 vector容量大小
函数原型:
- empty(); //判断容器是否为空
- capacity(); //容器的容量
- size(); //返回容器中元素的个数
- resize(int num); //重新指定容器长度为num,若容器变长,则以默认值填充新位置。 //如果容器变短,则末尾超出容器长度的元素被删除。
- resize(int num, elem); //重新指定容器长度为num,若容器变长,则以elem值填充新位置。 //如果容器变短,则末尾超出容器长度的元素被删除
注意:
- 若重新指定容器长度,若容器变长,则capacity()容器的容量和size()都会变长。
- 若后续又指定容器变短,则capacity()容器的容量不变,只有size()会变小。
- 只有size()可变大变小,capacity()容器的容量只会变大。
示例:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
//empty(); //判断容器是否为空
//capacity(); //容器的容量
//size(); //返回容器中元素的个数
//resize(int num); //重新指定容器的长度为num,若容器变长,则以默认值填充新位置。
// //如果容器变短,则末尾超出容器长度的元素被删除。
//resize(int num, elem);//重新指定容器的长度为num,若容器变长,则以elem值填充新位置。
// //如果容器变短,则末尾超出容器长度的元素被删除
void printVector(vector<int> v) {
for (vector<int>::iterator it = v.begin(); it < v.end(); it++) {
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void test() {
vector<int> v1;
for (int i = 1; i < 6; i++) {
v1.push_back(i);
}
printVector(v1);
if (v1.empty()) {
cout << "v1 为空" << endl;
}
else {
cout << "v1 不为空" << endl;
cout <<"capacity:"<< v1.capacity() << endl;
cout << "size:" << v1.size() << endl;
}
// 手动重新指定容器长度变大为10
v1.resize(10);
cout << "v1 手动重新指定容器长度变大" << endl;
cout << "capacity:" << v1.capacity() << endl; // 容量会扩展成10
cout << "size:" << v1.size() << endl; // 元素个数会变为10
printVector(v1); // 以默认值0填充
// 手动重新指定容器长度变小为3
v1.resize(3);
cout << "v1 手动重新指定容器长度变小" << endl;
cout << "capacity:" << v1.capacity() << endl; // ***容量不变 10
cout << "size:" << v1.size() << endl; // 元素个数会变少 3
printVector(v1); // 如果容器变短,则末尾超出容器长度的元素被删除。
// resize(int num, elem);利用重载版本,指定默认值填充方式,
v1.resize(5,10);
cout << "v1 指定默认值填充方式" << endl;
cout << "capacity:" << v1.capacity() << endl; // ***容量不变 10
cout << "size:" << v1.size() << endl; // 元素个数等于指定个数5
printVector(v1); //如果重新指定的比原来的长,用默认值填充10
}
int main() {
test();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
1.5 vector插入和删除
函数原型:
- push_back(ele); //尾部插入元素ele
- pop_back(); //删除最后一个元素
- insert(const_iterator pos, ele); //在迭代器指向位置pos插入元素ele
- insert(const_iterator pos, int count, ele); //在迭代器指向位置pos插入count个元素ele
- erase(const_iterator pos); //删除迭代器指向pos位置的元素
- erase(const_iterator start, const_iterator end); //删除迭代器[start,end)之间的元素,左闭右开
- clear(); //删除容器中所有元素
erase(v.begin(), v.end()); 与clear()效果一样,都是清空数据。
示例:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
//push_back(ele); //尾部插入元素ele
//pop_back(); //删除最后一个元素
//insert(const_iterator pos, ele); //在迭代器指向位置pos插入元素ele
//insert(const_iterator pos, int count, ele); //在迭代器指向位置pos插入count个元素ele
//erase(const_iterator pos); //删除迭代器指向pos位置的元素
//erase(const_iterator start, const_iterator end); //删除迭代器从start到end之间的元素
//clear(); //删除容器中所有元素
void printVector(vector<int> v) {
for (vector<int>::iterator it = v.begin(); it < v.end(); it++) {
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void test() {
vector<int> v1;
for (int i = 1; i < 6; i++) {
v1.push_back(i);
}
printVector(v1);
// 尾删
v1.pop_back();
printVector(v1);
//在迭代器指向位置pos插入元素ele
v1.insert(v1.begin() + 1, 10);
printVector(v1);
//insert(const_iterator pos, int count, ele);
//在迭代器指向位置pos插入count个元素ele
v1.insert(v1.begin() + 1,3,10);
printVector(v1);
//erase(const_iterator pos);//删除迭代器指向pos位置的元素
v1.erase(v1.begin() + 1);
printVector(v1);
//erase(const_iterator start, const_iterator end);
//删除迭代器从[start,end)之间的元素,左闭右开
v1.erase(v1.begin(),v1.begin()+1);
printVector(v1);
//clear();//删除容器中所有元素
//v1.erase(v1.begin(), v1.end()); 也是清空数据
v1.clear();
printVector(v1);
}
int main() {
test();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
1.6 vector数据存取
函数原型:
- at(int idx); //返回索引idx所指的数据
- operator[]; //返回索引idx所指的数据
- front(); //返回容器中第一个数据元素
- back(); //返回容器中最后一个数据元素
示例:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
//at(int idx); //返回索引idx所指的数据
//operator[]; //返回索引idx所指的数据
//front(); //返回容器中第一个数据元素
//back(); //返回容器中最后一个数据元素
void test() {
vector<int> v1;
for (int i = 1; i < 6; i++) {
v1.push_back(i);
}
cout << v1.at(3) << endl; // 第三个
cout << v1[3]<< endl; // 第三个
cout << v1.front() << endl; // 第一个
cout << v1.back() << endl; // 最后一个
}
int main() {
test();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
1.7 vector互换容器
函数原型:
swap(v); 将两个vector容器互换
实际用途:
巧用swap可以收缩内存空间。
示例:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
void printVector(vector<int> v) {
for (vector<int>::iterator it = v.begin(); it < v.end(); it++) {
cout << *it << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
void test() {
cout << "交换前:" << endl;
vector<int> v1;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
v1.push_back(i);
}
printVector(v1);
vector<int> v2;
for (int i = 9; i >=0; i--) {
v2.push_back(i);
}
printVector(v2);
cout << "交换后:" << endl;
v1.swap(v2);
printVector(v1);
printVector(v2);
}
// 实际用途
// 巧用swap可以收缩内存空间
void test2() {
vector<int> v;
for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++) {
v.push_back(i);
}
cout << "v的容量为:" << v.capacity() << endl; // 138255
cout << "v的长度为:" << v.size() << endl; // 100000
v.resize(3); // 重新指定大小。当大小变的很小时,capacity还是占用空间很大,不会缩小
cout << "v的容量为:" << v.capacity() << endl; // 138255
cout << "v的长度为:" << v.size() << endl; // 3
// 巧用swap收缩内存
// vector<int>(v) 利用v示例化一个匿名对象容器。这个容器容量和长度只有3
// swap(v) 交换匿名对象容器和v
vector<int>(v).swap(v);
cout << "v的容量为:" << v.capacity() << endl; // 3
cout << "v的长度为:" << v.size() << endl; // 3
}
int main() {
test2();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
1.8 vector预留空间
作用:
减少vector动态扩展容量的次数,提升性能。
函数原型:
reserve(int len); // 容器预留len个元素长的容量,预留位置的元素不会被初始化,元素不可访问。
使用时机:
如果知道数据量很大,就可以先使用reserve来预留空间。
示例:
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
void test() {
vector<int> v;
// 利用预留空间
v.reserve(100000);
// cout << v[0] << endl; // 会报错,0位置元素不可访问,未初始化。
int num = 0;
int* p = NULL;
for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++) {
v.push_back(i);
if (p != &v[0]) { // 如果v做了动态内存扩展p就不会指向&v[0]
p = &v[0]; // 让指针p指向v的首地址
num++; // 如果v做了动态内存扩展,num就增加一次
}
}
cout << num << endl;
}
int main() {
test();
system("pause");
return 0;
}
6 STL-vector的更多相关文章
- C++ STL vector容器学习
STL(Standard Template Library)标准模板库是C++最重要的组成部分,它提供了一组表示容器.迭代器.函数对象和算法的模板.其中容器是存储类型相同的数据的结构(如vector, ...
- STL vector
STL vector vector是线性容器,它的元素严格的按照线性序列排序,和动态数组很相似,和数组一样,它的元素存储在一块连续的存储空间中,这也意味着我们不仅可以使用迭代器(iterator)访问 ...
- STL vector用法介绍
STL vector用法介绍 介绍 这篇文章的目的是为了介绍std::vector,如何恰当地使用它们的成员函数等操作.本文中还讨论了条件函数和函数指针在迭代算法中使用,如在remove_if()和f ...
- STL vector+sort排序和multiset/multimap排序比较
由 www.169it.com 搜集整理 在C++的STL库中,要实现排序可以通过将所有元素保存到vector中,然后通过sort算法来排序,也可以通过multimap实现在插入元素的时候进行排序.在 ...
- STL vector 用法介绍
介绍 这篇文章的目的是为了介绍std::vector,如何恰当地使用它们的成员函数等操作.本文中还讨论了条件函数和函数指针在迭代算法中使用,如在remove_if()和for_each()中的使用.通 ...
- STL vector使用方法介绍
介绍 这篇文章的目的是为了介绍std::vector,怎样恰当地使用它们的成员函数等操作.本文中还讨论了条件函数和函数指针在迭代算法中使用,如在remove_if()和for_each()中的使用.通 ...
- stl——vector详解
stl——vector详解 stl——vector是应用最广泛的一种容器,类似于array,都将数据存储于连续空间中,支持随机访问.相对于array,vector对空间应用十分方便.高效,迭代器使ve ...
- C++STL vector详解(杂谈)
介绍 这篇文章的目的是为了介绍std::vector,如何恰当地使用它们的成员函数等操作.本文中还讨论了条件函数和函数指针在迭代算法中使用,如在remove_if()和for_each()中的使用.通 ...
- C++ stl vector介绍
转自: STL vector用法介绍 介绍 这篇文章的目的是为了介绍std::vector,如何恰当地使用它们的成员函数等操作.本文中还讨论了条件函数和函数指针在迭代算法中使用,如在remove_if ...
- 浅谈C++ STL vector 容器
浅谈C++ STL vector 容器 本篇随笔简单介绍一下\(C++STL\)中\(vector\)容器的使用方法和常见的使用技巧.\(vector\)容器是\(C++STL\)的一种比较基本的容器 ...
随机推荐
- LFS(Linux From Scratch)构建过程全记录(六):交叉编译临时工具
写在前面 本章将展示如何使用刚刚构建的跨工具链来交叉编译基本实用程序. M4安装 和前文一样,先进行解压,然后cd进入 注意:不需要构建build文件夹,直接输入以下配置文件 ./configure ...
- 助力培养高质量AI人才,璞公英乐学平台在日本深受好评!
璞公英乐学平台(原名"璞睿魔数")自进入日本市场以来,受到日本用户的广泛好评.近日,日本AI门户网站AIsmiley在发刊的杂志<AI人才育成指南>中对璞公英乐学平台做 ...
- null和undefined的区别、数组和伪数组的区别
null和undefined的区别 undefined: 字面意思是未定义的值,语义是希望表示一个变量最原始的状态,而非人为操作的结果.这种原始状态会在以下四个场景中出现: 声明了一个变量但没有赋值 ...
- salesforce零基础学习(一百一十八)Restrict Rule
本篇参考: https://help.salesforce.com/s/articleView?id=sf.security_restriction_rule.htm&type=5 https ...
- redis cluster 6.2集群
redis最新版本:redis-6.2.1.tar.gz 安装的版本是redis-6.0.3 采用的主机: djz-server-001 192.168.2.163 7001,7002,Admin@1 ...
- Kubernetes ConfigMap热更新
ConfigMap是用来存储配置文件的kubernetes资源对象,所有的配置内容都存储在etcd中. 总结 更新 ConfigMap 后: 使用该 ConfigMap 挂载的 Env 不会同步更新 ...
- 【Java8新特性】- Lambda表达式
Java8新特性 - Lambda表达式 生命不息,写作不止 继续踏上学习之路,学之分享笔记 总有一天我也能像各位大佬一样 一个有梦有戏的人 @怒放吧德德 分享学习心得,欢迎指正,大家一起学习成长! ...
- 为Azure-云准备一个基于Red Hat 8.x 的虚拟机镜像
由于公司最近要求部分项目上线到Azure云上,要求操作系统使用的Redhat 8.x,而且必须加固 而在Azure官网提供的镜像中,又没有Redhat,于是只有自己自定义Redhat镜像,最后加固,作 ...
- C# 传不定参数
1 public class MyClass 2 { 3 public static void UseParams(params int[] list) 4 { 5 for (int i = 0; i ...
- CQOI2015任务查询系统
题目链接 主席树. 把区间的影响挂在左端点与右端点,建树时顺便对应的插入与删除. 维护一段值域区间的和与数字个数,查询时要注意与第k大的数相同的数可能有很多. 复杂度O(nlogn) #include ...
