Bi-LSTM-CRF for Sequence Labeling
做了一段时间的Sequence Labeling的工作,发现在NER任务上面,很多论文都采用LSTM-CRFs的结构。CRF在最后一层应用进来可以考虑到概率最大的最优label路径,可以提高指标。
一般的深度学习框架是没有CRF layer的,需要手动实现。最近在学习PyTorch,里面有一个Bi-LSTM-CRF的tutorial实现。不得不说PyTorch的tutorial真是太良心了,基本涵盖了NLP领域各个流行的model实现。在这里从头梳理一遍,也记录下学习过程中的一些问题。
 Bi-LSTM-CRF的结构一般如上,最后一层利用CRF来学习一个最优路径。Bi-LSTM layer的输出维度是tag size,这就相当于是每个词
Bi-LSTM-CRF的结构一般如上,最后一层利用CRF来学习一个最优路径。Bi-LSTM layer的输出维度是tag size,这就相当于是每个词映射到tag的发射概率值,设Bi-LSTM的输出矩阵为
,其中
代表词
映射到
的非归一化概率。对于CRF来说,我们假定存在一个转移矩阵
,则
代表
转移到
的转移概率。
对于输入序列对应的输出tag序列
,定义分数为
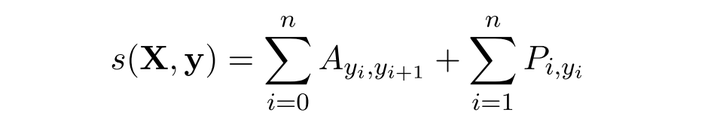 利用Softmax函数,我们为每一个正确的tag序列
利用Softmax函数,我们为每一个正确的tag序列定义一个概率值(
代表所有的tag序列,包括不可能出现的)
 因而在训练中,我们只需要最大化似然概率
因而在训练中,我们只需要最大化似然概率即可,这里我们利用对数似然
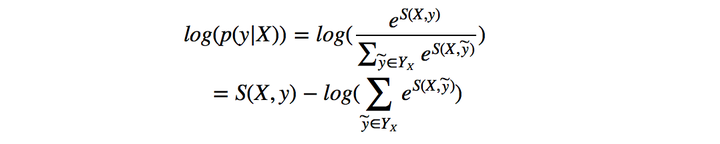
所以我们将损失函数定义为,就可以利用梯度下降法来进行网络的学习了。
在对损失函数进行计算的时候,的计算很简单,而
(下面记作logsumexp)的计算稍微复杂一些,因为需要计算每一条可能路径的分数。这里用一种简便的方法,对于到词
的路径,可以先把到词
的logsumexp计算出来,因为
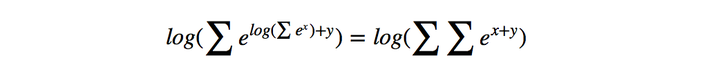 因此先计算每一步的路径分数和直接计算全局分数相同,但这样可以大大减少计算的时间。下面是PyTorch中的代码
因此先计算每一步的路径分数和直接计算全局分数相同,但这样可以大大减少计算的时间。下面是PyTorch中的代码
def _forward_alg(self, feats):
# Do the forward algorithm to compute the partition function
init_alphas = torch.Tensor(1, self.tagset_size).fill_(-10000.)
# START_TAG has all of the score.
init_alphas[0][self.tag_to_ix[START_TAG]] = 0.
# Wrap in a variable so that we will get automatic backprop
forward_var = autograd.Variable(init_alphas)
# Iterate through the sentence
for feat in feats:
alphas_t = [] # The forward variables at this timestep
for next_tag in range(self.tagset_size):
# broadcast the emission score: it is the same regardless of
# the previous tag
emit_score = feat[next_tag].view(
1, -1).expand(1, self.tagset_size)
# the ith entry of trans_score is the score of transitioning to
# next_tag from i
trans_score = self.transitions[next_tag].view(1, -1)
# The ith entry of next_tag_var is the value for the
# edge (i -> next_tag) before we do log-sum-exp
next_tag_var = forward_var + trans_score + emit_score
# The forward variable for this tag is log-sum-exp of all the
# scores.
alphas_t.append(log_sum_exp(next_tag_var))
forward_var = torch.cat(alphas_t).view(1, -1)
terminal_var = forward_var + self.transitions[self.tag_to_ix[STOP_TAG]]
alpha = log_sum_exp(terminal_var)
return alpha
在解码时,采用Viterbi算法
def _viterbi_decode(self, feats):
backpointers = []
# Initialize the viterbi variables in log space
init_vvars = torch.Tensor(1, self.tagset_size).fill_(-10000.)
init_vvars[0][self.tag_to_ix[START_TAG]] = 0
# forward_var at step i holds the viterbi variables for step i-1
forward_var = autograd.Variable(init_vvars)
for feat in feats:
bptrs_t = [] # holds the backpointers for this step
viterbivars_t = [] # holds the viterbi variables for this step
for next_tag in range(self.tagset_size):
# next_tag_var[i] holds the viterbi variable for tag i at the
# previous step, plus the score of transitioning
# from tag i to next_tag.
# We don't include the emission scores here because the max
# does not depend on them (we add them in below)
next_tag_var = forward_var + self.transitions[next_tag]
best_tag_id = argmax(next_tag_var)
bptrs_t.append(best_tag_id)
viterbivars_t.append(next_tag_var[0][best_tag_id])
# Now add in the emission scores, and assign forward_var to the set
# of viterbi variables we just computed
forward_var = (torch.cat(viterbivars_t) + feat).view(1, -1)
backpointers.append(bptrs_t)
# Transition to STOP_TAG
terminal_var = forward_var + self.transitions[self.tag_to_ix[STOP_TAG]]
best_tag_id = argmax(terminal_var)
path_score = terminal_var[0][best_tag_id]
# Follow the back pointers to decode the best path.
best_path = [best_tag_id]
for bptrs_t in reversed(backpointers):
best_tag_id = bptrs_t[best_tag_id]
best_path.append(best_tag_id)
# Pop off the start tag (we dont want to return that to the caller)
start = best_path.pop()
assert start == self.tag_to_ix[START_TAG] # Sanity check
best_path.reverse()
return path_score, best_path全部代码实现可以移步Bi-LSTM-CRF。
参考
Bidirectional LSTM-CRF Models for Sequence Tagging
Neural Architectures for Named Entity Recognition
Advanced: Making Dynamic Decisions and the Bi-LSTM CRF
Bi-LSTM-CRF for Sequence Labeling的更多相关文章
- TensorFlow (RNN)深度学习 双向LSTM(BiLSTM)+CRF 实现 sequence labeling 序列标注问题 源码下载
http://blog.csdn.net/scotfield_msn/article/details/60339415 在TensorFlow (RNN)深度学习下 双向LSTM(BiLSTM)+CR ...
- End to End Sequence Labeling via Bi-directional LSTM CNNs CRF
来看看今日头条首席科学家的论文: End-to-end Sequence Labeling via Bi-directional LSTM-CNNs-CRF 使用LSTM方法进行序列标注,完成大规模标 ...
- 关于bert+lstm+crf实体识别训练数据的构建
一.在实体识别中,bert+lstm+crf也是近来常用的方法.这里的bert可以充当固定的embedding层,也可以用来和其它模型一起训练fine-tune.大家知道输入到bert中的数据需要一定 ...
- pytorch lstm crf 代码理解 重点
好久没有写博客了,这一次就将最近看的pytorch 教程中的lstm+crf的一些心得与困惑记录下来. 原文 PyTorch Tutorials 参考了很多其他大神的博客,https://blog.c ...
- pytorch lstm crf 代码理解
好久没有写博客了,这一次就将最近看的pytorch 教程中的lstm+crf的一些心得与困惑记录下来. 原文 PyTorch Tutorials 参考了很多其他大神的博客,https://blog.c ...
- LSTM+CRF进行序列标注
为什么使用LSTM+CRF进行序列标注 直接使用LSTM进行序列标注时只考虑了输入序列的信息,即单词信息,没有考虑输出信息,即标签信息,这样无法对标签信息进行建模,所以在LSTM的基础上引入一个标签转 ...
- 转:pytorch版的bilstm+crf实现sequence label
http://blog.csdn.net/appleml/article/details/78664824 在理解CRF的时候费了一些功夫,将一些难以理解的地方稍微做了下标注,隔三差五看看加强记忆, ...
- 论文阅读笔记:《Contextual String Embeddings for Sequence Labeling》
文章引起我关注的主要原因是在CoNLL03 NER的F1值超过BERT达到了93.09左右,名副其实的state-of-art.考虑到BERT训练的数据量和参数量都极大,而该文方法只用一个GPU训了一 ...
- End to End Sequence Labeling via Bidirectional LSTM-CNNs-CRF论文小结
本篇论文是卡内基梅隆大学语言技术研究所2016年 arXiv:1603.01354v5 [cs.LG] 29 May 2016 今天先理解一下这个是什么意思: 找到的相关理解:arXi ...
随机推荐
- Leetcode874.Walking Robot Simulation模拟行走的机器人
机器人在一个无限大小的网格上行走,从点 (0, 0) 处开始出发,面向北方.该机器人可以接收以下三种类型的命令: -2:向左转 90 度 -1:向右转 90 度 1 <= x <= 9:向 ...
- Linux常用命令6 压缩解压命令
.zip是Linux和Windows共有的压缩格式 1.压缩解压命令:gzip 命令英文原意:GNU zip 命令所在路径:/bin/gzip 执行权限:所有用户 语法: gzip [文件] ...
- 【JZOJ4810】【NOIP2016提高A组五校联考1】道路规划
题目描述 输入 输出 样例输入 5 1 4 5 2 3 3 4 2 1 5 样例输出 3 数据范围 样例解释 解法 模型显然. 设第一列为a[],第二列为b[],f[i]为前i个数的最大答案. 顺序枚 ...
- ELK之elasticsearch安装&&kibana安装
1.ES和Kibana安装都是开箱即用的? 解压缩就可以用 elasticsearch解压缩之后,双击下图中的elasticsearch.bat,启动,kibana也是一样 双击之后, 我们看到上图有 ...
- 二.python数据结构的性能分析
目录: 1.引言 2.列表 3.字典 一.引言 - 现在大家对 大O 算法和不同函数之间的差异有了了解.本节的目标是告诉你 Python 列表和字典操作的 大O 性能.然后我们将做一些基于时间的实验来 ...
- 大数据技术之Zookeeper
第1章 Zookeeper入门 1.1 概述 Zookeeper是一个开源的分布式的,为分布式应用提供协调服务的Apache项目. 1.2 特点 1.3 数据结构 1.4 应用场景 提供的服务包括:统 ...
- Directx教程(27) 简单的光照模型(6)
原文:Directx教程(27) 简单的光照模型(6) 从myTutorialD3D11_15到myTutorialD3D11_19的工程中,我们都只有一个光源,光源的位置在LightCla ...
- jQuery左右循环滚动图片特效
在线演示 本地下载
- python 模块的执行环境
- JavaScript--自调用函数(小闭包)
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en"> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8&quo ...
