Understanding Memory Technology Devices in Embedded Linux
转:
NAND Chip Drivers
NAND technology users such as USB pen drives, DOMs, Compact Flash memory, and SD/MMC cards emulate standard storage interfaces such as SCSI or IDE over NAND flash, so you don't need to develop NAND drivers to communicate with them.5 On-board NAND flash chips need special drivers, however, and are the topic of this section.
As you learned previously in this chapter, NAND flash chips, unlike their NOR counterparts, are not connected to the CPU via data and address lines. They interface to the CPU through special electronics called a NAND flash controller that is part of many embedded processors. To read data from NAND flash, the CPU issues an appropriate read command to the NAND controller. The controller transfers data from the requested flash location to an internal RAM memory, also part of the controller. The data transfer is done in units of the flash chip's page size (for example, 2KB). In general, the denser the flash chip, the larger is its page size. Note that the page size is different from the flash chip's block size, which is the minimum erasable flash memory unit (for example, 16KB). After the transfer operation completes, the CPU reads the requested NAND contents from the internal RAM. Writes to NAND flash are done similarly, except that the controller transfers data from the internal RAM to flash. The connection diagram of NAND flash memory on an embedded device is shown in Figure 17.3.
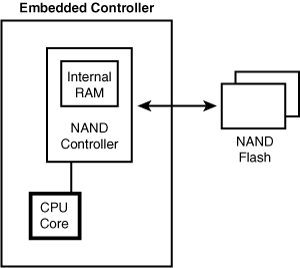
Figure 17.3 NAND flash connection.
Because of this unconventional mode of addressing, you need special drivers to work with NAND storage. MTD provides such drivers to manage NAND-resident data. If you are using a supported chip, you have to enable only the appropriate low-level MTD NAND driver. If you are writing a NAND flash driver, however, you need to explore two datasheets: the NAND flash controller and the NAND flash chip.
NAND flash chips do not support automatic configuration using protocols such as CFI. You have to manually inform MTD about the properties of your NAND chip by adding an entry to thenand_flash_ids[] table defined in drivers/mtd/nand/nand_ids.c. Each entry in the table consists of an identifier name, the device ID, page size, erase block size, chip size, and options such as the bus width.
There is another characteristic that goes hand in hand with NAND memory. NAND flash chips, unlike NOR chips, are not faultless. It's normal to have some problem bits and bad blocks scattered across NAND flash regions. To handle this, NAND devices associate a spare area with each flash page (for example, 64 bytes of spare area for each 2KB data page). The spare area contains out-of-band (OOB) information to help perform bad block management and error correction. The OOB area includes error correcting codes (ECCs) to implement error correction and detection. ECC algorithms correct single-bit errors and detect multibit errors. The nand_ecclayout structure defined ininclude/mtd/mtd-abi.h specifies the layout of the OOB spare area:
struct nand_ecclayout {
uint 32_t eccbytes;
uint32_t eccpos[64];
uint32_t oobavail;
struct nand_oobfree oobfree[MTD_MAX_OOBFREE_ENTRIES];
};
In this structure, eccbytes holds the number of OOB bytes that store ECC data, and eccpos is an array of offsets into the OOB area that contains the ECC data. oobfree records the unused bytes in the OOB area available to flash filesystems for storing flags such as clean markers that signal successful completion of erase operations.
Individual NAND drivers initialize their nand_ecclayout according to the chip's properties. Figure 17.4illustrates the layout of a NAND flash chip having a page size of 2KB. The OOB semantics used by the figure is the default for 2KB page-sized chips as defined in the generic NAND driver,drivers/mtd/nand/nand_base.c.
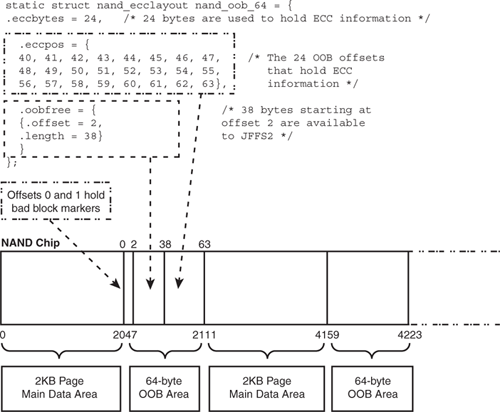
Figure 17.4 Layout of a NAND flash chip.
Often, the NAND controller performs error correction and detection in hardware by operating on the ECC fields in the OOB area. If your NAND controller does not support error management, however, you will need to get MTD to do that for you in software. The MTD nand_ecc driver (drivers/mtd/nand/nand_ecc.c) implements software ECC.
Figure 17.4 also shows OOB memory bytes that contain bad block markers. These markers are used to flag faulty flash blocks and are usually present in the OOB region belonging to the first page of each block. The position of the marker inside the OOB area depends on the properties of the chip. Bad block markers are either set at the factory during manufacture, or by software when it detects wear in a block. MTD implements bad block management in drivers/mtd/nand/nand_bbt.c.
The mtd_partition structure used in Listing 17.1 for the NOR flash in Figure 17.2 works for NAND memory, too. After you MTD-enable your NAND flash, you can access the constituent partitions using standard device nodes such as /dev/mtd/X and /dev/mtdblock/X. If you have a mix of NOR and NAND memories on your hardware, X can be either a NOR or a NAND partition. If you have a total of more than 32 flash partitions, accordingly change the value of MAX_MTD_DEVICES ininclude/linux/mtd/mtd.h.
To effectively make use of NAND storage, you need to use a filesystem tuned for NAND access, such as JFFS2 or YAFFS2, in tandem with the low-level NAND driver. We discuss these filesystems in the next section.
Understanding Memory Technology Devices in Embedded Linux的更多相关文章
- Linux MTD (Memory Technology Device) subsystem analysis -For Atheros char device
Linux MTD (Memory Technology Device) subsystem analysis For Atheros char device 读了Linux MTD 源代码分析 对这 ...
- (转)Understanding Memory in Deep Learning Systems: The Neuroscience, Psychology and Technology Perspectives
Understanding Memory in Deep Learning Systems: The Neuroscience, Psychology and Technology Perspecti ...
- 【转载】关于Embedded Linux启动的经典问题
转载自:http://linux.chinaunix.net/techdoc/install/2009/04/13/1107608.shtml 发信人: armlinux (armlinux), 信区 ...
- Understanding Memory Management(2)
Understanding Memory Management Memory management is the process of allocating new objects and remov ...
- Qt for Embedded Linux
1. Qt for Embedded Linux http://doc.qt.io/qt-5/embedded-linux.html 2. Installing Qt for Embedded Lin ...
- 构建自己的embedded linux系统
[教程]使用buildroot完全自定义自己的embedded linux系统(nand)http://www.eeboard.com/bbs/thread-38377-1-1.html [教程] [ ...
- [转]A Guide To using IMU (Accelerometer and Gyroscope Devices) in Embedded Applications.
原文地址http://www.starlino.com/imu_guide.html Introduction There’s now a FRENCH translation of this art ...
- Memory Leak Detection in Embedded Systems
One of the problems with developing embedded systems is the detection of memory leaks; I've found th ...
- How to Add Memory, vCPU, Hard Disk to Linux KVM Virtual Machine
ref: https://www.thegeekstuff.com/2015/02/add-memory-cpu-disk-to-kvm-vm/ In our previous article of ...
随机推荐
- 蓝桥杯_风险度量_dfs_无向图两节点间的所有路径
标题:风险度量 X星系的的防卫体系包含 n 个空间站.这 n 个空间站间有 m 条通信链路,构成通信网.两个空间站间可能直接通信,也可能通过其它空间站中转. 对于两个站点x和y (x != y), 如 ...
- 最小生成树 $Kruskal$ 算法
#include <bits/stdc++.h> using namespace std; const int maxn = 5e5 + 10; int h[maxn], v[maxn], ...
- 实用JS系列——事件类型
事件就是用户对窗口上各种组件的操作.JS中的事件中的事件即由访问Web页面的用户引起的一系列的操作.一般用于浏览器和用户操作进行交互,例如:用户的单击事件等. 类型分为: 内联模型.脚本模型和DOM2 ...
- SqlHelper——数据库小助手
SqlHelper其实就是一个类. 早就听说过"SqlHelper"这个名词,也查过相关的资料,但还是一头雾水.当真的去实践去用它时,就会发现其实它没那么神秘. 当敲第一个窗体的时 ...
- Win10 Ubuntu18.04 编译安装 nignx
nginx 下载页 http://nginx.org/en/download.html wget http://nginx.org/download/nginx-1.14.0.tar.gz //安装依 ...
- [hdu6435]Problem J. CSGO
题目大意:给定$n$个$A$类元素和$m$个$B$类元素,每类元素有值$S$和$k$个值$x_0,x_1,\dots,x_{k-1}(k\leqslant 5)$. 要求选出一个$A$类元素$a$和$ ...
- Snakes and Ladders LightOJ - 1151( 概率dp+高斯消元)
Snakes and Ladders LightOJ - 1151 题意: 有100个格子,从1开始走,每次抛骰子走1~6,若抛出的点数导致走出了100以外,则重新抛一次.有n个格子会单向传送到其他格 ...
- Printed Circuit Board (board)
Printed Circuit Board (board) 题目描述 给出一个N个顶点的简单多边形,对于每个顶点,假如它和原点连成的线段只在这个顶点处和多边形相交,就称为满足要求的顶点.你的任务是输出 ...
- 【HDU 1358 Period】
Time Limit: 2000/1000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 65536/32768 K (Java/Others) ...
- Git基本用法简介
一. git和svn的主要区别 git是一个分布式的版本控制工具,而svn是一个集中式版本控制工具. 二. git工具安装 首先下载git:https://gi ...
