Kubernetes 编写自定义 controller
原文链接:Kubernetes编写自定义controller
来自kubernetes官方github的一张图:
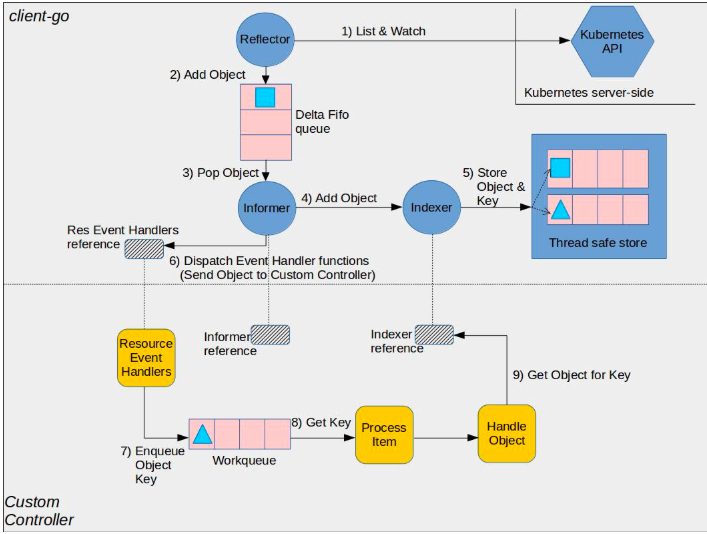
如图所示,图中的组件分为client-go和custom controller两部分:
client-go部分
- Reflector: 监视特定资源的k8s api, 把新监测的对象放入Delta Fifo队列,完成此操作的函数是ListAndWatch。
- Informer: 从Delta Fifo队列拿出对象,完成此操作的函数是processLoop。
- Indexer: 提供线程级别安全来存储对象和key。
custom-controller部分
- Informer reference: Informer对象引用
- Indexer reference: Indexer对象引用
- Resource Event Handlers: 被Informer调用的回调函数,这些函数的作用通常是获取对象的key,并把key放入Work queue,以进一步做处理。
- Work queue: 工作队列,用于将对象的交付与其处理分离,编写Resource event handler functions以提取传递的对象的key并将其添加到工作队列。
- Process Item: 用于处理Work queue中的对象,可以有一个或多个其他函数一起处理;这些函数通常使用Indexer reference或Listing wrapper来检索与该键对应的对象。
client-go官方代码例子
package main import (
"flag"
"fmt"
"time" "k8s.io/klog" "k8s.io/api/core/v1"
meta_v1 "k8s.io/apimachinery/pkg/apis/meta/v1"
"k8s.io/apimachinery/pkg/fields"
"k8s.io/apimachinery/pkg/util/runtime"
"k8s.io/apimachinery/pkg/util/wait"
"k8s.io/client-go/kubernetes"
"k8s.io/client-go/tools/cache"
"k8s.io/client-go/tools/clientcmd"
"k8s.io/client-go/util/workqueue"
) // 定义一个结构体Controller
type Controller struct {
indexer cache.Indexer
queue workqueue.RateLimitingInterface
informer cache.Controller
} // 获取controller的函数
func NewController(queue workqueue.RateLimitingInterface, indexer cache.Indexer, informer cache.Controller) *Controller {
return &Controller{
informer: informer,
indexer: indexer,
queue: queue,
}
} // 处理workqueue中的对象
func (c *Controller) processNextItem() bool {
// Wait until there is a new item in the working queue
key, quit := c.queue.Get()
if quit {
return false
}
// Tell the queue that we are done with processing this key. This unblocks the key for other workers
// This allows safe parallel processing because two pods with the same key are never processed in
// parallel.
defer c.queue.Done(key) // Invoke the method containing the business logic
err := c.syncToStdout(key.(string))
// Handle the error if something went wrong during the execution of the business logic
c.handleErr(err, key)
return true
} // syncToStdout is the business logic of the controller. In this controller it simply prints
// information about the pod to stdout. In case an error happened, it has to simply return the error.
// The retry logic should not be part of the business logic.
func (c *Controller) syncToStdout(key string) error {
obj, exists, err := c.indexer.GetByKey(key)
if err != nil { klog.Errorf("Fetching object with key %s from store failed with %v", key, err)
return err
} if !exists { // Below we will warm up our cache with a Pod, so that we will see a delete for one pod
fmt.Printf("Pod %s does not exist anymore\n", key)
} else {
// Note that you also have to check the uid if you have a local controlled resource, which
// is dependent on the actual instance, to detect that a Pod was recreated with the same name
fmt.Printf("Sync/Add/Update for Pod %s\n", obj.(*v1.Pod).GetName())
}
return nil
} // handleErr checks if an error happened and makes sure we will retry later.
func (c *Controller) handleErr(err error, key interface{}) {
if err == nil {
// Forget about the #AddRateLimited history of the key on every successful synchronization.
// This ensures that future processing of updates for this key is not delayed because of
// an outdated error history.
c.queue.Forget(key)
return
} // This controller retries 5 times if something goes wrong. After that, it stops trying.
if c.queue.NumRequeues(key) < {
klog.Infof("Error syncing pod %v: %v", key, err) // Re-enqueue the key rate limited. Based on the rate limiter on the
// queue and the re-enqueue history, the key will be processed later again.
c.queue.AddRateLimited(key)
return
} c.queue.Forget(key)
// Report to an external entity that, even after several retries, we could not successfully process this key
runtime.HandleError(err)
klog.Infof("Dropping pod %q out of the queue: %v", key, err)
} func (c *Controller) Run(threadiness int, stopCh chan struct{}) {
defer runtime.HandleCrash() // Let the workers stop when we are done
defer c.queue.ShutDown()
klog.Info("Starting Pod controller") go c.informer.Run(stopCh) // Wait for all involved caches to be synced, before processing items from the queue is started
if !cache.WaitForCacheSync(stopCh, c.informer.HasSynced) { runtime.HandleError(fmt.Errorf("Timed out waiting for caches to sync"))
return
} for i := ; i < threadiness; i++ {
go wait.Until(c.runWorker, time.Second, stopCh)
} <-stopCh
klog.Info("Stopping Pod controller")
} func (c *Controller) runWorker() {
for c.processNextItem() {
}
} func main() {
var kubeconfig string
var master string // 指定kubeconfig文件
flag.StringVar(&kubeconfig, "kubeconfig", "", "absolute path to the kubeconfig file")
flag.StringVar(&master, "master", "", "master url")
flag.Parse() // creates the connection
config, err := clientcmd.BuildConfigFromFlags(master, kubeconfig)
if err != nil { klog.Fatal(err)
} // creates the clientset
clientset, err := kubernetes.NewForConfig(config)
if err != nil { klog.Fatal(err)
} // create the pod watcher
podListWatcher := cache.NewListWatchFromClient(clientset.CoreV1().RESTClient(), "pods", v1.NamespaceDefault, fields.Everything()) // create the workqueue
queue := workqueue.NewRateLimitingQueue(workqueue.DefaultControllerRateLimiter()) // Bind the workqueue to a cache with the help of an informer. This way we make sure that
// whenever the cache is updated, the pod key is added to the workqueue.
// Note that when we finally process the item from the workqueue, we might see a newer version
// of the Pod than the version which was responsible for triggering the update.
indexer, informer := cache.NewIndexerInformer(podListWatcher, &v1.Pod{}, , cache.ResourceEventHandlerFuncs{
AddFunc: func(obj interface{}) {
key, err := cache.MetaNamespaceKeyFunc(obj)
if err == nil {
queue.Add(key)
}
},
UpdateFunc: func(old interface{}, new interface{}) {
key, err := cache.MetaNamespaceKeyFunc(new)
if err == nil {
queue.Add(key)
}
},
DeleteFunc: func(obj interface{}) {
// IndexerInformer uses a delta queue, therefore for deletes we have to use this
// key function.
key, err := cache.DeletionHandlingMetaNamespaceKeyFunc(obj)
if err == nil {
queue.Add(key)
}
},
}, cache.Indexers{}) controller := NewController(queue, indexer, informer) // We can now warm up the cache for initial synchronization.
// Let's suppose that we knew about a pod "mypod" on our last run, therefore add it to the cache. // If this pod is not there anymore, the controller will be notified about the removal after the // cache has synchronized. indexer.Add(&v1.Pod{ ObjectMeta: meta_v1.ObjectMeta{ Name: "mypod", Namespace: v1.NamespaceDefault, }, }) // Now let's start the controller
stop := make(chan struct{})
defer close(stop)
go controller.Run(, stop) // Wait forever
select {}
}
Kubernetes 编写自定义 controller的更多相关文章
- k8s自定义controller设计与实现
k8s自定义controller设计与实现 创建CRD 登录可以执行kubectl命令的机器,创建student.yaml apiVersion: apiextensions.k8s.io/v1bet ...
- 用mel编写自定义节点的属性编辑器界面
用mel编写自定义节点的属性编辑器界面比较麻烦,而且网上例子又少,下面给出一个范例,说明基本的格式 // 初始化节点时调用 global proc initControl(string $attrNa ...
- MVC自定义过滤器,自定义Area过滤器,自定义Controller,Action甚至是ViewData过滤器
实现MVC自定义过滤器,自定义Area过滤器,自定义Controller,Action甚至是ViewData过滤器 MVC开发中几种以AOP方式实现的Filters是非常好用的,默认情况下,我们通过A ...
- django “如何”系列4:如何编写自定义模板标签和过滤器
django的模板系统自带了一系列的内建标签和过滤器,一般情况下可以满足你的要求,如果觉得需更精准的模板标签或者过滤器,你可以自己编写模板标签和过滤器,然后使用{% load %}标签使用他们. 代码 ...
- RobotFramework自动化测试框架-使用Python编写自定义的RobotFramework Lib
使用Python构建Lib工程 可以用来开发Python Lib的IDE工具有很多,常见的有Pycharm,Eclipse with PyDev插件等,而且在RobotFramework官网中也已经提 ...
- SpringBoot编写自定义的starter 专题
What’s in a name All official starters follow a similar naming pattern; spring-boot-starter-*, where ...
- kubernetes nginx ingress controller部署
Kubernetes nginx ingress controller部署 1.下载kubernetes nginx的yaml文件 Wget https://raw.githubusercontent ...
- SpringBoot编写自定义配置信息
⒈编写自定义配置类 1.浏览器配置 package cn.coreqi.security.properties; public class BrowserProperties { private St ...
- R语言-编写自定义函数 ZZ
一.函数构造器 每一个R函数都包括三个部分:函数名,程序主体以及参数集合,在编写自定义R函数时,需要将三个部分各自储存在一个R对象中.这里需要使用function函数,形如: my_function& ...
随机推荐
- Python之生成器、迭代器
生成器 生成器类似返回值为数组的一个函数,这个函数可以接受参数,可被调用,但只能产生一个值,所以大大节省内存. 生成器表达式的语法非常简单,只需要将列表推导式的中括号改成小括号就可以了 [x+x fo ...
- 用友U8API 8.9-15.0接口开发前提,选好开发方式
在用友接口开发这条路上,走走停停过了好几年.对于如何选择哪种方式,目前总结几点, 对于开发,目前可以实现的有三种方式 一.是通过用友官方提供的(EAI/API)接口 这种方式的优点 ...
- postman~界面介绍
本文摘抄自https://www.jianshu.com/p/b8b02afa74b1 官方文档:https://learning.getpostman.com/docs/postman/launch ...
- PHP array_sum() 函数
实例 返回数组中所有值的和(5+15+25): <?php$a=array(5,15,25);echo array_sum($a);?> 运行实例 » 定义和用法 array_sum() ...
- PHP uksort() 函数
------------恢复内容开始------------ 实例 使用用户自定义的比较函数对数组 $arr 中的元素按键名进行排序: <?phpfunction my_sort($a,$b){ ...
- 解析Class文件
类文件解析的入口是ClassFileParser类中定义的parseClassFile()方法.上一小节得到了文件字节流stream后,接着会在ClassLoader::load_classfile( ...
- Hadoop学习之基础环境搭建
期望目的 基于VMware workstation 10.0 + CentOS 7 + hadoop 3.2.0,在虚拟机上搭建一套Hadoop集群环境,总共包含4个节点,其中1个master节点.3 ...
- 【Canal】互联网背景下有哪些数据同步需求和解决方案?看完我知道了!!
写在前面 在当今互联网行业,尤其是现在分布式.微服务开发环境下,为了提高搜索效率,以及搜索的精准度,会大量使用Redis.Memcached等NoSQL数据库,也会使用大量的Solr.Elastics ...
- 【AHOI2009】同类分布 题解(数位DP)
题目大意:求$[l,r]$中各位数之和能被该数整除的数的个数.$0\leq l\leq r\leq 10^{18}$. ------------------------ 显然数位DP. 搜索时记录$p ...
- 027_go语言中的通道选择器
代码演示 package main import "fmt" import "time" func main() { c1 := make(chan strin ...
