cf437D The Child and Zoo
2 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
Of course our child likes walking in a zoo. The zoo has n areas, that are numbered from 1 to n.
The i-th area contains ai animals
in it. Also there are m roads in the zoo, and each road connects two distinct areas. Naturally the zoo is connected, so you can reach any area of the zoo
from any other area using the roads.
Our child is very smart. Imagine the child want to go from area p to area q.
Firstly he considers all the simple routes from p to q.
For each route the child writes down the number, that is equal to the minimum number of animals among the route areas. Let's denote the largest of the written numbers as f(p, q).
Finally, the child chooses one of the routes for which he writes down the value f(p, q).
After the child has visited the zoo, he thinks about the question: what is the average value of f(p, q) for all pairs p, q (p ≠ q)?
Can you answer his question?
The first line contains two integers n and m (2 ≤ n ≤ 105; 0 ≤ m ≤ 105).
The second line contains n integers: a1, a2, ..., an (0 ≤ ai ≤ 105).
Then follow m lines, each line contains two integers xi and yi (1 ≤ xi, yi ≤ n; xi ≠ yi),
denoting the road between areas xi and yi.
All roads are bidirectional, each pair of areas is connected by at most one road.
Output a real number — the value of 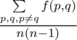 .
.
The answer will be considered correct if its relative or absolute error doesn't exceed 10 - 4.
4 3
10 20 30 40
1 3
2 3
4 3
16.666667
3 3
10 20 30
1 2
2 3
3 1
13.333333
7 8
40 20 10 30 20 50 40
1 2
2 3
3 4
4 5
5 6
6 7
1 4
5 7
18.571429
Consider the first sample. There are 12 possible situations:
- p = 1, q = 3, f(p, q) = 10.
- p = 2, q = 3, f(p, q) = 20.
- p = 4, q = 3, f(p, q) = 30.
- p = 1, q = 2, f(p, q) = 10.
- p = 2, q = 4, f(p, q) = 20.
- p = 4, q = 1, f(p, q) = 10.
Another 6 cases are symmetrical to the above. The average is 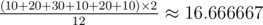 .
.
Consider the second sample. There are 6 possible situations:
- p = 1, q = 2, f(p, q) = 10.
- p = 2, q = 3, f(p, q) = 20.
- p = 1, q = 3, f(p, q) = 10.
Another 3 cases are symmetrical to the above. The average is 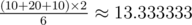 .
.
在鸿巨大的指导下才有了思路……orzlwh
首先把所有的点按权从大到小排序,然后顺序加入图中。对于一个新插入的点,可能有很多连出去的边,如果边的另一端已经在图中,就把它用并查集并起来,可以证明这些联通快之间的p就是新加入的点。然后统计答案。
黄巨大的题解:http://hzwer.com/3332.html
#include<iostream>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstdlib>
#include<cmath>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
struct sth
{
int v,bh;
}p[100010];
int n,m;
int sz,to[200010],pre[200010],last[100010];
int fa[100010],sum[100010];
bool mark[100010];
double ans;
void Ins(int a,int b)
{
sz++;to[sz]=b;pre[sz]=last[a];last[a]=sz;
}
inline bool comp(sth a,sth b)
{
return a.v>b.v;
}
int getfa(int x)
{
if(fa[x]==0) return x;
return fa[x]=getfa(fa[x]);
}
int main()
{
int i,j,x,y,a,b;
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
scanf("%d",&p[i].v);
p[i].bh=i;sum[i]=1;
}
for(i=1;i<=m;i++)
{
scanf("%d%d",&a,&b);
Ins(a,b);Ins(b,a);
}
sort(p+1,p+1+n,comp);
for(i=1;i<=n;i++)
{
x=p[i].bh;
for(j=last[x];j;j=pre[j])
if(mark[to[j]])
{
y=getfa(to[j]);
a=getfa(x);
if(a!=y)
{
ans+=(long long)sum[y]*sum[a]*p[i].v;
sum[y]+=sum[a];
fa[a]=y;
}
}
mark[x]=1;
}
ans/=n*1.0;
ans/=(n-1)*1.0;
ans*=2.0;
printf("%.12lf\n",ans);
return 0;
}
cf437D The Child and Zoo的更多相关文章
- CF437D(The Child and Zoo)最小生成树
题目: D. The Child and Zoo time limit per test 2 seconds memory limit per test 256 megabytes input sta ...
- Codeforces Round #250 (Div. 1) B. The Child and Zoo 并查集
B. The Child and Zoo Time Limit: 20 Sec Memory Limit: 256 MB 题目连接 http://codeforces.com/contest/438/ ...
- Codeforces 437D The Child and Zoo(贪心+并查集)
题目链接:Codeforces 437D The Child and Zoo 题目大意:小孩子去參观动物园,动物园分非常多个区,每一个区有若干种动物,拥有的动物种数作为该区的权值.然后有m条路,每条路 ...
- Codeforces 437 D. The Child and Zoo 并查集
题目链接:D. The Child and Zoo 题意: 题意比较难懂,是指给出n个点并给出这些点的权值,再给出m条边.每条边的权值为该条路连接的两个区中权值较小的一个.如果两个区没有直接连接,那么 ...
- Codeforces 437D The Child and Zoo - 树分治 - 贪心 - 并查集 - 最大生成树
Of course our child likes walking in a zoo. The zoo has n areas, that are numbered from 1 to n. The ...
- Codeforces D - The Child and Zoo
D - The Child and Zoo 思路: 并查集+贪心 每条边的权值可以用min(a[u],a[v])来表示,然后按边的权值从大到小排序 然后用并查集从大的边开始合并,因为你要合并的这两个联 ...
- Codeforces Round #250 (Div. 2) D. The Child and Zoo 并查集
D. The Child and Zoo time limit per test 2 seconds memory limit per test 256 megabytes input standar ...
- Codeforces 437D The Child and Zoo(并查集)
Codeforces 437D The Child and Zoo 题目大意: 有一张连通图,每个点有对应的值.定义从p点走向q点的其中一条路径的花费为途径点的最小值.定义f(p,q)为从点p走向点q ...
- The Child and Zoo 题解
题目描述 Of course our child likes walking in a zoo. The zoo has n areas, that are numbered from 1 to n. ...
随机推荐
- navicat 随笔提示的快捷键
1.ctrl+q 打开查询窗口2.ctrl+/ 注释sql语句3.ctrl+shift +/ 解除注释4.ctrl+r 运行查询窗口的sql语句5.ctrl+shift+r 只运行选中的sql语句6. ...
- css浮动+应用(瀑布流效果的实现)
首先是index.html文件: <!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="UTF-8"& ...
- android .9.png ”点九” 图片制作方法
“点九”是andriod平台的应用软件开发里的一种特殊的图片形式,文件扩展名为:.9.png 智能手机中有自动横屏的功能,同一幅界面会在随着手机(或平板电脑)中的方向传感器的参数不同而改变显示的方向, ...
- 戴明PDCA方法
戴明PDCA方法:即Plan(计划).Do(执行).Check(检查)和Action(处理)的缩写. P(plan)计划: 包括方针和目标的确定以及活动计划的制定; D(do)执行: 执行就是具体运作 ...
- 将vim改造成C/C++开发环境(IDE) 2011
[参考资料]吴垠的“手把手教你把Vim改装成一个IDE编程环境”在Fedora下成功将Vim打造成适用于C/C++的IDE用Vim搭建C/C++开发环境 Ubuntu下vim+ctags的配置 ...
- Protobuf实现Android Socket通讯开发教程
本节为您介绍Protobuf实现Android Socket通讯开发教程,因此,我们需要先了理一下protobuf 是什么? Protocol buffers是一种编码方法构造的一种有效而可扩展的格式 ...
- java对象Integer不能引用传递
java对象Integer不能引用传递 /** * The value of the <code>Integer</code>. * * @serial */ private ...
- 发布到IIS后 程序乱码
网站-功能视图-.net全球化 编码设置 请求:utf-8 文件:gb2312 响应:utf-8 响应头:utf-8 可以根据需要自己定义
- Android material design support library -- CollapsingToolbarLayout简介
本文是codetrick上material design support library教程的第三篇,主要讲的是CollapsingToolbarLayout的概念和应用方法. 原文链接:Materi ...
- Map Resource Definition 中type为 'ArcGIS Server Local'.
在使用 MapResourceManager, Map进行 地图显示 时, 在 Map Resource Definition 的 type 为 ArcGIS Server Local时概述. 1,打 ...
