Vision-Based Positioning for Internet-of-Vehicles
Vision-Based Positioning for Internet-of-Vehicles
Introduction
Ego-positioning aims at locating an object in a global coordinate system based on its sensor inputs. With the growth of mobile or wearable devices, accurate positioning has be- come increasingly important. Unlike indoor positioning, considerably less efforts have been put into developing high-accuracy ego-positioning systems for outdoor environments. Global Positioning System (GPS) is the most widely used technology implemented in vehicles. However, the precision of GPS sensors is approximately 3 to 20 meters, which is not sufficient for distinguishing the traffic lanes and highway lane levels critical for intelligent vehicles. In addition, the existing GPS systems do not work properly in urban areas where signals are obstructed by high rise buildings. Although several positioning methods based on expensive sensors, such as radar sensors and Velodyne 3D laser scanners, can achieve high accuracy, they are not widely adopted because of cost issues. Hence, it is important to develop accurate ready-to-deploy IoV approaches for outdoor environments.
We presents an algorithm for ego-positioning by using a low-cost monocular camera for systems based on the Internet-of-Vehicles (IoV). To reduce the computational and memory requirements, as well as the communication load, we tackle the model compression task as a weighted k-cover problem for better preserving the critical structures. For real-world vision-based positioning applications, we consider the issue of large scene changes and introduce a model update algorithm to address this problem. A large positioning dataset containing data collected for more than a month, 106 sessions, and 14,275 images is constructed. Extensive experimental results show that sub- meter accuracy can be achieved by the proposed ego-positioning algorithm, which outperforms existing vision-based approaches.
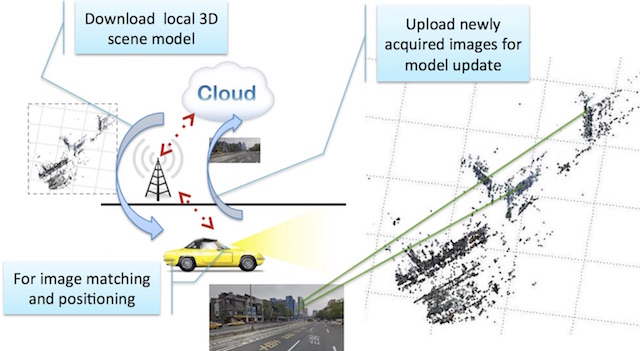
Overview of the algorithm
(a) training phase: images from passing vehicles are uploaded to a cloud server for model construction and compression;

(b) ego-positioning phase: SIFT features from images acquired on vehicles are matched against 3D models previously constructed for ego-positioning. In addition, the newly acquired images are used to update 3D models.
Result
Video on Youtube:http://www.youtube.com/embed/ZLjHGcqhbYA
Dataset
http://www.clarenceliang.com/dataset
Related Publications
[1] Kuan-Wen Chen, Chun-Hsin Wang, Xiao Wei, Qiao Liang, Ming-Hsuan Yang, Chu-Song Chen, and Yi-Ping Hung, “Vision-Based Positioning for Internet-of-Vehicles,” IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2017.
[2] Kuan-Wen Chen, Chun-Hsin Wang, Xiao Wei, Qiao Liang, Ming-Hsuan Yang, Chu-Song Chen, and Yi-Ping Hung, “Vision-Based Positioning with Sub-meter Accuracy for Internet-of-Vehicles,” the 28th IPPR Conference on Computer Vision, Graphics, and Image Processing, Aug., 2015. (Best Paper Award)
Vision-Based Positioning for Internet-of-Vehicles的更多相关文章
- VIPS: a VIsion based Page Segmentation Algorithm
VIPS: a VIsion based Page Segmentation Algorithm VIPS: a VIsion based Page Segmentation Algorithm In ...
- Computer English Notes
Chapter 1 : About Computer Answer the following - Abbreviation LBS - Location-Based Services HTML - ...
- REST is not the Best for Micro-Services GRPC and Docker makes a compelling case
原文:https://hackernoon.com/rest-in-peace-grpc-for-micro-service-and-grpc-for-the-web-a-how-to-908cc05 ...
- 【AR实验室】ARToolKit之概述篇
0x00 - 前言 我从去年就开始对AR(Augmented Reality)技术比较关注,但是去年AR行业一直处于偶尔发声的状态,丝毫没有其"异姓同名"的兄弟VR(Virtual ...
- Socket网络编程一
1.Socket参数介绍 A network socket is an endpoint of a connection across a computer network. Today, most ...
- Python之路,Day8 - Python基础 面向对象高级进阶与socket基础
类的成员 类的成员可以分为三大类:字段.方法和属性 注:所有成员中,只有普通字段的内容保存对象中,即:根据此类创建了多少对象,在内存中就有多少个普通字段.而其他的成员,则都是保存在类中,即:无论对象的 ...
- Python之路第一课Day8--随堂笔记(socket 承接上节---网络编程)
本节内容 Socket介绍 Socket参数介绍 基本Socket实例 Socket实现多连接处理 通过Socket实现简单SSH 通过Socket实现文件传送 作业:开发一个支持多用户在线的FTP程 ...
- python走起之第八话
1. Socket介绍 概念 A network socket is an endpoint of a connection across a computer network. Today, mos ...
- Python学习路程day8
Socket语法及相关 socket概念 A network socket is an endpoint of a connection across a computer network. Toda ...
- 大规模视觉识别挑战赛ILSVRC2015各团队结果和方法 Large Scale Visual Recognition Challenge 2015
Large Scale Visual Recognition Challenge 2015 (ILSVRC2015) Legend: Yellow background = winner in thi ...
随机推荐
- (转)linux sed命令就是这么简单
sed替换命令 原文:https://www.cnblogs.com/zd520pyx1314/p/6061337.html http://www.cnblogs.com/wangqiguo/p/67 ...
- Eclipse的企业开发时常用快捷键使用、优化配置(博主推荐)
不多说,直接上干货! 一.简介 eclipse可谓是Java开发界的神器,基本占据了大部分的Java开发市场,而且其官方还对其他语言提供支持,如C++,Ruby,JavaScript等等.为什么使用它 ...
- git读书笔记以及使用技巧
[添加文件] git add 把文件修改添加到暂存区 git commit -m '' 把暂存区的所有内容提交到当前分支 [查看历史] git log 查看提交历史 git log -- ...
- flask表单flask-wtf
一.安装pip install flask-wtf 二.创建一个flask的项目引入相对应的包 from flask import Flask,render_template import flask ...
- 【一】JMeter的介绍安装和使用
利用JMeter进行性能测试 一.JMeter介绍二.Jmeter安装三.工作原理四.脚本录制五.运行JMeter进行测试六.JMeter主要组件介绍七.参数化设置八.动态数据关联九.使用插件进行服务 ...
- git stash压栈
git stash 用于暂存当前正在进行的工作,如想pull最新的代码,又不想加新的commit,或者为了fix一个紧急的bug,先stash,返回到自己上一个commit. 修改完bug后,再执行g ...
- oracle中时间戳转为Date类型的数据
问题描述: 一个表中原本应该存放date类型的数据,但是不知道之前哪位大仙把两个字段的类型建成了NUMBER类型的了,这样在后台看时间肯定不方便.现在需要改成date类型,但是现在库中是有数据的,不能 ...
- Android4.4 在Framework新增内部资源编译不过的问题
如果在Frameworks新增内部资源,并在Java代码中使用类似形式来引用资源:com.android.internal.R.layout.xxx,需要在frameworks/base/core/r ...
- 初学orcale(一)
Oracle数据库学习: 01.数据库简介: (1)文件型数据库: Access Office组件: Foxpro (2)NoSql数据库(泛指非关系型数据库): NoSQL(NoSQL = Not ...
- linux环境下安装jdk(本文示例是jdk1.6.0_45)
第一步:创建一个文件夹安装jdk(虽说地址一般自定义,但是为了方便查找请按照笔者建议目录 ):/usr/java 将jdk-6u45-linux-x64.bin文件放到 /usr/java 文件夹 ...
