SpringBoot的自动装配原理
Spring Boot 的自动装配(Auto-Configuration)是其核心特性之一,它极大地简化了Spring应用的配置过程。
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class SpringBootLearnApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringBootLearnApplication.class, args);
}
}
1. 核心入口:@SpringBootApplication
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Inherited
@SpringBootConfiguration
@EnableAutoConfiguration
@ComponentScan(excludeFilters = { @Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = TypeExcludeFilter.class),
@Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = AutoConfigurationExcludeFilter.class) })
public @interface SpringBootApplication
- 这是一个复合注解,包含:
- @SpringBootConfiguration:标识这是一个配置类
- @EnableAutoConfiguration:启用自动配置
- @ComponentScan:启用组件扫描
2. @EnableAutoConfiguration注解
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Inherited
@AutoConfigurationPackage
@Import(AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class)
public @interface EnableAutoConfiguration {
/**
* Environment property that can be used to override when auto-configuration is
* enabled.
*/
String ENABLED_OVERRIDE_PROPERTY = "spring.boot.enableautoconfiguration";
/**
* Exclude specific auto-configuration classes such that they will never be applied.
* @return the classes to exclude
*/
Class<?>[] exclude() default {};
/**
* Exclude specific auto-configuration class names such that they will never be
* applied.
* @return the class names to exclude
* @since 1.3.0
*/
String[] excludeName() default {};
}
这个注解通过@Import引入了AutoConfigurationImportSelector类
- AutoConfigurationImportSelector 是核心类,负责加载自动配置类:
public class AutoConfigurationImportSelector implements DeferredImportSelector, BeanClassLoaderAware,
ResourceLoaderAware, BeanFactoryAware, EnvironmentAware, Ordered {\
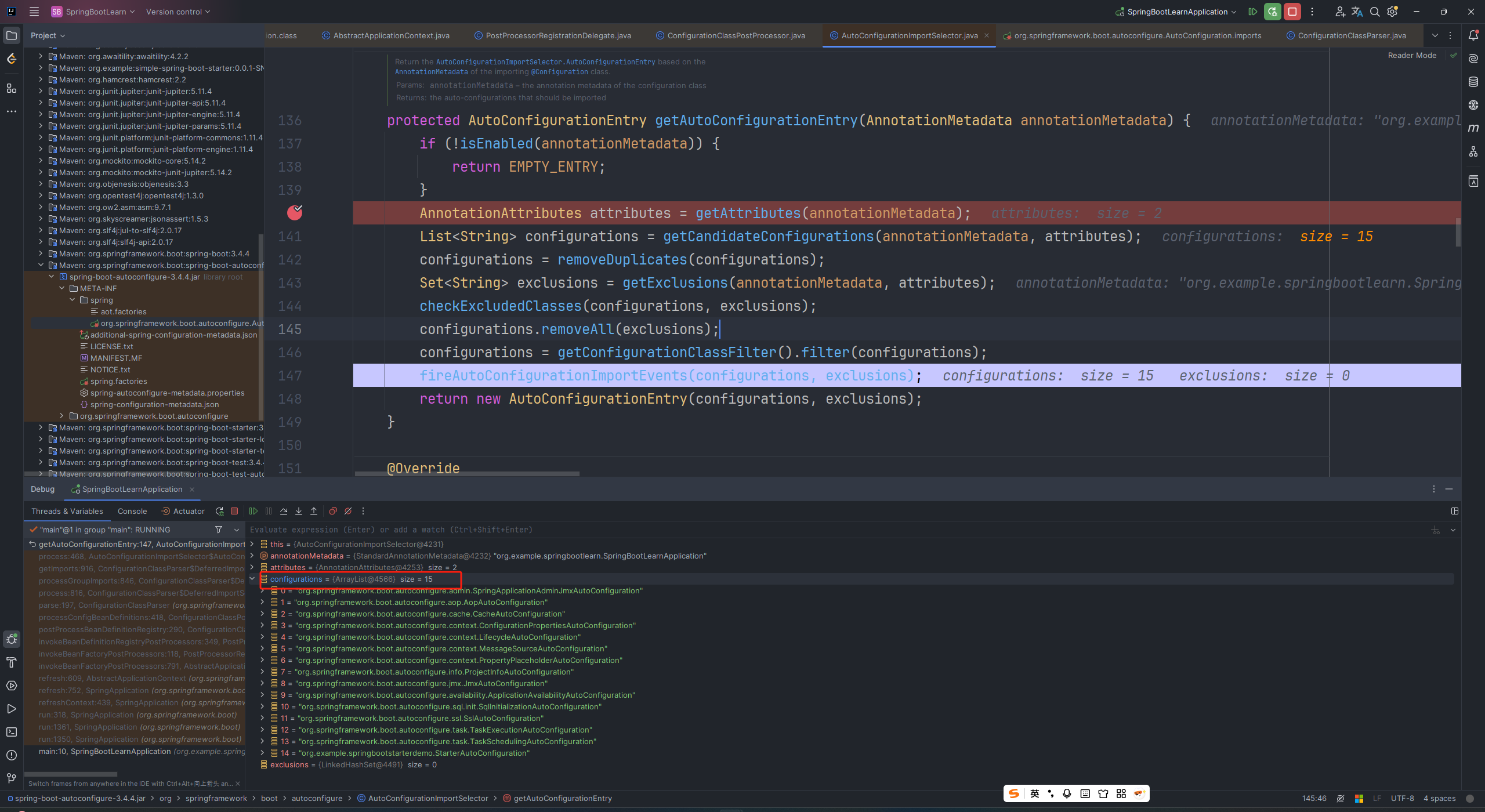
protected AutoConfigurationEntry getAutoConfigurationEntry(AnnotationMetadata annotationMetadata) {
if (!isEnabled(annotationMetadata)) {
return EMPTY_ENTRY;
}
AnnotationAttributes attributes = getAttributes(annotationMetadata);
List<String> configurations = getCandidateConfigurations(annotationMetadata, attributes);
configurations = removeDuplicates(configurations);
Set<String> exclusions = getExclusions(annotationMetadata, attributes);
checkExcludedClasses(configurations, exclusions);
configurations.removeAll(exclusions);
configurations = getConfigurationClassFilter().filter(configurations);
fireAutoConfigurationImportEvents(configurations, exclusions);
return new AutoConfigurationEntry(configurations, exclusions);
}
}


3. 自动配置类加载流程
3.1 加载候选配置类
从 META-INF/spring/org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.AutoConfiguration.imports 文件加载候选配置类(Spring Boot 2.7+ 后替代 spring.factories)
protected List<String> getCandidateConfigurations(AnnotationMetadata metadata, AnnotationAttributes attributes) {
ImportCandidates importCandidates = ImportCandidates.load(this.autoConfigurationAnnotation,
getBeanClassLoader());
List<String> configurations = importCandidates.getCandidates();
Assert.notEmpty(configurations,
"No auto configuration classes found in " + "META-INF/spring/"
+ this.autoConfigurationAnnotation.getName() + ".imports. If you "
+ "are using a custom packaging, make sure that file is correct.");
return configurations;
}
在 Spring Boot 3.x 中,自动配置类的加载方式从 spring.factories 过渡到 AutoConfiguration.imports,并引入了 ImportCandidates 类来处理这一变化。
3.2 通过条件注解过滤有效配置类

关键条件注解:
- @ConditionalOnClass:类路径存在指定类时生效
- @ConditionalOnMissingBean:容器中不存在指定 Bean 时生效
- @ConditionalOnProperty:配置属性匹配时生效
4. 实现一个自定义的Starter
4.1 新建一个maven项目
项目结构:

package org.example.springbootstarterdemo;
public class HelloWorldService {
private String message = "Hello from Starter!";
public void printMessage() {
System.out.println(message);
}
public String getMessage() {
return message;
}
public void setMessage(String message) {
this.message = message;
}
}
package org.example.springbootstarterdemo;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionalOnMissingBean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
public class StarterAutoConfiguration {
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public HelloWorldService helloWorldService() {
return new HelloWorldService();
}
}
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.AutoConfiguration.imports:
org.example.springbootstarterdemo.StarterAutoConfiguration
pom.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>3.4.4</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<groupId>org.example</groupId>
<artifactId>simple-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<properties>
<java.version>17</java.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-autoconfigure</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
# 在项目根目录执行
mvn clean install

4.2 SpringBoot 项目引入
在pom.xml添加
<dependency>
<groupId>org.example</groupId>
<artifactId>simple-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
</dependency>
package org.example.springbootlearn;
import org.example.springbootstarterdemo.HelloWorldService;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext;
@SpringBootApplication
public class SpringBootLearnApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = SpringApplication.run(SpringBootLearnApplication.class, args);
HelloWorldService bean = context.getBean(HelloWorldService.class);
System.out.println(bean.getMessage());
}
}
启动时添加 --debug 参数:
StarterAutoConfiguration#helloWorldService matched:
- @ConditionalOnMissingBean (types: org.example.springbootstarterdemo.HelloWorldService; SearchStrategy: all) did not find any beans (OnBeanCondition)

总结
Spring Boot 的自动装配通过以下步骤实现:
触发入口:@EnableAutoConfiguration 注解激活自动配置机制
加载候选:通过 AutoConfiguration.imports 文件加载所有候选配置类
条件过滤:利用 @Conditional 系列注解筛选有效配置
Bean注册:符合条件的配置类通过 @Bean 方法注册组件
动态适配:根据类路径、配置属性等环境因素动态调整最终配置
通过这种机制,Spring Boot 实现了 "约定大于配置" 的设计理念,显著减少了手动配置的工作量。
SpringBoot的自动装配原理的更多相关文章
- 【springboot】自动装配原理
摘自:https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/ZxY_AiJ1m3z1kH6juh2XHw 前言 Spring翻译为中文是"春天",的确,在某段时间内,它给Java开 ...
- SpringBoot启动流程分析(五):SpringBoot自动装配原理实现
SpringBoot系列文章简介 SpringBoot源码阅读辅助篇: Spring IoC容器与应用上下文的设计与实现 SpringBoot启动流程源码分析: SpringBoot启动流程分析(一) ...
- SpringBoot自动装配原理解析
本文包含:SpringBoot的自动配置原理及如何自定义SpringBootStar等 我们知道,在使用SpringBoot的时候,我们只需要如下方式即可直接启动一个Web程序: @SpringBoo ...
- springboot自动装配原理
最近开始学习spring源码,看各种文章的时候看到了springboot自动装配实现原理.用自己的话简单概括下. 首先打开一个基本的springboot项目,点进去@SpringBootApplica ...
- springboot自动装配原理,写一个自己的start
springboot自动装配原理 第一次使用springboot的时候,都感觉很神奇.只要加入一个maven的依赖,写几行配置,就能注入redisTemple,rabbitmqTemple等对象. 这 ...
- SpringBoot | 2.1 SpringBoot自动装配原理
@ 目录 前言 1. 引入配置文件与配置绑定 @ImportResource @ConfigurationProperties 1.1 @ConfigurationProperties + @Enab ...
- 【Springboot】Springboot自动装配原理
1.核心注解就是 EnableAutoConfiguration 该注解会激活SpringBoot的自动装配功能: 代码如下: @Target(ElementType.TYPE) @Retentio ...
- 深入理解SpringBoot之自动装配
SpringBoot的自动装配是拆箱即用的基础,也是微服务化的前提.其实它并不那么神秘,我在这之前已经写过最基本的实现了,大家可以参考这篇文章.这次主要的议题是,来看看它是怎么样实现的,我们透过源代码 ...
- Eureka 系列(03)Spring Cloud 自动装配原理
Eureka 系列(03)Spring Cloud 自动装配原理 [TOC] 0. Spring Cloud 系列目录 - Eureka 篇 本文主要是分析 Spring Cloud 是如何整合 Eu ...
- Spring Boot系列(二):Spring Boot自动装配原理解析
一.Spring Boot整合第三方组件(Redis为例) 1.加依赖 <!--redis--> <dependency> <groupId>org.springf ...
随机推荐
- 131:在红帽Linux中获得帮助
- Linux中如何将txt文件转为png格式
Linux中如何将txt文件转为png格式 linux将txt文件转为png格式如果文本中没有中文,使用enscript,如果文本包含中文,使用paps命令.但是实际使用中,paps部分版本也不支持中 ...
- Luogu P10581 蓝桥杯2024国A 重复的串 题解 [ 蓝 ] [ KMP ] [ 动态规划 ] [ 矩阵加速 ]
重复的串:KMP + dp 的板子题. 暴力 dp 设计 \(dp_{k,i,j}\) 表示主串匹配到第 \(i\) 位,模式串有 \(j\) 位已匹配完成,目前已完成 \(k\) 次匹配的方案数. ...
- Magnet AXIOM使用+2024獬豸杯实战
Magnet AXIOM+2024獬豸杯实战 百度网盘链接 2024獬豸杯:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1t_6Fwl6RgmEtF0UXRfVD1A?pwd=j583#list/ ...
- 新塘M051 关于 System Tick设置,3种方法操作
关于 System Tick设置,给出3种方法,学习并确认OK: 使用 M051BSPv3.01.001版本 一.使用函数CLK_EnableSysTick() 1 //Enable System T ...
- Scala面向对象之创建对象,重载构造方法,继承抽象类实现接口
package com.wyh.day01 object ScalaClass { def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = { val student = new ...
- “未能加载工具箱项xxx,将从工具箱中将其删除”提示出现原因及解决方案
https://www.thinbug.com/q/27289366 https://social.msdn.microsoft.com/Forums/vstudio/en-US/77e10b58-4 ...
- DeepSeek 官方推出的提示词库,AI内容生成的精准导航仪!
前言 在当今数字化时代,人工智能(AI)正以前所未有的速度改变着我们的生活方式和工作模式.从简单的数据处理到复杂的创意生成,AI技术正逐渐渗透到各个领域,成为推动社会进步的重要力量.然而,如何高效地利 ...
- 关于JS中继承
继承,我理解就是把所有实例可能用到的属性和方法抽出来,单独放在一个"超类"中,一方面避免重复写代码,另一方面也会节省内存.如果单独用原型继承,引用值的处理是个问题 如果单独用cal ...
- Go语言之sync包 WaitGroup的使用
WaitGroup 是什么以及它能为我们解决什么问题? WaitGroup在go语言中,用于线程同步,单从字面意思理解,wait等待的意思,group组.团队的意思,WaitGroup就是指等待一组, ...
