搞懂这两个组件,Spring 配置问题少一半!
案例
前置条件:
在 resources 目录下有 hello/hello.properties 文件,文件内容如下:
hello=nihao
案例一:
在 HelloController 类中通过 @PropertySource 注解引用 properties 文件的内容,然后就可以通过 @Value 注解引用这个配置文件中的 hello 这个 key 了。
@PropertySource({"classpath:hello/hello.properties"})
@RestController
public class HelloController {
@Value("${hello}")
private String hello;
@GetMapping("/hello")
public String hello() {
return hello;
}
}
案例一执行的结果是返回 nihao 这个字符串。
案例二:
在 AnotherController 类中通过 @PropertySource 注解引用 properties 文件的内容,在 HelloController 中仍然可以通过 @Value 注解引用这个配置文件中的 hello 这个 key 。
@RestController
public class HelloController {
@Value("${hello}")
private String hello;
@GetMapping("/hello")
public String hello() {
return hello;
}
}
@RestController
@PropertySource({"classpath:hello/hello.properties"})
public class AnotherController {
// 省略代码
}
案例二返回的结果和案例一一致,这说明了只需要一个 Bean 通过 @PropertySource 注解引用了 properties 配置文件后,其它的 Bean 无需再使用@PropertySource 注解引用即可通过 @Value 注入其中的值。
案例三:
@Getter
@Setter
public class TestBean {
private String attributeA;
private String attributeB;
}
@RestController
public class HelloController {
@Value("${hello}")
private String hello;
@Autowired
private TestBean testBean;
@GetMapping("/hello")
public String hello() {
System.out.println("AttributeA = " + testBean.getAttributeA());
System.out.println("AttributeB = " + testBean.getAttributeB());
return hello;
}
}
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd">
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:testBean/testBean.properties"/>
<bean id="testBean" class="com.test.TestBean">
<property name="attributeA" value="${valueA}"/>
<property name="attributeB" value="${valueB}"/>
<!-- 省略其它配置 -->
</bean>
</beans>
testBean.properties 配置文件中的值如下:
valueA=testA
valueB=testB
案例三执行的结果是 testBean 中的属性被正确替换为了 testBean.properties 配置文件中的值。
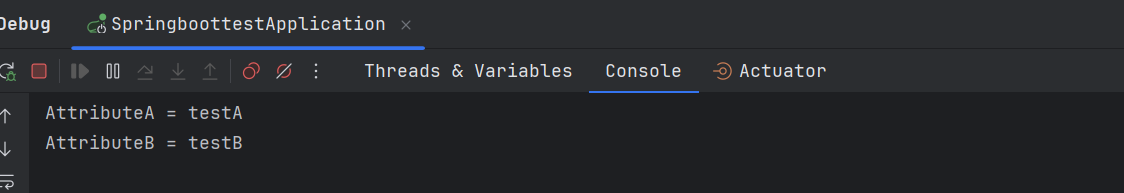
案例四:
在 hello.properties 文件中增加 attributeA 配置项,其它和案例三保持一致:
valueA=anotherTestA
案例四执行的结果是 testBean 中的 attributeA 属性被替换为了 hello.properties 中的值,attributeB 中的属性被替换为了 testBean.properties 中的值。
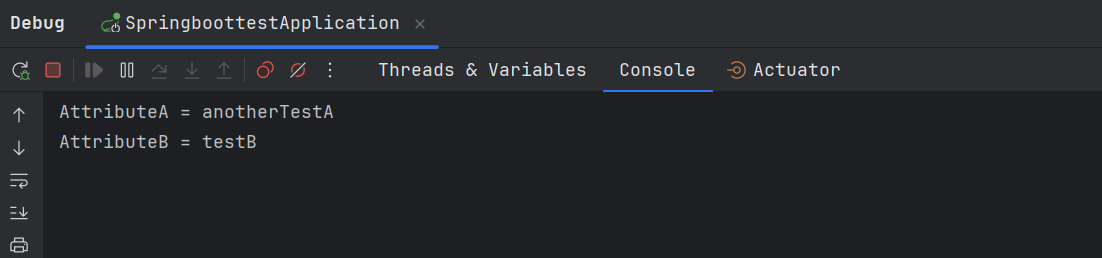
源码分析
@PropertySource注解
在 Spring 中提供了 BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor 接口,它提供了一个方法可以注册额外的 Bean 定义。代码如下:
public interface BeanDefinitionRegistryPostProcessor extends BeanFactoryPostProcessor {
void postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry(BeanDefinitionRegistry registry) throws BeansException;
}
Spring 中提供了 ConfigurationClassPostProcessor 做为实现类,在它的 postProcessBeanDefinitionRegistry() 通过 ConfigurationClassParser 去将 @Configuration 等注解修饰的类解析成 Bean 定义并注册。
而在 ConfigurationClassParser 中的 doProcessConfigurationClass() 方法会解析所有 @PropertySource 注解的配置信息,然后根据配置的路径加载对应路径下的配置文件,然后注册到 Environment 中。代码如下:
protected final SourceClass doProcessConfigurationClass(
ConfigurationClass configClass, SourceClass sourceClass,
Predicate<String> filter)
throws IOException {
// Process any @PropertySource annotations
for (AnnotationAttributes propertySource : AnnotationConfigUtils.attributesForRepeatable(
sourceClass.getMetadata(), org.springframework.context.annotation.PropertySource.class,
PropertySources.class, true)) {
if (this.propertySourceRegistry != null) {
this.propertySourceRegistry.processPropertySource(propertySource);
}
else {
logger.info("Ignoring @PropertySource annotation on [" + sourceClass.getMetadata().getClassName() +
"]. Reason: Environment must implement ConfigurableEnvironment");
}
}
}
在 PropertySourceRegistry 的 processPropertySource() 方法中获取到注解配置的文件的位置,然后又委托给了 PropertySourceProcessor 处理。代码如下:
void processPropertySource(AnnotationAttributes propertySource) throws IOException {
String name = propertySource.getString("name");
if (!StringUtils.hasLength(name)) {
name = null;
}
String encoding = propertySource.getString("encoding");
if (!StringUtils.hasLength(encoding)) {
encoding = null;
}
// 获取到注解中配置的配置文件的位置
String[] locations = propertySource.getStringArray("value");
Assert.isTrue(locations.length > 0, "At least one @PropertySource(value) location is required");
boolean ignoreResourceNotFound = propertySource.getBoolean("ignoreResourceNotFound");
Class<? extends PropertySourceFactory> factoryClass = propertySource.getClass("factory");
Class<? extends PropertySourceFactory> factoryClassToUse =
(factoryClass != PropertySourceFactory.class ? factoryClass : null);
PropertySourceDescriptor descriptor = new PropertySourceDescriptor(Arrays.asList(locations),
ignoreResourceNotFound, name, factoryClassToUse, encoding);
//
this.propertySourceProcessor.processPropertySource(descriptor);
this.descriptors.add(descriptor);
}
在 PropertySourceProcessor 的 processPropertySource() 方法中遍历每个配置文件位置加载配置文件,然后添加到 Environment 的 propertySources 中。代码如下:
public void processPropertySource(PropertySourceDescriptor descriptor) throws IOException {
String name = descriptor.name();
String encoding = descriptor.encoding();
List<String> locations = descriptor.locations();
boolean ignoreResourceNotFound = descriptor.ignoreResourceNotFound();
PropertySourceFactory factory = (descriptor.propertySourceFactory() != null ?
instantiateClass(descriptor.propertySourceFactory()) : defaultPropertySourceFactory);
for (String location : locations) { // 遍历每个配置文件位置加载配置文件
try {
String resolvedLocation = this.environment.resolveRequiredPlaceholders(location);
for (Resource resource : this.resourcePatternResolver.getResources(resolvedLocation)) {
addPropertySource(factory.createPropertySource(name, new EncodedResource(resource, encoding)));
}
} catch (RuntimeException | IOException ex) {
// 省略点
}
}
}
private void addPropertySource(PropertySource<?> propertySource) {
String name = propertySource.getName();
MutablePropertySources propertySources = this.environment.getPropertySources();
if (this.propertySourceNames.contains(name)) {
// 省略代码
}
if (this.propertySourceNames.isEmpty()) {
propertySources.addLast(propertySource);
}
else {
String lastAdded = this.propertySourceNames.get(this.propertySourceNames.size() - 1);
// 添加到 propertySources 中
propertySources.addBefore(lastAdded, propertySource);
}
this.propertySourceNames.add(name);
}
在 AbstractApplicationContext 中的 finishBeanFactoryInitialization() 方法中,会先判断是否有注册 EmbeddedValueResolver,如果没有再注册,如果有的话就不注册了,这里和 PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer 联动起来了。代码如下:
protected void finishBeanFactoryInitialization(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
// Register a default embedded value resolver if no BeanFactoryPostProcessor
// (such as a PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer bean) registered any before:
// at this point, primarily for resolution in annotation attribute values.
if (!beanFactory.hasEmbeddedValueResolver()) {
beanFactory.addEmbeddedValueResolver(strVal -> getEnvironment().resolvePlaceholders(strVal));
}
// Instantiate all remaining (non-lazy-init) singletons.
beanFactory.preInstantiateSingletons();
}
PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer
而 PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer 实现了 BeanFactoryPostProcessor 接口,它的 postProcessBeanFactory() 方法中,首先以 environment 对象构建一个 PropertySource 对象,添加到 propertySources 中;然后根据它自己配置的 location (即前面在xml中配置的)构建一个 PropertySource 对象,添加到 propertySources 中,默认添加在尾部,这个对于解释场景四很重要。最后基于 propertySources 构建了一个 ConfigurablePropertyResolver 对象去调用 processProperties() 方法。
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
if (this.propertySources == null) {
this.propertySources = new MutablePropertySources();
if (this.environment != null) {
PropertyResolver propertyResolver = this.environment;
// If the ignoreUnresolvablePlaceholders flag is set to true, we have to create a
// local PropertyResolver to enforce that setting, since the Environment is most
// likely not configured with ignoreUnresolvablePlaceholders set to true.
// See https://github.com/spring-projects/spring-framework/issues/27947
if (this.ignoreUnresolvablePlaceholders &&
(this.environment instanceof ConfigurableEnvironment configurableEnvironment)) {
PropertySourcesPropertyResolver resolver =
new PropertySourcesPropertyResolver(configurableEnvironment.getPropertySources());
resolver.setIgnoreUnresolvableNestedPlaceholders(true);
propertyResolver = resolver;
}
// 将environment构建为一个PropertySource对象
PropertyResolver propertyResolverToUse = propertyResolver;
this.propertySources.addLast(
new PropertySource<>(ENVIRONMENT_PROPERTIES_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME, this.environment) {
@Override
@Nullable
public String getProperty(String key) {
return propertyResolverToUse.getProperty(key);
}
}
);
}
try {
PropertySource<?> localPropertySource =
new PropertiesPropertySource(LOCAL_PROPERTIES_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME, mergeProperties());
if (this.localOverride) {
this.propertySources.addFirst(localPropertySource);
}
else { // 默认情况下是将配置加入到最后
this.propertySources.addLast(localPropertySource);
}
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new BeanInitializationException("Could not load properties", ex);
}
}
processProperties(beanFactory, createPropertyResolver(this.propertySources));
this.appliedPropertySources = this.propertySources;
}
在 processProperties() 方法中通过 ConfigurablePropertyResolver 对象又构造了一个 StringValueResolver 对象,然后调用了 doProcessProperties() 方法。代码如下:
protected void processProperties(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactoryToProcess,
final ConfigurablePropertyResolver propertyResolver) throws BeansException {
propertyResolver.setPlaceholderPrefix(this.placeholderPrefix);
propertyResolver.setPlaceholderSuffix(this.placeholderSuffix);
propertyResolver.setValueSeparator(this.valueSeparator);
propertyResolver.setEscapeCharacter(this.escapeCharacter);
// 构造了一个StringValueResolver对象
StringValueResolver valueResolver = strVal -> {
String resolved = (this.ignoreUnresolvablePlaceholders ?
propertyResolver.resolvePlaceholders(strVal) :
propertyResolver.resolveRequiredPlaceholders(strVal));
if (this.trimValues) {
resolved = resolved.trim();
}
return (resolved.equals(this.nullValue) ? null : resolved);
};
doProcessProperties(beanFactoryToProcess, valueResolver);
}
在 doProcessProperties() 方法中又通过 StringValueResolver 对象构造了一个 BeanDefinitionVisitor 对象,然后调用它的 visitBeanDefinition() 实现了对 Bean 定义中属性引用的解析。然后调用 BeanFactory 的 addEmbeddedValueResolver() 方法把 StringValueResolver 对象设置给了 BeanFactory,这里就和前面的AbstractApplicationContext 中的 finishBeanFactoryInitialization() 方法呼应起来了,这里设置了值,那边就不设置了,这里没有设置,那边就会设置。
protected void doProcessProperties(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactoryToProcess,
StringValueResolver valueResolver) {
// 构造BeanDefinitionVisitor对象
BeanDefinitionVisitor visitor = new BeanDefinitionVisitor(valueResolver);
String[] beanNames = beanFactoryToProcess.getBeanDefinitionNames();
for (String curName : beanNames) {
// Check that we're not parsing our own bean definition,
// to avoid failing on unresolvable placeholders in properties file locations.
if (!(curName.equals(this.beanName) && beanFactoryToProcess.equals(this.beanFactory))) {
BeanDefinition bd = beanFactoryToProcess.getBeanDefinition(curName);
try {
// 对Bean定义中引用的配置进行解析
visitor.visitBeanDefinition(bd);
}
catch (Exception ex) {
throw new BeanDefinitionStoreException(bd.getResourceDescription(), curName, ex.getMessage(), ex);
}
}
}
// Resolve placeholders in alias target names and aliases as well.
beanFactoryToProcess.resolveAliases(valueResolver);
// Resolve placeholders in embedded values such as annotation attributes.
// 添加到BeanFactory中
beanFactoryToProcess.addEmbeddedValueResolver(valueResolver);
}
在之前的文章Spring 中 @Value 注解实现原理中介绍了在 DefaultListableBeanFactory 的 resolveEmbeddedValue() 方法中实现了对 @Value 注解的解析,这里实际上就是调用的上面设置的 StringValueResolver 对象的 resolveStringValue() 方法来实现的。
public String resolveEmbeddedValue(@Nullable String value) {
if (value == null) {
return null;
}
String result = value;
for (StringValueResolver resolver : this.embeddedValueResolvers) {
result = resolver.resolveStringValue(result);
if (result == null) {
return null;
}
}
return result;
}
案例解答
对于案例二: 在解析 Bean 定义的时候会把所有 @PropertySource 注解定义配置文件解析到 Environment 集中保存起来,然后在解析 @Value 注解值的时候统一从这个集中的地方去查找。因此只需要有一个类通过 @PropertySource 注解引用这个配置即可。
对于案例三: 实际上是依赖实现了 BeanFactoryPostProcessor 接口,它的 postProcessBeanFactory() 方法中实现了在 Bean 真正创建之前,对 Bean 定义中引用属性的解析。
对于案例四: 在默认的情况下解析依赖的配置文件是所有 @PropertySource 引用的配置文件加上 PropertySourcesPlaceholderConfigurer 的 location 属性引用的配置文件,且 @PropertySource 引用的配置文件在它的 location 属性引用的配置文件前面,查找的时候是按照顺序查找的。@PropertySource 引用的配置文件中定义了相同的 key,则直接会获取值返回,不会再继续往后查找了,所以就出现了案例四中 hello.properties 配置文件中的相同配置项覆盖了 testBean.properties 配置文件中的配置项。t
同时 Spring 提供了一个配置项 local-override,当设置为 true 时,才会使用testBean.properties 配置覆盖hello.properties 配置。覆盖的原理就是把配置加到最前面。代码如下:
<context:property-placeholder location="classpath:testBean.properties" local-override="true" />
try {
PropertySource<?> localPropertySource =
new PropertiesPropertySource(LOCAL_PROPERTIES_PROPERTY_SOURCE_NAME, mergeProperties());
if (this.localOverride) { // 设置为true的时候将配置加入到最前面
this.propertySources.addFirst(localPropertySource);
}
else { // 默认情况下是将配置加入到最后
this.propertySources.addLast(localPropertySource);
}
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new BeanInitializationException("Could not load properties", ex);
}
搞懂这两个组件,Spring 配置问题少一半!的更多相关文章
- EOS 上线前,先搞懂这两个基本概念
如果你曾经尝试在本地运行 EOS 测试节点,会发现编译.运行并不是特别复杂,但官方教程里两个概念很容易把人搞晕: Account(账户)和 Wallet (钱包). EOS 的 Wallet 跟其他区 ...
- 搞懂分布式技术14:Spring Boot使用注解集成Redis缓存
本文内容参考网络,侵删 本系列文章将整理到我在GitHub上的<Java面试指南>仓库,更多精彩内容请到我的仓库里查看 https://github.com/h2pl/Java-Tutor ...
- 一张图搞懂Spring bean的完整生命周期
一张图搞懂Spring bean的生命周期,从Spring容器启动到容器销毁bean的全过程,包括下面一系列的流程,了解这些流程对我们想在其中任何一个环节怎么操作bean的生成及修饰是非常有帮助的. ...
- 五分钟学Java:一篇文章搞懂spring和springMVC
原创声明 本文作者:黄小斜 转载请务必在文章开头注明出处和作者. 本文思维导图 什么是Spring,为什么你要学习spring? 你第一次接触spring框架是在什么时候?相信很多人和我一样,第一次了 ...
- 五分钟学Java:一篇文章带你搞懂spring全家桶套餐
原创声明 本文首发于微信公众号[程序员黄小斜] 本文作者:黄小斜 转载请务必在文章开头注明出处和作者. 本文思维导图 什么是Spring,为什么你要学习spring? 你第一次接触spring框架是在 ...
- 这一次搞懂Spring事务注解的解析
前言 事务我们都知道是什么,而Spring事务就是在数据库之上利用AOP提供声明式事务和编程式事务帮助我们简化开发,解耦业务逻辑和系统逻辑.但是Spring事务原理是怎样?事务在方法间是如何传播的?为 ...
- Spring第四天,BeanPostProcessor源码分析,彻底搞懂IOC注入及注解优先级问题!
- 这一次搞懂Spring事务是如何传播的
文章目录 前言 正文 事务切面的调用过程 事务的传播性概念 实例分析 总结 前言 上一篇分析了事务注解的解析过程,本质上是将事务封装为切面加入到AOP的执行链中,因此会调用到MethodIncepto ...
- 从源码的角度彻底搞懂 HandlerMapping 和 HandlerAdapter
彻底搞懂 HandlerMapping和HandlerAdapter 知识点的回顾: 当Tomcat接收到请求后会回调Servlet的service方法,一开始入门Servlet时,我们会让自己的Se ...
- 这一次搞懂SpringMVC原理
@ 目录 前言 正文 请求入口 组件初始化 调用Controller 参数.返回值解析 总结 前言 前面几篇文章,学习了Spring IOC.Bean实例化过程.AOP.事务的源码和设计思想,了解了S ...
随机推荐
- Pycomcad快速绘制参数化多段线的一种方法
任务: 绘制出不同长度的相同型式的多段线,如上图所示,仅仅是300mm和500mm的区别,3个弯折处都一样,都是圆弧段,对于常规二次开发思路,是通过数学计算,计算出圆弧的圆心的位置,用固定的半径,绘制 ...
- maven导入org.apache.pdfbox
PDF和图片相互转换用到的maven依赖如下: <dependency> <groupId>org.apache.pdfbox</groupId> <arti ...
- win10 hyper-v 配置教程
非家庭版跳过以下这一步. pushd "%~dp0" dir /b %SystemRoot%\servicing\Packages\*Hyper-V*.mum >hv.txt ...
- BIO, NIO, AIO 大白话 - 澄澈大学生也能搞懂
最近天天吃沙县, 就拿沙县分析 BIO Block I/O 沙县分析 相近时间来了4个顾客 顾客 菜品 时间 A 筒骨饭 5min B 茄子肉丝盖饭 7min C 猪脚饭 3min D 茄子肉丝盖饭 ...
- FastAPI权限配置:你的系统真的安全吗?
url: /posts/96b6ede65030daa4613ab92da1d739a6/ title: FastAPI权限配置:你的系统真的安全吗? date: 2025-06-26T07:35:3 ...
- Golang基础笔记七之指针,值类型和引用类型
本文首发于公众号:Hunter后端 原文链接:Golang基础笔记七之指针,值类型和引用类型 本篇笔记介绍 Golang 里的指针,值类型与引用类型相关的概念,以下是本篇笔记目录: 指针 值类型与引用 ...
- C#/.NET/.NET Core技术前沿周刊 | 第 44 期(2025年6.23-6.30)
前言 C#/.NET/.NET Core技术前沿周刊,你的每周技术指南针!记录.追踪C#/.NET/.NET Core领域.生态的每周最新.最实用.最有价值的技术文章.社区动态.优质项目和学习资源等. ...
- HTML+CSS+JS日常问题和技巧1(删除某select下除第一个以外的option、双击删除本身、select的change()方法失效问题、实现div高度随背景图片的大小进行改变、实现禁止右键和键盘按键,以打开控制台为例)
1.删除某select下除第一个以外的option: 1 $("#selectId option:not(:first)").remove() 2.JS实现双击事件(双击删除本身) ...
- 前端开发系列125-进阶篇之Iterator
本文简单说明[ 迭代器接口 Iterator]() 接口的基本使用,涉及 Array .Set .Map 和 String 以及伪数组等数据结构,以及 `for...of`循环的用法等. Iterat ...
- Wordpress设置必须登录才能查看内容
参考文章地址 我是一个不会编程的小白,在网上查了好多篇的文章都没有实现这个功能.都是在改完php的代码后,网站就报废了.后来我还是求助了万能的谷歌,找了这篇文章. 上代码.大概猜测了一下,就是判断你现 ...
