Java集合类源码解析:AbstractList
今天学习Java集合类中的一个抽象类,AbstractList。
初识AbstractList
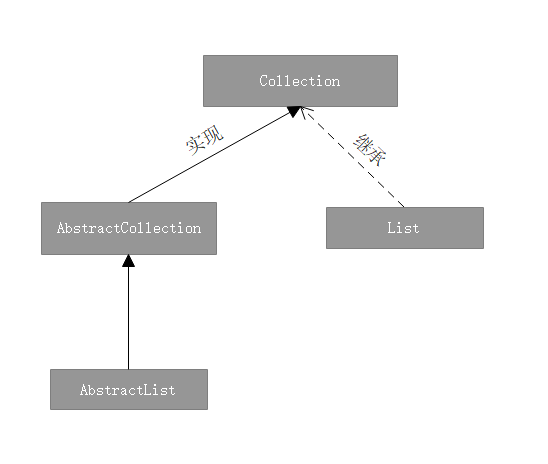
AbstractList 是一个抽象类,实现了List<E>接口,是隶属于Java集合框架中的 根接口 Collection 的分支,由其衍生的很多子类因为拥有强大的容器性能而被广泛应用,例如我们最为熟悉的ArrayList,这是它的类继承结构图:
特殊方法
AbstractList 虽然是抽象类,但其内部只有一个抽象方法 get():
abstract public E get(int index);
从字面上看这是获取的方法,子类必须实现它,一般是作为获取元素的用途,除此之外,如果子类要操作元素,还需要重写 add(), set(), remove() 方法,因为 AbstractList 虽然定义了这几个方法,但默认是不支持的,
public boolean add(E e) {
add(size(), e);
return true;
}
public void add(int index, E element) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
public E set(int index, E element) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
public E remove(int index) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
可以看到,在其默认实现里,直接是抛出UnsupportedOperationException 异常的,这里的处理跟AbstractMap 的 put() 方法有异曲同工之妙处,很大功能就是官方考虑到也许会有子类需要这些方法不可修改,需要修改的话直接重写即可。
两个迭代器实现类
AbstractList 中提供了两个迭代器的实现类,默认实现了迭代器接口,实现了对元素的遍历,它们就是Itr 和其子类 ListItr,分别来了解一下。
先看Itr类,Itr 实现了 Iterator 接口,重写了 next() 和 remove() 方法,下面是它的源码:
private class Itr implements Iterator<E> {
//游标
int cursor;
//最近迭代的元素位置,每次使用完默认置为-1
int lastRet;
//记录容器被修改的次数,值不相等说明有并发操作
int expectedModCount = modCount;
public boolean hasNext() {
return cursor != size();
}
public E next() {
//检测是否有并发
checkForComodification();
try {
int i = cursor;
// 获取容器对应游标位置的元素
E next = get(i);
//记录获取到的元素的索引
lastRet = i;
//获取下一个元素的索引
cursor = i + 1;
return var2;
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException var3) {
this.checkForComodification();
throw new NoSuchElementException();
}
}
public void remove() {
//还没读取元素就remove,报错
if (lastRet < 0) {
throw new IllegalStateException();
} else {
checkForComodification();
try {
AbstractList.this.remove(lastRet);
if (lastRet < cursor) {
--this.cursor;
}
//删除后,把最后迭代的记录位置置为-1
lastRet = -1;
expectedModCount = modCount;
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException var2) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
}
//两个值不一致,说明有并发操作,抛出异常
final void checkForComodification() {
if (modCount != expectedModCount) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
}
ListItr 是 Itr 的子类,在Itr 的基础上增强了对元素的操作,多了指定索引的赋值,以及向前读取,add 和 set 的方法。
private class ListItr extends Itr implements ListIterator<E> {
ListItr(int index) {
cursor = index; //设置游标为指定值
}
//游标不为第一个的话,前面都有元素的
public boolean hasPrevious() {
return cursor != 0;
}
public E previous() {
checkForComodification();
try {
int i = cursor - 1;
//获取游标的前一个元素
E previous = get(i);
//把最后操作的位置和游标都前移一位
lastRet = cursor = i;
return previous;
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
checkForComodification();
throw new NoSuchElementException();
}
}
public int nextIndex() {
return cursor;
}
public int previousIndex() {
return cursor-1;
}
public void set(E e) {
if (lastRet < 0)
throw new IllegalStateException();
checkForComodification();
try {
AbstractList.this.set(lastRet, e);
expectedModCount = modCount;
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
public void add(E e) {
checkForComodification();
try {
int i = cursor;
AbstractList.this.add(i, e);
lastRet = -1;
cursor = i + 1;
expectedModCount = modCount;
} catch (IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
}
两个类的源码还是比较简单的,加了注释相信大家也能看出大概的逻辑。使用上,AbstractList类中提供了两个方法,返回的各自实现的接口类型对象:
public Iterator<E> iterator() {
return new Itr();
}
public ListIterator<E> listIterator() {
return listIterator(0);
}
public ListIterator<E> listIterator(final int index) {
rangeCheckForAdd(index);
return new ListItr(index);
}
额。。。。。说错了,不是两个,是三个方法,懒得删,这句废话也加上吧。
获取对象索引
结合内部迭代器实现类,AbstractList 还提供了两个可以获取对象索引的方法,分别是
indexOf(): 获取指定对象 首次出现 的索引
public int indexOf(Object o) {
//返回迭代器类,此时默认游标位置是0
ListIterator<E> it = listIterator();
if (o==null) {
//向后遍历
while (it.hasNext())
//后面没元素了,返回游标前面元素的索引,这里为什么是返回前面索引呢?
//因为在ListIterator接口中,每次调用next()游标就会后移一位
//所以,当找到对应元素时,游标已经后移一位了,需要返回游标的前一个索引。
if (it.next()==null)
return it.previousIndex();
} else {
while (it.hasNext())
if (o.equals(it.next()))
return it.previousIndex();
}
return -1;
}
lastIndexOf() :获取指定对象最后一次出现的位置,原理和indexOf方法类似,只是改为后面向前
public int lastIndexOf(Object o) {
//返回迭代器了,此时游标在最后一位
ListIterator<E> it = listIterator(size());
if (o==null) {
//向前遍历
while (it.hasPrevious())
if (it.previous()==null)
return it.nextIndex();
} else {
while (it.hasPrevious())
if (o.equals(it.previous()))
return it.nextIndex();
}
return -1;
}
两个子类
AbstractList 提供了两个子类,可用于切分集合序列,这两个类是 SubList 和 RandomAccessSubList ,SubList 的内部实现和 AbstractList 很相似,无非是传递了两个变量,初识位置和结束位置来截取集合,具体原理就不做解析了,读者们自己看看吧,也不难,贴一下部分源码:
class SubList<E> extends AbstractList<E> {
private final AbstractList<E> l;
private final int offset;
private int size;
SubList(AbstractList<E> list, int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
if (fromIndex < 0)
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("fromIndex = " + fromIndex);
if (toIndex > list.size())
throw new IndexOutOfBoundsException("toIndex = " + toIndex);
if (fromIndex > toIndex)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("fromIndex(" + fromIndex +
") > toIndex(" + toIndex + ")");
l = list;
offset = fromIndex;
size = toIndex - fromIndex;
this.modCount = l.modCount;
}
public E set(int index, E element) {
rangeCheck(index);
checkForComodification();
return l.set(index+offset, element);
}
............
............
}
RandomAccessSubList 是 SubList 的子类,内部实现直接沿用父类,只是实现了RandomAccess接口,这是源码:
class RandomAccessSubList<E> extends SubList<E> implements RandomAccess {
RandomAccessSubList(AbstractList<E> list, int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
super(list, fromIndex, toIndex);
}
public List<E> subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex) {
return new RandomAccessSubList<>(this, fromIndex, toIndex);
}
}
不一样的是,RandomAccessSubList 实现了一个接口RandomAccess,打开后发现是空的,没有任何实现。
public interface RandomAccess {
}
它的作用是用于标识某个类是否支持 随机访问(随机访问,相对比“按顺序访问”)。一个支持随机访问的类明显可以使用更加高效的算法。例如遍历上,实现RandomAccess 接口的集合使用 get() 做迭代速度会更快,比起使用迭代器的话,
for (int i=0; i < list.size(); i++)
list.get(i);
for (Iterator i=list.iterator(); i.hasNext();)
i.next();
例如ArrayList 就是实现了这个接口,而关于该接口有如此功效的原因这里暂且不做深入研究,日后有机会单独写一篇讲解下。
最后
作为抽象类,AbstractList本身算是定义比较完善的结构体系了,继承了它的衣钵的子类也拥有不俗的表现,在Java开发中被广泛应用,有时间的话打算多写几篇关于它的子类,好了,关于 AbstractList 的知识就学到这里了,睡觉了~
Java集合类源码解析:AbstractList的更多相关文章
- Java集合类源码解析:Vector
[学习笔记]转载 Java集合类源码解析:Vector 引言 之前的文章我们学习了一个集合类 ArrayList,今天讲它的一个兄弟 Vector.为什么说是它兄弟呢?因为从容器的构造来说,Vec ...
- Java集合类源码解析:HashMap (基于JDK1.8)
目录 前言 HashMap的数据结构 深入源码 两个参数 成员变量 四个构造方法 插入数据的方法:put() 哈希函数:hash() 动态扩容:resize() 节点树化.红黑树的拆分 节点树化 红黑 ...
- Java集合类源码解析:ArrayList
目录 前言 源码解析 基本成员变量 添加元素 查询元素 修改元素 删除元素 为什么用 "transient" 修饰数组变量 总结 前言 今天学习一个Java集合类使用最多的类 Ar ...
- Java集合类源码解析:AbstractMap
目录 引言 源码解析 抽象函数entrySet() 两个集合视图 操作方法 两个子类 参考: 引言 今天学习一个Java集合的一个抽象类 AbstractMap ,AbstractMap 是Map接口 ...
- Java集合类源码解析:LinkedHashMap
前言 今天继续学习关于Map家族的另一个类 LinkedHashMap .先说明一下,LinkedHashMap 是继承于 HashMap 的,所以本文只针对 LinkedHashMap 的特性学习, ...
- 【转】Java HashMap 源码解析(好文章)
.fluid-width-video-wrapper { width: 100%; position: relative; padding: 0; } .fluid-width-video-wra ...
- JDK8集合类源码解析 - HashSet
HashSet 特点:不允许放入重复元素 查看源码,发现HashSet是基于HashMap来实现的,对HashMap做了一次“封装”. private transient HashMap<E,O ...
- Java——LinkedHashMap源码解析
以下针对JDK 1.8版本中的LinkedHashMap进行分析. 对于HashMap的源码解析,可阅读Java--HashMap源码解析 概述 哈希表和链表基于Map接口的实现,其具有可预测的迭 ...
- Java - TreeMap源码解析 + 红黑树
Java提高篇(二七)-----TreeMap TreeMap的实现是红黑树算法的实现,所以要了解TreeMap就必须对红黑树有一定的了解,其实这篇博文的名字叫做:根据红黑树的算法来分析TreeMap ...
随机推荐
- EF的简单认识
EF的简单认识 EF简介 EntityFramwork是微软提供的一款ORM框架(Object Relational Mapping),实体映射模型,它的底层是ADO.NET的机制,使用EF将省去 ...
- powerdesigner 不能自动生成注释的解决方法(三步解决)
解决power designer 不能自动生成注释的解决办法只需要3步: 一.快捷键 Ctrl+Shift+X 打开脚本编辑器:(快捷键不能执行的话可以从这个路径执行:Tools --> Exc ...
- SSIS - 5.优先约束
一.优先约束和执行逻辑 任务和容器是SSIS中的可执行文件,一个优先约束连接着两个可执行文件:优先的可执行文件和约束的可执行文件,如下图. 它的执行逻辑如下图: 1)先执行优先可执行文件 2)判断 ...
- Java作业七(2017-10-30)
/*造人*/ public class Tman { public int id; public String name; public int age; public String city; pu ...
- [译文]Domain Driven Design Reference(七)—— 大型战略设计结构
本书是Eric Evans对他自己写的<领域驱动设计-软件核心复杂性应对之道>的一本字典式的参考书,可用于快速查找<领域驱动设计>中的诸多概念及其简明解释. 上周末电脑硬盘文件 ...
- Pycharm中配置鼠标悬停快速提示方法参数
第一步: 第二步: 演示:
- [Swift]LeetCode796. 旋转字符串 | Rotate String
We are given two strings, A and B. A shift on A consists of taking string A and moving the leftmost ...
- 记录eclipse安装SpringBoot插件及搭建SpringBoot项目
刚学习了下SpringBoot 插件安装 创建项目在此记录下 在spring官网上下载相关的插件,然后导入到eclipse中,以下是下载步骤: 1.首先查看自己eclipse版本号 help--> ...
- 剖析项目多个logback配置(上)
来源:http://www.cnblogs.com/guozp/p/5949744.html 以下两个是我在使用slf4j + logback时候日志提示的问题,问题不大,都是WARN,并不真正影响运 ...
- scala查询dataFrame结构
println(dataFrame.printSchema)
