2022-11-12:以下rust语言代码中,结构体S实现了crate::T1::T2的方法,如何获取方法列表?以下代码应该返回[“m1“,“m2“,“m5“],顺序不限。m3是S的方法,但并不属于c
2022-11-12:以下rust语言代码中,结构体S实现了crate::T1::T2的方法,如何获取方法列表?以下代码应该返回[“m1”,“m2”,“m5”],顺序不限。m3是S的方法,但并不属于crate::T1::T2的。m4也是S的方法,但这是实现T3的,也不属于crate::T1::T2的。
pub struct S;
impl crate::T1::T2 for S {
fn m1(&mut self){}
fn m2(&mut self){}
}
impl S {
fn m3(&mut self){}
}
impl T3 for S {
fn m4(&mut self){}
}
impl crate::T1::T2 for S {
fn m5(&mut self){}
}
答案2022-11-12:
要解析rust的代码,syn,quote,proc-macro2合理利用这三个库。
使用场景是写框架。
代码如下:
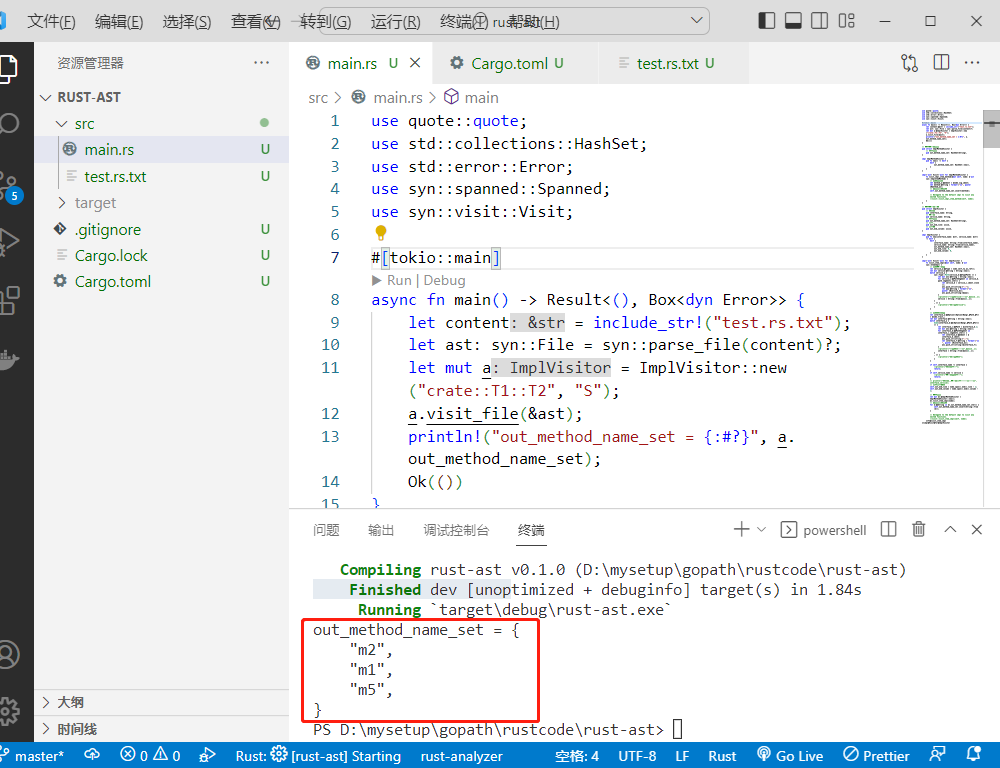
// main.rs文件内容如下:
use quote::quote;
use std::collections::HashSet;
use std::error::Error;
use syn::spanned::Spanned;
use syn::visit::Visit;
#[tokio::main]
async fn main() -> Result<(), Box<dyn Error>> {
let content = include_str!("test.rs.txt");
let ast: syn::File = syn::parse_file(content)?;
let mut a = ImplVisitor::new("crate::T1::T2", "S");
a.visit_file(&ast);
println!("out_method_name_set = {:#?}", a.out_method_name_set);
Ok(())
}
// 遍历服务的方法
pub struct ImplMethodVisitor {
// 收集方法
pub out_method_name_set: HashSet<String>,
}
impl ImplMethodVisitor {
pub fn new() -> Self {
Self {
out_method_name_set: HashSet::new(),
}
}
}
impl<'ast> Visit<'ast> for ImplMethodVisitor {
fn visit_impl_item_method(&mut self, node: &'ast syn::ImplItemMethod) {
// 获取方法名
let method_a = &node.sig.ident;
let method = format!("{}", quote! {#method_a});
// 将方法保存起来
self.out_method_name_set.insert(method);
// Delegate to the default impl to visit any nested functions.
//visit::visit_impl_item_method(self, node);
}
}
// 遍历服务的实现
pub struct ImplVisitor {
// 接口名
pub interface_name: String,
// 服务名
pub service_name: String,
// 收集方法
pub out_method_name_set: HashSet<String>,
// 结束行
pub out_end_line: usize,
// 结束列
pub out_end_column: usize,
}
impl ImplVisitor {
pub fn new(interface_name: &str, service_name: &str) -> Self {
Self {
interface_name: String::from(interface_name),
service_name: String::from(service_name),
out_method_name_set: HashSet::new(),
out_end_line: 0,
out_end_column: 0,
}
}
}
impl<'ast> Visit<'ast> for ImplVisitor {
fn visit_item_impl(&mut self, node: &'ast syn::ItemImpl) {
// 获取服务名称
let service_a = node.self_ty.as_ref();
let mut service = String::new();
match service_a {
syn::Type::Path(service_b) => {
let mut ans = String::new();
for service_c in service_b.path.segments.iter() {
let service_d = service_c.ident.clone();
ans.push_str("::");
let aaa = format!("{}", quote! {#service_d});
ans.push_str(&aaa);
}
//println!("找到Service----{}",&ans[2..]);
service = String::from(&ans[2..]);
}
_ => {
//println!("没找到Service");
}
}
// 获取接口名称
let interface_a = &node.trait_;
let mut interface = String::new();
match interface_a {
Some(interface_b) => {
let interface_c = &interface_b.1;
let mut ans = String::new();
for interface_d in interface_c.segments.iter() {
let interface_e = &interface_d.ident;
ans.push_str("::");
let interface_f = format!("{}", quote! {#interface_e});
ans.push_str(&interface_f);
}
//println!("找到接口----{}",&ans[2..]);
interface = String::from(&ans[2..]);
}
_ => {
//println!("没找到接口");
}
}
if self.interface_name != interface {
//println!("接口不匹配");
return;
}
if self.service_name != service {
//println!("服务名称不匹配");
return;
}
// println!("接口名和服务名都匹配----{}----{}",interface,service);
// 修改结束索引
self.out_end_line = node.span().end().line - 1;
self.out_end_column = node.span().end().column - 1;
// 遍历方法
let mut mv = ImplMethodVisitor::new();
mv.visit_item_impl(node);
// 将方法保存起来
for m in mv.out_method_name_set.iter() {
self.out_method_name_set.insert(String::from(m));
}
// Delegate to the default impl to visit any nested functions.
//visit::visit_item_impl(self, node);
}
}
// test.rs.txt内容如下:
pub struct S;
impl crate::T1::T2 for S {
fn m1(&mut self){}
fn m2(&mut self){}
}
impl S {
fn m3(&mut self){}
}
impl T3 for S {
fn m4(&mut self){}
}
impl crate::T1::T2 for S {
fn m5(&mut self){}
}
# Cargo.toml内容如下:
[package]
name = "rust-ast"
version = "0.1.0"
edition = "2021"
# See more keys and their definitions at https://doc.rust-lang.org/cargo/reference/manifest.html
[dependencies]
tokio = { version = "1.0", features = ["full"] }
anyhow = "1.0.66"
proc-macro2={ version = "1.0.47", features = ["span-locations"] }
syn = {version = "1.0",features=["full","extra-traits","visit"]}
quote = "1"
执行结果如下:
2022-11-12:以下rust语言代码中,结构体S实现了crate::T1::T2的方法,如何获取方法列表?以下代码应该返回[“m1“,“m2“,“m5“],顺序不限。m3是S的方法,但并不属于c的更多相关文章
- C语言中结构体对齐问题
C语言中结构体对齐问题 收藏 关于C语言中的结构体对齐问题 1,比如: struct{short a1;short a2;short a3;}A;struct{long a1;short a2;}B; ...
- Go语言中结构体的使用-第2部分OOP
1 概述 结构体的基本语法请参见:Go语言中结构体的使用-第1部分结构体.结构体除了是一个复合数据之外,还用来做面向对象编程.Go 语言使用结构体和结构体成员来描述真实世界的实体和实体对应的各种属性. ...
- 6. Go 语言中结构体的使用
1. 结构体的定义格式 在go语言中结果的定义格式如下: 123 type structName struct { filedList} 列子如下: 1234 type Person struct { ...
- C语言中结构体赋值问题的讨论
今天帮师姐调一个程序的BUG,师姐的程序中有个结构体直接赋值的语句,在我印象中结构体好像是不能直接赋值的,正如数组不能直接赋值那样,我怀疑这个地方有问题,但最后证明并不是这个问题.那么就总结一下C语言 ...
- C语言中结构体赋值问题的讨论(转载)
今天帮师姐调一个程序的BUG,师姐的程序中有个结构体直接赋值的语句,在我印象中结构体好像是不能直接赋值的,正如数组不能直接赋值那样,我怀疑这个地方有问题,但最后证明并不是这个问题.那么就总结一下C语言 ...
- Go语言中结构体的使用-第1部分结构体
1 概述 结构体是由成员构成的复合类型.Go 语言使用结构体和结构体成员来描述真实世界的实体和实体对应的各种属性.结构体成员,也可称之为成员变量,字段,属性.属性要满足唯一性.结构体的概念在软件工程上 ...
- Go语言基础之结构体
Go语言基础之结构体 Go语言中没有“类”的概念,也不支持“类”的继承等面向对象的概念.Go语言中通过结构体的内嵌再配合接口比面向对象具有更高的扩展性和灵活性. 类型别名和自定义类型 自定义类型 在G ...
- C语言第九讲,结构体
C语言第九讲,结构体 一丶结构体的定义 在C语言中,可以使用结构体(Struct)来存放一组不同类型的数据.结构体的定义形式为: struct 结构体名{ 结构体所包含的变量或数组 }; 结构体是一种 ...
- ndk学习之C语言基础复习----结构体、共用体与C++开端
自己实现sprintf功能: 关于C中的系统函数sprintf在上次[https://www.cnblogs.com/webor2006/p/7545627.html]学习中已经用到过了,这里再来回顾 ...
- GO学习-(13) Go语言基础之结构体
Go语言基础之结构体 Go语言中没有"类"的概念,也不支持"类"的继承等面向对象的概念.Go语言中通过结构体的内嵌再配合接口比面向对象具有更高的扩展性和灵活性. ...
随机推荐
- Python第九章实验报告
一.实验对象:<零基础学Python>第九章异常处理及程序调试的实例 二.实验环境:IDLE Shell 3.9.7 三.实验目的:了解和掌握常用的异常处理语句 四.实验过程: 实例01 ...
- Sitecore 应用与介绍
前言 因为工作需要,开始了 sitecore 之旅,在使用之中碰到了许多问题,后续开始写一下关于 sitecore 的文章. sitecore 官网:https://www.sitecore.com/ ...
- 使用VSCode调试C#时,Console.ReadLine()弹出命令框调试
原文链接:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_29503199/article/details/88351498 要在调试时读取输入,可以在 launch.json 中使用配置中的 ...
- SpringBoot笔记--配置文件分类+yaml相关知识+读取配置文件内容
配置文件 要是需要使用自己的配置替换默认配置时,需要使用后缀名为application.properties或者application.yml(application.yaml)进行配置 当然,几个文 ...
- 关于js通过修改行内样式来修改元素样式
关于js通过修改行内样式来修改元素样式 1.当我们通过使用js来修改html元素的样式时,使用的方法是为元素添加行内样式, 此时的js样式是生效的,因为行内样式优先级高于类名 2.如果已有同属性的行内 ...
- MasaFramework入门第二篇,安装MasaFramework了解各个模板
安装MasaFramework模板 执行以下命令安装最新Masa的模板 dotnet new --install Masa.Template 安装完成将出现四个模板 Masa Blazor App: ...
- Linux & 标准C语言学习 <DAY13>
一.字符串 字符:类字形单位或符号,包括字母.数字.运算符号.标点符号和其他符号,以及一些功能性符号 串:是一种数据结构,存储类型相同的若干个数据,对于串型结构的处理是批量性的,会从头 ...
- 63.C++类型转换
类型转换(cast)是将一种数据类型转换成另一种数据类型.例如,如果将一个整型值赋给一个浮点类型的变量,编译器会暗地里将其转换成浮点类型. 转换是非常有用的,但是它也会带来一些问题,比如在转换 ...
- Ocelot使用与设置路由Routing
一.安装Ocelot 在程序包管理器控制台输入以下命令安装Ocelot Install-Package Ocelot 二.新建两个项目 我们新建两个.Net Core WebAPI项目如下: 直接 ...
- java多线程--5 同步方法和同步块synchronized
java多线程--5 同步方法和同步块synchronized 同步方法和同步块 同步方法:关键字synchronized,包括synchronized方法和synchronized块 public ...
