机器学习作业(七)非监督学习——Matlab实现
题目下载【传送门】
第1题
简述:实现K-means聚类,并应用到图像压缩上。
第1步:实现kMeansInitCentroids函数,初始化聚类中心:
function centroids = kMeansInitCentroids(X, K) % You should return this values correctly
centroids = zeros(K, size(X, 2)); randidx = randperm(size(X, 1));
centroids = X(randidx(1:K), :); end
第2步:实现findClosestCentroids函数,进行样本点的分类:
function idx = findClosestCentroids(X, centroids) % Set K
K = size(centroids, 1); % You need to return the following variables correctly.
idx = zeros(size(X,1), 1); for i = 1:size(X, 1),
indexMin = 1;
valueMin = norm(X(i,:) - centroids(1,:));
for j = 2:K,
valueTemp = norm(X(i,:) - centroids(j,:));
if valueTemp < valueMin,
valueMin = valueTemp;
indexMin = j;
end
end
idx(i, 1) = indexMin;
end end
第3步:实现computeCentroids函数,计算聚类中心:
function centroids = computeCentroids(X, idx, K) % Useful variables
[m n] = size(X); % You need to return the following variables correctly.
centroids = zeros(K, n); centSum = zeros(K, n);
centNum = zeros(K, 1);
for i = 1:m,
centSum(idx(i, 1), :) = centSum(idx(i, 1), :) + X(i, :);
centNum(idx(i, 1), 1) = centNum(idx(i, 1), 1) + 1;
end
for i = 1:K,
centroids(i, :) = centSum(i, :) ./ centNum(i, 1);
end end
第4步:实现runkMeans函数,完成k-Means聚类:
function [centroids, idx] = runkMeans(X, initial_centroids, ...
max_iters, plot_progress) % Set default value for plot progress
if ~exist('plot_progress', 'var') || isempty(plot_progress)
plot_progress = false;
end % Plot the data if we are plotting progress
if plot_progress
figure;
hold on;
end % Initialize values
[m n] = size(X);
K = size(initial_centroids, 1);
centroids = initial_centroids;
previous_centroids = centroids;
idx = zeros(m, 1); % Run K-Means
for i=1:max_iters % Output progress
fprintf('K-Means iteration %d/%d...\n', i, max_iters);
if exist('OCTAVE_VERSION')
fflush(stdout);
end % For each example in X, assign it to the closest centroid
idx = findClosestCentroids(X, centroids); % Optionally, plot progress here
if plot_progress
plotProgresskMeans(X, centroids, previous_centroids, idx, K, i);
previous_centroids = centroids;
fprintf('Press enter to continue.\n');
pause;
end % Given the memberships, compute new centroids
centroids = computeCentroids(X, idx, K);
end % Hold off if we are plotting progress
if plot_progress
hold off;
end end
第5步:读取数据文件,完成二维数据的聚类:
% Load an example dataset
load('ex7data2.mat'); % Settings for running K-Means
K = 3;
max_iters = 10;
initial_centroids = [3 3; 6 2; 8 5]; % Run K-Means algorithm. The 'true' at the end tells our function to plot
% the progress of K-Means
[centroids, idx] = runkMeans(X, initial_centroids, max_iters, true);
fprintf('\nK-Means Done.\n\n');
运行结果:

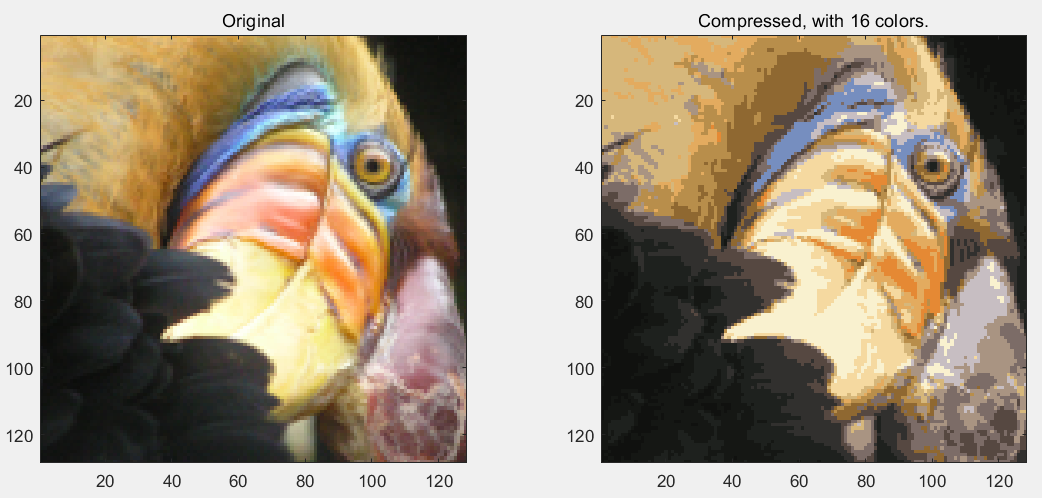
第6步:读取图片文件,完成图片颜色的聚类,转为16种颜色:
% Load an image of a bird
A = double(imread('bird_small.png')); % If imread does not work for you, you can try instead
% load ('bird_small.mat'); A = A / 255; % Divide by 255 so that all values are in the range 0 - 1 % Size of the image
img_size = size(A); % Reshape the image into an Nx3 matrix where N = number of pixels.
% Each row will contain the Red, Green and Blue pixel values
% This gives us our dataset matrix X that we will use K-Means on.
X = reshape(A, img_size(1) * img_size(2), 3); % Run your K-Means algorithm on this data
% You should try different values of K and max_iters here
K = 16;
max_iters = 10; % When using K-Means, it is important the initialize the centroids
% randomly.
% You should complete the code in kMeansInitCentroids.m before proceeding
initial_centroids = kMeansInitCentroids(X, K); % Run K-Means
[centroids, idx] = runkMeans(X, initial_centroids, max_iters); fprintf('Program paused. Press enter to continue.\n');
pause; % Find closest cluster members
idx = findClosestCentroids(X, centroids); % We can now recover the image from the indices (idx) by mapping each pixel
% (specified by its index in idx) to the centroid value
X_recovered = centroids(idx,:); % Reshape the recovered image into proper dimensions
X_recovered = reshape(X_recovered, img_size(1), img_size(2), 3); % Display the original image
subplot(1, 2, 1);
imagesc(A);
title('Original'); % Display compressed image side by side
subplot(1, 2, 2);
imagesc(X_recovered)
title(sprintf('Compressed, with %d colors.', K));
运行结果:
第2题
简述:使用PCA算法,完成维度约减,并应用到图像处理和数据显示上。
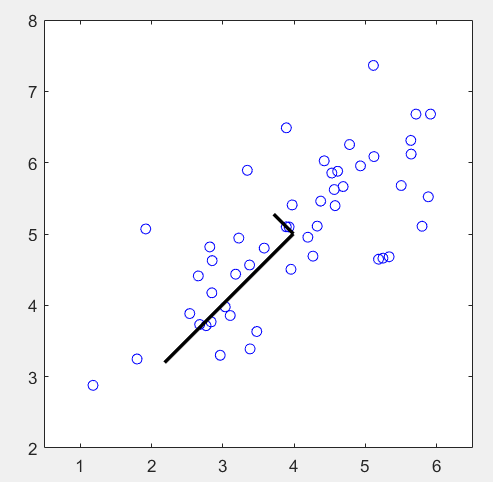
第1步:读取数据文件,并可视化:
% The following command loads the dataset. You should now have the
% variable X in your environment
load ('ex7data1.mat'); % Visualize the example dataset
plot(X(:, 1), X(:, 2), 'bo');
axis([0.5 6.5 2 8]); axis square;
第2步:对数据进行归一化,计算协方差矩阵Sigma,并求其特征向量:
% Before running PCA, it is important to first normalize X
[X_norm, mu, sigma] = featureNormalize(X); % Run PCA
[U, S] = pca(X_norm); % Compute mu, the mean of the each feature % Draw the eigenvectors centered at mean of data. These lines show the
% directions of maximum variations in the dataset.
hold on;
drawLine(mu, mu + 1.5 * S(1,1) * U(:,1)', '-k', 'LineWidth', 2);
drawLine(mu, mu + 1.5 * S(2,2) * U(:,2)', '-k', 'LineWidth', 2);
hold off;
其中featureNormalize函数:
function [X_norm, mu, sigma] = featureNormalize(X) mu = mean(X);
X_norm = bsxfun(@minus, X, mu); sigma = std(X_norm);
X_norm = bsxfun(@rdivide, X_norm, sigma); end
其中pca函数:
function [U, S] = pca(X) % Useful values
[m, n] = size(X); % You need to return the following variables correctly.
U = zeros(n);
S = zeros(n); Sigma = 1 / m * (X' * X);
[U, S, V] = svd(Sigma); end
运行结果:
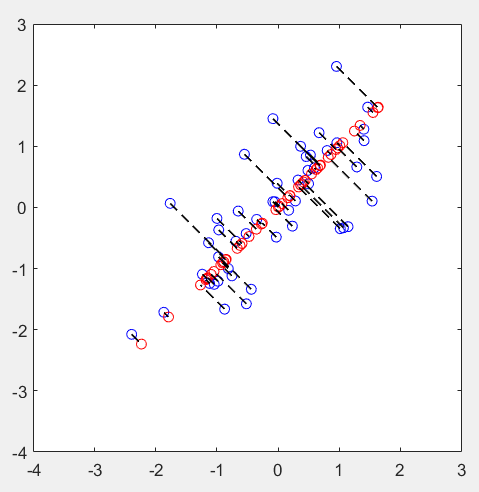
第3步:实现维度约减,并还原:
% Plot the normalized dataset (returned from pca)
plot(X_norm(:, 1), X_norm(:, 2), 'bo');
axis([-4 3 -4 3]); axis square % Project the data onto K = 1 dimension
K = 1;
Z = projectData(X_norm, U, K); X_rec = recoverData(Z, U, K); % Draw lines connecting the projected points to the original points
hold on;
plot(X_rec(:, 1), X_rec(:, 2), 'ro');
for i = 1:size(X_norm, 1)
drawLine(X_norm(i,:), X_rec(i,:), '--k', 'LineWidth', 1);
end
hold off
其中projectData函数:
function Z = projectData(X, U, K) % You need to return the following variables correctly.
Z = zeros(size(X, 1), K); Ureduce = U(:, 1:K);
Z = X * Ureduce; end
其中recoverData函数:
function X_rec = recoverData(Z, U, K) X_rec = zeros(size(Z, 1), size(U, 1)); Ureduce = U(:, 1:K);
X_rec = Z * Ureduce'; end
运行结果:
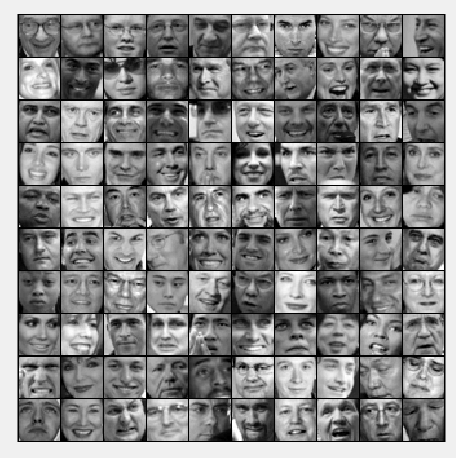
第4步:加载人脸数据,并可视化:
% Load Face dataset
load ('ex7faces.mat') % Display the first 100 faces in the dataset
displayData(X(1:100, :));
运行结果:

第5步:计算协方差矩阵的特征向量,并可视化:
% Before running PCA, it is important to first normalize X by subtracting
% the mean value from each feature
[X_norm, mu, sigma] = featureNormalize(X); % Run PCA
[U, S] = pca(X_norm); % Visualize the top 36 eigenvectors found
displayData(U(:, 1:36)');
运行结果:

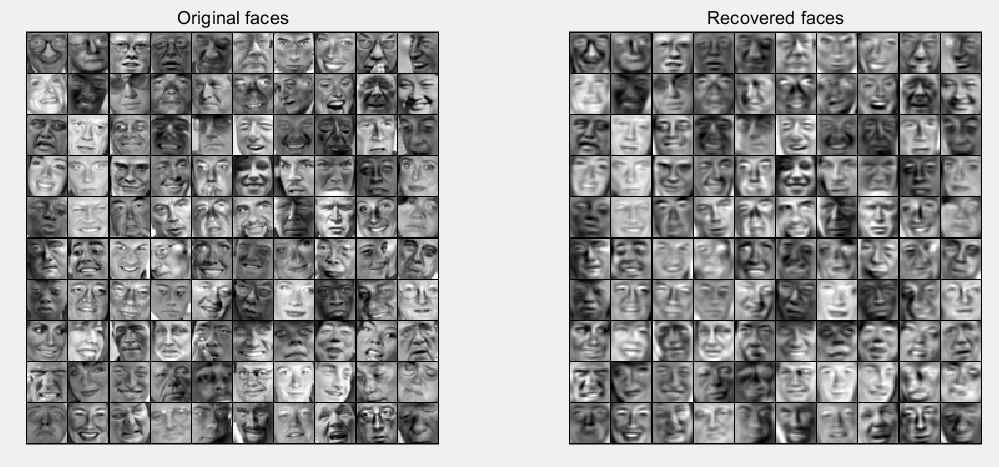
第6步:实现维度约减和复原:
K = 100;
Z = projectData(X_norm, U, K);
X_rec = recoverData(Z, U, K); % Display normalized data
subplot(1, 2, 1);
displayData(X_norm(1:100,:));
title('Original faces');
axis square; % Display reconstructed data from only k eigenfaces
subplot(1, 2, 2);
displayData(X_rec(1:100,:));
title('Recovered faces');
axis square;
运行结果:

第7步:对图片的3维数据进行聚类,并随机挑选1000个点可视化:
% Reload the image from the previous exercise and run K-Means on it
% For this to work, you need to complete the K-Means assignment first
A = double(imread('bird_small.png')); A = A / 255;
img_size = size(A);
X = reshape(A, img_size(1) * img_size(2), 3);
K = 16;
max_iters = 10;
initial_centroids = kMeansInitCentroids(X, K);
[centroids, idx] = runkMeans(X, initial_centroids, max_iters); % Sample 1000 random indexes (since working with all the data is
% too expensive. If you have a fast computer, you may increase this.
sel = floor(rand(1000, 1) * size(X, 1)) + 1; % Setup Color Palette
palette = hsv(K);
colors = palette(idx(sel), :); % Visualize the data and centroid memberships in 3D
figure;
scatter3(X(sel, 1), X(sel, 2), X(sel, 3), 10, colors);
title('Pixel dataset plotted in 3D. Color shows centroid memberships');
运行结果:

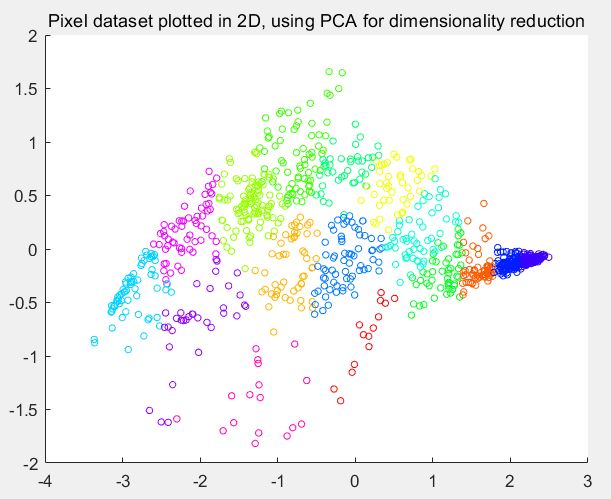
第8步:将数据降为2维:
% Subtract the mean to use PCA
[X_norm, mu, sigma] = featureNormalize(X); % PCA and project the data to 2D
[U, S] = pca(X_norm);
Z = projectData(X_norm, U, 2); % Plot in 2D
figure;
plotDataPoints(Z(sel, :), idx(sel), K);
title('Pixel dataset plotted in 2D, using PCA for dimensionality reduction');
运行结果:
机器学习作业(七)非监督学习——Matlab实现的更多相关文章
- Machine Learning——Unsupervised Learning(机器学习之非监督学习)
前面,我们提到了监督学习,在机器学习中,与之对应的是非监督学习.无监督学习的问题是,在未加标签的数据中,试图找到隐藏的结构.因为提供给学习者的实例是未标记的,因此没有错误或报酬信号来评估潜在的解决方案 ...
- Standford机器学习 聚类算法(clustering)和非监督学习(unsupervised Learning)
聚类算法是一类非监督学习算法,在有监督学习中,学习的目标是要在两类样本中找出他们的分界,训练数据是给定标签的,要么属于正类要么属于负类.而非监督学习,它的目的是在一个没有标签的数据集中找出这个数据集的 ...
- 5.1_非监督学习之sckit-learn
非监督学习之k-means K-means通常被称为劳埃德算法,这在数据聚类中是最经典的,也是相对容易理解的模型.算法执行的过程分为4个阶段. 1.首先,随机设K个特征空间内的点作为初始的聚类中心. ...
- 如何区分监督学习(supervised learning)和非监督学习(unsupervised learning)
监督学习:简单来说就是给定一定的训练样本(这里一定要注意,样本是既有数据,也有数据对应的结果),利用这个样本进行训练得到一个模型(可以说是一个函数),然后利用这个模型,将所有的输入映射为相应的输出,之 ...
- keras03 Aotuencoder 非监督学习 第一个自编码程序
# keras# Autoencoder 自编码非监督学习# keras的函数Model结构 (非序列化Sequential)# 训练模型# mnist数据集# 聚类 https://www.bili ...
- 【学习笔记】非监督学习-k-means
目录 k-means k-means API k-means对Instacart Market用户聚类 Kmeans性能评估指标 Kmeans性能评估指标API Kmeans总结 无监督学习,顾名思义 ...
- 作业七:Linux内核如何装载和启动一个可执行程序
作业七:Linux内核如何装载和启动一个可执行程序 一.编译链接的过程和ELF可执行文件格式 可执行文件的创建——预处理.编译和链接 在object文件中有三种主要的类型. 一个可重定位(reloca ...
- Deep Learning论文笔记之(三)单层非监督学习网络分析
Deep Learning论文笔记之(三)单层非监督学习网络分析 zouxy09@qq.com http://blog.csdn.net/zouxy09 自己平时看了一些论文,但老感 ...
- (转载)[机器学习] Coursera ML笔记 - 监督学习(Supervised Learning) - Representation
[机器学习] Coursera ML笔记 - 监督学习(Supervised Learning) - Representation http://blog.csdn.net/walilk/articl ...
随机推荐
- Linux下使用Nginx
模拟tomcat集群 1.下载tomcat7,/usr/local下新建目录tomcat,将tomcat7剪切到/usr/local/tomcat wget http://mirror.bit.edu ...
- Javascript 基础学习(六)js 的对象
定义 对象是JS中的引用数据类型.对象是一种复合数据类型,在对象中可以保存多个不同数据类型的属性.使用typeof检查一个对象时,会返回object. 分类 内置对象 由ES标准定义的对象,在任何ES ...
- 字节码操作、javassist使用
一.功能 1.动态生成新的类 2.动态改变某个类的结构(添加.删除.修改 新的属性.方法) 二.优势 1.比反射开销小,性能高 2.JAVAasist性能高于反射,低于ASM 使用javassis ...
- 反射机制(reflection)
一.反射: 1.反射指可以在运行时加载.探知.使用编译期间完全未知的类. 2.程序在运行状态中,可以动态加载一个只有名称的类,对于任意一个已加载的类,都能够知道这个类的所有属性和方法: 对于任意一个对 ...
- Lucene之分析器
什么是分析器? 分析(Analysis)在Lucene中指的是将域(Field)文本转换为最基本的索引表示单元—项(Term)的过程. 分析器(Analyzer)对分析操作进行了封装,通过执行一系列操 ...
- 极具性价比优势的工业控制以及物联网解决方案-米尔MYD-C8MMX开发板测评
今天要进行测评的板子是来自米尔电子的MYD-C8MMX开发板.MYD-C8MMX开发板是米尔电子基于恩智浦,i.MX 8M Mini系列嵌入式应用处理器设计的开发套件,具有超强性能.工业级应用.10年 ...
- 建造者模式(Builder)——从组装电脑开始
建造者模式(Builder)--从组装电脑开始 建造者模式概括起来就是将不同独立的组件按照一定的条件组合起来构成一个相对业务完整的对象.调用者无需知道构造的过程. 我们从组装电脑开始 让我们从买组装电 ...
- node post 大数据无响应超时
使用 express 框架,post 较大数据量(富文本,里面包含了图片base64数据,大约300k)时,node 无响应,把数据内容减少后能顺利提交. 是因为数据量大过body post 的限制导 ...
- 删除Win10菜单中的幽灵菜单(ms-resource:AppName/Text )
新建一个 .bat文件,输入以下内容 @echo off taskkill /f /im explorer.exe taskkill /f /im shellexperiencehost.exe ti ...
- H5_0022:判断平台和微信及弹出推广提示
1,原文 <script> var t = document.createElement("div"); t.style.cssText="position: ...
