Linux文件系统2---VFS的四个主要对象
1.引言
本文所述关于文件管理的系列文章主要是对陈莉君老师所讲述的文件系统管理知识讲座的整理。
Linux可以支持不同的文件系统,它源于unix文件系统,也是unix文件系统的一大特色。
Linux文件系统1--概述 中我们了解了文件系统的作用,以及为了使得所有的文件系统能在同一个操作系统上工作,而产生的虚拟文件系统。
本章我们开始分析万能的虚拟文件系统是怎么构成的,虚拟文件文件系统由四个主要的对象构成,分别是:超级块,索引结点,目录项,文件对象。
而所谓的文件系统主要是对文件对象进行管理,那么,其余的三个结构体是用来做什么的呢?
想一下,如果,你要查一份文件,必须要核对文件对象,那么文件对象越大,CPU则会浪费很多时间在核对上。
所以,我们给文件对象学着外国人一样, 起了三层结构的名字,目录项--索引结点--超级块,是不是很有趣。
2.文件系统的四个主要对象概述
- 超级块对象
存放系统中已安装文件系统的信息
- 索引节点对象
存放关于具体文件的一般信息
- 目录项对象
存放目录项与对应文件进行链接的信息
- 文件对象
存放打开文件与进程之间进行交互的有关信息
3. 超级块super_block
3.1 struct super_block
struct super_block {
struct list_head s_list; /* Keep this first 指向超级块链表的指针*/
dev_t s_dev; /* search index; _not_ kdev_t 具体文件系统的块设备描述符*/
unsigned char s_blocksize_bits;
unsigned long s_blocksize; /*以字节为单位的数据块的大小*/
loff_t s_maxbytes; /* Max file size */
struct file_system_type *s_type; /*文件系统类型*/
const struct super_operations *s_op; /*指向超级块操作的函数集合*/
const struct dquot_operations *dq_op;
const struct quotactl_ops *s_qcop;
const struct export_operations *s_export_op;
unsigned long s_flags;
unsigned long s_iflags; /* internal SB_I_* flags */
unsigned long s_magic;
struct dentry *s_root;
struct rw_semaphore s_umount;
int s_count;
atomic_t s_active;
#ifdef CONFIG_SECURITY
void *s_security;
#endif
const struct xattr_handler **s_xattr;
struct hlist_bl_head s_anon; /* anonymous dentries for (nfs) exporting */
struct list_head s_mounts; /* list of mounts; _not_ for fs use */
struct block_device *s_bdev;
struct backing_dev_info *s_bdi;
struct mtd_info *s_mtd;
struct hlist_node s_instances;
unsigned int s_quota_types; /* Bitmask of supported quota types */
struct quota_info s_dquot; /* Diskquota specific options */
struct sb_writers s_writers;
char s_id[]; /* Informational name */
u8 s_uuid[]; /* UUID */
void *s_fs_info; /* Filesystem private info 具体文件系统的私有数据*/
unsigned int s_max_links;
fmode_t s_mode;
/* Granularity of c/m/atime in ns.
Cannot be worse than a second */
u32 s_time_gran;
/*
* The next field is for VFS *only*. No filesystems have any business
* even looking at it. You had been warned.
*/
struct mutex s_vfs_rename_mutex; /* Kludge */
/*
* Filesystem subtype. If non-empty the filesystem type field
* in /proc/mounts will be "type.subtype"
*/
char *s_subtype;
/*
* Saved mount options for lazy filesystems using
* generic_show_options()
*/
char __rcu *s_options;
const struct dentry_operations *s_d_op; /* default d_op for dentries */
/*
* Saved pool identifier for cleancache (-1 means none)
*/
int cleancache_poolid;
struct shrinker s_shrink; /* per-sb shrinker handle */
/* Number of inodes with nlink == 0 but still referenced */
atomic_long_t s_remove_count;
/* Being remounted read-only */
int s_readonly_remount;
/* AIO completions deferred from interrupt context */
struct workqueue_struct *s_dio_done_wq;
struct hlist_head s_pins;
/*
* Keep the lru lists last in the structure so they always sit on their
* own individual cachelines.
*/
struct list_lru s_dentry_lru ____cacheline_aligned_in_smp;
struct list_lru s_inode_lru ____cacheline_aligned_in_smp;
struct rcu_head rcu;
struct work_struct destroy_work;
struct mutex s_sync_lock; /* sync serialisation lock */
/*
* Indicates how deep in a filesystem stack this SB is
*/
int s_stack_depth;
/* s_inode_list_lock protects s_inodes */
spinlock_t s_inode_list_lock ____cacheline_aligned_in_smp;
struct list_head s_inodes; /* all inodes 所有的inodes*/
};
- 超级块用来描述整个文件系统的信息
- 每个具体的文件系统都有自己的超级块
- VFS超级块是各种文件系统在安装时建立的,并在卸载时被自动删除,其数据结构是super_block
- 所有超级块对象都以双向循环链表的形式链接在一起
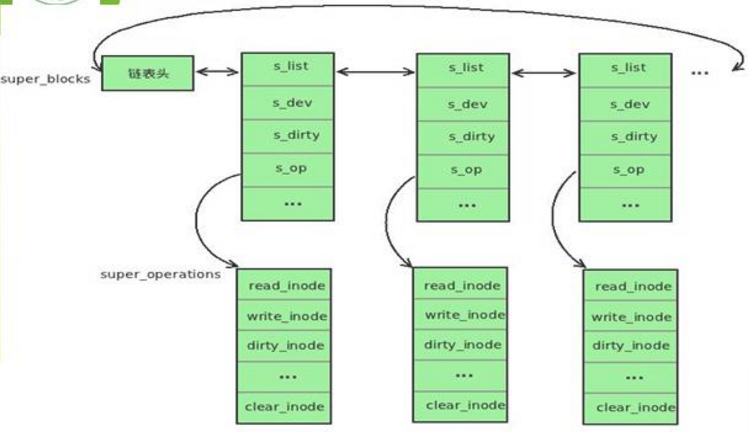
图 所有超级块链接在一起
3.2 struct super_operations

图 超级块对象的操作函数
- 与超级块关联的方法就是超级块操作表,这些操作是由struct super_operations来描述
3.3 打印超级块信息
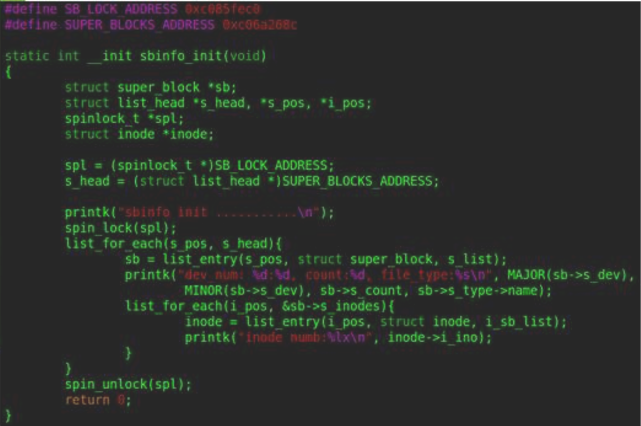
4.索引节点inode
4.1 struct inode
struct inode {
umode_t i_mode;
unsigned short i_opflags;
kuid_t i_uid;
kgid_t i_gid;
unsigned int i_flags;
#ifdef CONFIG_FS_POSIX_ACL
struct posix_acl *i_acl;
struct posix_acl *i_default_acl;
#endif
const struct inode_operations *i_op;
struct super_block *i_sb;
struct address_space *i_mapping;
#ifdef CONFIG_SECURITY
void *i_security;
#endif
/* Stat data, not accessed from path walking */
unsigned long i_ino;
/*
* Filesystems may only read i_nlink directly. They shall use the
* following functions for modification:
*
* (set|clear|inc|drop)_nlink
* inode_(inc|dec)_link_count
*/
union {
const unsigned int i_nlink;
unsigned int __i_nlink;
};
dev_t i_rdev;
loff_t i_size;
struct timespec i_atime;
struct timespec i_mtime;
struct timespec i_ctime;
spinlock_t i_lock; /* i_blocks, i_bytes, maybe i_size */
unsigned short i_bytes;
unsigned int i_blkbits;
blkcnt_t i_blocks;
#ifdef __NEED_I_SIZE_ORDERED
seqcount_t i_size_seqcount;
#endif
/* Misc */
unsigned long i_state; /*索引节点的状态标志*/
struct mutex i_mutex;
unsigned long dirtied_when; /* jiffies of first dirtying */
unsigned long dirtied_time_when;
struct hlist_node i_hash; /*指向哈希链表的指针*/
struct list_head i_io_list; /* backing dev IO list */
#ifdef CONFIG_CGROUP_WRITEBACK
struct bdi_writeback *i_wb; /* the associated cgroup wb */
/* foreign inode detection, see wbc_detach_inode() */
int i_wb_frn_winner;
u16 i_wb_frn_avg_time;
u16 i_wb_frn_history;
#endif
struct list_head i_lru; /* inode LRU list 指向索引节点链表的指针*/
struct list_head i_sb_list; /*指向超级块的指针*/
union {
struct hlist_head i_dentry;
struct rcu_head i_rcu;
};
u64 i_version;
atomic_t i_count;
atomic_t i_dio_count;
atomic_t i_writecount;
#ifdef CONFIG_IMA
atomic_t i_readcount; /* struct files open RO */
#endif
const struct file_operations *i_fop; /* former ->i_op->default_file_ops */
struct file_lock_context *i_flctx;
struct address_space i_data;
struct list_head i_devices;
union {
struct pipe_inode_info *i_pipe;
struct block_device *i_bdev;
struct cdev *i_cdev;
char *i_link;
};
__u32 i_generation;
#ifdef CONFIG_FSNOTIFY
__u32 i_fsnotify_mask; /* all events this inode cares about */
struct hlist_head i_fsnotify_marks;
#endif
void *i_private; /* fs or device private pointer */
};
- 文件系统处理文件所需要的所有信息都保存在称为索引节点的inode结构体中
- 同一个文件系统中,每个文件的索引节点号都是唯一的
- 与索引节点关联的方法由struct inode_operations来描述
- inode有两个设备号:i_dev(常规文件的设备号),i_rdev(某一设备的设备号)
- LInux文件系统的另外一大特色:设备即文件。驱动中设备号的来源
4.2 struct inode_operations

图 索引节点的操作函数
5.目录项dentry
5.1 struct dentry
struct dentry {
/* RCU lookup touched fields */
unsigned int d_flags; /* protected by d_lock */
seqcount_t d_seq; /* per dentry seqlock */
struct hlist_bl_node d_hash; /* lookup hash list */
struct dentry *d_parent; /* parent directory */
struct qstr d_name;
struct inode *d_inode; /* Where the name belongs to - NULL is
92 * negative */
unsigned char d_iname[DNAME_INLINE_LEN]; /* small names */
/* Ref lookup also touches following */
struct lockref d_lockref; /* per-dentry lock and refcount */
const struct dentry_operations *d_op;
struct super_block *d_sb; /* The root of the dentry tree */
unsigned long d_time; /* used by d_revalidate */
void *d_fsdata; /* fs-specific data */
union {
struct list_head d_lru; /* LRU list */
wait_queue_head_t *d_wait; /* in-lookup ones only */
};
struct list_head d_child; /* child of parent list */
struct list_head d_subdirs; /* our children */
/*
109 * d_alias and d_rcu can share memory
110 */
union {
struct hlist_node d_alias; /* inode alias list */
struct hlist_bl_node d_in_lookup_hash; /* only for in-lookup ones */
struct rcu_head d_rcu;
} d_u;
};
- 每个文件除了一个struct inode结构体外,还要一个目录项struct dentry结构
- dentry代表的逻辑意义上的文件,描述的是文件逻辑上的属性,目录项对象在磁盘上并没有对应的映像
- inode代表的是物理意义上的文件,记录的是物理上的属性,对于一个具体的文件系统,其inode在磁盘上有对应的映像
- 一个索引节点可能对应多个目录项对象
5.2 struct dentry_operations

图 目录项的操作函数
6. 文件对象(file)

6.1 struct file
struct file {
union {
struct llist_node fu_llist;//文件对象链表
struct rcu_head fu_rcuhead; //释放之后的RCU链表
} f_u;
struct path f_path;
struct inode *f_inode; /* cached value */
const struct file_operations *f_op;
/*
845 * Protects f_ep_links, f_flags.
846 * Must not be taken from IRQ context.
847 */
spinlock_t f_lock;
atomic_long_t f_count; //文件对象的使用计数
unsigned int f_flags; //当打开文件时所使用的标志
fmode_t f_mode; //文件的访问模式
struct mutex f_pos_lock;
loff_t f_pos; //文件当前的位移量
struct fown_struct f_owner; //拥有者通过信号量进行异步I/O传输
const struct cred *f_cred;
struct file_ra_state f_ra;
u64 f_version;
#ifdef CONFIG_SECURITY
void *f_security; //安全模块
#endif
/* needed for tty driver, and maybe others */
void *private_data; //tty 设备驱动的钩子
#ifdef CONFIG_EPOLL
/* Used by fs/eventpoll.c to link all the hooks to this file */
struct list_head f_ep_links; //事件池锁
struct list_head f_tfile_llink;
#endif /* #ifdef CONFIG_EPOLL */
struct address_space *f_mapping; //页缓存映射
} __attribute__((aligned())); /* lest something weird decides that 2 is OK */
- 进程通过文件描述符来访问文件
- LInux用一个file文件对象来保存打开文件的位置,这个对象称为打开的文件描述符
- file结构主要保存了文件位置,还把指向文件索引节点的指针也放在其中
- file结构形成一个双链表,称为系统打开文件表
6.2 struct file_operations
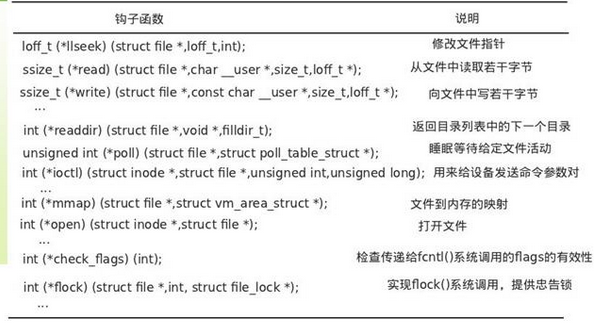
6.3 struct files_struct

- 文件描述符用来描述打开的文件
- 每个进程用一个files_struct结构来记录文件描述符的使用情况
- 这个files_stuct结构称为用户打开文件表,它是进程的私有数据
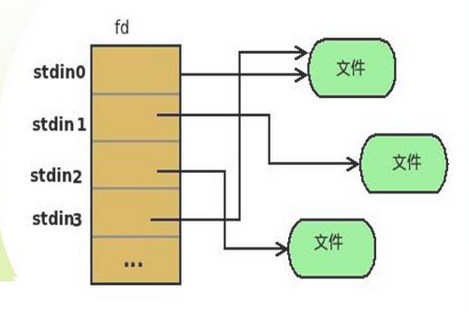
图 用户打开文件表
6.4 struct fs_struct
struct fs_struct {
int users;
spinlock_t lock;
seqcount_t seq;
int umask; //用于为新创建的文件设置初始文件许可权限
int in_exec;
struct path root, pwd;
};
- 描述进程与文件系统的关系
7. 主要数据结构之间的关系
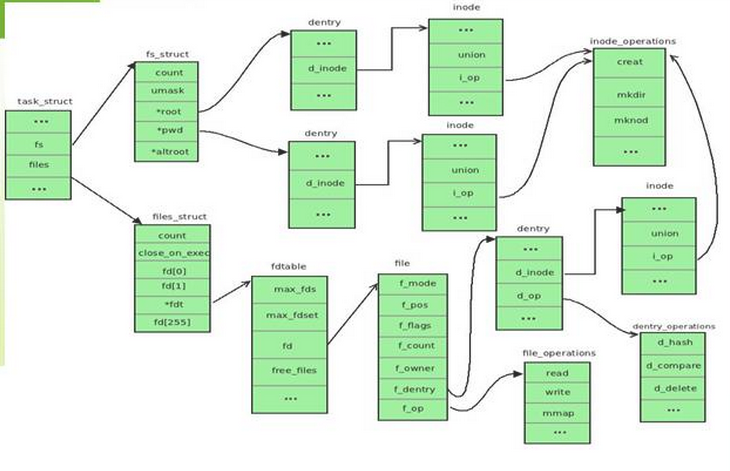
图 主要数据结构之间的关系
- 超级块是对一个文件系统的描述
- 索引节点是对一个文件物理属性的描述
- 目录项是对一个文件逻辑属性的描述
- 一个进程所处的位置由fs_struct描述
- 一个进程(或用户)打开的文件由files_struct描述
- 整个系统所打开的文件由 file结构来描述
Linux文件系统2---VFS的四个主要对象的更多相关文章
- linux文件系统软链接硬链接
引子 目前,UNIX的文件系统有很多种实现,例如UFS(基于BSD的UNIX文件系统).ext3.ext4.ZFS和Reiserfs等等. 不论哪一种文件系统,总是需要存储数据.硬盘的最小存储单位是扇 ...
- Linux文件系统的目录结构
Linux下的文件系统为树形结构,入口为/ 树形结构下的文件目录: 无论哪个版本的Linux系统,都有这些目录,这些目录应该是标准的.各个Linux发行版本会存在一些小小的差异,但总体来说,还是大体差 ...
- Linux 文件系统的目录结构
http://www.jb51.net/LINUXjishu/151820.htmlLinux下的文件系统为树形结构,入口为/ 树形结构下的文件目录: 无论哪个版本的Linux系统,都有这些目录,这些 ...
- 解析Linux中的VFS文件系统机制
转载:原文地址https://www.ibm.com/developerworks/cn/linux/l-vfs/ 1. 摘要 本文阐述 Linux 中的文件系统部分,源代码来自基于 IA32 的 2 ...
- linux文件系统体系结构 和 虚拟文件系统(VFS)
图 1. Linux 文件系统组件的体系结构 用户空间包含一些应用程序(例如,文件系统的使用者)和 GNU C 库(glibc),它们为文件系统调用(打开.读取.写和关闭)提供用户接口.系统调用接口的 ...
- Linux高级运维 第四章 文件的基本管理和XFS文件系统备份恢复
4.1 Linux系统目录结构和相对/绝对路径 4.1.1系统目录结构 在windows系统中,查看文件先进入相应的盘符,然后进入文件目录 在windows中,它是多根 c:\ d:\ e ...
- 学习笔记:CentOS7学习之十四:linux文件系统
目录 1. 机械硬盘结构 1.1 机械硬盘结构 1.2 簇和block 2.文件系统结构 2.1 文件名 2.2 inode的内容 2.3 inode的大小 2.4 目录文件 2.5 block块大小 ...
- 磁盘、分区及Linux文件系统 [Disk, Partition, Linux File System]
1.磁盘基础知识 1.1 物理结构 硬盘的物理结构一般由磁头与碟片.电动机.主控芯片与排线等部件组成:当主电动机带动碟片旋转时,副电动机带动一组(磁头)到相对应的碟片上并确定读取正面还是反面的碟面,磁 ...
- 24小时学通Linux内核之有关Linux文件系统实现的问题
有时间睡懒觉了,却还是五点多醒了,不过一直躺倒九点多才算起来,昨晚一直在弄飞凌的嵌入式开发板,有些问题没解决,自己电脑系统的问题,虽然Win10发布了,,但我还是好喜欢XP呀,好想回家用用家里的XP来 ...
随机推荐
- 21 Zabbix系统性能优化建议
点击返回:自学Zabbix之路 点击返回:自学Zabbix4.0之路 点击返回:自学zabbix集锦 21 Zabbix系统性能优化建议 1. Zabbix性能变慢的可能表现: zabbix队列有太多 ...
- android-support-v4.jar 免积分下载
资源名称:android扩展插件 android-support-v4.jar 资源大小:137KB 上传日期:2012-10-08 资源积分:1 下载次数:136 电信下载地址:http://www ...
- luogu4197 Peaks (kruskal重构树+主席树)
按照边权排序建出kruskal重构树,每次就变成了先找一个权值<=x的最远的祖先,然后看这个子树的第k小.离散化一下,在dfs序上做主席树即可 而且只需要建叶节点的主席树 注意输出的是第k小点的 ...
- tesseract-ocr 识别中文扫描图片
原文链接:http://www.cnblogs.com/alex-blog/articles/2714984.html 项目主页地址:http://code.google.com/p/tesser ...
- A1075. PAT Judge
The ranklist of PAT is generated from the status list, which shows the scores of the submittions. Th ...
- 解决React首屏加载白屏的问题
众所周知,在项目中如果在资源加载请求还未完成的时候,由于阻塞机制,会出现首页白屏的问题,产生很差的用户体验.本文以react为例,提供一个解决方法. 解决原理:使用 onreadystatechang ...
- malloc创建三维数组
#include <stdio.h> #include <stdlib.h> #include <malloc.h> int main() { //f[0],f[] ...
- mysql -- 逻辑语句
1.if语句 delimiter \\ create procedure p1() begin declare i ; then ; elseif i = then ; else ; end if; ...
- JS 中函数名后面加与不加括号的区别
a.onmouseover = fn1; a.onmouseout = fn2; function fn1(){ div.className = "erweima show"; } ...
- iPhone电源键坏了怎么开机和关机?
一.开机 1.将USB数据线插到iPhone上,此时先不要将另一头插到电脑上 2.长按Home键不要动 3.将数据线的另一头插到电脑上 这时iPhone就会自动开机 二.关机 1.进入设置找到“通用” ...
