[Python] 02 - String
字符串 string
考点
Bytes类型
In Python 3, bytes contains sequences of 8-bit values, str contains sequences of
Unicode characters. bytes and str instances can’t be used together with operators
(like > or +).
在Python3以后,字符串和bytes类型彻底分开了。字符串是以字符为单位进行处理的,bytes类型是以字节为单位处理的。
创建、与字符串的相互转化如下:
# (1)
b = b'' # 创建一个空的bytes
b = byte() # 创建一个空的bytes # (2)
b = b'hello' # 直接指定这个hello是bytes类型 # (3)
b = bytes('string',encoding='编码类型') #利用内置bytes方法,将字符串转换为指定编码的bytes
b = str.encode('编码类型') # 利用字符串的encode方法编码成bytes,默认为utf-8类型 bytes.decode('编码类型'):将bytes对象解码成字符串,默认使用utf-8进行解码。
基本性质和功能
不变性 Immutability
如果相变的话:string --> list --> string
string属性查看
>>> print(string.ascii_letters)
abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyzABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ
>>> print(string.ascii_lowercase)
abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyz
>>> print(string.ascii_uppercase)
ABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ
>>> print(string.hexdigits)
0123456789abcdefABCDEF
>>> print(string.digits)
0123456789
>>> print(string.octdigits)
01234567
>>> print(string.punctuation)
!"#$%&'()*+,-./:;<=>?@[\]^_`{|}~ >>> print(string.printable[: 94])
0123456789abcdefghijklmnopqrstuvwxyzABCDEFGHIJKLMNOPQRSTUVWXYZ!"#$%&'()*+,-./:;<=>?@[\]^_`{|}~
>>> print(ascii(string.printable[94: ]))
' \t\n\r\x0b\x0c'
>>> print(ascii(string.whitespace))
' \t\n\r\x0b\x0c
基础功能函数
基础功能
S = 'Spam"
S.find('pa')
S.replace('pa', 'XYZ')
S.isalpha(),
S.isdigit()
In [5]: dir(S)
Out[5]: ['__add__',
'__class__',
'__contains__',
'__delattr__',
'__dir__',
'__doc__',
'__eq__',
'__format__',
'__ge__',
'__getattribute__',
'__getitem__',
'__getnewargs__',
'__gt__',
'__hash__',
'__init__',
'__iter__',
'__le__',
'__len__',
'__lt__',
'__mod__',
'__mul__',
'__ne__',
'__new__',
'__reduce__',
'__reduce_ex__',
'__repr__',
'__rmod__',
'__rmul__',
'__setattr__',
'__sizeof__',
'__str__',
'__subclasshook__',
'capitalize',
'casefold',
'center',
'count',
'encode',
'endswith',
'expandtabs',
'find',
'format',
'format_map',
'index',
'isalnum',
'isalpha',
'isdecimal',
'isdigit',
'isidentifier',
'islower',
'isnumeric',
'isprintable',
'isspace',
'istitle',
'isupper',
'join',
'ljust',
'lower',
'lstrip',
'maketrans',
'partition',
'replace',
'rfind',
'rindex',
'rjust',
'rpartition',
'rsplit',
'rstrip',
'split',
'splitlines',
'startswith',
'strip',
'swapcase',
'title',
'translate',
'upper',
'zfill']
dir(S)
查看说明:
help(S.replace)
split 分割的应用
去掉前后空格
先去掉前后空格,再分割的过程。
>>> s.strip().split(',')
['hello', ' world', ' hao', '', '123']
string自带的分割
提取括号中的内容,如下。
str="hello boy<[www.baidu.com]>byebye"
print(str.split("[")[1].split("]")[0])
www.baidu.com
sys自带的分割
os.path.split() 函数
import os
print(os.path.split('/dodo/soft/python/')) # path + filename
('/dodo/soft/python', '')
print(os.path.split('/dodo/soft/python'))
('/dodo/soft', 'python')
文件后缀分割
filepath, tmpfilename = os.path.split(fileUrl)
shotname, extension = os.path.splitext(tmpfilename)
The os module contains two sub-modules os.sys (same as sys) and os.path that are dedicated to the system and directories; respectively.
import os
import os.sys
import os.path
读取输入
按行读取
逐行读取一行字符串
with open('somefile', 'r') as f:
for line in f:
print(line, end='')
"""
Hello
World
Python
"""
一次性全部读取到列表
with open('somefile','r') as f:
content = list(f)
print(content)
"""
['Hello\n', 'World\n', 'Python']
"""
以上的 list(f) 便是默认的readlines();
with open('somefile','r') as f:
content = f.readlines()
print(content)
"""
['Hello\n', 'World\n', 'Python']
"""
自动去掉”换行符“
with open('somefile','r') as f:
content = f.read().splitlines()
print(content)
"""
['Hello', 'World', 'Python']
"""
或者,自己手动使用 rstrip() 去掉结尾的“换行符号”;去掉行首就换为 strip();
with open('somefile','r') as f:
content = [line.rstrip('\n') for line in f]
print(content)
"""
['Hello', 'World', 'Python']
"""
enumerate 遍历
列表的遍历方法
>>>seq = ['one', 'two', 'three']
>>> for i, element in enumerate(seq):
... print i, element
0 one
1 two
2 three
遍历 sys.stdout
with open('somefile', 'r') as f:
for number, line in enumerate(f,start=1):
print(number, line, end='')
"""
1 Hello
2 World
3 Python
"""
打印输出
外部设置:sys.stdout 方法
() 定好方向 --> () 然后输出
将“输出口”打印
>>> import sys # Printing the hard way
>>> sys.stdout.write('hello world\n') // 默认打印到屏幕
hello world
指定“输出口”的字符串来源
C:\code> c:\python33\python
>>> import sys
>>> temp = sys.stdout # Save for restoring later
>>> sys.stdout = open('log.txt', 'a') # Redirect prints to a file
>>> print('spam') # Prints go to file, not here
>>> print(1, 2, 3)
>>> sys.stdout.close() # Flush output to disk >>> sys.stdout = temp # Restore original stream
>>> print('back here') # Prints show up here again
back here
>>> print(open('log.txt').read()) # Result of earlier prints
spam
1 2 3
内部设置:print(file=log) 方法【推荐】
log = open('log.txt', 'a') # 3.X
print(x, y, z, file=log) # Print to a file-like object
print(a, b, c) # Print to original stdout
# 老版本
log = open('log.txt', 'a') # 2.X
print >> log, x, y, z # Print to a file-like object
print a, b, c # Print to original stdout
日志显示和保存都兼顾,怎么办?
暂时写个函数,包含两种打印好了。
from __future__ import print_function
打印函数
若干种打印格式
(1) C语言格式;(2) index方式;(3) auto index方式;(4) dict方式;
第1~3种方式

第4种方式
# Dictionary-Based Formatting Expressions
>>> '%(qty)d more %(food)s' % {'qty': 1, 'food': 'spam'}
'1 more spam'
String Formatting Expressions --> 具体参见:268/1594
‘数字’ 打印 美观化
(a) 小数保留几位
(b) 数字占用宽度

(c) 位置的小技巧
print('%2d-%02d' % (3, 1))
3-01
其他技巧
- ASCII查看
len(S)
ord('\n') # 查看 ASCII
chr() # 查看 对应的char
- \0: a binary zero byte

- 多行打印
>>> msg = """
aaaaaaaaaaaaa
bbb'''bbbbbbbbbb""bbbbbbb'bbbb
cccccccccccccc
"""
>>> msg
'\naaaaaaaaaaaaa\nbbb\'\'\'bbbbbbbbbb""bbbbbbb\'bbbb\ncccccccccccccc\n'
- Raw print
In [40]: r"C:\new\test.spm"
Out[40]: 'C:\\new\\test.spm'
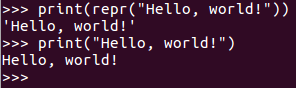
- str vs repr
From: http://blog.csdn.net/u013961718/article/details/51100464
- str出来的值是给人看的字符串,
- repr出来的值是给机器看的,括号中的任何内容出来后都是在它之上再加上一层引号。
日志函数
可以理解为更高级的打印方式,毕竟应用于项目中。
日志级别
五种日志类型
Ref: python logging 替代print 输出内容到控制台和重定向到文件
logging.DEBUG
logging.INFO
logging.WARNING
logging.ERROR
logging.CRITICAL
设置日志输出配置
import logging logging.basicConfig(level = logging.DEBUG,
format = '%(asctime)s %(filename)s[line:%(lineno)d] %(levelname)s %(message)s',
datefmt = '%a, %d %b %Y %H:%M:%S',
filename = 'myapp.log',
filemode = 'w')
#logging.config模块可以通过加载配置文件,从来配置日志属性
logging.debug('This is debug message')
logging.info('This is info message')
logging.warning('This is warning message')
日志打印到:./myapp.log 文件
./myapp.log文件中内容为:
Sun, 24 May 2009 21:48:54 demo2.py[line:11] DEBUG This is debug message
Sun, 24 May 2009 21:48:54 demo2.py[line:12] INFO This is info message
Sun, 24 May 2009 21:48:54 demo2.py[line:13] WARNING This is warning
将日志同时输出到 文件 和 屏幕
import logging logging.basicConfig(level=logging.DEBUG,
format='%(asctime)s %(filename)s[line:%(lineno)d] %(levelname)s %(message)s',
datefmt='%a, %d %b %Y %H:%M:%S',
filename='myapp.log',
filemode='w') #################################################################################################
#定义一个StreamHandler,将INFO级别或更高的日志信息打印到标准错误,并将其添加到当前的日志处理对象#
console = logging.StreamHandler()
console.setLevel(logging.INFO)
formatter = logging.Formatter('%(name)-12s: %(levelname)-8s %(message)s')
console.setFormatter(formatter)
logging.getLogger('').addHandler(console)
################################################################################################# logging.debug('This is debug message')
logging.info('This is info message')
logging.warning('This is warning message')
结果:
屏幕上打印:
root : INFO This is info message
root : WARNING This is warning message ./myapp.log文件中内容为:
Sun, 24 May 2009 21:48:54 demo2.py[line:11] DEBUG This is debug message
Sun, 24 May 2009 21:48:54 demo2.py[line:12] INFO This is info message
Sun, 24 May 2009 21:48:54 demo2.py[line:13] WARNING This is warning message
其他详见:六、Unicode Strings 160/1594,内容略
正则表达式 - Regex
正则引擎原理:[IR] XPath for Search Query
使用教程: 正则表达式30分钟入门教程
基础用法
re.match 法
典型应用:字符串信息提取,路径的提取;可以替代 split()。
In [8]: >>> import re
...:
...: >>> match = re.match('Hello[ \t]*(.*)world', 'Hello Python world')
...:
...: >>> match.group(1)
...:
Out[8]: 'Python '
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
In [9]: >>> match = re.match('[/:](.*)[/:](.*)[/:](.*)', '/usr/home:lumberjack')
...:
...: >>> match.groups()
...:
Out[9]: ('usr', 'home', 'lumberjack')
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
In [10]: >>> re.split('[/:]', '/usr/home/lumberjack')
Out[10]: ['', 'usr', 'home', 'lumberjack']
filter 筛选框架
一个简单的框架代码:
def filter_mail(emails):
return list(filter(fun, emails)) # 2.fun 是个自定义的函数,返回:True/False,也是个re.
if __name__ == '__main__':
n = int(input())
emails = []
for _ in range(n):
emails.append(input()) # 1.获取mail list
filtered_emails = filter_mail(emails)
filtered_emails.sort() # 3.排序
print(filtered_emails)
邮件格式匹配
Valid email addresses must follow these rules:
* It must have the username@websitename.extension format type.
* The username can only contain letters, digits, dashes and underscores.
* The website name can only have letters and digits.
* The maximum length of the extension is .
import re
re.search(r'^[A-Za-z0-9-_]+@[A-Za-z0-9]+\.\w?\w?\w$',s)
正则表达式
限定符 与 元字符
限定符

元字符

常用例子
常见字符串匹配
# 先是一个单词hi,然后是任意个任意字符(但不能是换行),最后是Lucy这个单词
\bhi\b.*\bLucy\b
# 匹配以字母a开头的单词——先是某个单词开始处(\b),然后是字母a,然后是任意数量的字母或数字(\w*),最后是单词结束处(\b)。
\ba\w*\b
# 匹配以.tif结尾的单词
re.search( ".*\\.tif",f)]
# 匹配1个或更多连续的数字。这里的+是和*类似的元字符,不同的是*匹配重复任意次(可能是0次),而+则匹配重复1次或更多次。
\d+
# 匹配刚好6个字符的单词。
\b\w{6}\b
# 填写的QQ号必须为5位到12位数字:开始--> ^ ... $ <--结束
^\d{5,12}$
电话号码
# 中国的电话号码 - 简单版本
0\d\d-\d\d\d\d\d\d\d\d 如下改进版
0\d{2}-\d{8}
# 匹配几种格式的电话号码,像(010)88886666,或022-22334455,或02912345678等。
- 首先是一个转义字符\(,它能出现0次或1次(?),
- 然后是一个0,后面跟着2个数字(\d{2}),
- 然后是)或-或空格中的一个,它出现1次或不出现(?),
- 最后是8个数字(\d{8})
\(?0\d{2}[) -]?\d{8}
However,也能匹配010)12345678或(022-87654321这样的“不正确”的格式。
那,怎么办?-- 分枝条件
# 匹配两种以连字号分隔的电话号码:一种是三位区号,8位本地号(如010-12345678),一种是4位区号,7位本地号(0376-2233445)。
0\d{2}-\d{8}|0\d{3}-\d{7}
继续补充。。。用到再说。
[Python] 02 - String的更多相关文章
- python的string用法
s.strip().lstrip().rstrip(',') S.lower() #小写 S.upper() #大写 S.swapcase() #大小写互换 S.capitalize() #首字母大写 ...
- Python 常用string函数
Python 常用string函数 字符串中字符大小写的变换 1. str.lower() //小写>>> 'SkatE'.lower()'skate' 2. str.upper ...
- python中string模块各属性以及函数的用法
任何语言都离不开字符,那就会涉及对字符的操作,尤其是脚本语言更是频繁,不管是生产环境还是面试考验都要面对字符串的操作. python的字符串操作通过2部分的方法函数基本上就可以解决所有的字符串 ...
- python中string格式化
python中可以对string, int, float等数据类型进行格式化操作.下面举例来说明一些常用操作. 先贴出 python 对 String Formatting Operations 讲解 ...
- PyQt的QString和python的string的区别
转载于http://blog.chinaunix.net/uid-200142-id-4018863.html python的string和PyQt的QString的区别 python string和 ...
- Java学习笔记 02 String类、StringBuilder类、字符串格式化和正则表达式
一.String类一般字符串 声明字符串 >>String str 创建字符串 >>String(char a[])方法用于将一个字符数组创建为String对象 >> ...
- python中string.casefold和string.lower区别
string.casefold和string.lower 区别 python 3.3 引入了string.casefold 方法,其效果和 string.lower 非常类似,都可以把字符串变成小写, ...
- 浅析python的string.Template
摘自:python参考手册. string模块定义了一种新字符串类型Template,简化了特定的字符串置换操作, Template定义一个类 1.template(s), #s是字符串 s='he ...
- 牛人总结python中string模块各属性以及函数的用法,果断转了,好东西
http://blog.chinaunix.net/uid-25992400-id-3283846.html http://blog.csdn.net/xiaoxiaoniaoer1/article/ ...
随机推荐
- Docker machine(Docker 虚拟机)
安装docker [root@lianxi ~]# yum -y install docker 启动docker [root@lianxi ~]# systemctl start docker 下载D ...
- php boolean
要明确地将一个值转换成 boolean,用 (bool) 或者 (boolean) 来强制转换 var_dump((); // true 当转换为 boolean 时,以下值被认为是 FALSE: 1 ...
- axios 取消请求的方法
开发中遇到需要取消请求的功能,,点击终止查询可以取消开始查询请求,再次点击开始查询又可以进行查询. 解决方法:axios官方文档上的CancelToken,一开始用了这个api后,可以成功取消请求,但 ...
- Selenium support for PhantomJS has been deprecated, please use headless
今天在使用Selenuim+PhantomJS动态抓取网页时,出现如下报错信息: C:\Python36\lib\site-packages\selenium-3.11.0-py3.6.egg\sel ...
- from String value ('{}'); no single-String constructor/factory
需要为类增加一个接受String的构造函数: 例如: public class B { private String name; public B(String b) { } public Strin ...
- 微软BI 之SSIS 系列 - Execute SQL Task 中的 Single Row 与 Full Result Set 的处理技巧
开篇介绍 Execute SQL Task 这个控件在微软BI ETL 项目中使用的频率还是非常高的,也是大部分入门 SSIS 初学者最早接触到的几个控制流控件. 我们通常使用 Execute SQL ...
- 基于Ubuntu 搭建 VNC 远程桌面服务
系统要求:Ubuntu 16.04.1 LTS 64 位操作系统 安装.启动 VNC VNC 远程桌面原理 注:本小节内容旨在帮助您更好地了解 Xorg.X11.VNC 等概念和原理,如果你不想了解原 ...
- redis性能测试报告
服务器配置:16核心,64G 250个并发读:250个并发写性能[内容8千byte] 163为读:164为写:
- 【SqlServer】SqlServer的异常处理
在SQLserver数据库中,如果有很多存储过程的时候,我们会使用动态SQL进行存储过程调用存储过程,这时候,很可能在某个环节就出错了,但是出错了我们很难去跟踪到出错的存储过程,此时我们就可以使用异常 ...
- FeignClient使用
在使用Spring Cloud开发微服务应用时中,各个微服务服务提供者都是以HTTP接口的形式对外提供服务,因此服务消费者在调用服务提供者时,通过HTTP Client的方式访问.当然我们可以使用JD ...
