CF#335 Intergalaxy Trips
2 seconds
256 megabytes
standard input
standard output
The scientists have recently discovered wormholes — objects in space that allow to travel very long distances between galaxies and star systems.
The scientists know that there are n galaxies within reach. You are in the galaxy number 1 and you need to get to the galaxy number n. To get from galaxy i to galaxy j, you need to fly onto a wormhole (i, j) and in exactly one galaxy day you will find yourself in galaxy j.
Unfortunately, the required wormhole is not always available. Every galaxy day they disappear and appear at random. However, the state of wormholes does not change within one galaxy day. A wormhole from galaxy i to galaxy j exists during each galaxy day taken separately with probability pij. You can always find out what wormholes exist at the given moment. At each moment you can either travel to another galaxy through one of wormholes that exist at this moment or you can simply wait for one galaxy day to see which wormholes will lead from your current position at the next day.
Your task is to find the expected value of time needed to travel from galaxy 1 to galaxy n, if you act in the optimal way. It is guaranteed that this expected value exists.
The first line of the input contains a single integer n (1 ≤ n ≤ 1000) — the number of galaxies within reach.
Then follows a matrix of n rows and n columns. Each element pij represents the probability that there is a wormhole from galaxy i to galaxy j. All the probabilities are given in percents and are integers. It is guaranteed that all the elements on the main diagonal are equal to 100.
Print a single real value — the expected value of the time needed to travel from galaxy 1 to galaxy n if one acts in an optimal way. Your answer will be considered correct if its absolute or relative error does not exceed 10 - 6.
Namely: let's assume that your answer is a, and the answer of the jury is b. The checker program will consider your answer correct, if 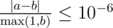 .
.
3
100 50 50
0 100 80
0 0 100
1.750000000000000
2
100 30
40 100
3.333333333333333
In the second sample the wormhole from galaxy 1 to galaxy 2 appears every day with probability equal to 0.3. The expected value of days one needs to wait before this event occurs is 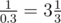 .
.
题意:有n个点,每天可以从i到j的概率是P(i, j),每天也可以选择留在原地,问去到n的期望天数。
分析:这题是这样的。
如果我们从终点往前推,会简单很多。因为从前往后的话很难确定有哪些点转移到自身。
从终点开始的话,显然一开是在终点的天数是0。
又发现,每个点显然只能从更优(期望更小)的点转移到自己。
由于是从后往前推,所以这意味这已经推过的点不会再推。
所以,这是一个类似最短路的过程。
推的过程是这样的
设比x点优秀的点是v[1],v[2].....v[c]
那么x的期望显然满足
dp[x] = dp[v[1]] * p(x, v[1]) + dp[v[2]] * p(x, v[2]) * (1 - p(x, v[1]) ) + dp[v[3]] * p(x, v[3]) * (1 - p(x, v[2]) ) * (1 - p(x, v[1]) ) + ..... + dp[v[c]] * p(x, v[c]) * (1 - p(x, v[2]) ) * (1 - p(x, v[1]) ) * ..... * (1 - p(x, v[c - 1])) + dp[x] * (1 - p(x, v[2]) ) * (1 - p(x, v[1]) ) * ..... * (1 - p(x, v[c])) + 1
其中(1 - p(x, v[2]) ) * (1 - p(x, v[1]) ) * ..... * (1 - p(x, v[c]))是它留在原地的概率。
然后变形
dp[x] = ( dp[v[1]] * p(x, v[1]) + dp[v[2]] * p(x, v[2]) * (1 - p(x, v[1]) ) + dp[v[3]] * p(x, v[3]) * (1 - p(x, v[2]) ) * (1 - p(x, v[1]) ) + ..... + dp[v[c]] * p(x, v[c]) * (1 - p(x, v[2]) ) * (1 - p(x, v[1]) ) * ..... * (1 - p(x, v[c - 1])) + 1 ) / (1 - (1 - p(x, v[2]) ) * (1 - p(x, v[1]) ) * ..... * (1 - p(x, v[c])) )
这样就可以转移了。。。
/**
Create By yzx - stupidboy
*/
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cmath>
#include <deque>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <map>
#include <set>
#include <ctime>
#include <iomanip>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
typedef double DB;
#define MIT (2147483647)
#define INF (1000000001)
#define MLL (1000000000000000001LL)
#define sz(x) ((int) (x).size())
#define clr(x, y) memset(x, y, sizeof(x))
#define puf push_front
#define pub push_back
#define pof pop_front
#define pob pop_back
#define mk make_pair inline int Getint()
{
int Ret = ;
char Ch = ' ';
bool Flag = ;
while(!(Ch >= '' && Ch <= ''))
{
if(Ch == '-') Flag ^= ;
Ch = getchar();
}
while(Ch >= '' && Ch <= '')
{
Ret = Ret * + Ch - '';
Ch = getchar();
}
return Flag ? -Ret : Ret;
} const DB EPS = 1e-;
const int N = ;
int n, data[N][N];
DB dp[N], stay[N], cnt[N];
bool visit[N]; inline void Input()
{
scanf("%d", &n);
for(int i = ; i <= n; i++)
for(int j = ; j <= n; j++)
scanf("%d", &data[i][j]);
} inline void Solve()
{
for(int i = ; i <= n; i++) dp[i] = INF, stay[i] = 1.0, cnt[i] = 0.0;
dp[n] = ;
for(int k = ; k <= n; k++)
{
int idx = -;
DB mn = INF;
for(int i = ; i <= n; i++)
if(!visit[i] && mn >= dp[i])
mn = dp[i], idx = i; if(idx == )
{
printf("%.12lf\n", dp[]);
break;
} visit[idx] = ;
for(int i = ; i <= n; i++)
if(!visit[i])
{
cnt[i] += stay[i] * dp[idx] * (0.01 * data[i][idx]);
stay[i] *= - 0.01 * data[i][idx];
if(fabs( - stay[i]) > EPS)
dp[i] = ( + cnt[i]) / ( - stay[i]);
}
}
} int main()
{
freopen("a.in", "r", stdin);
Input();
Solve();
return ;
}
CF#335 Intergalaxy Trips的更多相关文章
- 【CF605E】Intergalaxy Trips(贪心,动态规划)
[CF605E]Intergalaxy Trips(贪心,动态规划) 题面 Codeforces 洛谷 有\(n\)个点,每个时刻第\(i\)个点和第\(j\)个点之间有\(p_{ij}\)的概率存在 ...
- CodeForces 605 E. Intergalaxy Trips
E. Intergalaxy Trips time limit per test:2 seconds memory limit per test:256 megabytes input:standar ...
- CF605E Intergalaxy Trips
CF605E Intergalaxy Trips 考虑你是不知道后来的边的出现情况的,所以可以这样做:每天你都选择一些点进行观察,知道某天往这些点里面的某条边可用了,你就往这条边走.这样贪心总是对的. ...
- CF#335 Freelancer's Dreams
Freelancer's Dreams time limit per test 2 seconds memory limit per test 256 megabytes input standard ...
- CF#335 Board Game
Board Game time limit per test 2.5 seconds memory limit per test 256 megabytes input standard input ...
- CF#335 Lazy Student
Lazy Student time limit per test 2 seconds memory limit per test 256 megabytes input standard input ...
- CF#335 Sorting Railway Cars
Sorting Railway Cars time limit per test 2 seconds memory limit per test 256 megabytes input standar ...
- CF #335 div1 A. Sorting Railway Cars
题目链接:http://codeforces.com/contest/605/problem/A 大意是对一个排列进行排序,每一次操作可以将一个数字从原来位置抽出放到开头或结尾,问最少需要操作多少次可 ...
- [Codeforces]605E Intergalaxy Trips
小C比较棘手的概率期望题,感觉以后这样的题还会贴几道出来. Description 给定一个n*n的邻接矩阵,邻接矩阵中元素pi,j表示的是从 i 到 j 这条单向道路在这一秒出现的概率百分比,走一条 ...
随机推荐
- 解决eclipse中maven web工程打包成war(发布到tomcar)时lib中没有jar包的解决方法
可能有两个原因:1.maven中某些jar包下载不下来 从其他地方下载jar文件放到相应maven本地库的.m2里2..classpath文件中缺少(下面代码的作用是制定maven的jar发布路径)& ...
- iOS 文档分享相关
在非系统预览情况下 指定文件打开系统分享菜单 NSString *savedPath = [NSHomeDirectory() stringByAppendingString:[NSString s ...
- 《Thinking in Java》十七章_容器深入研究_练习13(Page484)
练习13: 单词计数器 import java.io.BufferedReader; import java.io.FileInputStream; import java.io.FileNotFou ...
- php 租房子练习
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD XHTML 1.0 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/ ...
- 昨天一日和彭讨论post请求数据的问题
上午写了一个for循环,下午与同学视频才知道没有解决根本问题,接口是url单个的数据请求,而导入的是多个员工的考勤数据也就是要有多个请求同时发出,利用这个做法是有链接超时的情况,所以昨天晚上彭为了导入 ...
- .net学习笔记---webconfig的读与写
System.ConfigurationManager类用于对配置文件的读取.其具有的成员如下: 一.AppSettings AppSetting是最简单的配置节,读写非常简单. 名称 说明 AppS ...
- Spring+Maven+Dubbo+MyBatis+Linner+Handlebars—Web开发环境搭建
本文主要分三部分,分别是:后台核心业务逻辑.桥梁辅助控制和前台显示页面. 本Web开发环境综合了多种工具,包括Maven包管理与编译工具.Dubbo分布式服务框架.MyBatis数据持久化工具.Lin ...
- js获取url参数值(HTML之间传值)
<h3>未设置设备: <a href="javascript:addTab('设备列表','PKE_DeviceContent/PKE_DeviceContent.aspx ...
- x86架构的android手机兼容性问题
x86架构的android手机兼容性问题 http://www.cnblogs.com/guoxiaoqian/p/3984934.html 自从CES2012上Intel发布了针对移动市场的Medf ...
- 【翻译三】java-并发之线程对象和实现
Thread Objects Each thread is associated with an instance of the class Thread. There are two basic s ...
