Java基础—IO小结(一)概述与节点流
一、File类的使用
由于file类是一个基础类,所以我们从file类开始了解。(SE有完善的中文文档,建议阅读)
构造器:
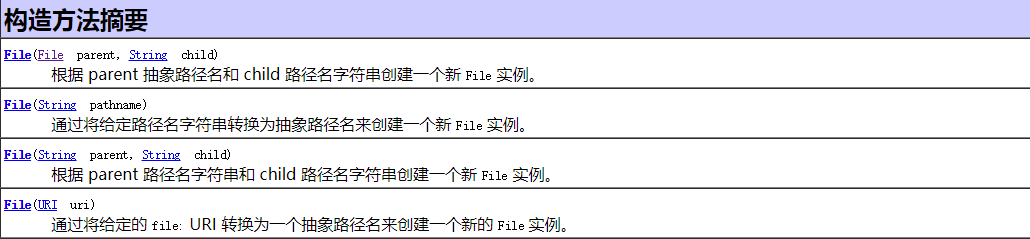
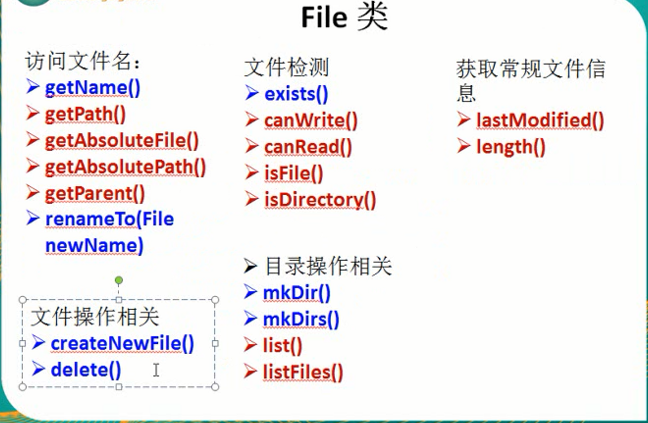
常用方法:——完整方法请参见API API API!!!
File做的是面上的事——文件的新建、删除、重命名等。有关文件内容的操作,需要流来进行,所以,它经常作为形参。
文件名:
测试文件:
测试代码:
@Test
public void test1() {
// 通过绝对路径创建File对象——对应一个文件或者文件夹
File file = new File("D:\\test\\hello.txt");
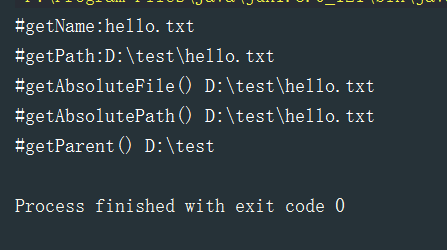
// getName()——文件或目录名
System.out.println("#getName:"+file.getName());
// getPath()——路径字符串,若是相对路径,返回相对路径字符串
System.out.println("#getPath:"+file.getPath());
// getAbsoluteFile()——绝对路径形式,返回File
System.out.println("#getAbsoluteFile() "+file.getAbsoluteFile());
// getAbsolutePath()——绝对路径字符串
System.out.println("#getAbsolutePath() "+file.getAbsolutePath());
// getParent() ——返回父目录
System.out.println("#getParent() "+file.getParent()); }
测试结果:
文件检测:
测试文件:
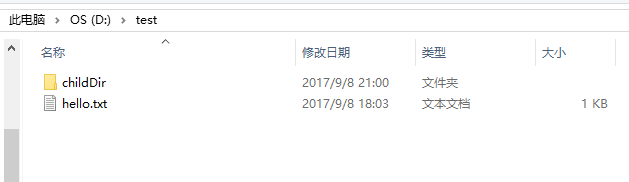
测试代码:
@Test
public void test2() {
File file1 = new File("D:\\test\\hello.txt"); // 文件
File file2 = new File("D:\\test\\childDir"); // 文件夹
// exists()——文件或目录是否存在
System.out.println("#exists()"+file1.exists());
// canRead() canWrite() ——是否可读可写
System.out.println("#canRead()"+file1.canRead());
System.out.println("#canWrite()"+file1.canWrite());
// isFile() isDirectory() ——是否是文件/目录
System.out.println("#isFile()"+file1.isFile());
System.out.println("#isFile()"+file2.isFile());
System.out.println("#isDirectory()"+file1.isDirectory());
System.out.println("#isDirectory()"+file2.isDirectory());
}
测试结果:
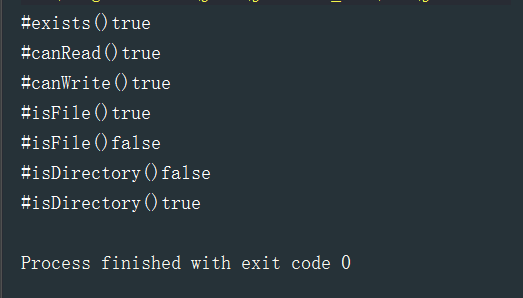
获取常规文件信息:
测试文件:上文hello.txt
测试代码:
@Test
public void test3() {
File file = new File("D:\\test\\hello.txt");
// lastModified() ——文件最后修改时间
System.out.println("lastModified() :"+ new Date(file.lastModified()));
// length()——文件长度(字节)
System.out.println("length:"+file.length());
}
测试结果:
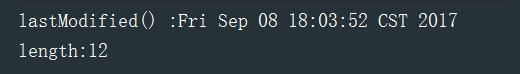
文件操作相关:
测试代码:
@Test
public void test4() throws IOException {
File file = new File("D:\\test\\hello1.txt"); //文件不存在
// createNewFile() ——不存在时创建新文件
if (!file.exists()) {
boolean b = file.createNewFile();
System.out.println("创建空文件结果:"+ b);
}
// delete() ——文件长度(字节)
System.out.println("delete() :" + file.delete());
}
测试结果:

目录操作相关:
测试文件:
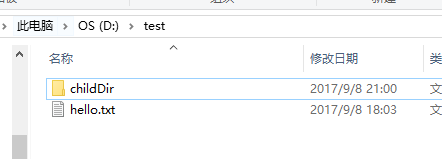
测试代码:
@Test
public void test5() throws IOException {
File file1 = new File("D:\\test\\childDir"); // 文件夹
if (!file1.exists()) {
// mkdir()——创建一个文件目录 mkdirs()——递归创建
boolean b = file1.mkdir();
System.out.println("新建文件夹结果:"+ b);
}
File file = new File("D:\\test");
// 与Linux命令的ls类似,list返回字符串,listFiles返回文件
String[] files = file.list();
for (String s : files) {
System.out.println(s);
}
}
测试结果:
二、IO流的分类
读取外部设备中到程序中,称之为 input,输入;从程序向外输出到外部,称之为 ouput,输出;
也就是,站在程序的角度来理解输入输出!
A.根据处理数据类型的不同分为:字符流和字节流
B.根据数据流向不同分为:输入流和输出流
C.按功能分:节点流(一线的,离源最近的)和处理流
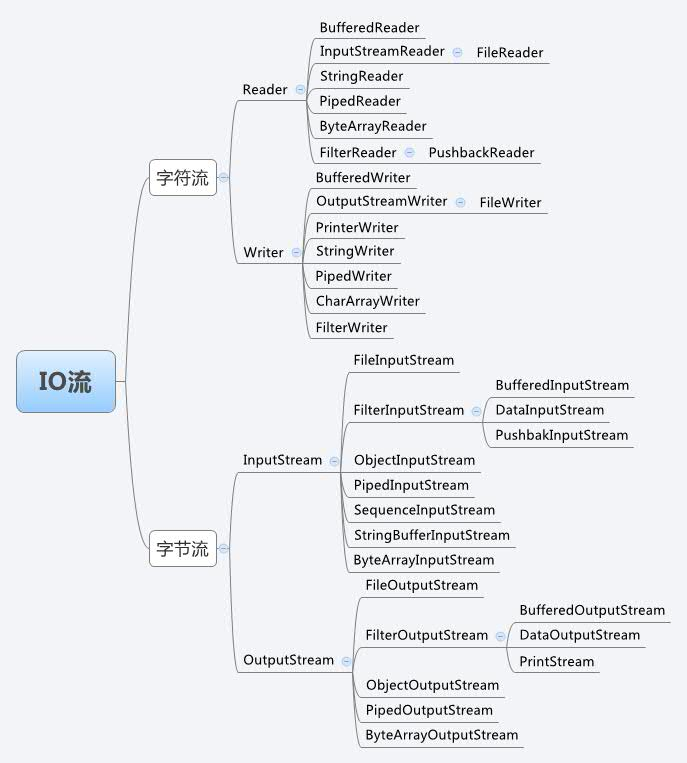
都是由四个最基本的 抽象类派生而成

三、节点流的使用

请注意:由于流不是JVM的资源,不会被回收,所以:必须手动显式关闭!
1.fis与fos
FileInputStream
构造器:
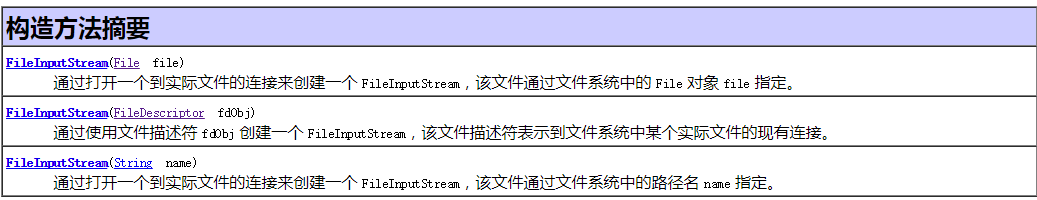
方法摘要:输入流对应读的方法
read()方法:
@Test
public void testFis1() throws Exception{
// 从硬盘读取一个文件(File类与文件建立联系),将其文件内容读取到程序中
File file = new File("D:\\test\\hello.txt");
// 通过file构建一个输入流
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(file);
// 调用fis的方法进行文件的操作
/*
* read():读取文件的一个字节(java中int为4字节),到结尾时返回-1
* */
// int b = fis.read();
// while (b != -1) {
// System.out.print((char)b);
// b = fis.read();
// }
int b;
while ((b = fis.read()) != -1) {
System.out.print((char)b);
}
// 必须手动关闭流!
fis.close();
}
结果:
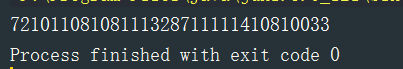
//实际上,txt中文件为Hello World,仔细看 72便是H的ASCII值(char型转为Int型了)
若要显示英文字符,可以进行强转:
System.out.print((char)b);
当然,这里直接thorws的做法是及其不靠谱的,至少,当前面出现异常时,后续的代码(如colse())不会继续执行,也就是说,资源无法关闭!
我们稍加改进:—— IO的操作请注意写法!
@Test
public void testFis2(){
FileInputStream fis = null;
try {
// 从硬盘读取一个文件(File类与文件建立联系),将其文件内容读取到程序中
File file = new File("D:\\test\\hello.txt");
// 通过file构建一个输入流
fis = new FileInputStream(file);
// 调用fis的方法进行文件的操作 int b;
while ((b = fis.read()) != -1) {
System.out.print((char)b);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
// 必须手动关闭流!
try {
fis.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
} }
当然,一个一个字节读,在实际中是不可能的,我们可以使用它的重载方法:

@Test
public void testFis3() {
FileInputStream fis = null;
try {
File file = new File("D:\\test\\hello.txt");
fis = new FileInputStream(file);
// 定义每次读取的字节数组,这里定义长度为5
byte[] bytes = new byte[5];
int len; // 每次读取的字节长度
while ((len = fis.read(bytes)) != -1) {
/* 这里必须注意bytes.length与len的区别,len是实际读到的长度,
bytes.length是数组长度,可能会有之前读到的老的字符,读到的字节是依次放入bytes中,
将原先数组的进行替换,若未替换完,则保留了老的字节,不能遍历!
*/
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++) {
System.out.print((char)bytes[i]);
}
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
try {
// 手动关闭流
fis.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
//相关注意的问题请看注释!
FileOutputStream
构造器:
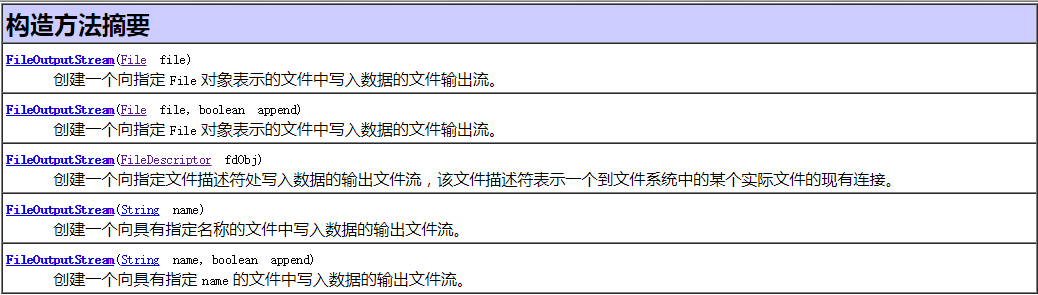
方法摘要:对应写的方法
测试代码:
@Test
public void testFos1() {
// 文件可以不存在,将会自动创建
File file = new File("D:\\test\\hello1.txt");
FileOutputStream fos = null;
try {
// 同样,使用文件作为构造器,关联上一个文件
fos = new FileOutputStream(file);
// 使用字节数组写入数据到文件
fos.write(new String("I love China").getBytes());
System.out.println("fos done!");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (fos != null) { //增加空判断,防止空指针异常
try {
fos.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
//稍微改进异常处理时流的关闭引发的NPE
结果:若文件存在不是追加,而是直接覆盖文件
fos与fis实现文件的复制:
测试代码:
@Test
public void testFisAndFos1() {
// 已经存在,用于输入流读取
File file1 = new File("D:\\test\\0.jpg");
// 不存在,用于输入流写出
File file2 = new File("D:\\test\\1.jpg");
FileInputStream fis = null;
FileOutputStream fos = null;
try {
fis = new FileInputStream(file1);
fos = new FileOutputStream(file2);
int len;
byte[] bytes = new byte[5];
while ((len = fis.read(bytes)) != -1) {
// 将取到的字节写入新的文件,注意读的长度
// 考虑 fos.write(bytes);的写法的错误之处
fos.write(bytes, 0, len);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (fis != null) {
try {
fis.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (fos != null) {
try {
fos.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
// 后续将会升级为缓冲流
测试结果:
// 无论字节或者字符,都可以使用字节流进行处理
2.fr与fw
FileReader与FileWriter处理的步骤与上述是基本一样的,不同的是字符流处理的单位稍有差异
构造器:

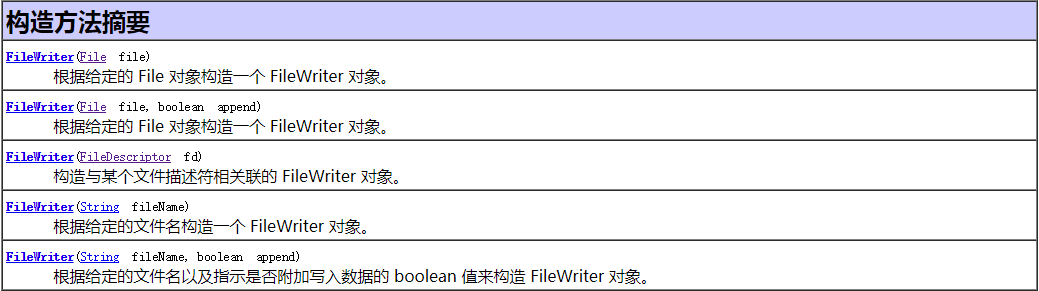
FileReader
测试代码:
@Test
public void testFr1() {
File file = new File("D:\\test\\hello.txt");
FileReader fr = null;
try {
// 同样的,根据文件构建一个输入流
fr = new FileReader(file);
int len;
// 实际操作请根据文件大小修改字符数组大小
char[] cbuf = new char[5];
while ((len = fr.read(cbuf)) != -1) {
String s = new String(cbuf, 0, len);
System.out.print(s);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (fr != null) {
try {
fr.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
} }
测试结果即为输出文本文件到控制台
FileReader与FileWriter进行文本文件复制与之前类似,只是数组类型不同:
@Test
public void testFrAndFw1() {
// 需要关联的文件
File file1 = new File("D:\\test\\hello.txt");
File file2 = new File("D:\\test\\hello3.txt");
FileReader fr = null;
FileWriter fw = null;
try {
// 通过文件创建流
fr = new FileReader(file1);
fw = new FileWriter(file2);
int len;
char[] cbuf = new char[5];
while ((len = fr.read(cbuf)) != -1) {
fw.write(cbuf, 0, len);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
if (fr != null) {
try {
fr.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if (fw != null) {
try {
fw.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
Java基础—IO小结(一)概述与节点流的更多相关文章
- Java基础—IO小结(二)缓冲流与其它流的使用
一.缓冲流的使用 每个字节流都有对应的缓冲流: BufferedInputStream / BufferedOutputStream 构造器: 方法摘要与对应节点流类似 使用缓冲流实现文件复制:实际中 ...
- Java基础-IO流对象之转换流(InputStreamReader与OutoutStreamWriter)
Java基础-IO流对象之转换流(InputStreamReader与OutoutStreamWriter) 作者:尹正杰 版权声明:原创作品,谢绝转载!否则将追究法律责任. 一.转换流概述 我们之前 ...
- Java基础-IO流对象之File类
Java基础-IO流对象之File类 作者:尹正杰 版权声明:原创作品,谢绝转载!否则将追究法律责任. 一.IO技术概述 回想之前写过的程序,数据都是在内存中,一旦程序运行结束,这些数据都没有了,等下 ...
- Java基础IO流(二)字节流小案例
JAVA基础IO流(一)https://www.cnblogs.com/deepSleeping/p/9693601.html ①读取指定文件内容,按照16进制输出到控制台 其中,Integer.to ...
- Java基础-IO流对象之压缩流(ZipOutputStream)与解压缩流(ZipInputStream)
Java基础-IO流对象之压缩流(ZipOutputStream)与解压缩流(ZipInputStream) 作者:尹正杰 版权声明:原创作品,谢绝转载!否则将追究法律责任. 之前我已经分享过很多的J ...
- Java基础-IO流对象之随机访问文件(RandomAccessFile)
Java基础-IO流对象之随机访问文件(RandomAccessFile) 作者:尹正杰 版权声明:原创作品,谢绝转载!否则将追究法律责任. 一.RandomAccessFile简介 此类的实例支持对 ...
- Java基础-IO流对象之内存操作流(ByteArrayOutputStream与ByteArrayInputStream)
Java基础-IO流对象之内存操作流(ByteArrayOutputStream与ByteArrayInputStream) 作者:尹正杰 版权声明:原创作品,谢绝转载!否则将追究法律责任. 一.内存 ...
- Java基础-IO流对象之数据流(DataOutputStream与DataInputStream)
Java基础-IO流对象之数据流(DataOutputStream与DataInputStream) 作者:尹正杰 版权声明:原创作品,谢绝转载!否则将追究法律责任. 一.数据流特点 操作基本数据类型 ...
- Java基础-IO流对象之打印流(PrintStream与PrintWriter)
Java基础-IO流对象之打印流(PrintStream与PrintWriter) 作者:尹正杰 版权声明:原创作品,谢绝转载!否则将追究法律责任. 一.打印流的特性 打印对象有两个,即字节打印流(P ...
随机推荐
- textarea高度跟随文字高度而变化
html部分: <textarea id="textarea">哈喽哈喽哈喽哈喽哈喽哈喽哈喽哈喽哈喽哈喽哈喽哈喽</textarea> js部分: < ...
- 【日常记录】【unity3d】 OnTriggerEnter 和 OnCollisionEnter (2D) 的区别
问题:两个物体A,B 两者都有碰撞体 collider(Box Collider,Sphere Collider,Capsule Collider等)当两物体相撞时,会进入 OnTriggerEnte ...
- jquery validation表单验证插件2。
<!DOCTYPE html> <html> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <title> ...
- error MSB3552: Resource file "**/*.resx" cannot be found. [/ConsoleApp1.csproj]
问题场景: 练习在docker下操作netcore,镜像为centos7,安装完netcore sdk 2.2后,执行操作: dotnet new consoledotnet run 出现报错: /u ...
- Tomcat – Java.Lang.OutOfMemoryError: PermGen Space
很多时候,在开发阶段Tomcat重复的重启过程中会遇到java.lang.OutOfMemoryError : PermGen space 错误. 1 2 3 4 java.lang.OutOfMem ...
- mysql-sql-standard
https://github.com/zhishutech/mysql-sql-standard
- 通过ffplay实现摄像头preview
通过ffplay实现摄像头preview 硬件平台:Jetson TK1 开发板(NVIDIA Tegra K1 Mobile Processor 32bit),宁波舜宇光电SP103A(OV1682 ...
- Ogre学习教程:Ogre1.8.1+VS2010环境配置(转)
http://blog.csdn.net/yangtrees/article/details/8724120 http://blog.csdn.net/cll611/article/details/8 ...
- 解决 hibernate cannot define positional parameter after any named parameters have been defined
解决 hibernate cannot define positional parameter after any named parameters have been defined 把模糊查询的 ...
- 激活office软件
1. 打开校园软件正版化激活网址 http://nic.seu.edu.cn/2015/0113/c12333a115290/page.htm 2. 下载KMS激活脚本 3. 登陆easyconnec ...
