leetcode——链表
- 206. 反转链表(易)
反转一个单链表。
示例:
输入: 1->2->3->4->5->NULL
输出: 5->4->3->2->1->NULLc++:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverseList(ListNode* head) {
ListNode *newHead=NULL;
while(head){
ListNode *next=head->next;
head->next=newHead;
newHead=head;
head=next;
}
return newHead;
}
};python:
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = None class Solution:
def reverseList(self, head: ListNode) -> ListNode:
newHead=None
while head!=None:
nxt=head.next
head.next=newHead
newHead=head
head=nxt
return newHeadjava:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
ListNode newHead=null;
while(head!=null){
ListNode next=head.next;
head.next=newHead;
newHead=head;
head=next;
}
return newHead;
}
} 92. 反转链表 II(中)反转从位置 m 到 n 的链表。请使用一趟扫描完成反转。
说明:
1 ≤ m ≤ n ≤ 链表长度。
示例:
输入: 1->2->3->4->5->NULL, m = 2, n = 4
输出: 1->4->3->2->5->NULL
c++:/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode* reverseBetween(ListNode* head, int m, int n) {
ListNode* sta=head;
int len=n-m+1;
ListNode* pre=NULL;
while(--m&&head){
pre=head;
head=head->next;
}
ListNode* e=head;
ListNode* newHead=NULL;
while(len--&&head){
ListNode* next=head->next;
head->next=newHead;
newHead=head;
head=next;
}
e->next=head;
if(pre)
pre->next=newHead;
else
sta=newHead;
return sta;
}
};python:
# Definition for singly-linked list.
# class ListNode:
# def __init__(self, x):
# self.val = x
# self.next = None class Solution:
def reverseBetween(self, head: ListNode, m: int, n: int) -> ListNode:
sta=head
len = n-m+1
pre=None
while m!=1 and head!=None :
pre=head
m-=1
head=head.next
newHead=None
ed=head
while len!=0 and head!=None:
nxt=head.next
head.next=newHead
newHead=head
head=nxt
len-=1
ed.next=head
if pre!=None:
pre.next=newHead
else :
sta=newHead
return stajava:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode reverseBetween(ListNode head, int m, int n) {
int len=n-m+1;
ListNode pre=null,sta=head;
while(--m!=0&&head!=null){
pre=head;
head=head.next;
}
ListNode ed=head,newHead=null,nxt=null;
while(len--!=0&&head!=null){
nxt=head.next;
head.next=newHead;
newHead=head;
head=nxt;
}
ed.next=head;
if(pre==null){
return newHead;
}else {
pre.next=newHead;
return sta;
}
}
}160. 相交链表 (易)
编写一个程序,找到两个单链表相交的起始节点。
如下面的两个链表:
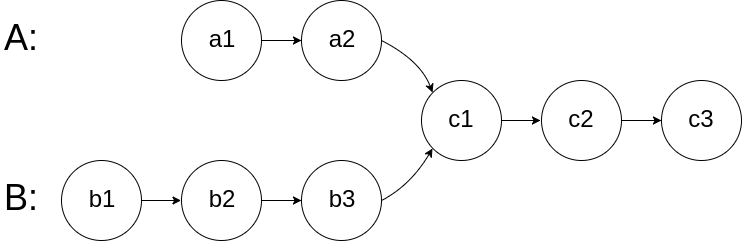
在节点 c1 开始相交。
c++:/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode *getIntersectionNode(ListNode *headA, ListNode *headB) {
int a=0,b=0;
ListNode *A=headA,*B=headB;
while(A){
a++;
A=A->next;
}
while(B){
b++;
B=B->next;
}
if(a>b){
int c=a-b;
while(c--&&headA){
headA=headA->next;
}
while(headA&&headB){
if(headA==headB)
return headA;
else
headA=headA->next,headB=headB->next;
}
}else {
int c=b-a;
while(c--&&headB){
headB=headB->next;
}
while(headA&&headB){
if(headA==headB)
return headA;
else
headA=headA->next,headB=headB->next;
}
}
return NULL;
}
};142. 环形链表 II(中)
给定一个链表,返回链表开始入环的第一个节点。 如果链表无环,则返回 null。
为了表示给定链表中的环,我们使用整数 pos 来表示链表尾连接到链表中的位置(索引从 0 开始)。 如果 pos 是 -1,则在该链表中没有环。
说明:不允许修改给定的链表。
c++:
map直接搞:/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode *detectCycle(ListNode *head) {
unordered_map<ListNode*,int> m;
while(head){
if(m[head]){
return head;
}
m[head]=1;
head=head->next;
}
return NULL;
}
};快慢指针:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode *next;
* ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
* };
*/
class Solution {
public:
ListNode *detectCycle(ListNode *head) {
ListNode *slow=head,*fast=head,*meet=NULL;
while(slow&&fast){
slow=slow->next;
fast=fast->next;
if(!fast){
return NULL;
}
fast=fast->next;
if(slow==fast){
// printf("%d %d",slow->val,fast->val);
// puts("gg");
meet=slow;
break;
}
}
// printf("hh");
if(meet==NULL)
return NULL;
// printf("hh");
while(meet&&head){
if(meet==head){
return meet;
}
meet=meet->next;
head=head->next;
}
return NULL;
}
};2. 两数相加(中)
给出两个 非空 的链表用来表示两个非负的整数。其中,它们各自的位数是按照 逆序 的方式存储的,并且它们的每个节点只能存储 一位 数字。
如果,我们将这两个数相加起来,则会返回一个新的链表来表示它们的和。
您可以假设除了数字 0 之外,这两个数都不会以 0 开头。
示例:
输入:(2 -> 4 -> 3) + (5 -> 6 -> 4)
输出:7 -> 0 -> 8
原因:342 + 465 = 807思路:题意要理解清楚,模拟即可,很简单但要注意细节。
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
ListNode t=new ListNode(0);
ListNode cur=t;
int pre=0;
while(l1!=null||l2!=null){
int x=(l1==null?0:l1.val);
int y=(l2==null?0:l2.val);
int sum=(x+y+pre);
cur.next=new ListNode(sum%10);
cur=cur.next;
pre=sum/10;
if(l1!=null)
l1=l1.next;
if(l2!=null)
l2=l2.next;
}
if(pre!=0){
cur.next=new ListNode(pre);
}
return t.next;
}
}
leetcode——链表的更多相关文章
- [LeetCode] [链表] 相关题目总结
刷完了LeetCode链表相关的经典题目,总结一下用到的技巧: 技巧 哑节点--哑节点可以将很多特殊case(比如:NULL或者单节点问题)转化为一般case进行统一处理,这样代码实现更加简洁,优雅 ...
- Leetcode链表
Leetcode链表 一.闲聊 边学边刷的--慢慢写慢慢更 二.题目 1.移除链表元素 题干: 思路: 删除链表节点,就多了一个判断等值. 由于是单向链表,所以要删除节点时要找到目标节点的上一个节点, ...
- [LeetCode] 链表反转相关题目
暂时接触到LeetCode上与链表反转相关的题目一共有3道,在这篇博文里面总结一下.首先要讲一下我一开始思考的误区:链表的反转,不是改变节点的位置,而是改变每一个节点next指针的指向. 下面直接看看 ...
- LeetCode链表解题模板
一.通用方法以及题目分类 0.遍历链表 方法代码如下,head可以为空: ListNode* p = head; while(p!=NULL) p = p->next; 可以在这个代码上进行修改 ...
- LeetCode链表相加-Python<二>
上一篇:LeetCode两数之和-Python<一> 题目:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/add-two-numbers/description/ 给定 ...
- leetcode 链表类型题总结
链表测试框架示例: // leetcodeList.cpp : 定义控制台应用程序的入口点.vs2013 测试通过 // #include "stdafx.h" #include ...
- leetcode链表相关
目录 2/445两数相加 综合题(328奇偶链表, 206反转链表, 21合并两个有序链表 ) 92反转链表 II 链表排序(148排序链表, 876链表的中间结点) 142环形链表 II 160相交 ...
- LeetCode 链表题 ( Java )
leetcode 237. 删除链表中的节点 链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/delete-node-in-a-linked-list/ 示例 : 输入: he ...
- LeetCode 链表的插入排序
Sort a linked list using insertion sort 创建一个新的链表,将旧链表的节点插入到正确的位置 package cn.edu.algorithm.huawei; pu ...
- leetcode 链表类型题目解题总结
最基础的方式要做到非常熟练,要熟练到不思考就能写,但又需明白各处的要求和陷阱 合并两个有序链表的操作,在前面加上一个初始节点,注意while循环和退出时的处理,理解如何处理其中一个链表遍历完的情况 L ...
随机推荐
- CoderForces-Round60D(1117) Magic Gems
D. Magic Gems time limit per test 3 seconds memory limit per test 256 megabytes input standard input ...
- 2017 CCPC秦皇岛 G题 Numbers
DreamGrid has a nonnegative integer . He would like to divide into nonnegative integers and minimi ...
- 2017 CCPC秦皇岛 A题 A Ballon Robot
The 2017 China Collegiate Programming Contest Qinhuangdao Site is coming! There will be teams parti ...
- IoTClient开发5 - ModBusRtu协议
前言 前面我们介绍了ModBusTcp协议.今天我们接着来介绍ModBusRtu协议.和ModBusTcp不同的是ModBusRtu基于串口通信,ModBusTcp是基于Tcp以太网通信. 所以我们在 ...
- 【python测试开发栈】—理解python深拷贝与浅拷贝的区别
内存的浅拷贝和深拷贝是面试时经常被问到的问题,如果不能理解其本质原理,有可能会答非所问,给面试官留下不好的印象.另外,理解浅拷贝和深拷贝的原理,还可以帮助我们理解Python内存机制.这篇文章将会通过 ...
- python笔记03
day03 一.今日内容: 1.整型 2.字符串 3.布尔类型 二.内容回顾和补充 脑图--xmind软件,processon 1.运算符补充(in.not in) value = "我是中 ...
- 大数据学习笔记——HDFS理论知识之编辑日志与镜像文件
HDFS文件系统——编辑日志和镜像文件详细介绍 我们知道,启动Hadoop之后,在主节点下会产生Namenode,即名称节点进程,该节点的目录下会保存一份元数据,用来记录文件的索引,而在从节点上即Da ...
- JS基础-变量类型和类型转换
JS 变量类型 JS中有 6 种原始值,分别是: boolean number string undefined symbol null 引用类型: 对象 数组 函数 JS中使用typeof能得到哪些 ...
- C语言每日一练——第5题
一.题目要求 选出大于100小于1000的所有个位数与十位数字之和被10除所得余数恰好是百位数字的所有数字(如293).计算并输出上述这些素数的个数cnt以及这些素数值得sum,最后把结果cnt和su ...
- hdu 5532 Almost Sorted Array (水题)
Almost Sorted Array Time Limit: 4000/2000 MS (Java/Others) Memory Limit: 262144/262144 K (Java/Ot ...
