[LeetCode] 850. Rectangle Area II 矩形面积之二
We are given a list of (axis-aligned) `rectangles`. Each `rectangle[i] = [x1, y1, x2, y2] `, where (x1, y1) are the coordinates of the bottom-left corner, and (x2, y2) are the coordinates of the top-right corner of the `i`th rectangle.
Find the total area covered by all rectangles in the plane. Since the answer may be too large, return it modulo 10^9 + 7.
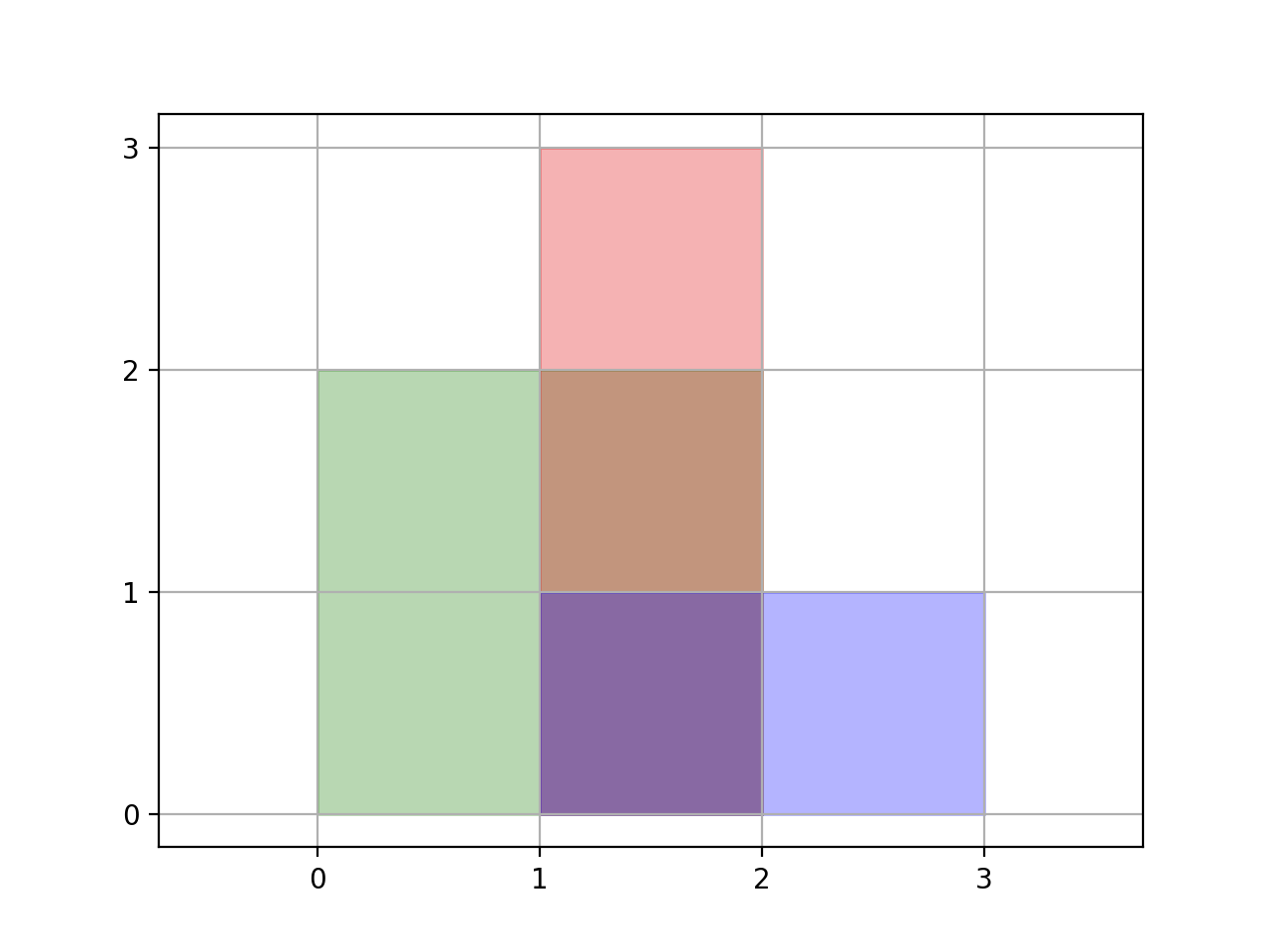
Example 1:
Input: [[0,0,2,2],[1,0,2,3],[1,0,3,1]]
Output: 6
Explanation: As illustrated in the picture.
Example 2:
Input: [[0,0,1000000000,1000000000]]
Output: 49
Explanation: The answer is 10^18 modulo (10^9 + 7), which is (10^9)^2 = (-7)^2 = 49.
Note:
1 <= rectangles.length <= 200rectanges[i].length = 40 <= rectangles[i][j] <= 10^9- The total area covered by all rectangles will never exceed
2^63 - 1and thus will fit in a 64-bit signed integer.
这道题是之前那道 [Rectangle Area](http://www.cnblogs.com/grandyang/p/4563153.html) 的拓展,那道题只有两个矩形重叠,而这道题有多个矩形可能同时重叠,整体难度一下就上来了,那么通过将所有矩形面积加起来再减去重叠区域的方法这里就不太适用了,因为多个矩形在同一区域重叠的话,都减去重叠面积是会错的,还得把多减的补回来,相当的麻烦。这里我们需要换一种解题的思路,不能一股脑儿的把所有的矩形都加起来,而是应该利用微积分的思想,将重叠在一起的区域拆分成一个个的小矩形,分别累加面积,因为这里的矩形是不会旋转的,所以是可以正常拆分的。思路有了,新建一个二维数组 all 来保存所有的矩形,然后遍历给定的矩形数组,对于每个遍历到的数组,调用一个子函数,将当前的矩形加入 all 中。下面主要来看一下这个子函数 helper 该如何实现?首先要明白这个函数的作用是将当前矩形加入 all 数组中,而且用的是递归的思路,所以要传入一个 start 变量,表示当前和 all 数组中正在比较的矩形的 index,这样在开始的时候,检查一下若 start 大于等于 all 数组长度,表示已经检测完 all 中所有的矩形了,将当前矩形加入 all 数组,并返回即可。否则的话则取出 start 位置上的矩形 rec,此时就要判断当前要加入的矩形和这个 rec 矩形是否有重叠,这在 LeetCode 中有专门一道题是考察这个的 [Rectangle Overlap](https://www.cnblogs.com/grandyang/p/10367583.html),这里用的就是那道题的判断方法,假如判断出当前矩形 cur 和矩形 rec 没有交集,就直接对 all 数组中下一个矩形调用递归函数,并返回即可。假如有重叠的话,就稍微麻烦一点,由于重叠的部位不同,所以需要分情况讨论一下,参见下图所示:
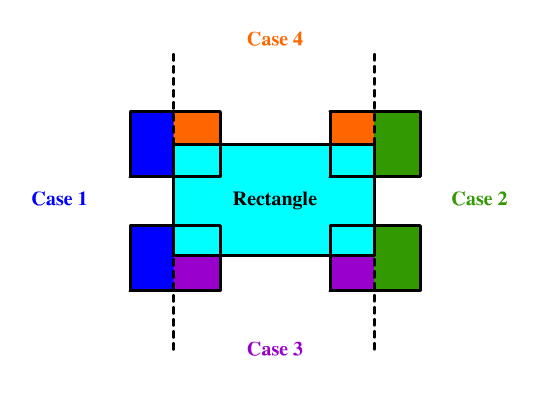
对于一个矩形 Rectangle,若有另外一个矩形跟它有重叠的话,可以将重叠区域分为四个部分,如上图的 Case1,Case2,Case3,Case4 所示,非重叠部分一定会落在一个或多个区域中,则可以把这些拆开的小矩形全部加入到矩形数组 all 中。仔细观察上图可以发现,对于将矩形 cur 拆分的情况可以分为下面四种:
- 落入区间1,条件为 cur[0] < rec[0],产生的新矩形的两个顶点为 {cur[0], cur[1], rec[0], cur[3]}。
- 落入区间2,条件为 cur[2] > rec[2],产生的新矩形的两个顶点为 {rec[2], cur[1], cur[2], cur[3]}。
- 落入区间3,条件为 cur[1] < rec[1],产生的新矩形的两个顶点为 {max(rec[0], cur[0]), cur[1], min(rec[2], cur[2]), rec[1]}。
- 落入区间4,条件为 cur[3] > rec[3],产生的新矩形的两个顶点为 {max(rec[0], cur[0]), rec[3], min(rec[2], cur[2]), cur[3]}。
这样操作下来的话,整个所有的区域都被拆分成了很多个小矩形,每个矩形之间都不会有重复,最后只要分别计算每个小矩形的面积,并累加起来就是最终的结果了,参见代码如下:
解法一:
class Solution {
public:
int rectangleArea(vector<vector<int>>& rectangles) {
long res = 0, M = 1e9 + 7;
vector<vector<int>> all;
for (auto rectangle : rectangles) {
helper(all, rectangle, 0);
}
for (auto &a : all) {
res = (res + (long)(a[2] - a[0]) * (long)(a[3] - a[1])) % M;
}
return res;
}
void helper(vector<vector<int>>& all, vector<int> cur, int start) {
if (start >= all.size()) {
all.push_back(cur); return;
}
auto rec = all[start];
if (cur[2] <= rec[0] || cur[3] <= rec[1] || cur[0] >= rec[2] || cur[1] >= rec[3]) {
helper(all, cur, start + 1); return;
}
if (cur[0] < rec[0]) {
helper(all, {cur[0], cur[1], rec[0], cur[3]}, start + 1);
}
if (cur[2] > rec[2]) {
helper(all, {rec[2], cur[1], cur[2], cur[3]}, start + 1);
}
if (cur[1] < rec[1]) {
helper(all, {max(rec[0], cur[0]), cur[1], min(rec[2], cur[2]), rec[1]}, start + 1);
}
if (cur[3] > rec[3]) {
helper(all, {max(rec[0], cur[0]), rec[3], min(rec[2], cur[2]), cur[3]}, start + 1);
}
}
};
下面这种解法更是利用了微积分的原理,把x轴长度为1当作一个步长,然后计算每一列有多少个连续的区间,每个连续区间又有多少个小正方形,题目中给的例子每一个列都只有一个连续区间,但事实上是可以有很多个的,只要算出了每一列 1x1 小正方形的个数,将所有列都累加起来,就是整个区域的面积。这里求每列上小正方形个数的方法非常的 tricky,博主也不知道该怎么讲解,大致就是要求同一列上每个连续区间中的小正方形个数,再累加起来。对于每个矩形起始的横坐标,映射较低的y值到1,较高的y值到 -1,对于结束位置的横坐标,刚好反过来一下,映射较低的y值到 -1,较高的y值到1。这种机制跟之前那道 [The Skyline Problem](http://www.cnblogs.com/grandyang/p/4534586.html) 有些异曲同工之妙,都还是为了计算高度差服务的。要搞清楚这道题的核心思想,不是一件容易的事,博主的建议是就拿题目中给的例子带入到下面的代码中,一步一步执行,并分析结果,是能够初步的了解解题思路的,若实在有理解上的问题,博主可以进一步写些讲解,参见代码如下:
解法二:
class Solution {
public:
int rectangleArea(vector<vector<int>>& rectangles) {
long res = 0, pre_x = 0, height = 0, start = 0, cnt = 0, M = 1e9 + 7;
map<int, vector<pair<int, int>>> groupMap;
map<int, int> cntMap;
for (auto &a : rectangles) {
groupMap[a[0]].push_back({a[1], 1});
groupMap[a[0]].push_back({a[3], -1});
groupMap[a[2]].push_back({a[1], -1});
groupMap[a[2]].push_back({a[3], 1});
}
for (auto &group : groupMap) {
res = (res + (group.first - pre_x) * height) % M;
for (auto &a : group.second) {
cntMap[a.first] += a.second;
}
height = 0, start = 0, cnt = 0;
for (auto &a : cntMap) {
if (cnt == 0) start = a.first;
cnt += a.second;
if (cnt == 0) height += a.first - start;
}
pre_x = group.first;
}
return res;
}
};
Github 同步地址:
https://github.com/grandyang/leetcode/issues/850
类似题目:
参考资料:
https://leetcode.com/problems/rectangle-area-ii/
https://leetcode.com/problems/rectangle-area-ii/discuss/138028/Clean-Recursive-Solution-Java
[LeetCode All in One 题目讲解汇总(持续更新中...)](https://www.cnblogs.com/grandyang/p/4606334.html)
[LeetCode] 850. Rectangle Area II 矩形面积之二的更多相关文章
- leetcode 850. Rectangle Area II
给定一些矩形2 求覆盖面积 矩形不超过200个 1 算法1 朴素思想 虽然朴素但是代码却有意思 利用容斥原理 复杂度高达 N*2^N class Solution: def intersect(rec ...
- LeetCode 223 Rectangle Area(矩形面积)
翻译 找到在二维平面中两个相交矩形的总面积. 每一个矩形都定义了其左下角和右上角的坐标. (矩形例如以下图) 如果,总占地面积永远不会超过int的最大值. 原文 分析 这题前天试过,写了一堆推断.终究 ...
- [LeetCode] 223. Rectangle Area 矩形面积
Find the total area covered by two rectilinearrectangles in a 2D plane. Each rectangle is defined by ...
- [LeetCode]223. Rectangle Area矩形面积
/* 像是一道数据分析题 思路就是两个矩形面积之和减去叠加面积之和 */ public int computeArea(int A, int B, int C, int D, int E, int F ...
- (easy)LeetCode 223.Rectangle Area
Find the total area covered by two rectilinear rectangles in a 2D plane. Each rectangle is defined b ...
- [Swift]LeetCode850. 矩形面积 II | Rectangle Area II
We are given a list of (axis-aligned) rectangles. Each rectangle[i] = [x1, y1, x2, y2] , where (x1, ...
- leetcode之Rectangle Area
Find the total area covered by two rectilinear rectangles in a 2D plane. Each rectangle is defined b ...
- leetcode:Rectangle Area
Find the total area covered by two rectilinear rectangles in a 2D plane. Each rectangle is defined b ...
- LeetCode(41)-Rectangle Area
题目: Find the total area covered by two rectilinear rectangles in a 2D plane. Each rectangle is defin ...
随机推荐
- 解决python3.7 ModuleNotFoundError: No module named bz2
解决: ModuleNotFoundError: No module named bz2 ModuleNotFoundError: No module named '_lzma' 1.在操作系统中安 ...
- HTML+css基础 css选择器的种类
css选择器的种类 标签 权重是001 类 class权重是0010 相当于255个标签选择器 Id 权重是0100相当于255个类 *通配符 代表所有的标签 权重是0000 后代选 ...
- Windows重要的win键
win+↓ 当前窗口操作,多按几下就缩没了(同理,其他箭头也一样) win+e 打开此电脑 win+v 展开剪切板 win+k 访问蓝牙 win+a win10的通知 win+d (切到桌面,再用能切 ...
- Spring源码系列 — 容器Extend Point(一)
前言 前文介绍了Spring中的BeanDefinition的细节,随着Spring的启动流程,这节我们介绍Spring的后续处理过程 - Spring的扩展点: BeanFactoryPostPro ...
- kali渗透综合靶机(十三)--Dina 1.0靶机
kali渗透综合靶机(十三)--Dina 1.0靶机 一.主机发现 1.netdiscover -i eth0 -r 192.168.10.0/24 二.端口扫描 1. masscan --rate= ...
- .net core中serilog的基本使用
Serilog的基本使用 (一) 引言 (二) 导入包 (三) 配置 直接配置 配置文件配置 (四) 使用 (五) 结语 一 引言 作为一枚小白,来复习一下serilog的使用,如果有错误的 ...
- Kafka Network层解析,还是有人把它说清楚了
我们知道kafka是基于TCP连接的.其并没有像很多中间件使用netty作为TCP服务器.而是自己基于Java NIO写了一套. 几个重要类 先看下Kafka Client的网络层架构. 本文主要分析 ...
- Linux软件安装——安装软件的命令
Linux软件安装——安装软件的命令 摘要:本文主要学习了如何在Linux系统中安装.更新.卸载软件. rpm命令 rpm命令用来在Linux系统上进行软件的安装. 基本语法 安装命令: rpm -i ...
- Web Api 模型绑定 二
[https://docs.microsoft.com/zh-cn/aspnet/core/web-api/?view=aspnetcore-2.2] 1.ApiController属性使模型验证错误 ...
- ZKEACMS 无法运行问题汇总
前言 如果你还不知道ZKEACMS,不妨先了解一下. ASP.NET MVC 开源建站系统 ZKEACMS 推荐,从此网站“拼”起来 官方地址:http://www.zkea.net/zkeacms ...
